CASE REPORT
A 39-year-old woman with a prior diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) presented after impaction of 3 cellulose/citric acid hydrogel capsules for weight loss taken together before eating, as the instruction stated. She reported feeling the capsules stuck in her esophagus, and she was unable to tolerate swallowing. At the time of presentation, she was not followed by a gastroenterologist or taking any medications for EoE because she had been treated previously and finished her course. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy was performed and demonstrated gelatinized capsules within the esophagus at 20 cm and extending 5 cm distally. The impaction was broken down with graspers and retrieval devices, and the remaining material was pushed into the stomach. Owing to the gelatinous content, it was challenging to capture the loose material to be removed. Biopsies were taken of the esophagus which contained 15 eosinophils per high-power field. Esophageal impaction and dysphagia can occur if capsules are not swallowed properly, particularly in patients with EoE. To reduce this risk, users should consider swallowing each of the 3 capsules individually, followed each time by a cup of water. This method of administration will likely prevent the expansion of the capsular contents into the larger gelatinous material in the esophagus (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
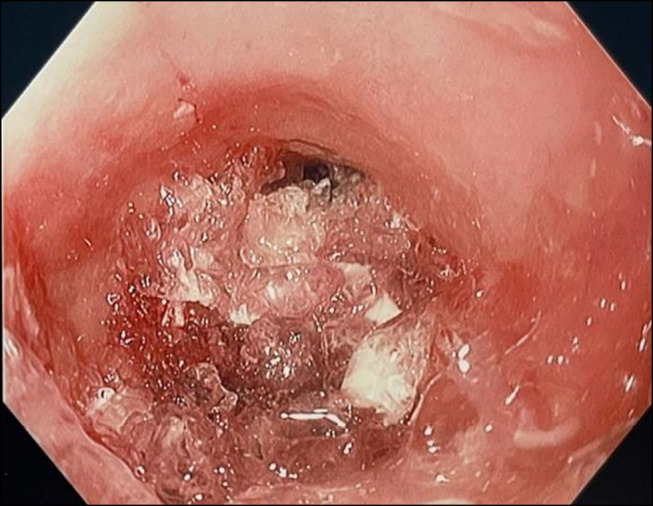
Impaction of gelatinized content from 3 cellulose/citric acid hydrogel capsules 20 cm into the esophagus.
DISCLOSURES
Author contributions: M. Wend was the primary author of this paper. J. Kupferman wrote this initial abstract and case description. All other authors were directly involved in the management of the patient described in the case report.
Financial disclosure: None to report.
Informed consent has been obtained for this case report.
Contributor Information
Judah Kupferman, Email: kupfermj@nychhc.org.
Vennis Lourdusamy, Email: lourdusv@nychhc.org.
Aaron Walfish, Email: walfisha@nychhc.org.
Joshua Aron, Email: aronjo@nychhc.org.
Krishna Gurram, Email: gurramk@nychhc.org.


