Abstract
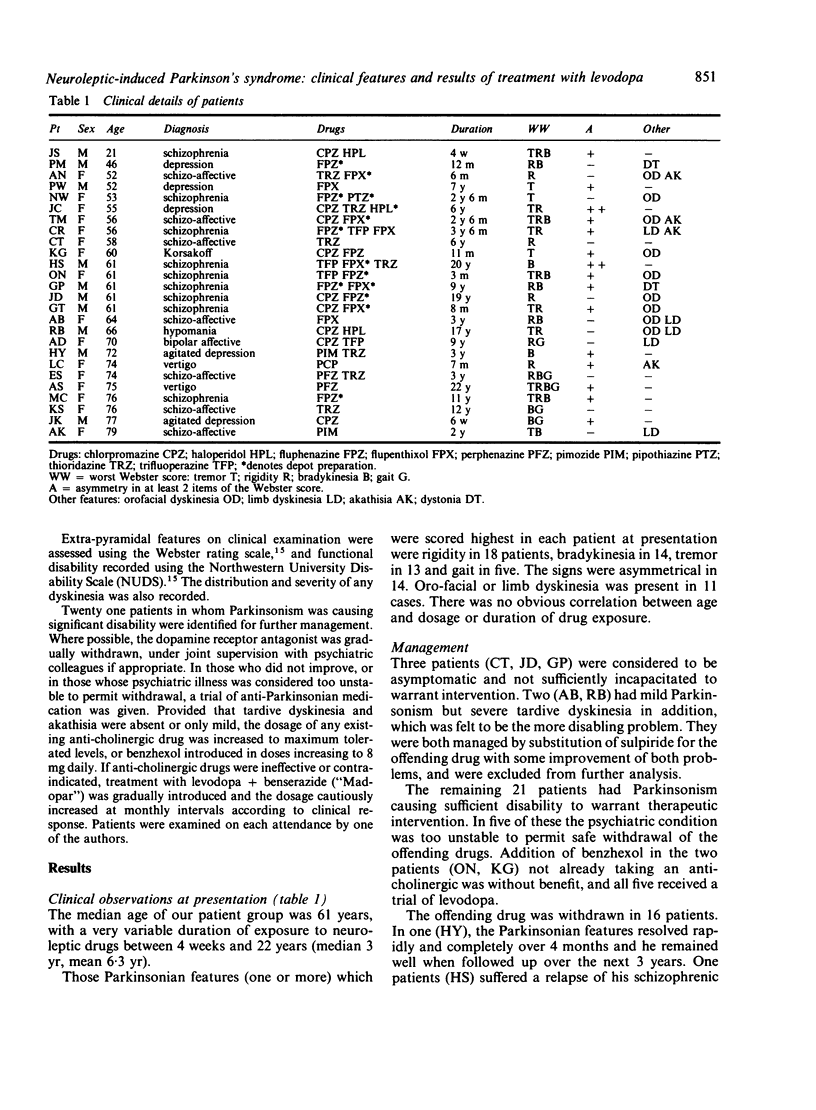
Twenty six consecutive patients with neuroleptic-induced Parkinson's syndrome (NIPS) are described. Their median age was 61 years, 60% were female, and most had received chronic neuroleptic medication for psychiatric indications. The clinical features were indistinguishable from idiopathic Parkinson's disease, except for the presence of co-existing orofacial chorea, limb dyskinesia or akathisia which provided an aetiological clue in 11 cases. Complete resolution of NIPS occurred in only two patients, one of whom later developed Parkinson's disease. Sixteen patients were treated with 300-1000 mg levodopa/benserazide for up to 4 years with few adverse effects but therapeutic response was disappointing.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AYD F. J., Jr A survey of drug-induced extrapyramidal reactions. JAMA. 1961 Mar 25;175:1054–1060. doi: 10.1001/jama.1961.03040120016004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angrist B., Sathananthan G., Gershon S. Behavioral effects of L-dopa in schizophrenic patients. Psychopharmacologia. 1973 Jul 4;31(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00429294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruno A., Bruno S. C. Effects of L-DOPA on pharmacological parkinsonism. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1966;42(3):264–271. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1966.tb01931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunney W. E., Jr, Murphy D. L., Brodie H. K., Goodwin F. K. L-dopa in depressed patients. Lancet. 1970 Feb 14;1(7642):352–352. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90722-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chouinard G., Annable L., Mercier P., Turnier L. Long-term effects of L-dopa and procyclidine on neuroleptic-induced extrapyramidal and schizophrenic symptoms. Psychopharmacol Bull. 1987;23(1):221–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chouza C., Scaramelli A., Caamaño J. L., De Medina O., Aljanati R., Romero S. Parkinsonism, tardive dyskinesia, akathisia, and depression induced by flunarizine. Lancet. 1986 Jun 7;1(8493):1303–1304. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91223-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curson D. A., Barnes T. R., Bamber R. W., Platt S. D., Hirsch S. R., Duffy J. C. Long-term depot maintenance of chronic schizophrenic out-patients: the seven year follow-up of the Medical Research Council fluphenazine/placebo trial. III. Relapse postponement or relapse prevention? The implications for long-term outcome. Br J Psychiatry. 1985 May;146:474–480. doi: 10.1192/bjp.146.5.474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson M., Keefe R. S., Mohs R. C., Siever L. J., Losonczy M. F., Horvath T. B., Davis K. L. L-dopa challenge and relapse in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 1987 Jul;144(7):934–938. doi: 10.1176/ajp.144.7.934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREYHAN F. A. Psychomotility and parkinsonism in treatment with neuroleptic drugs. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1957 Nov;78(5):465–472. doi: 10.1001/archneurpsyc.1957.02330410029003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel P. E., Stancer H. C. L-Dopa and schizophrenia. Can Psychiatr Assoc J. 1976 Feb;21(1):27–29. doi: 10.1177/070674377602100105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardie R. J., Lees A. J., Stern G. M. Sustained levodopa therapy in tardive dyskinesia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1983 Jul;46(7):685–685. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.46.7.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausner R. S. Neuroleptic-induced parkinsonism and Parkinson's disease: differential diagnosis and treatment. J Clin Psychiatry. 1983 Jan;44(1):13–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch S. R., Gaind R., Rohde P. D., Stevens B. C., Wing J. K. Outpatient maintenance of chronic schizophrenic patients with long-acting fluphenazine: double-blind placebo trial. Report to the Medical Research Council Committee on Clinical Trials in Psychiatry. Br Med J. 1973 Mar 17;1(5854):633–637. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5854.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inanaga K., Inoue K., Tachibana H., Oshima M., Kotorii T. Effect of L-dopa in schizophrenia. Folia Psychiatr Neurol Jpn. 1972;26(2):145–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1819.1972.tb01119.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnstone E. C., Crow T. J., Johnson A. L., MacMillan J. F. The Northwick Park Study of first episodes of schizophrenia. I. Presentation of the illness and problems relating to admission. Br J Psychiatry. 1986 Feb;148:115–120. doi: 10.1192/bjp.148.2.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataria M., Traub M., Marsden C. D. Extrapyramidal side-effects of metoclopramide. Lancet. 1978 Dec 9;2(8102):1254–1255. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92126-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura N., Tsukue I. L-DOPA therapy in drug-induced parkinsonism evaluated by the method measuring the facial expression. Hiroshima J Med Sci. 1971 Mar;20(1):55–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klawans H. L., Jr, Bergen D., Bruyn G. W. Prolonged drug-induced Parkinsonism. Confin Neurol. 1973;35(6):368–377. doi: 10.1159/000102857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff J. P., Wing J. K. Trial of maintenance therapy in schizophrenia. Br Med J. 1971 Sep 11;3(5775):599–604. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5775.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Jenner P. The pathophysiology of extrapyramidal side-effects of neuroleptic drugs. Psychol Med. 1980 Feb;10(1):55–72. doi: 10.1017/s003329170003960x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Schachter M. Assessment of extrapyramidal disorders. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1981 Feb;11(2):129–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1981.tb01118.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland H. A. Assessment of drugs in schizophrenia. Discussion on assessment of drug-induced extrapyramidal reactions. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1976 Jun;3(3 Suppl 2):401–403. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1976.tb03733.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland H. A., Blessed G., Bhate S., Ali N., Clarke P. A. The abrupt withdrawal of antiparkinsonian drugs in schizophrenic patients. Br J Psychiatry. 1974 Feb;124(579):151–159. doi: 10.1192/bjp.124.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mindham R. H. Assessment of drugs in schizophrenia. Asessment of drug-induced extrapyramidal reactions and of drugs given for their control. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1976 Jun;3(3 Suppl 2):395–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1976.tb03732.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mindham R. H., Gaind R., Anstee B. H., Rimmer L. Comparison of amantadine, orphenadrine, and placebo in the control of phenothiazine-induced Parkinsonism. Psychol Med. 1972 Nov;2(4):406–413. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700045220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutch W. J., Dingwall-Fordyce I., Downie A. W., Paterson J. G., Roy S. K. Parkinson's disease in a Scottish city. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Feb 22;292(6519):534–536. doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6519.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogura C., Kishimoto A., Nakao T. Clinical effect of L-dopa on schizophrenia. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 1976 Sep;20(3):308–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pall H. S., Williams A. C. Extrapyramidal disturbances caused by inappropriate prescribing. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 Jul 4;295(6589):30–31. doi: 10.1136/bmj.295.6589.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajput A. H., Rozdilsky B., Hornykiewicz O., Shannak K., Lee T., Seeman P. Reversible drug-induced parkinsonism. Clinicopathologic study of two cases. Arch Neurol. 1982 Oct;39(10):644–646. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1982.00510220042009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers D. The motor disorders of severe psychiatric illness: a conflict of paradigms. Br J Psychiatry. 1985 Sep;147:221–232. doi: 10.1192/bjp.147.3.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephen P. J., Williamson J. Drug-induced parkinsonism in the elderly. Lancet. 1984 Nov 10;2(8411):1082–1083. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91516-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters W. E. Headache and the eye. A community study. Lancet. 1970 Jul 4;2(7662):1–4. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)92471-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. A., Primrose W. R. Drug induced parkinsonism. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Oct 11;293(6552):957–957. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6552.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaryura-Tobias J. A., Diamond B., Merlis S. The action of L-dopa on schizophrenic patients (a preliminary report). Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 1970 Aug;12(8):528–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaryura-Tobias J. A., Wolpert A., Dana L., Merlis S. Action of L-Dopa in drug induced extrapyramidalism. Dis Nerv Syst. 1970 Jan;31(1):60–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


