Abstract
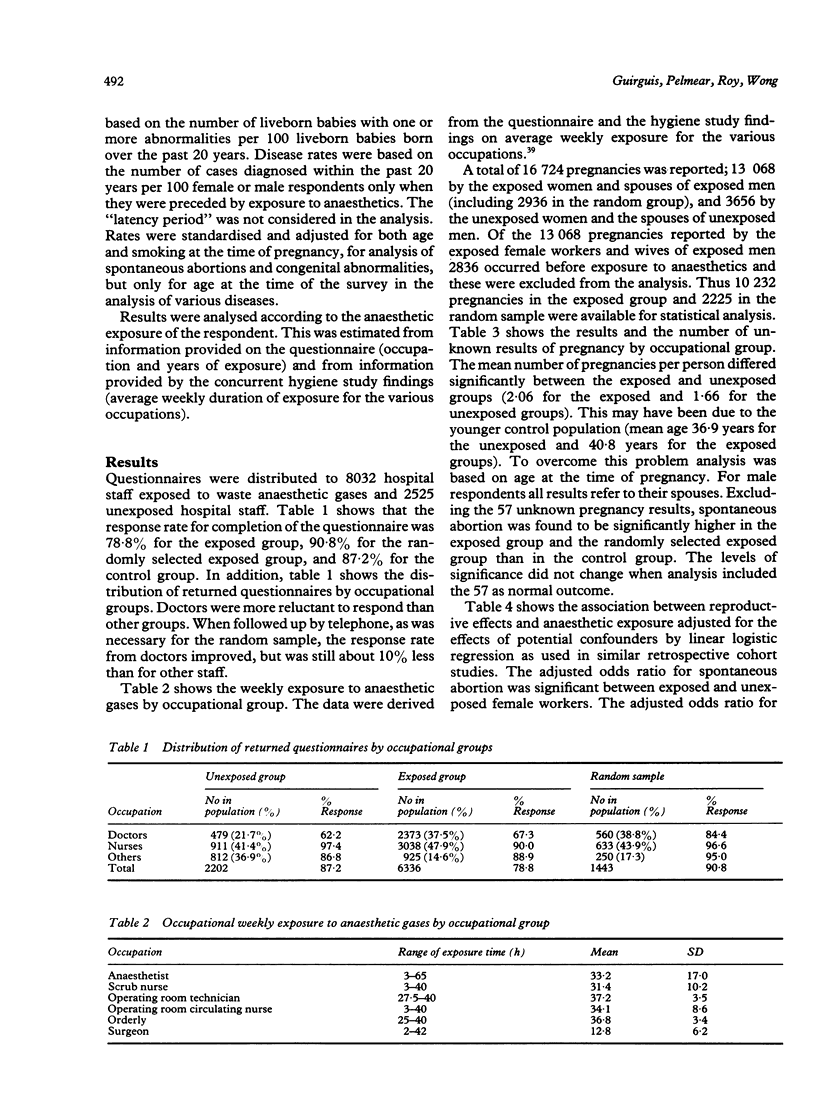
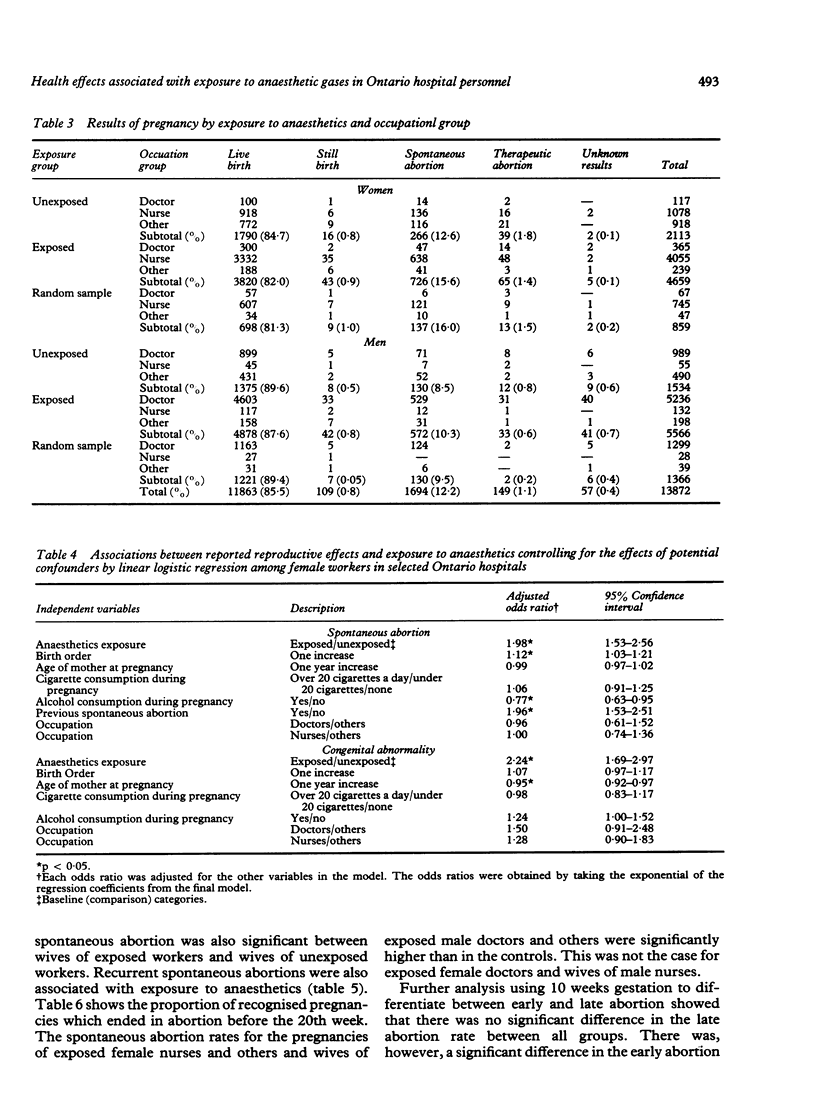
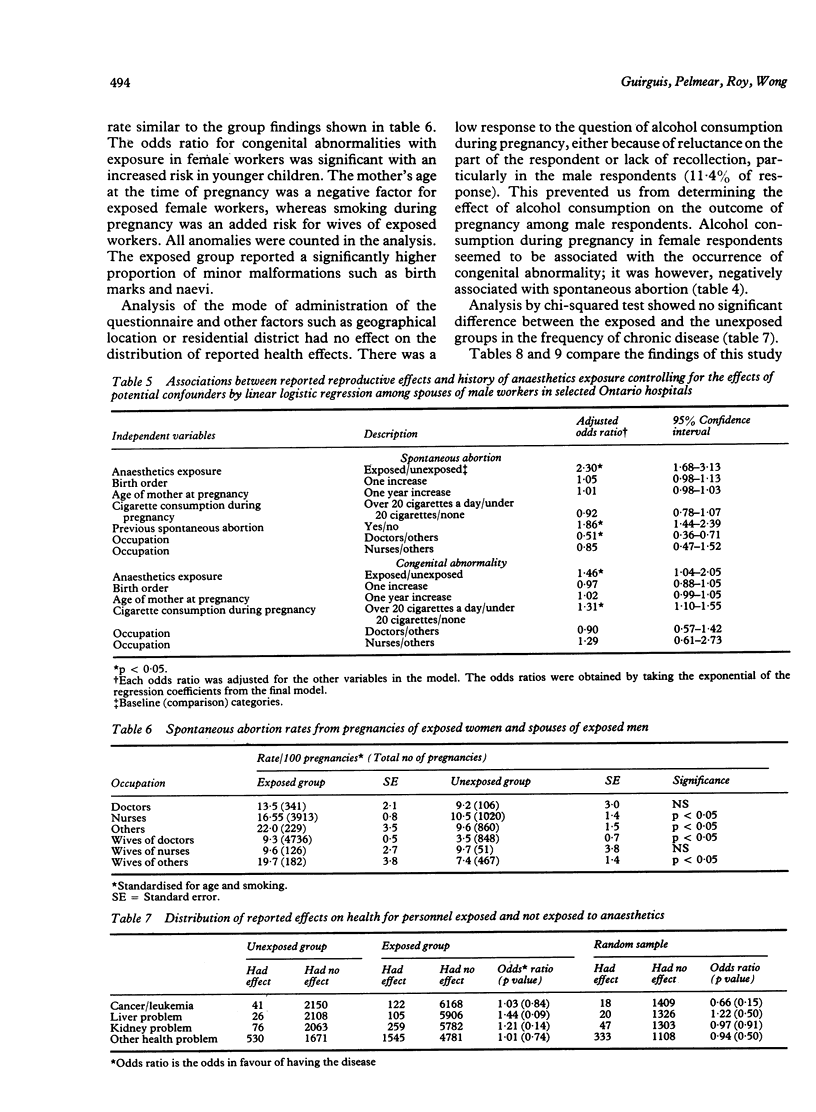
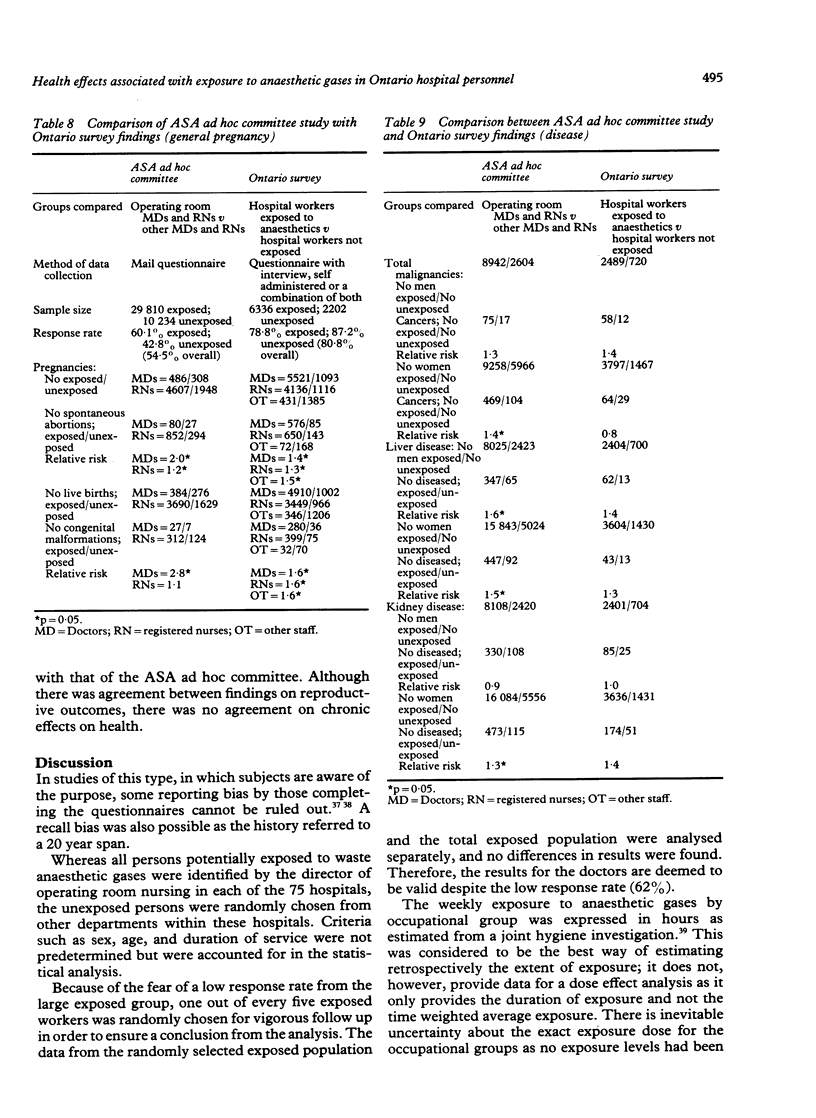
In a retrospective study (by questionnaire) of 8032 personnel exposed to anaesthetic gases in operating and recovery rooms in Ontario hospitals, and 2525 non-exposed hospital staff, the response was 78.8% for the exposed and 87.2% for the unexposed personnel during the period 1981-5. Logistic regression analysis, with age and smoking standardised, showed that women in the exposed group had significantly increased frequencies of spontaneous abortion and their children had significantly more congenital abnormalities (p less than 0.05). No chronic disease was significantly associated with the exposed group. These findings, together with similar ones from other studies, suggest that it is prudent to minimise exposure to waste anaesthetic gases.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Askrog V., Harvald B. Teratogen effekt af inhalationsanaestetika. Nord Med. 1970 Apr 16;83(16):498–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelsson G., Rylander R. Exposure to anaesthetic gases and spontaneous abortion: response bias in a postal questionnaire study. Int J Epidemiol. 1982 Sep;11(3):250–256. doi: 10.1093/ije/11.3.250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelsson G., Rylander R. Validation of questionnaire reported miscarriage, malformation and birth weight. Int J Epidemiol. 1984 Mar;13(1):94–98. doi: 10.1093/ije/13.1.94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basford A. B., Fink B. R. The teratogenicity of halothane in the rat. Anesthesiology. 1968 Nov-Dec;29(6):1167–1173. doi: 10.1097/00000542-196811000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce D. L., Bach M. J. Psychological studies of human performance as affected by traces of enflurane and nitrous oxide. Anesthesiology. 1975 Feb;42(2):194–205. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197502000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce D. L., Eide K. A., Linde H. W., Eckenhoff J. E. Causes of death among anesthesiologists: a 20-year survey. Anesthesiology. 1968 May-Jun;29(3):565–569. doi: 10.1097/00000542-196805000-00039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce D. L., Eide K. A., Smith N. J., Seltzer F., Dykes M. H. A prospective survey of anesthesiologist mortality, 1967-1971. Anesthesiology. 1974 Jul;41(1):71–74. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197407000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. W., Dudley A. W., Jr, Lee Y. K., Katz J. Ultrastructural studies of the hepatocytes after chronic exposure to low levels of halothane. Exp Mol Pathol. 1975 Aug;23(1):35–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(75)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen E. N., Bellville J. W., Brown B. W., Jr Anesthesia, pregnancy, and miscarriage: a study of operating room nurses and anesthetists. Anesthesiology. 1971 Oct;35(4):343–347. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197110000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen E. N., Brown B. W., Jr, Bruce D. L., Cascorbi H. F., Corbett T. H., Jones T. W., Whitcher C. E. A survey of anesthetic health hazards among dentists. J Am Dent Assoc. 1975 Jun;90(6):1291–1296. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1975.0270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen E. N., Gift H. C., Brown B. W., Greenfield W., Wu M. L., Jones T. W., Whitcher C. E., Driscoll E. J., Brodsky J. B. Occupational disease in dentistry and chronic exposure to trace anesthetic gases. J Am Dent Assoc. 1980 Jul;101(1):21–31. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1980.0345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett T. H., Cornell R. G., Endres J. L., Millard R. I. Effects of low concentrations of nitrous oxide on rat pregnancy. Anesthesiology. 1973 Sep;39(3):299–301. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197309000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett T. H., Cornell R. G., Lieding K., Endres J. L. Incidence of cancer among Michigan nurse-anesthetists. Anesthesiology. 1973 Mar;38(3):260–263. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197303000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienstag J. L. Halothans hepatitis: allergy or idiosyncrasy? N Engl J Med. 1980 Jul 10;303(2):102–104. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198007103030209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doll R., Peto R. Mortality among doctors in different occupations. Br Med J. 1977 Jun 4;1(6074):1433–1436. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6074.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson A., Källén B. Survey of infants born in 1973 or 1975 to Swedish women working in operating rooms during their pregnancies. Anesth Analg. 1979 Jul-Aug;58(4):302–305. doi: 10.1213/00000539-197907000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink B. R., Shepard T. H., Blandau R. J. Teratogenic activity of nitrous oxide. Nature. 1967 Apr 8;214(5084):146–148. doi: 10.1038/214146a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene N. M. Editorial: Traces of anesthetics. Anesthesiology. 1974 Oct;41(4):317–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes H. C., Jr, Lang C. M. Hepatic necrosis produced by repeated administration of halothane to guinea pigs. Anesthesiology. 1972 May;36(5):466–471. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197205000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knill-Jones R. P., Rodrigues L. V., Moir D. D., Spence A. A. Anaesthetic practice and pregnancy. Controlled survey of women anaesthetists in the United Kingdom. Lancet. 1972 Jun 17;1(7764):1326–1328. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91048-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane G. A., Nahrwold M. L., Tait A. R., Taylor-Busch M., Cohen P. J., Beaudoin A. R. Anesthetics as teratogens: nitrous oxide is fetotoxic, xenon is not. Science. 1980 Nov 21;210(4472):899–901. doi: 10.1126/science.7434002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layzer R. B., Fishman R. A., Schafer J. A. Neuropathy following abuse of nitrous oxide. Neurology. 1978 May;28(5):504–506. doi: 10.1212/wnl.28.5.504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pharoah P. O., Alberman E., Doyle P., Chamberlain G. Outcome of pregnancy among women in anaesthetic practice. Lancet. 1977 Jan 1;1(8001):34–36. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91666-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajhans G. S., Brown D. A., Whaley D., Wong L., Guirguis S. S. Hygiene aspects of occupational exposure to waste anaesthetic gases in Ontario hospitals. Ann Occup Hyg. 1989;33(1):27–45. doi: 10.1093/annhyg/33.1.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramazzotto L. J., Carlin R. D., Warchalowski G. A. Effects of nitrous oxide during organogenesis in the rat. J Dent Res. 1979 Sep;58(9):1940–1943. doi: 10.1177/00220345790580092201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg P., Kirves A. Miscarriages among operating theatre staff. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand Suppl. 1973;53:37–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1974.tb00780.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W. T., Jr, Cardell R. R., Jr Effects of halothane on the ultrastructure of rat liver cells. Am J Anat. 1972 Sep;135(1):5–22. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001350103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah R. M., Burdett D. N., Donaldson D. The effects of nitrous oxide on the developing hamster embryos. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1979 Nov;57(11):1229–1232. doi: 10.1139/y79-185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. E., Gaub M. L., Moya F. Teratogenic effects of anesthetic agents: nitrous oxide. Anesth Analg. 1965 Nov-Dec;44(6):726–732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira E., Cleaton-Jones P., Austin J. C., Moyes D. G., Shaw R. Effects of low concentrations of nitrous oxide on rat fetuses. Anesth Analg. 1980 Mar;59(3):175–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira E. Effect of the chronic administration of nitrous oxide 0.5% to gravid rats. Br J Anaesth. 1979 Apr;51(4):283–287. doi: 10.1093/bja/51.4.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


