Abstract
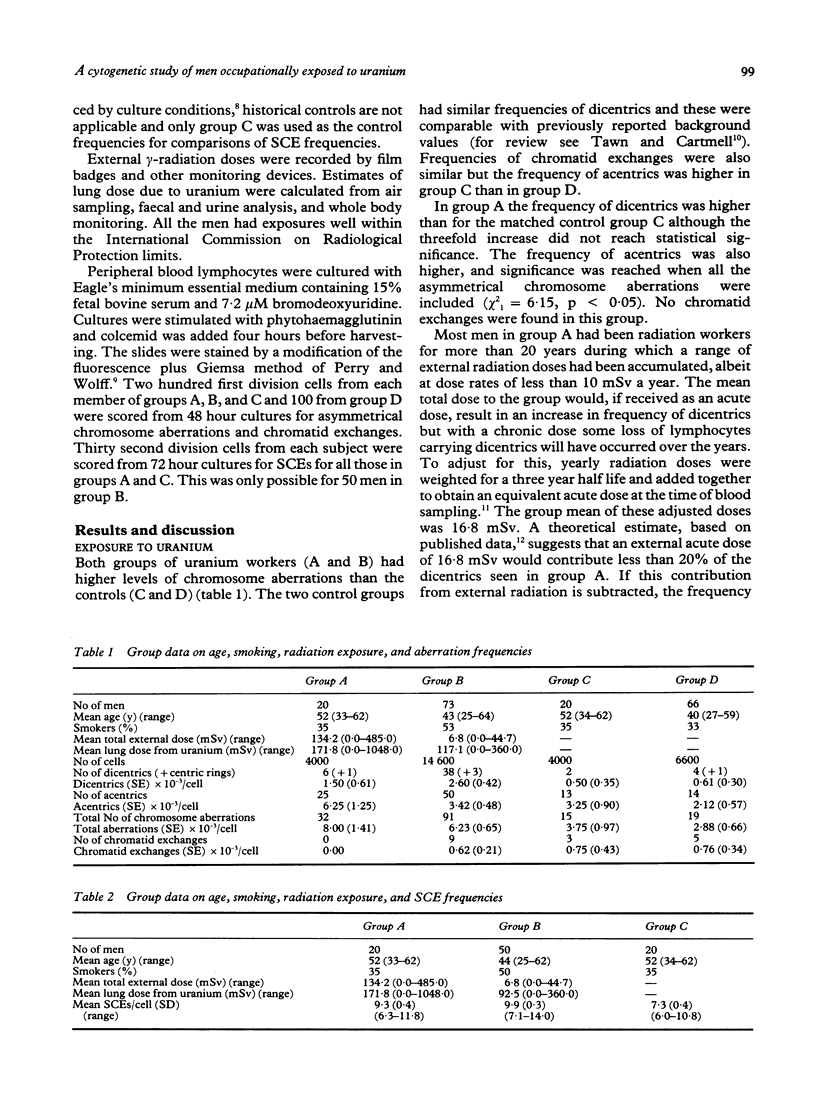
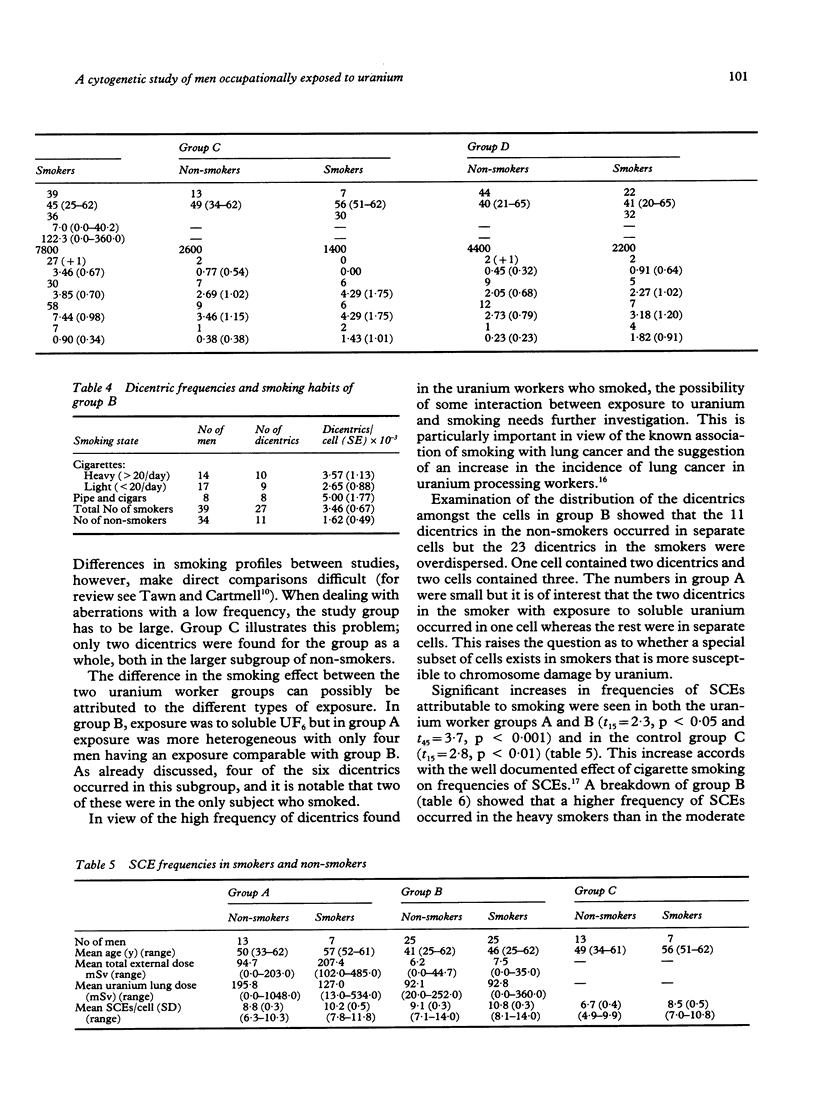
Blood lymphocyte cultures from two groups of workers occupationally exposed to uranium were examined for asymmetrical chromosome aberrations and sister chromatid exchanges (SCEs). Significant increases in both cytogenetic endpoints were seen. For dicentrics this appeared to be particularly associated with exposure to soluble uranium. The external radiation exposure experienced by these men was insufficient to explain the increase in dicentrics, and irradiation of lymphocytes by internally deposited uranium would have been minimal. As the SCEs were also raised, the genotoxic effect is likely to be due to the chemical nature of the compound. The increase in frequency of dicentrics associated with smoking was greatest in the group with exposure to soluble uranium suggesting some interaction between the two clastogens. No such interactive effect was seen for SCE frequencies, in which increases attributable to smoking were similar in the worker and control groups.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aghamohammadi S. Z., Goodhead D. T., Savage J. R. Induction of sister chromatid exchanges (SCE) in G0 lymphocytes by plutonium-238 alpha-particles. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1988 Jun;53(6):909–915. doi: 10.1080/09553008814551271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNARD S. R. Maximum permissible amounts of natural uranium in the body, air and drinking water based on human experimental data. Health Phys. 1958 Dec;1(3):288–305. doi: 10.1097/00004032-195807000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender M. A., Preston R. J., Leonard R. C., Pyatt B. E., Gooch P. C., Shelby M. D. Chromosomal aberration and sister-chromatid exchange frequencies in peripheral blood lymphocytes of a large human population sample. Mutat Res. 1988 Mar;204(3):421–433. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(88)90038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandom W. F., Saccomanno G., Archer V. E., Archer P. G., Bloom A. D. Chromosome aberrations as a biological dose-response indicator of radiation exposure in uranium miners. Radiat Res. 1978 Oct;76(1):159–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandom W. F., Saccomanno G., Archer V. E., Archer P. G., Coors M. E. Chromosome aberrations in uranium miners occupationally exposed to 222 radon. Radiat Res. 1972 Oct;52(1):204–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamberti L., Bigatti Ponzetto P., Ardito G. Cell kinetics and sister-chromatid-exchange frequency in human lymphocytes. Mutat Res. 1983 May;120(2-3):193–199. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(83)90163-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd D. C., Purrott R. J., Reeder E. J. The incidence of unstable chromosome aberrations in peripheral blood lymphocytes from unirradiated and occupationally exposed people. Mutat Res. 1980 Aug;72(3):523–532. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(80)90123-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry P., Evans H. J. Cytological detection of mutagen-carcinogen exposure by sister chromatid exchange. Nature. 1975 Nov 13;258(5531):121–125. doi: 10.1038/258121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry P., Wolff S. New Giemsa method for the differential staining of sister chromatids. Nature. 1974 Sep 13;251(5471):156–158. doi: 10.1038/251156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polednak A. P., Frome E. L. Mortality among men employed between 1943 and 1947 at a uranium-processing plant. J Occup Med. 1981 Mar;23(3):169–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tawn E. J., Cartmell C. L. The effect of smoking on the frequencies of asymmetrical and symmetrical chromosome exchanges in human lymphocytes. Mutat Res. 1989 Oct;224(2):151–156. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(89)90150-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tawn E. J. The frequency of chromosome aberrations in a control population. Mutat Res. 1987 Dec;182(6):303–308. doi: 10.1016/0165-1161(87)90072-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrenn M. E., Durbin P. W., Howard B., Lipsztein J., Rundo J., Still E. T., Willis D. L. Metabolism of ingested U and Ra. Health Phys. 1985 May;48(5):601–633. doi: 10.1097/00004032-198505000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


