Abstract
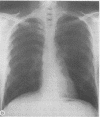
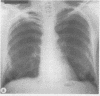
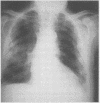
Four patients occupationally exposed to asbestos, each suffering at least eight years of disabling, persistent, and often bilateral pleuritic pain are described. Radiographic evidence of pleural disease ranged from plaques seen only on computed tomography to typical bilateral plaques or diffuse thickening to extensive diffuse and circumscribed pleural fibrosis and calcification. There was no history or evidence of acute pleuritis or pleural effusion in three patients. Intermittent pleural friction rubs have been present in all four; one patient showed pleural uptake of gallium-67. Extensive workups including repeated pulmonary ventilation-perfusion scans and cardiac catheterisation have not yielded other diagnoses to explain the pain. It is proposed that persistent pleuritic pain be added to the manifestations of benign asbestos induced pleural disease.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bass H. The flow volume loop: normal standards and abnormalities in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Chest. 1973 Feb;63(2):171–176. doi: 10.1378/chest.63.2.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISENSTADT H. B. ASBESTOS PLEURISY. Dis Chest. 1964 Jul;46:78–81. doi: 10.1378/chest.46.1.78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISENSTADT H. B. BENIGN ASBESTOS PLEURISY. JAMA. 1965 May 3;192:419–421. doi: 10.1001/jama.1965.03080180077029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epler G. R., McLoud T. C., Gaensler E. A. Prevalence and incidence of benign asbestos pleural effusion in a working population. JAMA. 1982 Feb 5;247(5):617–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDMAN H. I., BECKLAKE M. R. Respiratory function tests; normal values at median altitudes and the prediction of normal results. Am Rev Tuberc. 1959 Apr;79(4):457–467. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1959.79.4.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaensler E. A., Kaplan A. I. Asbestos pleural effusion. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Feb;74(2):178–191. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-74-2-178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Järvholm B., Sandén A. Pleural plaques and respiratory function. Am J Ind Med. 1986;10(4):419–426. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700100409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattson S. B. Monosymptomatic exudative pleurisy in persons exposed to asbestos dust. Scand J Respir Dis. 1975;56(5):263–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A., Thornton J. C., Warshaw R., Anderson H., Teirstein A. S., Selikoff I. J. Single breath diffusing capacity in a representative sample of the population of Michigan, a large industrial state. Predicted values, lower limits of normal, and frequencies of abnormality by smoking history. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Mar;127(3):270–277. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.3.270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A., Thornton J. C., Warshaw R., Bernstein J., Selikoff I. J., Teirstein A. S. Mean and instantaneous expiratory flows, FVC and FEV1: prediction equations from a probability sample of Michigan, a large industrial state. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1986 Nov-Dec;22(6):589–597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson B. W., Musk A. W. Benign asbestos pleural effusion: diagnosis and course. Thorax. 1981 Dec;36(12):896–900. doi: 10.1136/thx.36.12.896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teirstein A. S., Chahinian P., Goldsmith S. J., Sorek M. Gallium scanning in differentiating malignant from benign asbestos-related pleural disease. Am J Ind Med. 1986;9(5):487–494. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700090509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing E. J., Stanko R. T., Winkelstein A., Adibi S. A. Fasting-enhanced immune effector mechanisms in obese subjects. Am J Med. 1983 Jul;75(1):91–96. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)91172-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zitting A., Huuskonen M. S., Alanko K., Mattsson T. Radiographic and physiological findings in patients with asbestosis. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1978 Dec;4(4):275–283. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]