Abstract
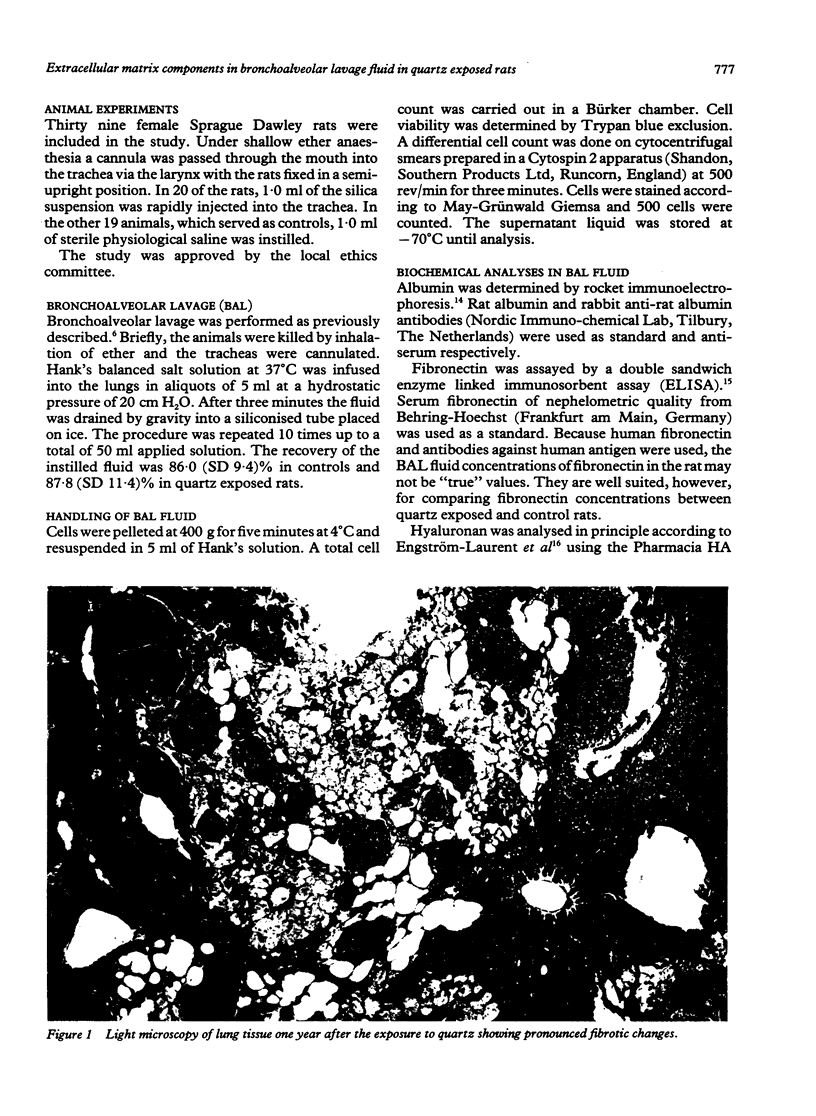
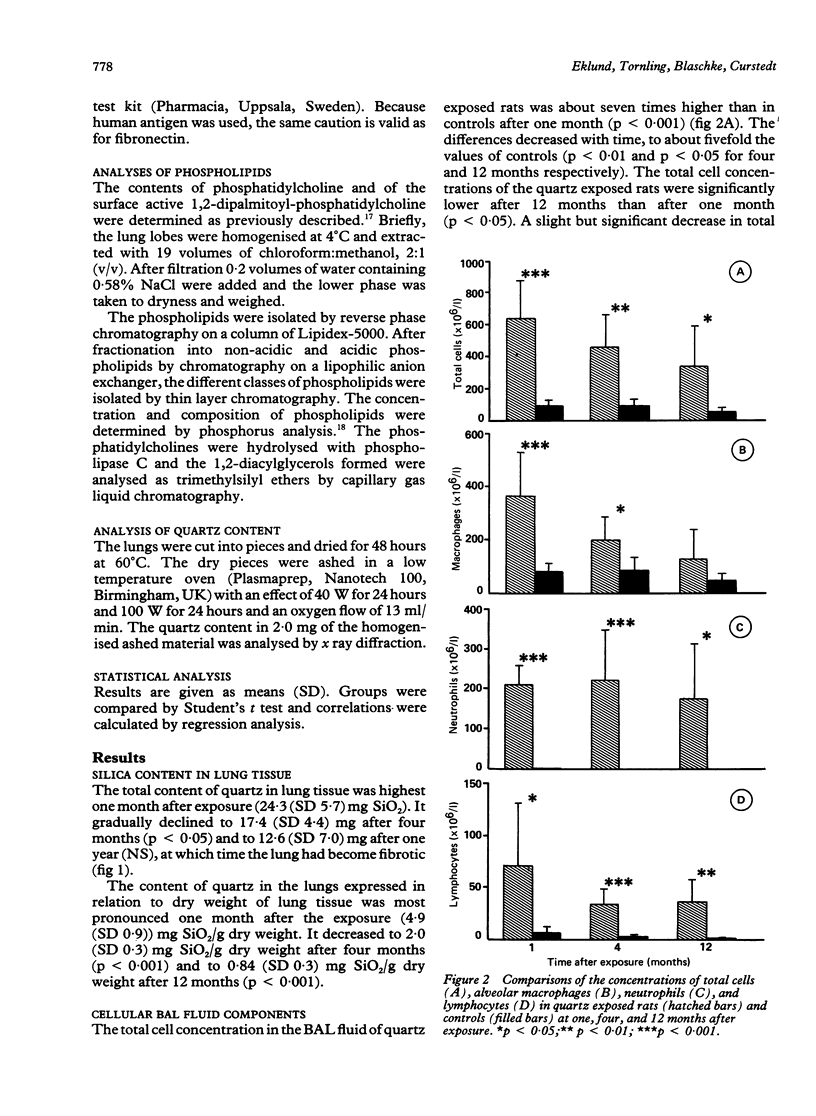
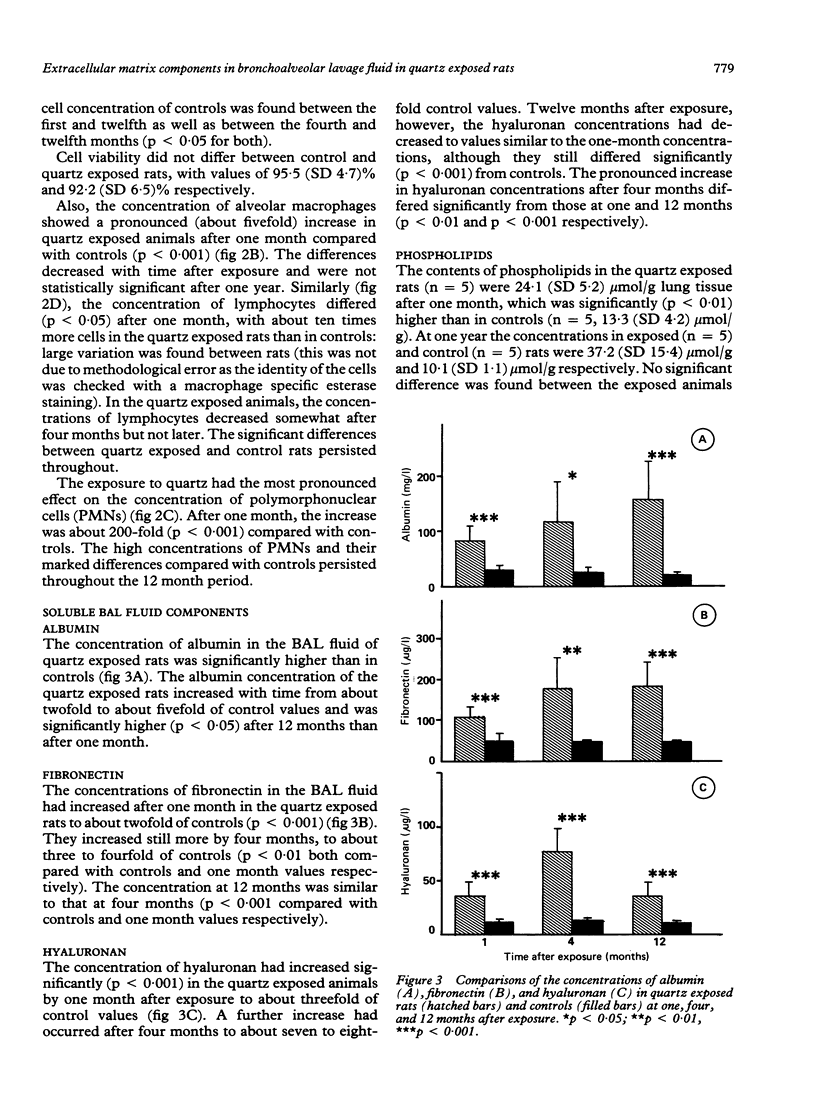
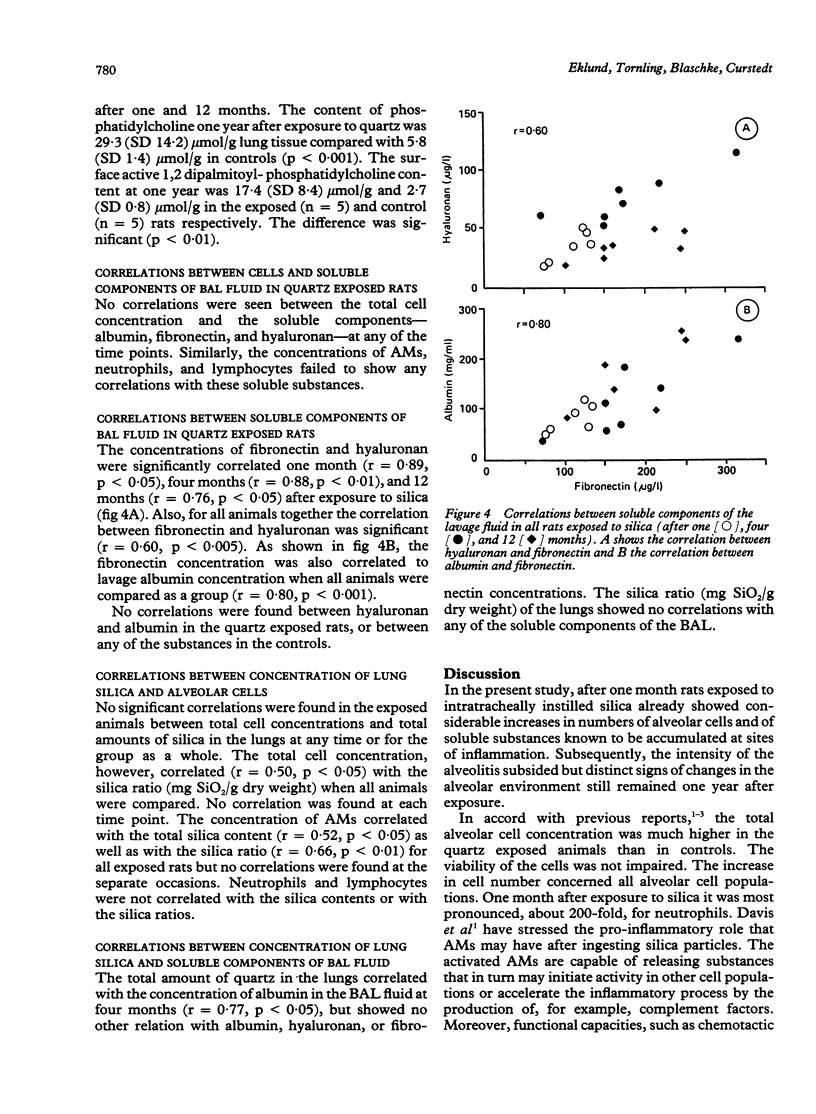
To investigate the long term effects of quartz, bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) and analysis of lung silica were performed in rats (n = 20) one, four, and 12 months after exposure to intratracheally instilled crystalline silica. Total and relative concentrations of silica in the lungs were highest one month after exposure. At this time BAL fluid concentrations of total cells, macrophages, and lymphocytes increased five to 10-fold compared with saline instilled controls (n = 19). The number of polymorphonuclear cells (PMNs) increased about 200-fold. The increased number of PMNs persisted during the year. Furthermore, albumin and fibronectin concentrations increased continually during the year, about two to fivefold the values of controls. Hyaluronan, by contrast, increased during the four month period (about eightfold) but decreased after one year to the one month concentration. Phospholipids in BAL fluid, raised already after one month, remained high at one year. The findings suggest progressive damage of the alveolar and interstitial tissues. Moreover, the increases in components of the extracellular matrix capable of building fibrotic networks are in agreement with the microscopical findings of fibrosis. Because only total cells, macrophages, and albumin concentrations correlated weakly with the silica contents of the lung, it is unlikely that the relation between quartz burden and the reaction in the lung is simple.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison A. C., Harington J. S., Birbeck M. An examination of the cytotoxic effects of silica on macrophages. J Exp Med. 1966 Aug 1;124(2):141–154. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.2.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson S. C., Belton J. C., Scheve L. G. Regulation of lung fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis by alveolar macrophages in experimental silicosis. I: Effect of macrophage conditioned medium from silica instilled rats. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 1986 Sep-Dec;7(1-2):87–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson S. C., Belton J. C., Scheve L. G. Regulation of lung fibroblast proliferation and protein synthesis by bronchiolar lavage in experimental silicosis. Environ Res. 1986 Oct;41(1):61–78. doi: 10.1016/s0013-9351(86)80168-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitterman P. B., Rennard S. I., Adelberg S., Crystal R. G. Role of fibronectin as a growth factor for fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;97(6):1925–1932. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.6.1925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bégin R. O., Cantin A. M., Boileau R. D., Bisson G. Y. Spectrum of alveolitis in quartz-exposed human subjects. Chest. 1987 Dec;92(6):1061–1067. doi: 10.1378/chest.92.6.1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bégin R., Dufresne A., Cantin A., Possmayer F., Sébastien P., Fabi D., Bilodeau G., Martel M., Bisson D., Pietrowski B. Quartz exposure, retention, and early silicosis in sheep. Exp Lung Res. 1989 May;15(3):409–428. doi: 10.3109/01902148909087868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casarett-Bruce M., Camner P., Curstedt T. Changes in pulmonary lipid composition of rabbits exposed to nickel dust. Environ Res. 1981 Dec;26(2):353–362. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(81)90211-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christman J. W., Emerson R. J., Graham W. G., Davis G. S. Mineral dust and cell recovery from the bronchoalveolar lavage of healthy Vermont granite workers. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Aug;132(2):393–399. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.2.393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czop J. K., McGowan S. E., Center D. M. Opsonin-independent phagocytosis by human alveolar macrophages: augmentation by human plasma fibronectin. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 May;125(5):607–609. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.125.5.607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis G. S. Pathogenesis of silicosis: current concepts and hypotheses. Lung. 1986;164(3):139–154. doi: 10.1007/BF02713638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dethloff L. A., Gilmore L. B., Gladen B. C., George G., Chhabra R. S., Hook G. E. Effects of silica on the composition of the pulmonary extracellular lining. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1986 Jun 15;84(1):66–83. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(86)90417-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson K., Brown G. M., Brown D. M., Slight J., Robertson M. D., Davis J. M. Impaired chemotactic responses of bronchoalveolar leukocytes in experimental pneumoconiosis. J Pathol. 1990 Jan;160(1):63–69. doi: 10.1002/path.1711600113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund A., Blaschke E. Relationship between changed alveolar-capillary permeability and angiotensin converting enzyme activity in serum in sarcoidosis. Thorax. 1986 Aug;41(8):629–634. doi: 10.1136/thx.41.8.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engström-Laurent A., Laurent U. B., Lilja K., Laurent T. C. Concentration of sodium hyaluronate in serum. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1985 Oct;45(6):497–504. doi: 10.3109/00365518509155249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross P., DeTreville R. T. Alveolar proteinosis. Its experimental production in rodents. Arch Pathol. 1968 Sep;86(3):255–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Håkansson L., Venge P. The combined action of hyaluronic acid and fibronectin stimulates neutrophil migration. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2735–2739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawada H., Horiuchi T., Shannon J. M., Kuroki Y., Voelker D. R., Mason R. J. Alveolar type II cells, surfactant protein A (SP-A), and the phospholipid components of surfactant in acute silicosis in the rat. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Aug;140(2):460–470. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.2.460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Electroimmuno assay. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1972;124:21–37. doi: 10.3109/00365517209102748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nettelbladt O., Hällgren R. Hyaluronan (hyaluronic acid) in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid during the development of bleomycin-induced alveolitis in the rat. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Oct;140(4):1028–1032. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.4.1028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postlethwaite A. E., Keski-Oja J., Balian G., Kang A. H. Induction of fibroblast chemotaxis by fibronectin. Localization of the chemotactic region to a 140,000-molecular weight non-gelatin-binding fragment. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):494–499. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennard S. I., Hunninghake G. W., Bitterman P. B., Crystal R. G. Production of fibronectin by the human alveolar macrophage: mechanism for the recruitment of fibroblasts to sites of tissue injury in interstitial lung diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7147–7151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuyler M. R., Gaumer H. R., Stankus R. P., Kaimal J., Hoffmann E., Salvaggio J. E. Bronchoalveolar lavage in silicosis. Evidence of type II cell hyperplasia. Lung. 1980;157(2):95–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöstrand M., Rylander R. Lysosomal enzyme activity and fibroblast stimulation of lavage from guinea pigs exposed to silica dust. Br J Exp Pathol. 1987 Jun;68(3):309–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhar D., Harbeck R. J., Mason R. J. Lymphocyte populations in lung tissue, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, and peripheral blood in rats at various times during the development of silicosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Jan;139(1):28–32. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.1.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornling G., Eklund A., Engström-Laurent A., Hällgren R., Unge G., Westman B. Hyaluronic acid in bronchoalveolar lavage in rats exposed to quartz. Br J Ind Med. 1987 Jul;44(7):443–445. doi: 10.1136/oem.44.7.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



