Abstract
Objective
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is characterised by an abundant desmoplastic stroma composed of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAF) and interspersed immune cells. A non-canonical CD8+ T-cell subpopulation producing IL-17A (Tc17) promotes autoimmunity and has been identified in tumours. Here, we evaluated the Tc17 role in PDAC.
Design
Infiltration of Tc17 cells in PDAC tissue was correlated with patient overall survival and tumour stage. Wild-type (WT) or Il17ra-/- quiescent pancreatic stellate cells (qPSC) were exposed to conditional media obtained from Tc17 cells (Tc17-CM); moreover, co-culture of Tc17-CM-induced inflammatory (i)CAF (Tc17-iCAF) with tumour cells was performed. IL-17A/F-, IL-17RA-, RAG1-deficient and Foxn1nu/nu mice were used to study the Tc17 role in subcutaneous and orthotopic PDAC mouse models.
Results
Increased abundance of Tc17 cells highly correlated with reduced survival and advanced tumour stage in PDAC. Tc17-CM induced iCAF differentiation as assessed by the expression of iCAF-associated genes via synergism of IL-17A and TNF. Accordingly, IL-17RA controlled the responsiveness of qPSC to Tc17-CM. Pancreatic tumour cells co-cultured with Tc17-iCAF displayed enhanced proliferation and increased expression of genes implicated in proliferation, metabolism and protection from apoptosis. Tc17-iCAF accelerated growth of mouse and human tumours in Rag1-/- and Foxn1nu/nu mice, respectively. Finally, Il17ra-expressed by fibroblasts was required for Tc17-driven tumour growth in vivo.
Conclusions
We identified Tc17 as a novel protumourigenic CD8+ T-cell subtype in PDAC, which accelerated tumour growth via IL-17RA-dependent stroma modification. We described a crosstalk between three cell types, Tc17, fibroblasts and tumour cells, promoting PDAC progression, which resulted in poor prognosis for patients.
Keywords: pancreatic cancer, cancer immunobiology, cytokines, immune response, inflammatory mechanisms
WHAT IS ALREADY KNOWN ON THIS TOPIC
CD8+ T-cell enrichment is beneficial against pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC).
Interleukin 17A promotes early pancreatic cancer development.
IL-17A alters stroma in PDAC mouse models.
WHAT THIS STUDY ADDS
Enrichment of Tc17 cells significantly associates with shorter overall survival in PDAC.
Tc17-cell frequency correlates with tumour size and with advanced tumour stage in PDAC.
Tc17- but not Th17-cell prevalence is a prognostic marker for PDAC.
Tc17 cells via synergism of IL-17A and TNF induce inflammatory cancer-associated fibroblasts (iCAF).
Tc17-induced iCAF (Tc17-iCAF) promote pancreatic cancer growth in vivo.
Tc17-iCAF change the transcriptional profile of pancreatic cancer cells towards increased proliferation, signal transduction and metabolism.
IL-17RA-sufficient CAF mediate Tc17-driven pancreatic tumour growth in vivo.
HOW THIS STUDY MIGHT AFFECT RESEARCH, PRACTICE OR POLICY.
Tc17 cells may function as a biomarker for the prognosis of PDAC patients.
Tc17 cells may be suitable as a therapeutic target in PDAC.
Combination of anti-IL-17A and anti-TNF therapy to block Tc17 effects on stroma may have an antitumour effect in the adjuvant therapy setting.
Combining anti-IL-17A plus anti-TNF therapy with inhibition of tumour cell metabolism may be suitable to target induction of iCAF and tumour metabolism, respectively.
Assessing the frequency of Tc17 cells within the CD8+ T cell pool may serve to stratify patients for checkpoint inhibitor therapy.
Introduction
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) belongs to the deadliest solid malignancies, with a 5-year overall survival (OS) rate of approximately 9%.1 Abundant desmoplastic stroma consisting of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) and immune cells, which constitute an inflammatory environment, supports the progression, heterogeneity and drug resistance in PDAC.2 CAF strongly influence tumour microenvironment (TME) through synthesis and remodelling of the extracellular matrix (ECM), and through production of factors, which direct cell infiltration and function.3 Depending on the subtype, CAFs are suggested to either promote or inhibit PDAC progression. CAF expressing α-smooth muscle actin (αSMA encoded by Acta2) are termed myofibroblastic CAF (myCAF) and can exhibit a tumour-restricting or tumour-promoting function, dependent on the phenotype.4 5 TGFβ produced by tumour cells, myeloid cells and regulatory T cells (Treg) drives myCAF differentiation.4 6 7 Genetic depletion of Treg led to an accelerated tumour progression and differentiation of inflammatory CAF (iCAF) as well as myeloid cell infiltration in a mouse model of PDAC.7 Thus, iCAF differentiation is directed by tumour-secreted ligands including IL-1 and TNF, which are characterised by inflammatory gene expression, the marker Ly6c and a PDAC-promoting function.4 6 8
IL-17A signals through the receptor (IL-17R) consisting of the specific IL-17RC and the common IL-17RA chains as a homodimer or IL-17A/F as heterodimer. Likewise, IL-17F homodimers bind to the same receptor, however, induce signalling with a lower potency.9 In non-haematopoietic cells, IL-17A induces production of CXCL1, CXCL2, CXCL8, IL-6 and G-CSF, which drive myeloid cell infiltration.10 In the context of PDAC, IL-17A supports early carcinogenesis (pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia, PanIN),11 12 regulates PDAC stem cell features,13 promotes tumour growth14 15 and mediates resistance to checkpoint inhibitors via induction of neutrophil extracellular traps.16 Furthermore, it has recently been shown that IL-17A modulates CAF transcriptome in Kras LSL-G12D/+; Trp53LSL-R172H/+; Pdx1-Cre (KPC)-driven tumours.17
IL-17A can be produced by different lymphocyte populations including adaptive CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, termed Th17 and Tc17 cells, respectively, but also by innate lymphocytes (ILC).18 In contrast to conventional IFNγ-producing and TNF-producing CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL), Tc17 cells are non-cytotoxic; they express the transcription factor RORγt and produce IL-17A/F and, to a lesser extent IFNγ, TNF, IL-21.18 Tc17 cells play an important role in tissue homoeostasis and protection from infections.19 20 During chronic inflammation, including autoimmunity of the skin (psoriasis)21 22 or the central nervous system (multiple sclerosis),23 24 Tc17 cells display a disease-promoting function. Likewise, in cancers of the gastrointestinal-tract, Tc17 cells are linked to poor survival suggesting a pathogenic contribution.25–27However, a subpopulation of Tc17/IFNγ+ cells, displayed anti-glioma activity and cytotoxicity on IL-12 treatment.28 29 In PDAC, Tc17 presence and function has not been described so far.
Here, we provide data pointing to Tc17 as a new pathogenic cell population in the pancreatic TME, responsible for hitherto unknown stroma-modulating mechanisms that accelerates PDAC growth in mouse models and most likely in patients.
Materials and methods
Detailed methods are described in online supplemental information.
gutjnl-2022-327855supp001.pdf (16.5MB, pdf)
Results
Increased Tc17 cell frequency correlates with advanced tumour stage and poor survival in PDAC
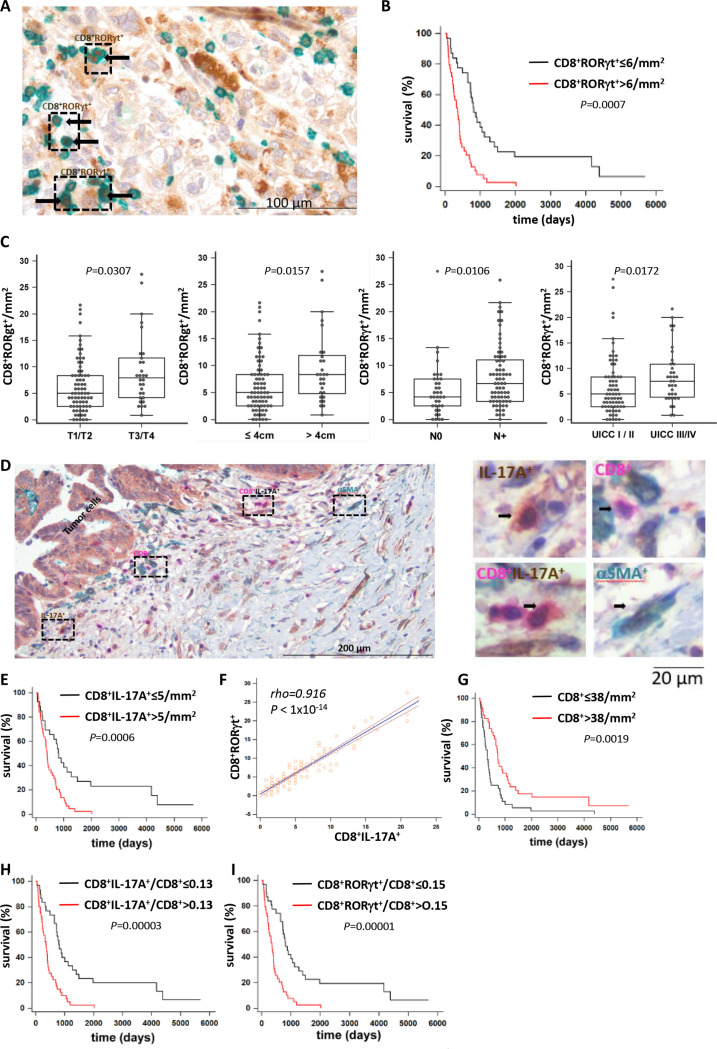
To evaluate the potential role of Tc17 cells in PDAC, we collected pancreatic tissue from 112 patients (online supplemental table 1) and identified the presence of two Tc17 markers, RORγt or IL-17A, within infiltrating CD8+ cells (figure 1A, D, online supplemental figure 1A, B). Analysis of RORγt+ or IL-17A+ CD8+ T-cells revealed a highly significant correlation between their enrichment and shorter OS (figure 1B, E). Increased Tc17 abundance was significantly associated with tumour size, lymph node metastases (N+) and advanced tumour stage (UICCIII/IV), but not with histological grading (figure 1C, online supplemental figure 1C–E). A strong correlation was found between frequencies of CD8+RORγt+ and CD8+IL-17A+ cells, underscoring reliability of the Tc17 detection (figure 1F). Furthermore, enrichment in single-positive IL-17A+-cells associated with shorter OS, and IL-17A+ cells correlated with Tc17 prevalence, indicating Tc17 contribution to IL-17A-mediated PDAC progression (online supplemental figure 1F–H). Finally, increased Tc17 abundance in PDAC in comparison to adjacent non-neoplastic tissue was detected using flow cytometry (online supplemental figure 1I, J).
Figure 1.
Increased Tc17 infiltration associates with shorter survival in PDAC. (A) Double immunostaining of PDAC tissue sections using antibodies against CD8α (green) and RORγt (brown), scale bar 100 µm. (B) Kaplan-Meier curve of overall survival (survival %) of patients with surgically resected PDAC showing≤6/mm2 vs >6/mm2 CD8+ RORγt+ cell infiltation (n=71, p values determined by log-rank test). (C) CD8+ RORγt+ cell frequency per mm2 in T1/2 vs T3/T4 tumours (n=105), in tumours ≤4 cm vs >4 cm (n=105), No vs n+tumours (n=109) and UICC stage I/II vs III/IV (n=106). Box-plots depict the lower and upper adjacent values (whiskers) and the upper and lower quartiles (top and bottom edges of the box). Horizontal lines inside boxes indicate median, p values determined by Mann-Whitney U test. Each dot represents one individual. (D) Triple immunostaining of PDAC tissue for CD8α, IL-17A, and alpha−smooth muscle actin (αSMA). Left, PDAC tissue areas are denoted with single-positive IL-17A+ cells (brown), single-positive CD8+ cells (magenta), double-positive CD8+IL-17A+ (magenta-brown) and single-positive αSMA+ cells (green), scale bar 200 µm. Right, image magnification of cells highlighted in the left panel, scale bar 20 µm. (E) Kaplan-Meier curve of overall survival (survival %) of patients with surgically resected PDAC showing ≤5/mm2 vs >5/mm2 CD8+ IL-17A+ cell infiltration (n=71, p values determined by log-rank test). (F) Linear regression analysis of CD8+RORγt+ vs CD8+IL-17A+ cell frequencies in PDAC tissue. Linear regression line, Spearman’s correlation coefficient rho, and respective p value is shown in the plot (n=111). (G–I) Kaplan-Meier curves of overall survival (survival %) of patients with surgically resected PDAC showing ≤38/mm2 vs >38/mm2 single-positive CD8+ cell infiltration (G), intratumoural CD8+IL-17A+/CD8 ratios + ≤0.13 vs >0.13 (H) and intratumoural CD8+RORγt +/CD8+ ratios ≤0.15 vs >0.15 (I) (n=71, p values determined by log-rank test). PDAC, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Consistent with previous reports,30–32 enhanced accumulation of total CD8+ T cells, associated with longer OS (figure 1G), confirming their favourable role in PDAC. A high ratio of Tc17 to total CD8+ T cells correlated with a shorter OS (figure 1H, I), indicating an overriding protumourigenic Tc17 effect. Multivariate Cox-regression analysis confirmed Tc17 frequency as an independent prognostic marker for PDAC (online supplemental tables 2 and 3).
Interestingly, increased accumulation of Th17 cells (CD4+RORγt+, (online supplemental figure 2A) failed to correlate with shorter OS, tumour size, lymph node metastases, or tumour-grading, but it associated with advanced PDAC stage (online supplemental figure 2B–D). Th17 outnumbered Tc17 cells and the frequencies of both populations moderately correlated in tumour tissues (online supplemental figure 2E–G). Multivariate Cox-regression analysis further confirmed the prevalence of Tc17, but not of Th17, as a prognostic marker for PDAC (online supplemental tables 4–6).
Recent transcriptome analysis in PDAC identified two major subtypes termed ‘classical’ and ‘basal-like’, with a prolonged and a shorter OS, respectively.33 34 To evaluate, whether presence of Tc17 cells associates with the PDAC subtype, we stained tumour tissues for GATA6 and cytokeratin 5 (CK5) as surrogate markers for the ‘classical’ and ‘basal-like’ subtype, respectively.35 Although GATA6 and CK5 expression was moderately inverse, they failed to correlate with OS and, consequently with Tc17 abundance in the PDAC tissues (online supplemental figure 3A–D).
Next, we examined Tc17 presence in KPC mice, and in a subcutaneous model applying murine pancreatic tumour cells expressing a model antigen ovalbumin (PancOVA). We found an infiltration of Tc17 cells in both KPC-derived and PancOVA-derived PDAC tumours (online supplemental figure 3E–I).
Taken together, in contrast to total CD8+ T cells or Th17 cells, enrichment of Tc17 cells strongly associates with shorter OS and is an independent prognostic marker for PDAC. Moreover, Tc17 correlate with advanced tumour stage, increased tumour size, and metastases, suggesting their involvement in disease aggressiveness.
Tc17 cells enhance pancreatic tumour growth in a mouse model
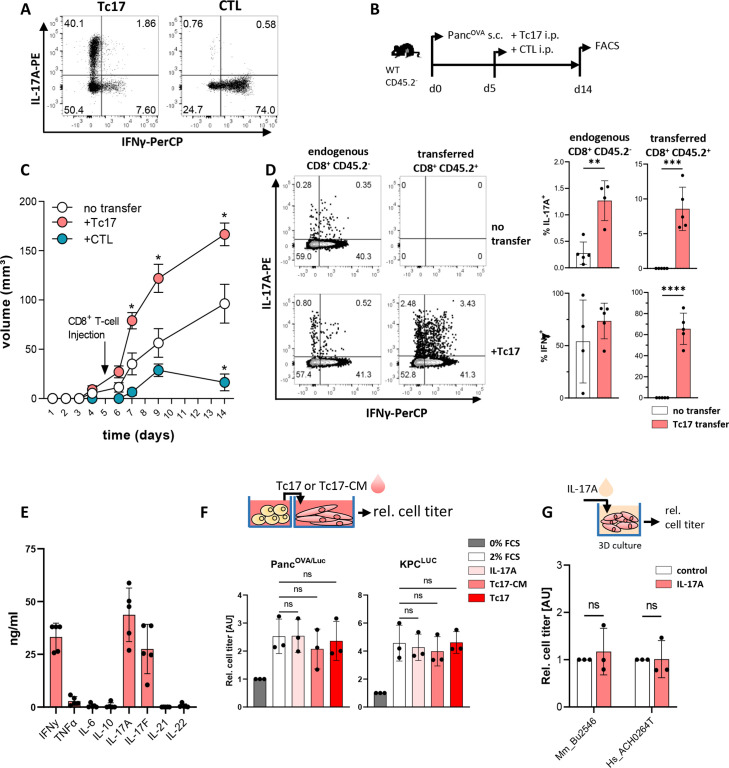
To examine the function of Tc17 cells in PDAC, murine Tc17 and control (CTL) cells were generated in vitro. Their cytokine patterns were confirmed by flow cytometry (figure 2A). These cells were adoptively transferred into PancOVA tumour-bearing congenic (CD45.2-) mice (figure 2B). In comparison to mice without T-cell transfer, mice treated with CTLs rejected tumours as expected (figure 2C), while Tc17 significantly accelerated tumour growth. At the experimental endpoint, the transferred (CD45.2+) and endogenous (CD45.2-) intratumoural Tc17 cells were detectable, indicating that they invaded tumours and maintained their cytokine profile (figure 2D). Interestingly, Tc17 transfer triggered an enhanced accumulation of endogenous IL-17 but not IFNγ producing CD8+ T cells in tumours. Thus, transferred Tc17 cells are stable, migrate and accelerate endogenous Tc17 accumulation, and thereby promote tumour growth.
Figure 2.
Tc17 cells enhance pancreatic tumour growth in vivo. (A) Purified CD8+ T cells isolated from CD45.2+OT-I mice were stimulated with anti-CD3/CD28 antibodies in the presence of TGFβ+IL-6 (Tc17) or IL-12+IL-2 (CTL) for 4 days. Differentiation was confirmed by intracellular staining for IL-17A and IFNγ and subsequent FACS analysis. Representative FACS plots are shown. (B) Scheme of experimental design. Congenic CD45.2- mice were subcutaneously (s.c.) injected with 106 PancOVA cells. After 5 days, tumour-bearing mice were injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) with 106 Tc17 or CTLs obtained from CD45.2+OT-I mice or with PBS (no transfer). The analysis was performed at the indicated end of the experiment. (C) Tumour-growth curve of subcutaneous tumours is shown (tumour volume in mm3 (mean±SE, n=5–7 mice). *p<0.05 indicates the tumour volume comparisons between mice without transfer and mice with Tc17 or CTL transfer. (D) FACS analysis of IL-17A and IFNγ production after restimulation of tumour single-cell suspensions with PMA/Ionomycin in the presence of brefeldin A for 5 hours. Data from endogenous CD45.2- or transferred CD45.2+ CD8+ T cells. Left, representative FACS plots are shown. Right, quantification of the frequency of IL-17A+ (top) or IFNγ+ (bottom) among endogenous (CD45.2-) or transferred (CD45.2+) CD8+ T cells with or without Tc17 transfer (n=4–5 tumours). (E) Quantification of cytokines (ng/mL) produced by in vitro differentiated Tc17 cells after restimulation with plate-bound anti-CD3 antibodies for 24 hours (n=5). (F) Top, scheme of the experimental design showing the relative titre of tumour cells cultured for 36 hours with Tc17 cells generated from WT CD8+ T cells or with Tc17-conditional media (Tc17-CM). Tc17-CM were obtained after restimulation of differentiated Tc17 cells with plate-bound anti-CD3 for 24 hours. Bottom, the tumour-cell titre was obtained from PancOVA or KPC cells tagged with firefly luciferase (PancOVA/Luc, KPCLuc) and assessed as fold of luciferase activity, normalised to the control (0% FCS), which was arbitrarily set to 1. Tumour cells were cultured alone in 0% FCS (control) or 2% FCS (2% FCS), or in 2% FCS containing IL-17A (IL-17A), Tc17-CM (Tc17-CM) or Tc17 cells (Tc17) (n=3). (G) Top, scheme of the experimental design showing treatment of matrigel-embedded 3D organoid cultures with 50 ng/mL IL-17A. Bottom, cell titre assay of mouse (Mm_Bu2548) or human (Hs_ACH0264T) PDAC organoids treated with recombinant murine (rm) or recombinant human (rh)IL-17A (n=3). The relative cell titre without IL-17A treatment (control) was arbitrarily set to 1. (D–G) Bars show mean±SD; biological replicates are plotted. In (C) *p<0.05 determined by mixed-effects model (REML), in (D) **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001 by t-test, in (F) statistics evaluated by two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD multiple comparison test, ns (non-significant) in (G) statistics evaluated by Mann-Whitney U test. ANOVA, analysis of variance; HSD, honestly significant difference; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; PDAC, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
To understand, how Tc17 cells promote tumourigenesis, we examined the Tc17 secretome and detected mainly IL-17A, IL-17F, IFNγ and low TNF (figure 2E), suggesting an involvement of these cytokines. However, culturing PancOVA, or KPC, or primary human PDAC cells together with IL-17A, or in conditional media obtained from Tc17 cultures (Tc17-CM), or with Tc17 cells failed to enhance tumour cell growth (figure 2F, G), suggesting an indirect Tc17 effect.
Tc17-CM promote iCAF differentiation via synergism of IL-17A and TNF
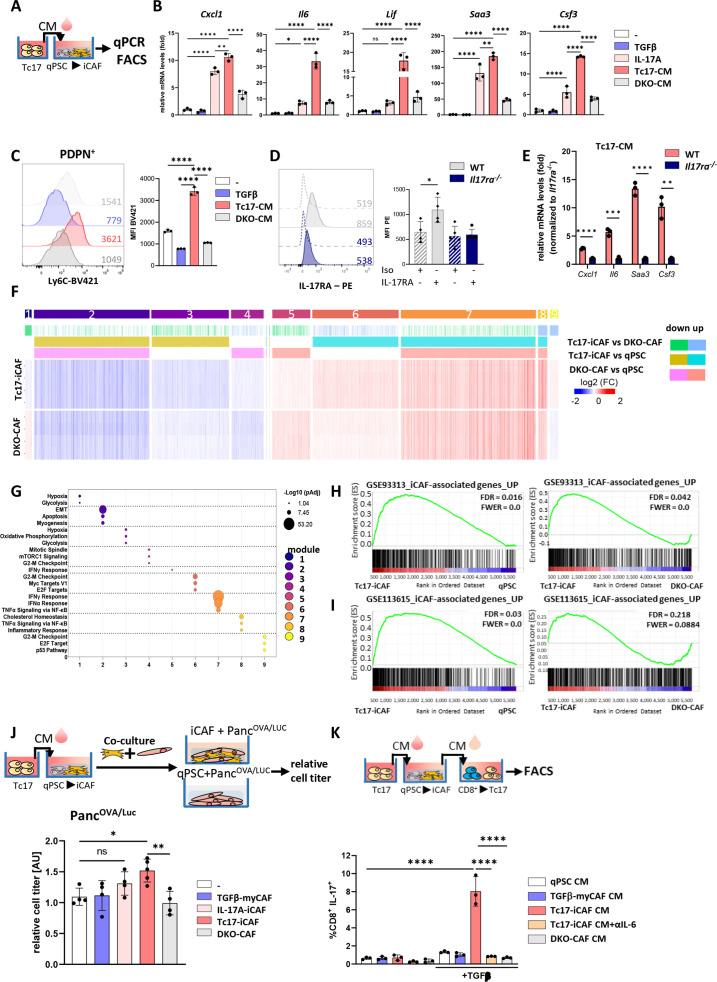
Considering the highly desmoplastic character of PDAC with CAFs modulating tumourigenesis, we examined the impact of Tc17-CM on the differentiation of quiescent pancreatic stellate cells (qPSC), recently described to regulate stromal microenvironment associated with PDAC aggressiveness36 (figure 3A). We employed IL-17A or CM generated from IL-17A/F double-knockout Tc17 cells (DKOTc17, DKO-CM) as controls. DKOTc17 failed to produce any IL-17A/F, but secreted IFNγ and TNF, and expressed RORγt and T-bet to similar extent as WT Tc17 cells, indicating their bona fide Tc17 character (online supplemental figure 4A-C). Culture of qPSC with Tc17-CM upregulated Cxcl1, Il6, Lif, Saa3, Csf3 and Ly6C expression, representing iCAF-associated markers, but not myCAF transcripts (figure 3B, C, online supplemental figure 4D). IL-17A upregulated the expression of some iCAF-specific genes to higher extent comparing to DKO-CM, indicating qPSC reactivity to IL-17A. Accordingly, qPSC, TGFβ-myCAF and Tc17-induced-iCAF (Tc17-iCAF) expressed both receptor chains for IL-17A/F (IL-17RA and IL-17RC) (online supplemental figure 3E). CRISPR/Cas9-mediated deletion of IL-17RA in PSC, strongly restricted their responsiveness to Tc17-CM with respect to inflammatory gene induction (figure 3D, E, online supplemental figure 3F, G).
Figure 3.
Reciprocal crosstalk between Tc17 cells and iCAF. (A) Scheme of the experimental design showing Tc17-CM production. Tc17-CM was used to stimulate matrigel-embedded quiescent murine quiescent pancreatic stellate cells (qPSC) and to evaluate mRNA expression of iCAF-specific transcripts (B) or Ly6c+ phenotype (C). (B) qPCR for indicated iCAF transcripts in PSC after a 48- hour incubation with control medium (-), +TGFβ(2 ng/mL) (TGFβ), +IL-17A(50 ng/mL) (IL-17A), 30% Tc17-CM (Tc17-CM) or 30% CM obtained from IL-17A/FDKO Tc17 cells (DKO-CM), respectively. All incubations were done in control medium supplemented with the respective compounds or media. Fold mRNA expression is shown, normalised to the control (-), which was arbitrarily set to 1; (n=3). (C) FACS analysis of Ly6c levels by PSC after 48 hours incubation as described in B; mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) is shown. Left, representative histograms. Right, quantification of Ly6c levels, (n=3). (D) FACS analysis of WT qPSC and Il17ra-/- qPSC for IL-17RA levels, MFI is shown. Left, representative histograms. Right, quantification of IL-17RA levels (n=3). (E) qPCR analysis of the indicated iCAF transcripts in WT or Il17ra-/- PSC after incubation with Tc17-CM for 48 hours. Fold mRNA expression is shown, normalised to Il17ra-/- PSC, which was arbitrarily set to 1; (n=3). (F) Heatmap of differentially expressed genes (Z score normalised, FDR≤0.001) by PSC after incubation with control medium (qPSC) or with control medium containing 30% Tc17-CM (Tc17-iCAF) or 30% DKOTc17-CM (DKO-CAF) for 48 hours classified into modules based on the mutual upregulation or downregulation (n=4, biological replicates). (G) Pathway enrichment analysis for Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB) Hallmark 2020. Bubble graph displays the three most significant enriched pathways by –log10 value (p adj) for nine modules established in (F). (H, I) Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) to identify differential expression of iCAF-associated genes based on raw data RNA-Seq GSE933134 (H) or GSE1136156 (I) in Tc17-iCAF vs qPSC (left) or DKO-CAF (right). (J) Top, scheme of the experimental design showing Tc17-iCAF induction, thereafter co-culture with PancOVA/Luccells for 36 hours. Bottom, tumour-cell titre was obtained from PancOVA cells tagged with firefly luciferase (PancOVA/Luc) after culture with control medium (-) or co-culture with TGFβ-myCAF (TGFβ-myCAF), IL-17A-iCAF (IL-17A-iCAF), Tc17-iCAF (Tc17-iCAF) or DKO-CAF (DKO-CAF). Tumour cell titre was assessed as fold of luciferase activity normalised to the control (-), which was arbitrarily set to 1, (n=4–5). (K) Top, scheme of the experimental design showing the production of CM from qPSC, TGFβ-myCAF, Tc17-iCAF, DKO-CAF, which were added to purified CD8+ T cells. Bottom, quantification of FACS analysis showing frequencies of IL-17A-producing CD8+ T cells after anti-CD3/CD28 activation in the presence or absence of TGFβ and with/without 50% CM obtained from qPSC (qPSC CM), TGFβ-myCAF (TGFβ-myCAF CM), Tc17-iCAF (Tc17-iCAF CM), Tc17-iCAF+αIL-6 (Tc17-iCAF CM +αIL-6) or DKO-iCAF (DKO-CAF CM) after 72 hours (n=3). (B–E, J, K) Bars show mean±SD; biological replicates are plotted. In (B, C, J, K) *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001 evaluated by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD multiple comparison test, ns (non-significant) (D, E) *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001 evaluated by two-tailed, unpaired t-test. ANOVA, analysis of variance; HSD, honestly significant difference; iCAF, inflammatory cancer-associated fibroblast.
RNA-sequencing of qPSC, Tc17-iCAF and DKOTc17-induced-CAF (DKO-CAF) cells revealed differential gene expression (DEG=5639, padj<0.001). DEG were classified in nine modules, depending on the mutual upregulation or downregulation, and examined by Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB Hallmark 2020). Pathways characteristic of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and myogenesis (module 2) were downregulated in Tc17-iCAF and DKO-CAF comparing to qPSC, indicating suppression of myCAF differentiation-potential. Along with qPCR results, Tc17-iCAF comparing to DKO-CAF strongly upregulated genes associated with inflammatory response and TNF-signalling (module 8), and with proliferation (modules 4, 6 and 9) (figure 3F, G), confirming their inflammatory character. Interestingly, the expression of Ilr1 mediating induction and maintenance of iCAF by tumour-derived factors,6 was significantly upregulated in Tc17-iCAF ersus qPSC (online supplemental figure 4H). Further, gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA)37 using published gene signatures4 6 revealed that Tc17-iCAF transcriptome was enriched with genes expressed by tumour-driven iCAF comparing to DKO-CAF or qPSC (figure 3H, I, online supplemental figure 4I), indicating that Tc17 and tumour-derived factors drive a similar inflammatory state in PSC.
To understand the contribution of Tc17-secreted cytokines in iCAF induction, we treated murine qPSC with IL-17A/F alone or in combination. In contrast to IL-17A, IL-17F only marginally affected the inflammatory gene expression (online supplemental figure 4J). Since TNF is produced by Tc17 and promotes iCAF differentiation,6 we examined its contribution. Neutralisation of TNF in Tc17-CM led to a significant reduction of iCAF gene expression; accordingly, combining it with IL-17A synergistically enhanced their levels (online supplemental figure 4K, L). Human PSC expressed the IL-17RA/C and responded to IL-17A/F with a similar inflammatory gene induction, indicating species-specific differences. However, as for mouse PSC, the IL-17A effect was synergistically upregulated by TNF also in human PSC (online supplemental figure 5A–C). Thus, Tc17-CM via synergism of IL-17A and TNF promotes iCAF differentiation.
The iCAF-promoting effect applied for both Tc17-CM and Th17-CM. However, Tc17-CM induced higher Il6 expression comparing to Th17-CM, while Th17-CM strongly enhanced Saa3 and Csf3 levels in PSC (online supplemental figure 5D). Analysis of 8 different cytokines revealed a significantly higher content of TNF and IFNγ in Tc17-CM vs Th17-CM (online supplemental figure 5E, F), suggesting that a specific cytokine-composition secreted by Tc17 versus Th17 cells affects the iCAF transcriptome. Considering that G-CSF encoded by Csf3 directs neutrophil-like cell infiltration38 and Saa3 was suggested to regulate metabolite supply for tumour cells,39 while IL-6 promotes angiogenesis, myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), and PDAC invasiveness,40 one can speculate that Tc17 versus Th17 cells can differentially shape PDAC towards MDSCs accumulation, angiogenesis and invasiveness versus nutrient supply and neutrophilia, respectively.
To understand if Tc17-iCAF influence pancreatic tumour growth, we co-cultured them with PancOVA cells expressing luciferase. Besides Tc17-iCAF, we used qPSC, TGFβ-myCAF, IL-17A-driven-iCAF or DKO-CAF, as controls. This assay revealed that solely Tc17-iCAF promoted pancreatic cancer cell proliferation (figure 3J).
In CM obtained from Tc17-iCAF (Tc17-iCAF-CM) their marker cytokine IL-6 was readily detectable (online supplemental figure 5G). Consistent with the known Tc17 induction by IL-6 together with TGFβ,18 Tc17-iCAF-CM in combination with TGFβ promoted IL-17, but not IFNγ production by CD8+ T cells in IL-6-dependent manner (figure 3K, online supplemental figure 5H, I), indicating a reciprocal crosstalk between Tc17 and iCAF positively enhancing each phenotype.
Thus, IL-17RA expression by PSC is required for Tc17-iCAF differentiation, which is mediated via synergism of IL-17A and TNF. Tc17-iCAF enhance tumour cell proliferation and promote Tc17 differentiation via IL-6 in a positive feedback loop.
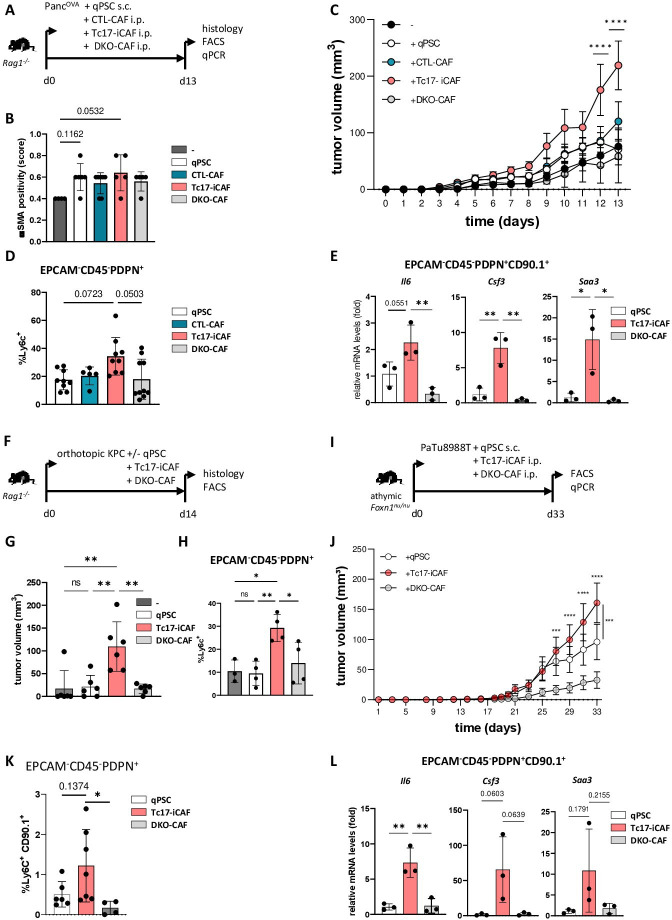
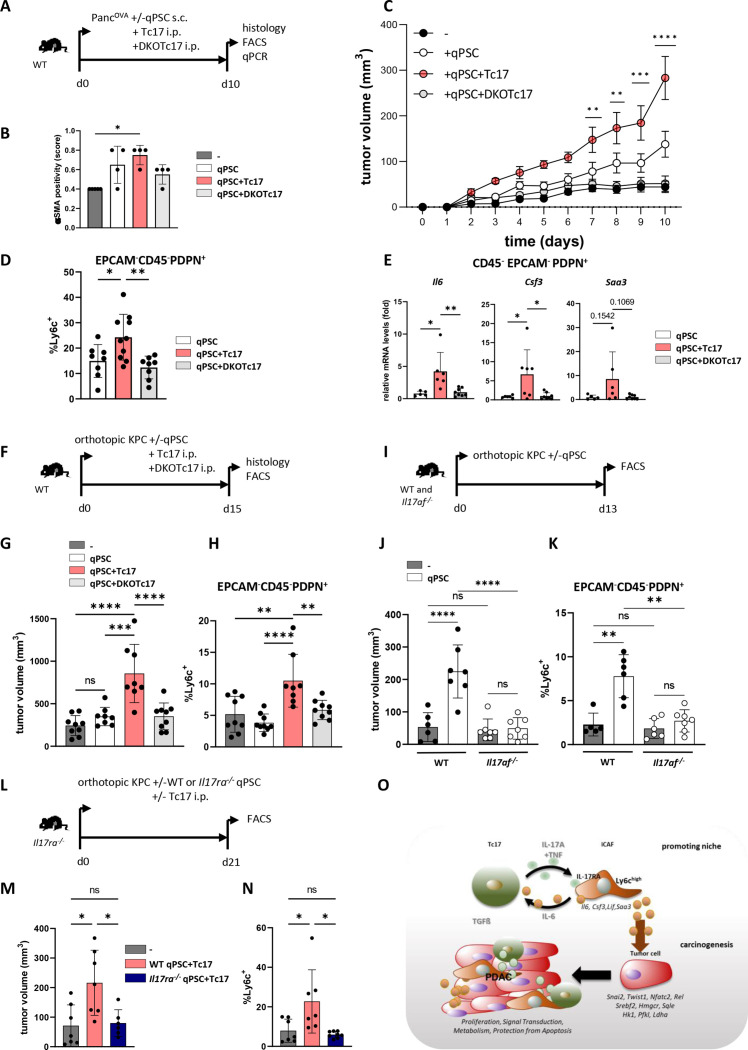
Tc17-iCAF promote tumour growth in vivo
To investigate if Tc17-iCAF promote pancreatic tumour growth in vivo, we transduced PSC with a congenic marker CD90.1 to enable their separation from endogenous (CD90.2+CD90.1-) CAFs. These transduced PSC were used to generate in vitro qPSC, CTL-CAF, Tc17-iCAF or DKO-iCAF, which were coinjected subcutaneously with PancOVA cells into immunodeficient Rag1-/- mice (figure 4A). In samples with CAF co-injection, higher amounts of αSMA+ cells were detectible; however, there was only slight collagen deposition, probably due to fast tumour growth (figure 4B, online supplemental figure 6A, B). Tc17-iCAF strongly promoted tumour growth (figure 4C) and displayed Ly6chigh phenotype (figure 4D, online supplemental figure 6C, D). They expressed Il6, Csf3 and Saa3 at higher levels as compared with DKO-CAF or qPSC, while myCAF markers were rather downregulated (figure 4E, online supplemental figure 6E), indicating maintenance of an inflammatory phenotype in vivo. Interestingly, CTL-CAF promoted tumour growth to lower extent than Tc17-iCAF. Consistently, the CTL cytokine IFNγ, comparing to IL-17A alone or in combination with TNF, displayed a restricted proinflammatory effect on qPSC. Accordingly, Tc17-CM promoted stronger iCAF profile compared with CTL-CM (online supplemental figure 6F, G), indicating context-specific TNF effects modulating PSC differentiation.
Figure 4.
Tc17-iCAF promote pancreatic tumour growth in vivo. (A) Scheme of the experimental design. 5×105 PancOVA tumour cells ±5×105 in vitro differentiated CD90.1+qPSC, CD90.1+CTL-CAF, CD90.1+Tc17-iCAF or CD90.1+DKO-CAF were subcutaneously co-injected into immunodeficient Rag1-/- mice. Histology and CAF analyses were performed at the indicated end of the experiment. (B) Quantification of αSMA staining in tumour tissue of mice injected with PancOVA cells alone (-) or co-injected with qPSC (qPSC), with CTL-CAF (CTL-CAF), with Tc17-iCAF (Tc17-iCAF) or with DKO-CAF (DKO-CAF), based on previously published scoring,17 (n=4–7). (C) Tumour-growth curve of subcutaneous tumours is shown (tumour volume in MM3; mean±SEM, n=5–7, a representative of two independent experiments each with 5–7 mice). ****p<0.0001 indicates the tumour volume comparisons between mice with Tc17-iCAF vs qPSC injection. (D) FACS analysis of Ly6chigh cell frequency in gated EPCAM-CD45-PDPN+ fibroblasts in subcutaneous tumours (n=5–10). (E) qPCR analysis of the indicated genes expressed by transferred EPCAM-CD45-PDPN+CD90.1+ fibroblasts sorted from subcutaneous tumours (mean±SD, n=3). Fold of mRNA expression is shown, normalised to the qPSC group, which was arbitrarily set to 1, (n=3). (F) Scheme of the experimental design. 2×104 KPC tumour cells±2 × 104 CD90.1+qPSC, CD90.1+Tc17-iCAF or CD90.1+DKO-CAF were orthotopically co-injected into Rag1-/- mice. The tumour volume and CAF phenotype were analysed at the indicated end of the experiment. (G) Tumour volume of orthotopic tumours of mice injected with KPC cells alone (-) or co-injected with qPSC (qPSC), with Tc17-iCAF (Tc17-iCAF) or with DKO-CAF (DKO-CAF) is shown (mean±SD, n=6 mice). (H) FACS analysis of Ly6chigh cell frequency in gated EPCAM-CD45-PDPN+ cells in orthotopic tumours of mice treated as indicated (mean±SD, n=3–4). (I) Scheme of the experimental design. 5×105 PaTu8988T human PDAC cells together with 5×105 in vitro differentiated CD90.1+qPSC or CD90.1+Tc17-iCAF or CD90.1+DKO-CAF or were co-injected subcutaneously into immunodeficient athymic Foxn1nu/nu nude mice. CAF analysis was performed at the indicated end of the experiment. (J) Tumour-growth curve of subcutaneous tumours (MM3) of mice co-injected with PaTU8988T cells and with qPSC (qPSC) or with Tc17-iCAF (Tc17-iCAF) or with DKO-CAF (DKO-CAF) (mean±SEM, n=10 mice). ***p<0.001 and ****p<0.0001 above the PaTu8988T-Tc17-iCAF curve indicate the comparisons between mice with Tc17-iCAF vs DKO-iCAF co-injection. ***p<0.0005 on the right side of the graph indicates the comparison between mice with Tc17-iCAF vs qPSC co-injection. (K) FACS analysis of Ly6chigh cell frequency in gated EPCAM-CD45-PDPN+ fibroblasts in subcutaneous tumours (n=4–6). (L) qPCR analysis of the indicated gene expression by sorted from subcutaneous tumours transferred EPCAM-CD45-PDPN+CD90.1+ fibroblasts (mean±SD, n=3). Fold of mRNA expression is shown, normalised to the qPSC group, which was arbitrarily set to 1 (n=3). (B, D, E, G, H, J, K, L) biological replicates are plotted. In (B, D, K) statistics by Kruskal-Wallis-Test, *p<0.05, ns (non-significant) (C, J) ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001 determined by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test, (E, G, H, L) *p<0.05, **p<0.01 and p values by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD multiple comparison test. αSMA, a-smooth muscle actin; ANOVA, analysis of variance; HSD, honestly significant difference; iCAF, inflammatory cancer-associated fibroblasts; qPSC, quiescent pancreatic stellate cell.
We confirmed the Tc17-iCAF-driven tumour-growth function and maintenance of inflammatory Ly6chigh phenotype in comparison to qPSC or DKO-CAF in the pancreatic tissue applying KPC tumour cells as described before41 (figure 4F–H, online supplemental figure 6H, I). Likewise, Tc17-iCAF partially maintained the phenotype and strongly promoted growth of human PaTu8988T PDAC cells in athymic nude mice comparing to qPSC or DKO-CAF (figure 4I–L, online supplemental figure 6J), indicating phenotype retention and growth-promoting function for mouse and human tumours.
Tc17-iCAF alter the transcriptional programme of pancreatic tumour cells
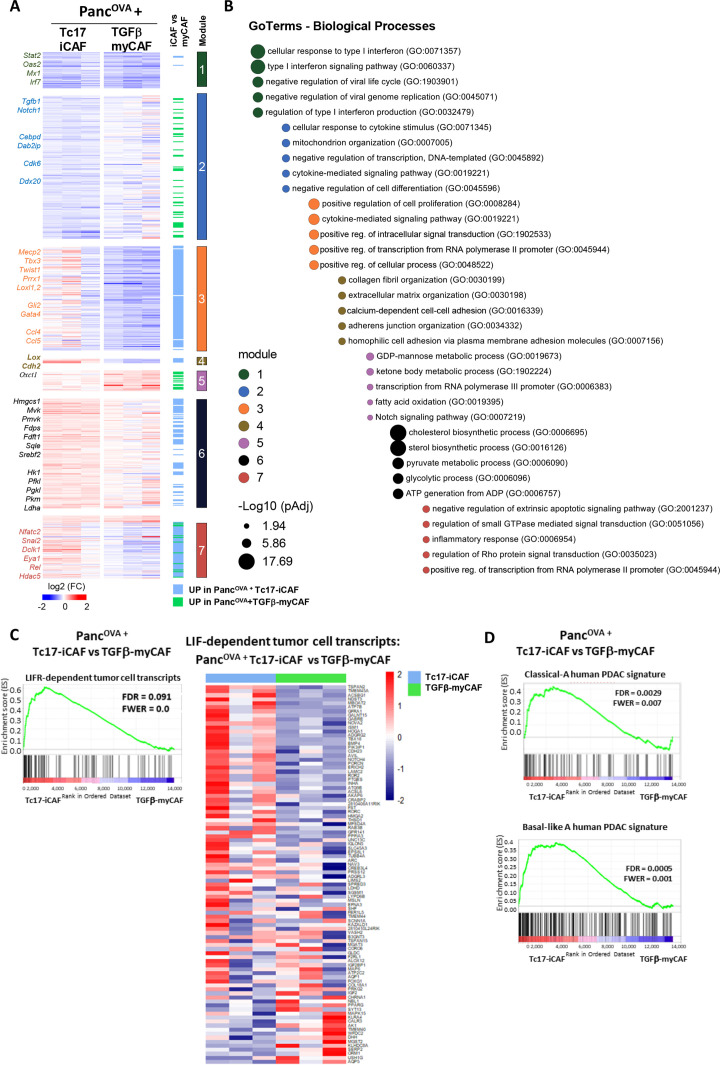
To identify the mechanisms by which Tc17-iCAF promote pancreatic tumour growth, we performed RNA-sequencing of sorted PancOVA cells after co-culture with Tc17-iCAF, or TGFβ-myCAFs, or qPSC (online supplemental figure 7A). The comparison of Tc17-iCAF- with TGFβ-myCAF-induced tumour-cell transcriptome defined DEGs (1400, padj<0.1), which were classified into seven modules (1–7, based on the mutual upregulation or downregulation), and examined by gene ontology (figure 5A, B, online supplemental figure 7B). Most genes in modules 3, 4, 6 and 7 were upregulated by Tc17-iCAF comparing to TGFβ-myCAF. Gene module three captured the expression of genes associated with proliferation and cytokine-signalling, while module four transcripts were linked to cell–cell interactions and ECM organisation. Module 6 was enriched with genes related to metabolism. Finally, module 7 contained genes linked to negative regulation of apoptosis and inflammatory response. Thus, Tc17-iCAF imprinted pancreatic tumour cells with a unique transcriptional profile characterised by proliferation, ECM organisation, protection from apoptosis and metabolism comparing to TGFβ-myCAFs.
Figure 5.
Tc17-iCAF affect pancreatic tumour cell transcriptional profile. (A) Heatmap of differentially expressed genes (Z score normalised, FDR ≤0.1) by PancOVA cells after 36 hours of co-culture with Tc17-iCAF or TGFβ-myCAF classified into modules based on the mutual upregulation or downregulation (n=3, biological replicates). (B) Pathway enrichment analysis for gene ontologies (GO): Biological processes. Bubble graph displays the five most significantly enriched pathways by –log10 value (p adj) for seven modules established in (A). (C) GSEA for differential expression of LIF-dependent pancreatic cancer cell transcripts obtained from LifrWT KPf/fCL vs Lifrf/fKPf/fCL mice42 in PancOVA tumour cells after co-culture with Tc17-iCAF vs TGFβ-myCAF. (C, right), heatmap of color-coded z-scores from the rlog transformed expression values based on the GSEA. (D) GSEA for differential expression of classical-A or Basal-like A human PDAC transcripts33 in PancOVA tumour cells after co-culture with Tc17-iCAF vs TGFβ-myCAFs. CAF, cancer-associated fibroblasts; GSEA, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; PDAC, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
The CM obtained from Tc17 cells enhanced Lif expression in iCAF (figure 3B), and LIF promotes PSC-dependent tumourigenesis in KPC mice.42 Comparison of our data set with LIF-dependent KPC tumour-cell signature42 revealed enrichment of Tc17-iCAF upregulated genes versus TGFβ-myCAF in the LIF-dependent tumour transcriptome (figure 5C), indicating an overlap between Tc17-iCAF and PSC-LIF-mediated pancreatic tumour profile.
Furthermore, we compared our data set with human PDAC tumour cell transcriptome, split into two main subgroups, the classical-A/B associated with early disease and the Basal-like A with advanced stage.33 In contrast to TGFβ-myCAF, Tc17-iCAF upregulated genes were significantly enriched in Classical-A and Basal-like A profile (figure 5D, online supplemental figure 7C).
In contrast, Tc17 cells caused only minor changes in PancOVA gene expression comparing to Tc17-iCAF as visualised by principal component analysis and heatmap (online supplemental figure 8A–C). Among upregulated genes by Tc17-iCAF in PancOVA cells, we found in module 3, besides transcripts associated with metabolism and ECM organisation, similarly to our results shown in figure 5A, B, also genes associated with hypoxia and extracellular vesicle production (module 4, online supplemental figure 8D). As before, the transcriptional profile of PancOVA cells co-cultured with Tc17-iCAF versus Tc17, displayed similarities to the LIF-dependent tumour transcriptome as well as to human classical-A and Basal-like A profiles (online supplemental figure 8E, F)
Thus, Tc17-iCAF but not Tc17 cells, induce a specific transcriptional programme in tumour cells, which is enriched in LIFR-sufficient KPC tumour profiles as well as in human classical-A and Basal-like-A PDAC subtype signatures, indicating a potential involvement of Tc17-iCAF in human disease and the KPC model.
IL-17RA-sufficient iCAF are required for Tc17 cell-driven tumour growth in vivo
To investigate if Tc17 cells can induce iCAF during tumourigenesis, Tc17 cells from WT or DKO mice generated in vitro were adoptively transferred into WT mice, which were co-injected subcutaneously or orthotopically with PancOVA or KPC tumour cells alone or together with qPSC (figure 6A, F, online supplemental figure 9A). As before, tumours with qPSC co-injection harboured higher frequency of αSMA+ cells (figure 6B, online supplemental figure 9B, I). Tc17 cells significantly enhanced tumour growth as compared with DKOTc17 or no T-cell transfer (figure 6C, G, online supplemental figure 9C, J), confirming the tumour-promoting role of IL-17A/F-producing Tc17 cells in PancOVA and KPC tumours in the subcutaneous and orthotopic setting. CAF obtained from mice injected with Tc17 cells displayed Ly6chigh phenotype (figure 6D, H, online supplemental figure 9D, E) and higher inflammatory gene expression comparing to DKOTc17 or qPSC co-injection without T-cell transfer (figure 6E, online supplemental figure 9F). Consistent with the responsivity to Tc17 cells, ex vivo isolated CAF expressed both IL-17A/F receptor chains (online supplemental figure 9G). Thus, IL-17A/F-producing Tc17 cells promote iCAF phenotype and tumour growth in subcutaneous and orthotopic PDAC model.
Figure 6.
Tc17 cells promote tumour growth in vivo via IL-17RA+iCAF. (A) Scheme of the experimental design. 5 ×105 PancOVA tumour cells±5 × 105 CD90.1+qPSC were subcutaneously co-injected into WT mice, which on the same day received i.p. injections of PBS or of 106 WT (Tc17) or IL-17A/FDKO Tc17 (DKOTc17) cells differentiated from WT or IL-17A/FDKO CD8+ T cells in the presence of TGFβ+IL-6. Histology and CAF analysis were performed at the indicated end of the experiment. (B) Quantification of αSMA staining in tumour tissue of mice injected with PancOVA cells alone (-) or co-injected with qPSC (qPSC), with qPSC+Tc17 cells (qPSC+Tc17) or with qPSC+DKOTc17 cells (qPSC+DKOTc17), based on previously published scoring,17 (n=4). (C) Tumour-growth curve of subcutaneous tumours is shown (tumour volume mm,3 mean±SEM, n=5 mice, one representative of two independent experiments each with 5–7 mice). **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001 indicate the tumour volume comparisons between the groups with qPSC+Tc17 versus qPSC. (D) FACS analysis of Ly6chigh cell frequency in gated EPCAM-CD45-PDPN+ fibroblasts in subcutaneous tumours (n=8–10). (E) qPCR analysis of the indicated gene expression by sorted from subcutaneous tumours EPCAM-CD45-PDPN+ fibroblasts (mean±SD, n=5–8). Fold of mRNA expression is shown, normalised to the qPSC group, which was arbitrarily set to 1. (F) Scheme of the experimental design. 2×104 KPC tumour cells with/without 2×104 CD90.1+qPSC were orthotopically injected into WT mice, which received on the next day i.p. injections of PBS or 106 WT (Tc17) or IL-17A/FDKO Tc17 (DKOTc17) cells or PBS. The tumour volume and CAF were analysed at the indicated end of the experiment. (G) Tumour volume of orthotopic tumours of mice injected with KPC cells alone (-) or co-injected with qPSC (qPSC), with qPSC+Tc17 cells (qPSC+Tc17) or with qPSC+DKOTc17 cells (qPSC+DKOTc17) is shown (tumour volume in MM3; mean±SD, n=8–9 mice). (H) FACS analysis of Ly6chigh cell frequency in gated EPCAM-CD45-PDPN+ cells in orthotopic tumours of mice treated as indicated (mean±SD, n=8–9). (I) Scheme of the experimental design. 1.5×104 KPC tumour cells±6 × 104 CD90.1+qPSC were orthotopically injected into WT or Il17af-/- mice. The tumour volume and CAF were analysed at the indicated end of the experiment. (J) Tumour volume of orthotopic tumours of WT and Il17af-/- mice injected with KPC cells alone (-) or co-injected with qPSC (qPSC) is shown (tumour volume in MM3; mean±SD, n=6–7 mice). (K) FACS analysis of Ly6chigh cell frequency in gated EPCAM-CD45-PDPN+ fibroblasts in orthotopic tumours (n=6–7). (L) Scheme of the experimental design. 2×104 KPC tumour cells±2 × 104 WT or Il17ra-/- CD90.1+qPSC were orthotopically injected into Il17ra-/- mice, which received on the next day i.p. injection of PBS or 106 Tc17 cells. The CAF analysis was performed at the indicated end of the experiment. (M) Tumour volume of orthotopic tumours of Il17ra-/- mice injected with KPC cells alone (-) or co-injected with WT qPSC+Tc17 cells (WT qPSC+Tc17) or with Il17ra-/- qPSC+Tc17 cells (Il17ra-/- qPSC+Tc17) is shown (tumour volume in MM3; mean±SD, n=8–10 mice). (N) FACS analysis of Ly6chigh cell frequency in gated EPCAM-CD45-PDPN+ cells in tumours of mice treated as indicated (mean±SD, n=6–7). (O) Summary with the proposed mechanism of an indirect cancer-promoting role of Tc17 cells in PDAC. Tc17 cells via synergistic effect of secreted cytokines, IL-17A and TNF, shift PSC differentiation towards iCAF formation in an IL-17RA-dependent manner. In turn, Tc17-induced iCAF promote Tc17 differentiation via secreted IL-6 in combination with TGFβ. Furthermore, Tc17-induced iCAF imprint pancreatic tumour cells with a unique transcriptional profile characterised by the expression of genes involved in proliferation, signal transduction, metabolism and protection from apoptosis, thereby enhancing tumour growth. (B, D, E, G, H, J, K, M, N) Biological replicates are plotted. In (C) *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001 determined by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test, in (B, D, N) *p<0.05, **p<0.01 by Kruskal-Wallis-test, in (E, G, H, J, K, M) *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001 and p values by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD multiple comparison test. ANOVA, analysis of variance; iCAF, inflammatory cancer-associated fibroblasts; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; PDAC, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Consistently, increased tumour growth and enhanced Ly6c expression by fibroblasts was detectable in WT, but not in Il17af-/- mice, co-injected with qPSC comparing to the sole KPC-cell injection (figure 6I–K, online supplemental figure 10A), indicating that endogenously produced IL-17A/F enhance PSC-driven tumour growth and a Ly6chigh fibroblast phenotype in the pancreatic tissue.
Finally, we analysed if IL-17RA expressed by fibroblasts contributes to Tc17-driven pancreatic tumour growth. Therefore, we adoptively transferred Tc17 cells into IL-17RA-deficient mice, which were co-injected orthotopically with KPC or subcutaneously with PancOVA cells along with IL-17RA-sufficient (WT) or IL-17RA-deficient (Il17ra-/- ) qPSC (figure 6L, online supplemental figure 10B). Along with the contribution of IL-17A/F to Tc17-mediated effects, WT PSC promoted tumour growth to a significantly higher extent comparing to Il17ra-/- PSC in orthotopic and subcutaneous settings. This was accompanied by significantly higher abundance of Ly6high fibroblasts in tumours of mice injected with WT vs Il17ra-/- PSC (figure 6M, N, online supplemental figure 10C-F). Thus, IL-17RA expressed by fibroblasts is required for the Tc17-mediated iCAF phenotype and tumour-growth promoting function in vivo.
Discussion
The hallmark of PDAC is the abundant desmoplastic stroma which accounts for up to 90% of tumour mass.43 The stroma consists of CAF-producing ECM components and soluble factors, and of infiltrating immune cells. Within this microenvironment, reciprocal interactions between immune and non-immune cells take place, which impact tumourigenesis. As graphically summarised in figure 6O, we demonstrated a reciprocal crosstalk between tumour-infiltrating Tc17 cells and CAF, in which Tc17 skewed the IL-17RA+CAF towards an inflammatory phenotype via synergism of IL-17A and TNF. In turn, Tc17-iCAF via secreted IL-6 directed TGF-β-dependent Tc17 differentiation, indicating an amplification loop. Further, Tc17-iCAF evoked gene-regulatory events in PDAC cells, thereby promoting growth of mouse and human tumours.
CD8+ T-cell functional understanding in PDAC was hitherto linked to the conventional tumour-eradicating CTL, along with the association of CD8+ T-cell enrichment in tumour tissue with longer OS.31 32 We identified, for the first time in PDAC, Tc17 cells using two different markers, IL-17A and RORγt, thereby establishing reliability of our analysis. In contrast to the infiltration of total CD8+ T cells, increased Tc17 abundance strongly associated with shorter OS, indicating their disease-promoting function. Accordingly, increased frequency of Tc17 cells correlated with tumour size and with progressed stage. Thus, our findings extend the knowledge regarding the role of CD8+ T cells in PDAC, by revealing the presence of pathogenic Tc17 cells, which can be useful for patient stratification and selection of targeted treatments.
The prevalence of the second adaptive IL-17A-producing subpopulation, namely Th17 cells (CD4+RORγt+), associated with advanced tumour stage, however, it failed to correlate with shorter patient survival and to act as an independent prognostic marker for PDAC, further emphasising the unique Tc17 pathogenic role in PDAC. Besides Tc17 and Th17 cells, other populations including γδT17 cells, ILC3 and lymphoid tissue inducers, which express RORγt, a transcription factor regulating IL-17A, might contribute to PDAC to a differential extent. Further studies are necessary to address this issue in depth.
Tc17-CM directed the expression of typical iCAF-associated transcripts. Accordingly, RNA-Seq analysis identified downregulated pathways associated with myCAF fate, while inflammatory genes were upregulated in Tc17-iCAF compared with qPSC or DKO-CAF. Furthermore, GSEA revealed similarities between Tc17-iCAF transcriptome and published profiles of iCAF induced by tumour-secreted ligands,4 6 indicating that besides tumour also Tc17-products can drive an iCAF-specific transcriptome. Thus, with Tc17 cells, we introduce a novel cell type modifying PDAC stroma towards tumour-promoting function. Interestingly, also Th17-CM induced iCAF-marker expression, however, with differences in specific genes as compared with Tc17-CM, which probably resulted from a unique secretome including higher IFNγ and TNF production by Tc17 vs Th17 cells. Therefore, we propose that Tc17 versus Th17 differentially modify stroma and thereby probably tumourigenesis. That idea is supported by our histological analysis revealing a moderate correlation between Th17 and Tc17 infiltration in PDAC.
Tc17 cells induced iCAF-marker genes via synergism of IL-17A and TNF. We uncovered this mechanism by exposing qPSC to IL-17A and TNF, or to Tc17-CM with TNF-neutralisation. The synergistic proinflammatory effect of IL-17A and TNF is already known,44 but not for PSC, thus we add a new mechanism promoting human and mouse iCAF differentiation. In line, recent study has shown that TNF in the PDAC TME enforces basal-like aggressive PDAC subtype.41 In contrast, the CTL-derived IFNγ displayed a restricted proinflammatory effect, pointing to T-cell subpopulation-specific cytokine effects modulating stroma.
Along with the inflammatory phenotype, Tc17-iCAF boosted growth of murine and human tumours as compared with qPSC, CTL-CAF or DKO-CAF in Rag1-/- and Foxn1nu/nu mice. The injected qPSC or CTL-CAF enhanced tumour growth in comparison to sole tumour-cell injection and displayed an inflammatory phenotype, but to a lower extent as compared with Tc17-iCAF, suggesting that human and mouse TME can stabilise and probably further promote the iCAF phenotype already induced by Tc17. Considering an enhanced Ilr1 expression by Tc17-iCAF in comparison to qPSC in vitro, it is conceivable that tumour-derived factors stabilise Tc17-iCAFs via IL-1-dependent signalling in vivo.
Besides in vitro effects, Tc17 and IL-17A/F promoted iCAF phenotype and tumour growth in mouse orthotopic and subcutaneous models including PancOVA and KPC-derived tumour cells. Accordingly, qPSC and CAF expressed both IL-17R chains. IL-17RA-expression by qPSC was required to sense Tc17 signals mediating iCAF differentiation, and thereby to promote tumour growth as uncovered by reconstitution experiments in IL-17RA-deficient mice. Thus, we reveal an indirect IL-17RA-dependent iCAF tumour-promoting mechanism mediated by IL-17A/F-producing Tc17 cells. This evidence is supported by the finding that Tc17 cells had a minor impact on pancreatic cancer-cell transcriptome in the co-culture system. Although our study is limited to adoptive Tc17 transfers, dissecting of Tc17 characteristics and their antigen-specificity in PDAC will be important for understanding of their biology to develop new targeting strategies in the future.
IL-17A directly enhances early carcinogenesis,11–13 15 and mediates neutrophil driven resistance to checkpoint inhibitors.16 Moreover a recent report analysing IL-17A-deficient versus IL-17A-sufficient KPC mice demonstrated differences in the transcriptional profile of CAFs obtained from these models.17 We confirm the contribution of IL-17A to stroma modification; however, our data differ, likely due to the complexity of multiple Tc17-secreted factors comparing to a single-cytokine deletion.
Analysis of pancreatic cancer-cell transcriptome after co-culture with Tc17-iCAF versus TGFβ-myCAF revealed that Tc17-iCAF upregulated gene-pathways associated with regulation of proliferation, adhesion, metabolism, apoptosis and inflammation. This was accompanied by enhanced expression of factors associated with epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (Twist1, Prrx1, Loxl1,2, Cdh2, Cdh17),45 46 aggressive phenotype (Lox, Gli2, Mecp2),47–49 stemness (Dclk, Tbx3),13 50 pancreatic lineage differentiation (Gata4),33 canonical NF-kB signalling (Rel) and calcium/calcineurin signalling (Nfatc2).51 Furthermore, transcripts involved in cholesterol biosynthesis and glycolysis were upregulated in consistency with the involvement of cholesterol52 53 and glycolysis54 55 in PDAC progression.
Despite the limitation elicited by the co-culture, including soluble and cell-associated factors, the relevance of the RNA-Seq data for the in vivo tumourigenesis was confirmed by the enrichment of Tc17-iCAF upregulated genes among the Lifr-dependent KPC tumour-cell transcripts.42 Regarding the LIF contribution to a paracrine PDAC progression and increased Lif levels expressed by Tc17-iCAF versus qPSC, our data suggest a possible LIF involvement in the Tc17-mediated tumourigenesis in vivo. Furthermore, transcripts upregulated by Tc17-iCAF versus TGFβ-myCAF were enriched among human PDAC genes with a Basal-like A and a Classical-A profile, which coexist in the same tumours,33 suggesting a Tc17-iCAF participation in human disease.
In conclusion, our study reveals a crucial pathogenic role of a newly described Tc17-cells, which sustain a self-perpetuating communication with iCAF, thereby mediating PDAC progression. Considering that Tc17 cells, via synergism of IL-17A and TNF, trigger the protumourigenic iCAF function, the neutralisation of this cytokine combination may hinder PDAC from establishing tumour-favouring niches and, therefore, could be beneficial in personalised cancer therapy.
Acknowledgments
We thank Ms. Bonny Adami for excellent technical support. We thank Dr. Tommy Regen and Dr. Florian Kurschuss for providing of IL-17RA-deficient mice. We thank Dr. Hosam Shams-Eldin and Mr. Guido Schemken for taking care and import of all mice strains. We thank Dr. Addi Josua Romero Olmedo for critical reading of the manuscript.
Footnotes
Twitter: @r_savai, @ariwaisman, @ShivKSingh6, @LukasKlein01
FSRP, VL and AB contributed equally.
Contributors: FSRP, VL and ABr contributed equally. Contributors MH, MG and ML designed the experiments. FSRP, VL, ABr, FN, TR, AH, HR, MK, TB, PIP, RS, IP, AW, SM, H-DC, SH, DKB, MB, MT, LK, CB, RL and ABu conducted the experiments. MH supervised this work and wrote the manuscript. MG, PM, SS, ML, TMG and H-RC assisted in data interpretation and edited the manuscript. MH is responsible for the overall content as guarantor.
Funding: This work was supported by the German Research Foundation (DFG) HU-1824/7-1 (414259009), KFO325 (329116008 TP1) to MH, GRK-2573 (416910386 TP2) to MH, Ga-1818/2-3 (321664872), SFB1292 (318346496 TP22 and TPQ1) to MMG, KFO 5002 (426671079) to SKS, German Cancer Aid (70112999, 70115054) to SKS.
Competing interests: None declared.
Patient and public involvement: Patients and/or the public were not involved in the design, or conduct, or reporting, or dissemination plans of this research.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Supplemental material: This content has been supplied by the author(s). It has not been vetted by BMJ Publishing Group Limited (BMJ) and may not have been peer-reviewed. Any opinions or recommendations discussed are solely those of the author(s) and are not endorsed by BMJ. BMJ disclaims all liability and responsibility arising from any reliance placed on the content. Where the content includes any translated material, BMJ does not warrant the accuracy and reliability of the translations (including but not limited to local regulations, clinical guidelines, terminology, drug names and drug dosages), and is not responsible for any error and/or omissions arising from translation and adaptation or otherwise.
Data availability statement
Data are available in a public, open access repository. Data are available on reasonable request. All data relevant to the study are included in the article or uploaded as online supplemental information.
Ethics statements
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
References
- 1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin 2020;70:7–30. 10.3322/caac.21590 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Huber M, Brehm CU, Gress TM, et al. The immune microenvironment in pancreatic cancer. Int J Mol Sci 2020;21:7307. 10.3390/ijms21197307 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Sahai E, Astsaturov I, Cukierman E, et al. A framework for advancing our understanding of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat Rev Cancer 2020;20:174–86. 10.1038/s41568-019-0238-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Öhlund D, Handly-Santana A, Biffi G, et al. Distinct populations of inflammatory fibroblasts and myofibroblasts in pancreatic cancer. J Exp Med 2017;214:579–96. 10.1084/jem.20162024 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Krishnamurty AT, Shyer JA, Thai M, et al. LRRC15+ myofibroblasts dictate the stromal setpoint to suppress tumour immunity. Nature 2022;611:148–54. 10.1038/s41586-022-05272-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Biffi G, Oni TE, Spielman B, et al. Il1-Induced JAK/STAT signaling is antagonized by TGFβ to shape CAF heterogeneity in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Discov 2019;9:282–301. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-0710 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Zhang Y, Lazarus J, Steele NG, et al. Regulatory T-cell depletion alters the tumor microenvironment and accelerates pancreatic carcinogenesis. Cancer Discov 2020;10:422–39. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-0958 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Elyada E, Bolisetty M, Laise P, et al. Cross-Species single-cell analysis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma reveals antigen-presenting cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cancer Discov 2019;9:1102–23. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-0094 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Li X, Bechara R, Zhao J, et al. Il-17 receptor-based signaling and implications for disease. Nat Immunol 2019;20:1594–602. 10.1038/s41590-019-0514-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. McGeachy MJ, Cua DJ, Gaffen SL. The IL-17 family of cytokines in health and disease. Immunity 2019;50:892–906. 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.03.021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. McAllister F, Bailey JM, Alsina J, et al. Oncogenic KRAS activates a hematopoietic-to-epithelial IL-17 signaling axis in preinvasive pancreatic neoplasia. Cancer Cell 2014;25:621–37. 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.03.014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Loncle C, Bonjoch L, Folch-Puy E, et al. Il17 functions through the novel reg3β-JAK2-STAT3 inflammatory pathway to promote the transition from chronic pancreatitis to pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res 2015;75:4852–62. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-0896 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Zhang Y, Zoltan M, Riquelme E, et al. Immune cell production of interleukin 17 induces stem cell features of pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia cells. Gastroenterology 2018;155:210–23. 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.03.041 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Alam MS, Gaida MM, Bergmann F, et al. Selective inhibition of the p38 alternative activation pathway in infiltrating T cells inhibits pancreatic cancer progression. Nat Med 2015;21:1337–43. 10.1038/nm.3957 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Wang X, Chen H, Jiang R, et al. Interleukin-17 activates and synergizes with the notch signaling pathway in the progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Lett 2021;508:1–12. 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.03.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Zhang Y, Chandra V, Riquelme Sanchez E, et al. Interleukin-17-Induced neutrophil extracellular traps mediate resistance to checkpoint blockade in pancreatic cancer. J Exp Med 2020;217:e20190354. 10.1084/jem.20190354 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Mucciolo G, Curcio C, Roux C, et al. Il17A critically shapes the transcriptional program of fibroblasts in pancreatic cancer and switches on their protumorigenic functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2021;118:e2020395118. 10.1073/pnas.2020395118 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Lückel C, Picard FSR, Huber M. Tc17 biology and function: novel concepts. Eur J Immunol 2020;50:1257–67. 10.1002/eji.202048627 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Linehan JL, Harrison OJ, Han S-J, et al. Non-classical immunity controls microbiota impact on skin immunity and tissue repair. Cell 2018;172:784–96. 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.033 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Nanjappa SG, McDermott AJ, Fites JS, et al. Antifungal tc17 cells are durable and stable, persisting as long-lasting vaccine memory without plasticity towards IFNγ cells. PLoS Pathog 2017;13:e1006356. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006356 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Di Meglio P, Villanova F, Navarini AA, et al. Targeting CD8(+) T cells prevents psoriasis development. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2016;138:274–6. 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.10.046 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Matos TR, O’Malley JT, Lowry EL, et al. Clinically resolved psoriatic lesions contain psoriasis-specific IL-17-producing αβ T cell clones. J Clin Invest 2017;127:4031–41. 10.1172/JCI93396 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Lückel C, Picard F, Raifer H, et al. IL-17+ CD8+ T cell suppression by dimethyl fumarate associates with clinical response in multiple sclerosis. Nat Commun 2019;10:5722. 10.1038/s41467-019-13731-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Huber M, Heink S, Pagenstecher A, et al. IL-17A secretion by CD8+ T cells supports TH17-mediated autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Clin Invest 2013;123:247–60. 10.1172/JCI63681 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Zhuang Y, Peng L-S, Zhao Y-L, et al. CD8(+) T cells that produce interleukin-17 regulate myeloid-derived suppressor cells and are associated with survival time of patients with gastric cancer. Gastroenterology 2012;143:951–62. 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.06.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Kuang D-M, Peng C, Zhao Q, et al. Tumor-Activated monocytes promote expansion of IL-17-producing CD8+ T cells in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. J Immunol 2010;185:1544–9. 10.4049/jimmunol.0904094 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Chellappa S, Hugenschmidt H, Hagness M, et al. Cd8+ T cells that coexpress RORγt and T-bet are functionally impaired and expand in patients with distal bile duct cancer. J Immunol 2017;198:1729–39. 10.4049/jimmunol.1600061 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Ohkuri T, Kosaka A, Ikeura M, et al. IFN-γ- and IL-17-producing CD8+ T (tc17-1) cells in combination with poly-ICLC and peptide vaccine exhibit antiglioma activity. J Immunother Cancer 2021;9:e002426. 10.1136/jitc-2021-002426 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Tajima M, Wakita D, Satoh T, et al. IL-17/IFN-γ double producing CD8+ T (tc17/IFN-γ) cells: a novel cytotoxic T-cell subset converted from tc17 cells by IL-12. Int Immunol 2011;23:751–9. 10.1093/intimm/dxr086 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Balli D, Rech AJ, Stanger BZ, et al. Immune cytolytic activity stratifies molecular subsets of human pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2017;23:3129–38. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-2128 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Carstens JL, Correa de Sampaio P, Yang D, et al. Spatial computation of intratumoral T cells correlates with survival of patients with pancreatic cancer. Nat Commun 2017;8:15095. 10.1038/ncomms15095 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Balachandran VP, Łuksza M, Zhao JN, et al. Identification of unique neoantigen qualities in long-term survivors of pancreatic cancer. Nature 2017;551:512–6. 10.1038/nature24462 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Chan-Seng-Yue M, Kim JC, Wilson GW, et al. Transcription phenotypes of pancreatic cancer are driven by genomic events during tumor evolution. Nat Genet 2020;52:231–40. 10.1038/s41588-019-0566-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Collisson EA, Bailey P, Chang DK, et al. Molecular subtypes of pancreatic cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019;16:207–20. 10.1038/s41575-019-0109-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. O’Kane GM, Grünwald BT, Jang G-H, et al. Gata6 expression distinguishes classical and basal-like subtypes in advanced pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2020;26:4901–10. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-3724 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Helms EJ, Berry MW, Chaw RC, et al. Mesenchymal lineage heterogeneity underlies nonredundant functions of pancreatic cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cancer Discov 2022;12:484–501. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-0601 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005;102:15545–50. 10.1073/pnas.0506580102 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Pickup MW, Owens P, Gorska AE, et al. Development of aggressive pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas depends on granulocyte colony stimulating factor secretion in carcinoma cells. Cancer Immunol Res 2017;5:718–29. 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-16-0311 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Djurec M, Graña O, Lee A, et al. Saa3 is a key mediator of the protumorigenic properties of cancer-associated fibroblasts in pancreatic tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2018;115:E1147–56. 10.1073/pnas.1717802115 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. van Duijneveldt G, Griffin MDW, Putoczki TL. Emerging roles for the IL-6 family of cytokines in pancreatic cancer. Clin Sci (Lond) 2020;134:2091–115. 10.1042/CS20191211 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Tu M, Klein L, Espinet E, et al. TNF-α-producing macrophages determine subtype identity and prognosis via AP1 enhancer reprogramming in pancreatic cancer. Nat Cancer 2021;2:1185–203. 10.1038/s43018-021-00258-w [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Shi Y, Gao W, Lytle NK, et al. Targeting LIF-mediated paracrine interaction for pancreatic cancer therapy and monitoring. Nature 2019;569:131–5. 10.1038/s41586-019-1130-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Erkan M, Hausmann S, Michalski CW, et al. The role of stroma in pancreatic cancer: diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012;9:454–67. 10.1038/nrgastro.2012.115 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Noack M, Beringer A, Miossec P. Additive or synergistic interactions between IL-17A or IL-17F and TNF or IL-1β depend on the cell type. Front Immunol 2019;10:1726. 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01726 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. De Craene B, Berx G. Regulatory networks defining EMT during cancer initiation and progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2013;13:97–110. 10.1038/nrc3447 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Kaszak I, Witkowska-Piłaszewicz O, Niewiadomska Z, et al. Role of cadherins in cancer-a review. Int J Mol Sci 2020;21:7624. 10.3390/ijms21207624 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Miller BW, Morton JP, Pinese M, et al. Targeting the LOX/hypoxia axis reverses many of the features that make pancreatic cancer deadly: inhibition of LOX abrogates metastasis and enhances drug efficacy. EMBO Mol Med 2015;7:1063–76. 10.15252/emmm.201404827 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Wang H, Li J, He J, et al. Methyl-Cpg-Binding protein 2 drives the furin/TGF-β1/smad axis to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncogenesis 2020;9:76. 10.1038/s41389-020-00258-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Adams CR, Htwe HH, Marsh T, et al. Transcriptional control of subtype switching ensures adaptation and growth of pancreatic cancer. Elife 2019;8:e45313. 10.7554/eLife.45313 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Perkhofer L, Walter K, Costa IG, et al. Tbx3 fosters pancreatic cancer growth by increased angiogenesis and activin/nodal-dependent induction of stemness. Stem Cell Res 2016;17:367–78. 10.1016/j.scr.2016.08.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Baumgart S, Glesel E, Singh G, et al. Restricted heterochromatin formation links NFATc2 repressor activity with growth promotion in pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology 2012;142:388–98. 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.11.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Oni TE, Biffi G, Baker LA, et al. Soat1 promotes mevalonate pathway dependency in pancreatic cancer. J Exp Med 2020;217:e20192389. 10.1084/jem.20192389 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Gabitova-Cornell L, Surumbayeva A, Peri S, et al. Cholesterol pathway inhibition induces TGF-β signaling to promote basal differentiation in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell 2020;38:567–83. 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.08.015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Yan L, Raj P, Yao W, et al. Glucose metabolism in pancreatic cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2019;11:1460. 10.3390/cancers11101460 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Ying H, Kimmelman AC, Lyssiotis CA, et al. Oncogenic KRAS maintains pancreatic tumors through regulation of anabolic glucose metabolism. Cell 2012;149:656–70. 10.1016/j.cell.2012.01.058 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
gutjnl-2022-327855supp001.pdf (16.5MB, pdf)
Data Availability Statement
Data are available in a public, open access repository. Data are available on reasonable request. All data relevant to the study are included in the article or uploaded as online supplemental information.