ABSTRACT
This work reports the draft genome of Agrobacterium fabrum strain 1D1416. The assembled genome is composed of a 2,837,379-bp circular chromosome, a 2,043,296-bp linear chromosome, a 519,735-bp AT1 plasmid, a 188,396-bp AT2 plasmid, and a 196,706-bp Ti virulence plasmid. The nondisarmed strain produces gall-like structures in citrus tissue.
ANNOUNCEMENT
Here, we present the novel genome from Agrobacterium fabrum strain 1D1416. Strain 1D1416 was isolated from Euonymus japonicus and received by the Kado lab, University of California, Davis, 17 August 1979. The lyophilized strain was revived, and a single colony was streaked to purity. This was grown in Luria broth at 28 to 30°C with shaking at 200 rpm. Genomic DNA collection followed the Puregene kit (Qiagen) extraction protocol. Characterization by our lab demonstrated gall formation (pathogenicity) by 1D1416 in citrus tissue and the ability to transfer a binary plasmid-derived transfer DNA (T-DNA) by producing DsRed-expressing tissue (Fig. 1) (1).
FIG 1.
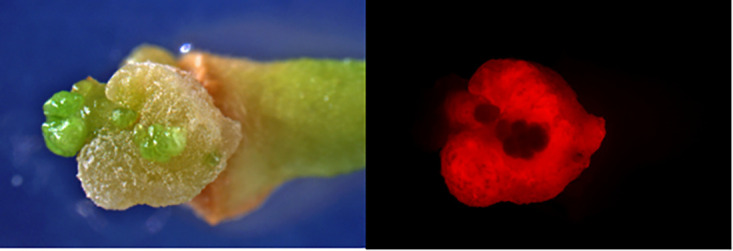
Gall formation and stable DsRed expression in citrus epicotyl tissue transformed with wild-type Agrobacterium fabrum strain 1D1416 harboring the binary vector pCTAGV-KCN3. Left panel, gall viewed under white light. Right panel, same gall displaying DsRed expression. The binary plasmid and the protocol used for citrus transformation were previously published (1).
Genomic DNA was isolated (2) using Qiagen blood and cell culture DNA maxikit 13362 and genomic DNA buffer set 19060 (Qiagen) (3). The DNA was evaluated by gel electrophoresis and quantified using both a 2100 Nanodrop spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and a Qubit fluorimeter (Invitrogen) with the Qubit double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) high-sensitivity (HS) assay kit (Invitrogen). Genomic DNA was sheared with g-TUBE (Covaris). A 20-kb DNA library was constructed from the manufacturer’s instructions and using the BluePippin size selection system and sequenced using single-molecule real-time (SMRT) sequencing technology on the PacBio RS system. The PacBio libraries were made with the SMRTbell template prep kit 1.0 following the procedure and checklist for 20-kb template preparation using the BluePippin size selection system. SMRT sequencing data were generated at an average coverage of 169.87×, with a mean read length of 18,396 bp and the total number of reads being 137,961. De novo genome assembly, in which circular consensus sequence (CCS) reads were used as input and assembly, was conducted using the hierarchical genome assembly process (HGAP) workflow (SMRT Portal; Pacific Biosciences), protocol “RS_HGAP_Assembly.3” (4), and Smrtanalysis_2.3.0 software (http://www.pacb.com/support/software-downloads/). Default parameters were used for all software unless otherwise specified.
The assembly generated 6 polished contigs with an N50 contig length of 2,043,295 bp and a sum of contig lengths of 5,927,307 bp. Linear contigs were manually aligned using SnapGene software until alignment was no longer possible. A 28,929-bp overlap was removed for the circular chromosome, which showed a final composition of 2,837,379 bp with a GC content of 59.4%. The linear chromosome was determined to be 2,043,296 bp with a GC content of 59.3%. The AT1 plasmid was composed of 589,645 bp with a GC content of 57.4%. The AT2 plasmid was composed of 188,396 bp with a GC content of 58.1%, and the virulence vector pTi-1D1416 was composed of 196,706 bp with a GC content of 56.1%. An unaligned contig was determined to be 10,295 bp with a GC content of 59.7%.
Assembled and raw read sequences were entered into the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), and BLAST was used for identification (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). Automated annotation was performed on a local RAST pipeline (5) (https://rast.nmpdr.org), but the public version of the genome was annotated by the prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline (PGAP) (6). Agrobacterium fabrum strain 1D1416 contains 5,761 predicted coding sequences, 595 subsystems, and 65 predicted RNA-coding genes.
Data availability.
The whole-genome shotgun sequence for Agrobacterium fabrum strain 1D1416 was deposited at DDBJ/ENA/GenBank under the accession no. JANPYJ000000000 and hyperlink https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/JANPYJ000000000.1/, SubmissionID SUB11886101, BioProject PRJNA863297, BioSample SAMN30028576, and SRA file SRX16758217 and hyperlink https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/SRX16758217.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This work was supported by the USDA Agricultural Research Service CRIS project 2030-21000-020. Mention of trade names or commercial products is solely for the purpose of providing specific information and does not imply recommendation or endorsement by the US Department of Agriculture.
Contributor Information
James G. Thomson, Email: James.Thomson@usda.gov.
David A. Baltrus, The University of Arizona
REFERENCES
- 1.de Oliveira MLP, Stover E, Thomson JG. 2015. The codA gene as a negative selection marker in Citrus. Springerplus 4:264. doi: 10.1186/s40064-015-1047-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wise AA, Liu Z, Binns AN. 2006. Nucleic acid extraction from Agrobacterium strains, p 67–76. In Wang K (ed), Agrobacterium protocols, 2nd ed, vol 1. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ. doi: 10.1385/1-59745-130-4:67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Qiagen. 2013–2023. CLC Genomics Workbench 8.5. Qiagen, Redwood City, CA. https://digitalinsights.qiagen.com/products-overview/discovery-insights-portfolio/analysis-and-visualization/qiagen-clc-microbial-genomics-module/?cmpid=QDI_GA_CLC&gclid=EAIaIQobChMIiqjlvNC-_wIVHBOtBh0qBAZUEAAYASAAEgIK0_D_BwE.
- 4.Chin C-S, Alexander DH, Marks P, Klammer AA, Drake J, Heiner C, Clum A, Copeland A, Huddleston J, Eichler EE, Turner SW, Korlach J. 2013. Nonhybrid, finished microbial genome assemblies from long-read SMRT sequencing data. Nat Methods 10:563–569. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Brettin T, Davis JJ, Disz T, Edwards RA, Gerdes S, Olsen GJ, Olson R, Overbeek R, Parrello B, Pusch GD, Shukla M, Thomason JA, III, Stevens R, Vonstein V, Wattam AR, Xia F. 2015. RASTtk: a modular and extensible implementation of the RAST algorithm for building custom annotation pipelines and annotating batches of genomes. Sci Rep 5:8365. doi: 10.1038/srep08365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tatusova T, DiCuccio M, Badretdin A, Chetvernin V, Nawrocki EP, Zaslavsky L, Lomsadze A, Pruitt KD, Borodovsky M, Ostell J. 2016. NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res 44:6614–6624. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The whole-genome shotgun sequence for Agrobacterium fabrum strain 1D1416 was deposited at DDBJ/ENA/GenBank under the accession no. JANPYJ000000000 and hyperlink https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/JANPYJ000000000.1/, SubmissionID SUB11886101, BioProject PRJNA863297, BioSample SAMN30028576, and SRA file SRX16758217 and hyperlink https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/SRX16758217.


