Abstract
Despite advances in neurosurgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy, glioblastoma remains one of the most treatment-resistant CNS malignancies, and the tumour inevitably recurs. The majority of recurrences appear in or near the resection cavity, usually within the area that received the highest dose of radiation. Many new therapies focus on combatting these local recurrences by implementing treatments directly in or near the tumour bed. In this Review, we discuss the latest developments in local therapy for glioblastoma, focusing on recent preclinical and clinical trials. The approaches that we discuss include novel intraoperative techniques, various treatments of the surgical cavity, stereotactic injections directly into the tumour, and new developments in convection-enhanced delivery and intra-arterial treatments.
Glioblastoma remains one of the most lethal neurological malignancies despite decades of unrelenting effort by the research and medical communities to combat this disease. Few new therapies have shown efficacy for mitigating glioblastoma since the introduction of temozolomide as part of the Stupp standard of care protocol in 2005 (REF.1). Before the Stupp protocol was introduced, median survival was around 12 months, which has since increased to 16 months owing to various improvements in treatment, including optimization of the Stupp protocol, advances in imaging and radiotherapy, and gross total resection safeguarded by intraoperative mapping2,3. In addition, tumour treating fields therapy, in which mitosis is hindered by alternating electric fields, has produced improvements in long-term overall survival (OS) in patients with primary or recurrent glioblastoma4,5.
Although these improvements are encouraging, the long-term prospects for patients with glioblastoma remain extremely poor. The absence of new treatment modalities for glioblastoma cannot be attributed to lack of effort: currently, 1,593 trials are registered under “glioblastoma” on ClinicalTrials.gov. The resistance of glioblastoma to treatment is widely known and can be explained by several distinctive characteristics of the tumour. Glioblastoma is notoriously heterogeneous, with an abundance of signalling pathways even within the same tumour mass, thereby limiting the options for targeted therapies6,7. The tumour microenvironment strengthens the resistance of glioblastoma resistance to radiation and chemotherapy8, and the low immunogenicity of glioblastoma hinders a strong immunological response 9. In addition, infiltration of glioma (stem) cells deep into the brain excludes effective treatment by resection alone10. Moreover, the blood–brain barrier (BBB) prevents many systemically administered chemotherapeutics from reaching sufficient concentrations in the brain without serious adverse effects.
At present, finding a cure for glioblastoma remains a distant prospect, and efforts have instead been focused on delaying recurrence. Approximately 80% of glioblastoma recurrences arise inside or at the margin of the radiation field, and this local recurrence is associated with substantially shortened progression-free survival (PFS)11. Furthermore, the extent of resection is a crucial outcome variable: patients who have undergone gross total resections have significantly longer OS than patients with subtotal resections12. Some centres have demonstrated further improvements in outcomes after supratotal resections13, but more evidence is required to substantiate these claims14. Together, these findings suggest that the resection cavity is an important location to prevent early tumour recurrence. In addition, the isolation of the brain by the BBB creates a unique opportunity to deliver aggressive treatment locally with a limited risk of systemic toxicity.
In this Review, we discuss current and future local therapies for glioblastoma, examining treatment of the tumour cavity (FIG. 1) and other direct approaches to the tumour (FIG.2). We highlight landmark studies to provide an overview of local therapies that have been — or are currently being — explored in patients with glioblastoma.
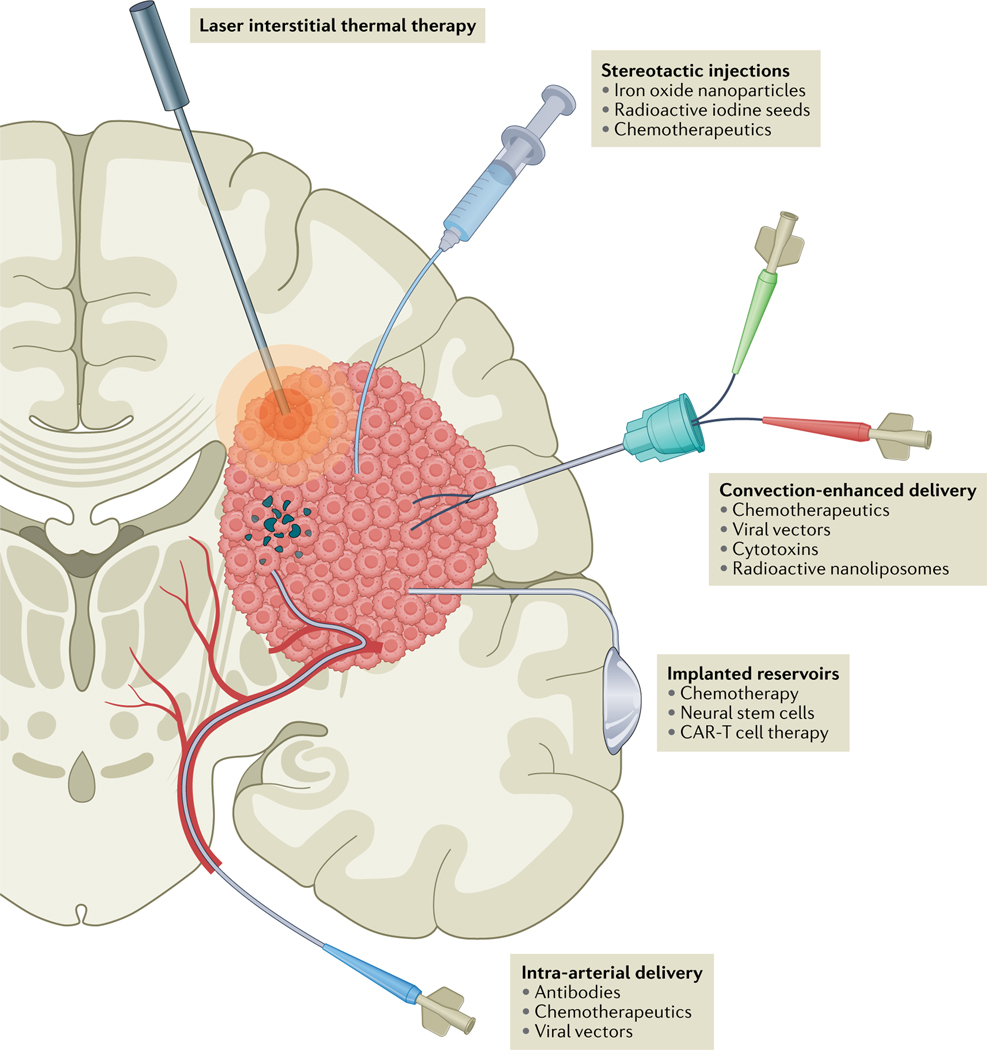
Fig. 1 |. Methods of local treatment in glioblastoma.
In laser interstitial thermal therapy, tumour tissue is heated with a laser probe, destroying the tissue and disrupting the blood–brain barrier (BBB), usually under MRI guidance. Various compounds can be injected via stereotactic injections directly into the tumour with the aid of neuronavigation, frequently coupled with intraoperative CT or MRI. Convection-enhanced delivery involves continuous injection of various compounds using a pressure gradient to improve distribution. Ommaya or Rickham reservoirs can be implanted, enabling intermittent injections of therapy over an extended period of time. Catheters can be placed in the tumour or resection cavity or in the cerebral ventricles. For intra-a rterial delivery, catheters can be positioned directly into the feeding arteries, allowing local delivery of high-dose therapeutics. This technique can be combined with BBB disruption. CAR, chimaeric antigen receptor.
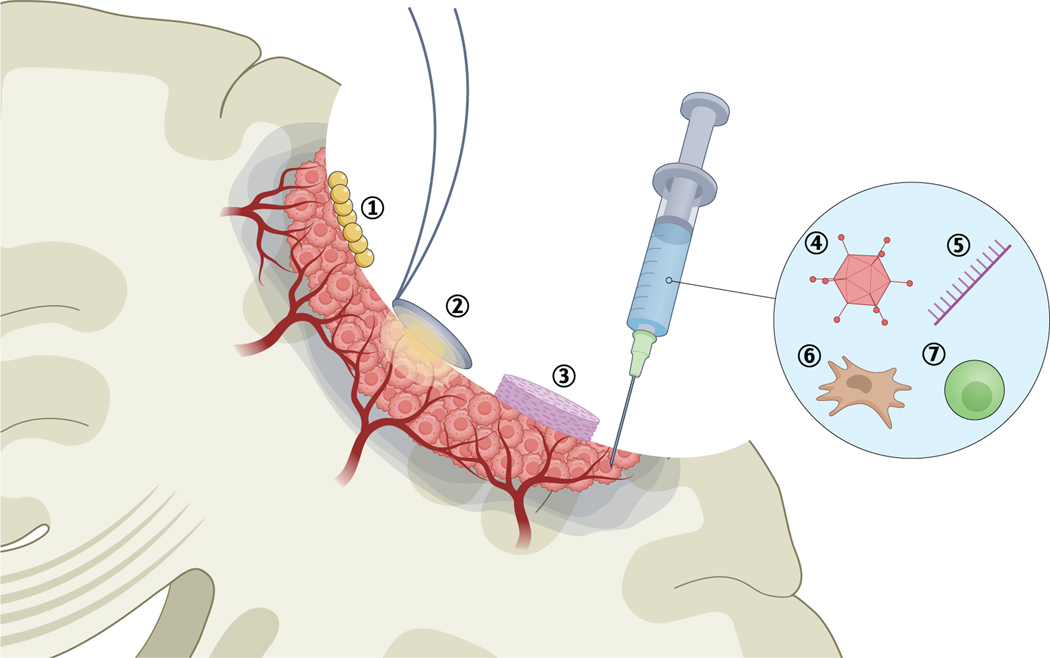
Fig. 2 |. Tumour cavity treatments for glioblastoma.
Injection of iron oxide nanoparticles (1) enables magnetic hyperthermia. In photodynamic therapy (2), photosensitizing agents are applied to the cavity and are activated by light at a specific wavelength to generate reactive oxygen species. Implantation of wafers (3) designed to release chemotherapy. Injection of viral vectors (4), immune-s timulating oligodeoxynucleotides (5), engineered neural stem cells (6) or chimaeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells (7) into the cavity wall.
Intraoperative treatment modalities
Over the years, many tools have been introduced to aid the surgeon in the resection of lesions in the brain. Inventions such as surgical microscopes, high-resolution imaging, fluorescence-guided surgery and neuronavigation are widely used in neurosurgery and are beyond the scope of this Review. In this section, we discuss new intraoperative treatments that aid direct destruction of malignant tissue at the time of surgery, can disrupt the BBB and can enhance the immune response after surgery.
Localized thermal therapy
Thermal therapy is based on the ability of heat to induce apoptosis and necrosis in the brain15. Both in vitro and animal studies have shown that glioma cells are especially vulnerable to heat16, an effect that is probably enhanced in patients by the relatively fragile neovasculature and the hypoxic microenvironment of glioblastomas17. Aside from direct apoptosis and necrosis, hyperthermia can sensitize glioma cells to radiation therapy18 and chemotherapy19, trigger an immune response20 and provide transient BBB disruption15. Currently, three methods — laser interstitial thermal therapy (LITT), magnetic hyperthermia and focused ultrasound (FUS) — are at various stages of regulatory approval for local treatment of glioblastoma.
Laser interstitial thermal therapy.
In LITT, an optical fibre is stereotactically inserted into the tumour through a burr hole (FIG. 1a). The tissue is then heated with laser light (at a wavelength of 1,064 nm or 980 nm depending on the system)21 to 42.5–45.5 °C for several minutes while MRI thermometry is employed to monitor the temperature in the lesion in real time22. Constant monitoring is vital, as the optical properties of tissue vary, especially in tumours. LITT has been in development since the early 1990s, and various studies have assessed its safety and efficacy for treating glioblastoma22. Although safety and targeting have improved with the introduction of intraoperative MRI thermometry, randomized clinical trials of LITT for glioblastoma have not been forthcoming. A retrospective analysis compared 24 patients treated with LITT for primary glioblastoma with a control cohort, matched for gender, age, tumour size and location, who had undergone biopsy only23 (TABLE 1). No differences in PFS or OS were observed, but four of the 24 patients treated with LITT experienced permanent worsening of their neurological symptoms. Similarly, in 54 patients treated with LITT for primary or recurrent glioblastoma, 15.5% developed serious adverse events, such as cerebral oedema, seizures and hydrocephalus, with two patients dying within 30 days of surgery, and OS did not improve24 (TABLE 1).
Table 1 |.
Clinical trials in high-grade glioma: intraoperative treatment modalities
| Study | Treatment | Study type | Patient cohort | Results | Adverse events (number of patients) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Localized thermotherapy | |||||
| Kamath et al. (2019)24 | LITT followed by standard chemoradiotherapy | Retrospective cohort | Primary or recurrent glioblastoma (n = 54) | Median OS, 11.5 months; median PFS, 6.6 months | Cerebral oedema (3), seizures (3), hydrocephalus (1), postoperative infection leading to death (1) |
| Mohammadi et al. (2019)23 | LITT followed by standard chemoradiotherapy vs chemoradiotherapy only | Retrospective, matched cohort | Primary glioblastoma (n = 48) | Median OS, 14.4 months in LITT group vs 15.8 months in controls; median PFS, 4.3 vs 5.9 months | Transient worsening of neurological deficits (6), permanent deficit (2) |
| Maier-Hauff et al. (2011)29 | Stereotactic injection of magnetic beads + 30 Gy radiotherapy | Phase II | Primary (n = 7) or recurrent (n = 59) glioblastoma | Median OS, 13 months; median PFS, 8 months | Seizures (15), transient worsening of neurological deficits (14) |
| Grauer et al. (2019)30 | Intracavitary superparamagnetic iron oxide particles + 60 Gy radiotherapy | Phase I | Recurrent glioblastoma (n = 6) | Median OS, 8.3 months; median PFS, 6.25 months | Inflammation and oedema requiring treatment (6), removal of beads owing to mass effect (4) |
| PDT | |||||
| Schipmann et al. (2020)43 | Peroperative PDT of resection cavity in 5-aminolevulinic acid-treated patients | Phase I | Recurrent high-grade glioma (n = 20) | Median OS not reached, 75% alive after 6 months; median PFS, 6.0 months; 75% of tumours recurred at site of PDT | Surgical site infection (1) |
| Eljamel et al. (2008)42 | Fluorescent-guided resection followed by five sessions of PDT + radiotherapy vs non-fluorescent-guided resection + radiotherapy | Phase III | Primary glioblastoma (n = 27) | Median OS, 12.2 months in PDT group vs 5.6 months in controls; median PFS, 8.6 vs 4.8 months | Deep vein thrombosis (3) |
LITT, laser interstitial thermal therapy; OS, overall survival; PDT, photodynamic therapy; PFS, progression-free survival.
Balancing treatment effectiveness against adverse effects is a challenge in LITT. The extent of ablation seems to be an important determinant of efficacy: near-total ablation correlated with improved PFS and OS in individual studies23,25 and in a literature review21. The increased aggressiveness of the treatment is likely to increase the risk of adverse effects, with complication rates as high as 33% in one review focused on newly diagnosed glioblastoma26. Currently, LITT might bene fit patients with tumours that are inoperable owing to location or poor functional status, and could also have cost-effectiveness advantages in selected patient groups27,28. However, well-designed trials are needed to assess the true efficacy of LITT, possibly in combination with other treatments. Several trials are underway or have recently been completed, studying LITT in combination with anti-PD1 therapy (ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03341806 and NCT03277638), radiotherapy (NCT04181684), lomustine (NCT03022578) or the Stupp protocol (NCT02970448).
Magnetic hyperthermia.
Magnetic hyperthermia is a technique in which heat is generated by stimulating magnetic nanoparticles within the tumour or resection cavity with an external alternating magnetic field (FIGS 1b,2a). Repeated cycles of thermotherapy can be administered without additional surgery, and the treatment has the potential to synergize with radiotherapy or chemotherapy. A prospective phase II trial examined the feasibility of magnetic hyperthermia in 59 patients with recurrent glioblastoma29. Iron oxide nanoparticles were injected into the tumour using a stereotactic frame, and six semi-weekly 1-h thermotherapy sessions were combined with stereotactic radiotherapy to a total of 30 Gy (TABLE 1). Possible improvements in survival were found, although some patients experienced adverse effects, such as seizures during treatment or worsening of motor disturbances after treatment29.
An alternative approach is to line the resection cavity with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles after resection. In a phase I trial in six patients with recurrent glioblastoma, a paste containing these particles was administered to the resection cavity after removal of the tumour30 (TABLE 1). The participants also received 60 Gy stereotactic radiotherapy. No notable adverse effects were observed immediately after six rounds of treatment, but 2–5 months later, all patients had developed a tumour flare reaction with prominent oedema around the nanoparticles. As a result, all patients required high-dose corticosteroids, and four of the six underwent repeat craniotomy to remove the particles. Surgery relieved the acute symptoms but most patients required long-term corticosteroids to fully suppress the oedema. Histological analysis and flow cytometry of tissue acquired during removal of the beads showed increased infiltration of CD8+ T cells, CD4+ T cells and CD63+ macrophages in areas containing large numbers of nanoparticles, indicating that an immune response had been triggered30.
Like LITT, magnetic hyperthermia is still in its infancy. Adverse effects are common, can be severe and are poorly understood, and efficacy has not been convincingly demonstrated. Intracavitary magnetic hyperthermia seems to induce a potent inflammatory response, and as glioblastomas are known to be immuno logically ‘cold’ tumours, this therapy might help improve the immune response and/or the efficacy of immune therapies31. At present, however, the mechanisms and optimal treatment strategies remain to be fully elucidated. A new phase I trial is currently being developed to identify the optimal temperature (45 °C, 50 °C or 55 °C) for intracavitary treatment in recurrent glioblastoma30.
Focused ultrasound.
FUS is rapidly emerging as an exciting new tool to treat a wide range of neurological diseases32. In the case of glioblastoma, efforts are mainly concentrated on using FUS to transiently disrupt the BBB, thereby improving the delivery of chemotherapies that normally show poor diffusion across the BBB33. FUS can also be used for thermoablation and has been approved by the FDA for thalamotomy in patients with essential tremor34. To date, only one experimental study, published in 1991, has evaluated FUS in glioblastoma35. This study evaluated the use and optimal settings of a single element transducer, which was placed within the tumour through a craniotomy, in 15 patients with glioblastoma. The methods used in this study have long become obsolete, and the study offers limited clinical insight for modern glioblastoma treatment.
However, modern developments in FUS techniques, including vastly improved flexibility and precision, might uncover new possibilities for glioblastoma treatment. Ongoing trials (for example, NCT03712293 and NCT03551249) are evaluating whether BBB disruption with FUS can improve the effects of systemic chemotherapy. One study aims to combine FUS with sensitization by 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA; NCT04845919), and another is exploring possible synergy with radiotherapy (NCT04988750) (Supplementary Table 1).
Photodynamic therapy
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) utilizes photosensitizing agents, which, following activation by light at a certain wavelength, generate reactive oxygen species (ROS)36 (FIG.1b). ROS interact with DNA, proteins, lipids and other macromolecules to disrupt many cellular pathways, including extensive DNA damage, leading to apoptosis of the cell37. Furthermore, PDT damages vascular endothelial cells, leading to local thrombosis, vessel constriction and, ultimately, destruction of the microvasculature38. Together, these effects also induce a strong anti-glioma immune response, as shown in mouse models39. Two photosensitizing agents have primarily been studied in glioblastoma: Photofrin, which is approved by the FDA for the treatment of oesophageal cancer40, and 5-A LA, which is approved for visualization of glioblastoma cells during surgery41.
One phase III trial involving Photofrin in the treatment of glioblastoma has been published42. Patients who received five daily sessions of PDT via an implanted laser in the resection cavity showed improved survival compared with patients who did not receive PDT (TABLE 1). A major confounding variable is that the those who received this therapy also underwent fluorescence-guided resection, which itself improves outcomes41. Only 15% of patients in both groups received temozolomide, thereby limiting the generalizability of the findings.
A phase I trial studied intraoperative PDT, using 5-ALA, in 20 patients with recurrent glioblastoma43 (TABLE 1). 5-ALA-guided resection was followed by insertion of between one and four cylindrical laser diffusers in the resection cavity. PDT was then delivered with the patient under general anaesthesia for 60 min. Postoperative MRI scans showed cytotoxic oedema along the margin of the resection cavity with contrast enhancement observed in some patients, which eventually regressed or disappeared after 4–5 months. Median PFS was 6 months, which is comparable to that achieved with standard of care in recurrent glioblastoma44.
One of the main caveats in PDT is that the laser light has to reach cells containing the sensitizing agents. With commonly used lasers with a wavelength range of 630–690 nm, penetration is rarely beyond 5 mm in most tissues45. The effects of PDT might reach somewhat further, with MRI showing an average penetration of 9.1 mm (REF.43) and post-mortem histopathological analysis indicating penetration up to 12.7 mm (REF.46). However, deeper-lying malignant cells will still be entirely unaffected. Furthermore, one study showed that 75% of tumour recurrences occurred within the area of PDT43, casting doubt on the long-term effects even in the resection cavity itself. Nevertheless, in view of the clinical availability of 5-ALA and the low-risk nature of this therapy, further studies into its applicability for glioblastoma are warranted47. Preliminary data from the phase I INDYGO study have shown safety and feasibility of 5-A LA-based PDT in primary glioblastoma47. Two other trials will provide further data on stereotactic PDT in primary (NCT03897491) and recurrent (NCT04469699) glioblastoma (Supplementary Table 1).
Local delivery of chemotherapy
Convection-enhanced delivery
Convection-enhanced delivery (CED) (FIG.1c) is a delivery method rather than a therapy itself. Compounds injected directly into brain parenchyma or tumour tissue usually diffuse poorly; for example, it can take up to 3 days for an immunoglobulin to diffuse 1 mm from an injection site in the brain48. CED establishes a positive pressure gradient and can be left in situ for an extended period of time. This approach improves spatial distribution, with lower concentrations of compounds being necessary to treat a similar area. CED occurs independently of the molecular weight or diffusivity of an agent49.
Although CED of chemotherapy has been successful in the laboratory, translation to the clinic has proved difficult, and several challenges have been identified that need to be addressed to improve the use of CED in patients49. Accurate cannula placement is challenging, with one major trial (PRECISE, discussed in detail below) noting that less than 70% of cannulas were positioned in accordance with protocol guidelines50. Post hoc analysis suggested that correct catheter placement correlated with an increase in survival. Although the neurosurgeons in this study were trained and a steering committee monitored catheter placement, the learning curve remained steep. CED trials should ideally be restricted to centres with adequate experience in this procedure.
Distribution of the infusate through the tumour is another important factor. Glioblastoma is heterogeneous in nature, with varying degrees of necrosis, angiogenesis and metabolism rates even within the same tumour, leading to wide-ranging rates of clearance51,52. Methods are being developed to monitor the infusate and visualize the spread through the tumour and beyond. Gadolinium-based compounds have been used in animal models53,54, and various case reports55,56 indicate that this approach is feasible and safe. In a phase I dose-escalation trial, nimustine hydrochloride (ACNU) was delivered with 1 mM of gadolinium-tetraazacyclododecanetetraacetic acid (Gd-DOTA) via CED to patients with recurrent diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG) or recurrent glioblastoma located in the brainstem57 (TABLE 2). The volume of infusion correlated closely with the signal on MRI but stopped increasing after several hours despite continued administration of Gd-DOTA. The authors concluded that the retention of Gd-DOTA following local infusion was insufficient, thereby hindering precise monitoring for longer periods. Outcomes were variable, with four of six patients who received the highest doses of ACNU showing regression of tumour volume and one showing complete remission. Transient worsening of symptoms occurred in 11 of 16 patients and persisted in three of these individuals.
Table 2 |.
Clinical trials in high-grade glioma: local delivery of chemotherapeutic agents
| Study | Treatment | Study type | Patient cohort | Results | Adverse events (number of patients) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Convection-enhanced delivery | |||||
| Saito et al. (2020)57 | Single dose of ACNU via convection-enhanced delivery | Phase I, dose-e scalation | Diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma or recurrent brainstem glioblastoma (n = 16) | Decrease in tumour volume in four of six patients at highest dose | Transient worsening of neurological deficits (11) |
| Implanted and injected modalities | |||||
| Westphal et al. (2003)60 | Implanted biodegradable carmustine or placebo wafers after surgery, followed by radiotherapy | Phase III | Primary high-grade glioma or metastasis (n = 240) | Median OS (glioblastoma only), 13.5 months in carmustine group vs 11.4 months in controls; median PFS (glioblastoma only), 5.9 months in both groups | Increased occurrence of intracranial hypertension and cerebrospinal fluid leaks |
| De Bonis et al. (2012)62 | Carmustine wafers in resection cavity + temozolomide and radiotherapy vs temozolomide + radiotherapy only | Retrospective analysis | Primary or recurrent glioblastoma (n = 165) | Median OS (primary glioblastoma), 14 months in carmustine group vs 11 months in controls; median OS (recurrent glioblastoma), 8 months vs 9 months | Increased adverse events in patients who received eight wafers |
| Yang et al. (2018)64 | ACNU into resection cavity via Ommaya reservoir with transient BBB disruption vs standard chemoradiotherapy only | Phase II | Primary glioblastoma (n = 71) | Median OS, 18.5 months in ACNU group vs 16.0 months in controls; median PFS, 8.8 vs 7.0 months | No increase in adverse events |
| Intra-arterial delivery | |||||
| Boockvar et al. (2011)68 | Single dose of intra-a rterial bevacizumab with osmotic BBB disruption | Phase I | Recurrent glioblastoma (n = 30) | Radiographic reduction in tumour size in most patients, most pronounced in patients who had not previously received bevacizumab (reduction in tumour enhancement on MRI, 34.7% vs 15.2% in previously treated group) | Seizures (2), peroperative rupture of right anterior cerebral artery causing subarachnoid haemorrhage and left hemiparesis (1) |
| Chakraborty et al. (2016)71 | Single dose of intra-a rterial cetuximab with osmotic BBB disruption |
Phase I | Recurrent glioblastoma (n = 15) | Well tolerated to 250 mg/m2 | Anaphylaxis (1), seizure (1), cerebral oedema with seizure (1) |
| Fortin et al. (2014)72 | Repeated intracarotid carboplatin injection every 4 weeks |
Phase II | Recurrent glioblastoma (n = 51) | 3 complete responses, 22 partial responses, 14 with stable disease | Transient carotid spasms (3) |
ACNU, nimustine hydrochloride; BBB, blood–brain barrier; OS, overall survival; PFS, progression-free survival.
As glioblastomas are highly infiltrative, compounds need not only penetrate deeply into the tissue but also distinguish between malignant and normal tissue to avoid serious adverse effects. Therefore, many trials are studying CED of tumour-targeting compounds, such as cytokines, viruses, gene therapies and antibodies. These approaches are discussed in more detail below.
Advances in CED are ongoing, with continual improvements in cannula design, treatment plans and modelling of optimal delivery49,58,59. Several phase I trials to study and improve CED — including image-guided approaches — for the delivery of agents such as irinotecan liposomes (NCT03086616 and NCT02022644) and MTX110 (NCT03566199) in people with DIPG or glioblastoma have recently been completed or are currently recruiting patients (Supplementary Table 2), and the data are awaited.
Implanted and injected modalities
Biodegradable carmustine wafers were developed to deliver high-dose chemotherapy within the resection cavity (FIG. 2c). One randomized controlled trial in patients with primary glioblastoma who were receiving surgery and radiotherapy indicated that these wafers increased median survival from 11.4 months to 13.5 months60 (TABLE 2). The diagnosis was only made after wafer implantation, so the study also included patients with other tumour types such as oligodendroglioma and brain metastases. As the power analysis did not take this into account, the results for patients with glioblastoma were not adequately powered to draw definitive conclusions.
A meta-analysis of data collected after the Stupp protocol was introduced showed that carmustine wafers have limited additional benefits in terms of OS and substantially increased the risk of adverse events in patients receiving temozolomide61 (TABLE 2). Of note, in one major retrospective analysis that compared carmustine wafers plus the Stupp protocol with the Stupp protocol alone in 165 patients with primary or recurrent glioblastoma, implantation of eight carmustine wafers (27 patients) — but not seven wafers or fewer (20 patients) — was associated with an increased risk of adverse events62. This study noted a trend towards prolonged OS in patients with primary glioblastoma who received wafers, but it was not sufficiently powered to draw definitive conclusions. Nevertheless, these findings raise the possibility that an optimal dose, with acceptable levels of toxicity, can be found for carmustine wafers in combination with the Stupp protocol. One study (NCT03234595) is currently evaluating wafer-mediated delivery of n-butylidenephthalide, which showed pro mise in preclinical models63, in patients with recurrent glioblastoma (Supplementary Table 2).
Placement of an Ommaya or Rickham reservoir connected to the resection cavity or cerebral ventricles enables delivery of high-dose chemotherapy to the tumour over extended time periods (FIG. 1d) The reserv oir is implanted under the skin and can be accessed intermittently, allowing more flexibility for the patient and clinician during the course of treatment. One study delivered ACNU into the resection cavity via an Ommaya reservoir during temozolomide treatment and radiotherapy in 71 patients with glioblastoma64 (TABLE 2). Each injection was combined with transient BBB disruption with mannitol and dexamethasone. No serious adverse events were noted; however, improvement in OS (median 18.5 months compared with 16.0 months for standard therapy) and PFS (8.8 months versus 7.0 months) was minimal64. Furthermore, the interpretation of the results was limited by several factors: the study was non-r andomized in that patients were allowed to choose the treatment and had to be able to afford the extra treatment; imaging data were not available; and the ACNU group also received mannitol and dexamethasone to disrupt the BBB. A more robust randomized trial might shed more light on the efficacy of this approach.
Generally, wafers and reservoirs can enable long-term delivery of compounds. The current literature is critical of implantable carmustine wafers, but adjustments of compounds, dose and implantation techniques might improve their efficacy and safety61. CED seems to be more effective at diffusing compounds directly into tumour tissue but is also more invasive. Implanted reservoirs might serve a specific function in the treatment of the resection cavity or delivery to the cerebral ventricles over extended periods of time but have yet to find a defined role in the treatment of glioblastoma.
Intra-arterial delivery
Intra-arterial delivery of chemotherapeutics (FIG. 1e)) was seen as a promising treatment in the early days of glioblastoma treatment when few other modalities were available65. With the advent of temozolomide, radiotherapy and improved neurosurgical techniques, interest in intra-arterial delivery diminished at the end of the 1990s owing to concerns over neurotoxicity and other adverse events. However, recent improvements in angiographic techniques have led to renewed interest, as reviewed in 2020 by D’Amico et al.66. In this section, we briefly highlight the most notable developments.
High dosages of therapeutic drugs can be administered directly to the tumour bed via intra-arterial catheters. Usually, this technique is combined with transient BBB disruption to maximize passage of the compound across the BBB. This disruption can be achieved with drugs such as mannitol, or with FUS67. Nuances and considerations regarding BBB disruption are beyond the scope this Review and can be found elsewhere67. Several phase I trials have studied intra-arterial administration of bevacizumab in patients with glioblastoma, and have shown an acceptable safety profile with variable responses to treatment68–70 (TABLE 2). Various phase I and II trials for primary and recurrent glioblastoma are currently underway (for example, NCT01269853, NCT02285959 and NCT01811498), but no phase III trials are planned at present (Supplementary Table 2). Intra-arterial delivery of cetuximab, an epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor, is also under investigation (NCT02800486 and NCT02861898) after a phase I trial showed that delivery is well tolerated, even at high doses71 (TABLE 2). With regard to chemotherapeutics, intra-arterial delivery of carboplatin without BBB disruption seems to be safe in individuals with recurrent glioblastoma, with minor haematological adverse effects and no neurological complications being observed72. Of 51 patients in this trial, 25 showed a complete or partial response. A phase II trial (NCT03672721) is now underway (Supplementary Table 2).
Overall, selective intra-arterial delivery, combined with BBB disruption, shows considerable promise, either as salvage therapy in inoperable patients or in combination with current standard of care. The experience gained from other intra-arterial cerebral treatments, such as coiling and thrombectomy, has improved the availability and safety of these techniques, and many compounds are available to be tested. Drug selection is important, and factors such as local and systemic toxicity, ease of uptake on first pass and tissue retention must be carefully considered66. Furthermore, hydrodynamic factors differ between tumours, and even within the same tumour, which can influence the delivery and, thus, the efficacy of compounds73–75. Tumours with low blood flow are thought to respond better to intra-arterial chemotherapy75, so techniques are being developed to transiently decrease or arrest blood flow when therapy is administered76,77. The field would benefit from standardized methods and treatment protocols to allow comparison between different compounds and doses. Randomized phase III trials are urgently awaited to explore the potential of intra-arterial delivery in glioblastoma.
Localized immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is among the most studied new treatments for glioblastoma. The low immunogenicity of glioblastoma coupled with an immunosuppressive tumour microenvironment helps the tumour evade an antitumour immune response8,9,78. As a result, many new systemic and local therapies have been designed to enhance the immune system and, effectively, turn it against glioblastoma. Various reviews have discussed immunotherapy for glioblastoma at length79,80; here we focus on local treatment approaches that have shown promise in clinical trials.
Viral therapy
Viral therapy can be used in various ways to combat glioblastoma. In the case of gene therapy, replication-defective viruses can function as the delivery vehicle for a transgene and hijack a cancer cell to produce the therapeutic compound. By contrast, oncolytic viruses are often replication-competent and are designed to induce cytotoxicity selectively in tumour cells81. Both of these approaches aim to trigger an immune response, thereby stimulating antitumour immunity82. Local delivery of the viruses increases efficiency and limits systemic spread of viral load. Many viral therapies have been studied in patients with glioblastoma and are extensively reviewed elsewhere81,83. Here, we discuss locally delivered viral therapeutics that have been tested in clinical trials since the beginning of the temozolomide era.
Gene therapy.
Several viral gene therapies are in development for the treatment of glioblastoma. One of the most studied viruses is a replication-incompetent adenoviral vector known as AdvHSV-t k, which delivers the herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) thymidine kinase gene84. When an antiviral prodrug such as ganciclovir is subsequently administered, thymidine kinase phosphorylates this prodrug, causing it to bind to DNA during double-strand break repair (FIG.3). This process eventually disrupts mitosis and DNA repair mechanisms, leading to cell apoptosis and necrosis, and increases sensitivity to chemoradiation85,86. Addition of this treatment to standard therapy has shown some promise in recurrent and primary glioblastoma, and a phase III trial is currently in development87,88 (TABLE 3). Repeated intra-arterial delivery of AdvHSV-tk and ganciclovir has been shown to be safe and feasible and might further improve the efficacy of this treatment88 (TABLE 3).
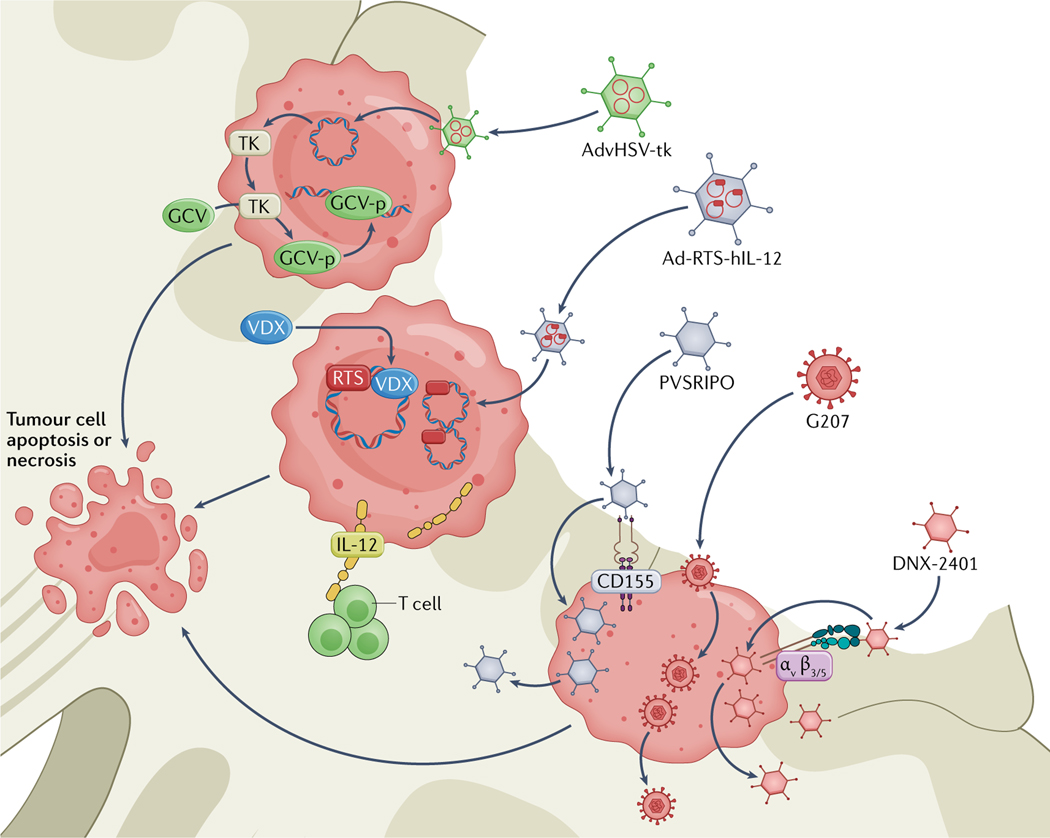
Fig. 3 |. Mechanisms of local viral therapies in development for glioblastoma.
AdvHSV-t k is a replication-incompetent adenoviral vector that delivers herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) thymidine kinase (TK). The transgene is introduced to the cell, and TK is produced. TK phosphorylates systemically administered ganciclovir (GCV) to generate GCV-p, which interferes with DNA repair and replication, eventually leading to tumour cell apoptosis or necrosis. Ad-RTS-hIL-12 is a replication-incompetent adenoviral vector that encodes human IL-12 preceded by a RheoSwitch Therapeutic System (RTS). The DNA construct is introduced into the cell, but can only be transcribed in the presence of veledimex (VDX). When VDX is administered systemically, IL-12 is produced. IL-12 activates T cells and generates an antitumour microenvironment. PVSRIPO is a replication-competent oncolytic polio–rhinovirus chimaera. PVSRIPO enters the cell via CD155, which is abundantly expressed in most glioblastomas. The virus then replicates in the tumour cell, leading to apoptosis and spreading of the virus. G207 is a replication-competent, oncolytic HSV-1 virus that is designed to replicate in tumour cells, causing apoptosis and viral spread. DNX-2401 is a replication-c ompetent adenovirus. The virus enters the cell via αvβ3 and αvβ5 integrins, which are present on glioma stem cells, and cannot replicate when a functional retinoblastoma pathway is present. As this pathway is often inactivated in tumour cells, the virus can cause selective apoptosis or necrosis of these cells.
Table 3 |.
Clinical trials in high-g rade glioma: localized immunotherapy
| Study | Treatment | Study type | Patient cohort | Results | Adverse events (number of patients) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viral therapy | |||||
| Wheeler et al. (2016)87 | AdvHSV-tk injection in resection cavity wall + ganciclovir with standard of care | Phase II, with historical controls | Primary glioblastoma (n = 48) | 3 × 1011 particles well tolerated; median survival, 17.1 months vs 13.5 months in historical controls; median OS after gross total resection, 25.0 vs 16.9 months | Worsening of existent hemiparesis (1) |
| Ji et al. (2016)88 | Repeated dosing of intra-arterial AdvHSV-tk with BBB disruption and standard of care vs standard of care | Phase II | Recurrent WHO grade III or IV glioma (n = 53) | Median OS, 10.4 months in AdvHSV-tk group vs 3.3 months in controls; median PFS, 6.8 vs 1.9 months; treatment of controls (surgery, chemotherapy or palliative care) not stated | No increased risk of adverse events |
| Chiocca et al. (2019)89 | Ad-RTS-hIL-12 in resection cavity wall + systemic veledimex | Phase I | Recurrent glioblastoma (n = 31) | Maximum tolerated dose of veledimex, 20 mg; median survival, 12 months | Reversible cytokine release syndrome (10 grade 2, 6 grade 3), brain oedema (1), confusion (1), aseptic meningitis (1) |
| Desjardins et al. (2018)96 | Single dose of PVSRIPO via CED | Phase I | Recurrent glioblastoma (n = 61) | Median OS, 12.5 months vs. 11.3 months in historical controls | Haemorrhage leading to hemiparesis (1), peritumoural inflammation requiring bevacizumab (32), requiring surgery (4) |
| Lang et al. (2018)98 | DNX-2401 in resection cavity wall | Phase I | Recurrent glioblastoma (n = 37) | 20% of patients survived >3 years, three showed >95% tumour reduction; OS, 13.0 months | Transient fever, headache and malaise (2) |
| Markert et al. (2014)102 | Single stereotactic injection of G207 combined with radiotherapy | Phase I | Recurrent glioblastoma (n = 9) | Six patients showed stabilization of disease or partial response; median OS, 7.5 months; median PFS, 2.5 months | Seizures and hemiparesis (number of patients unclear) |
| Friedman et al. (2021)104 | Single injection of G207 via CED combined with radiotherapy | Phase I | Paediatric recurrent high-grade glioma (n = 12) | Radiological and/or clinical response in 11 patients; median OS, 12.2 months | No dose-l imiting adverse effects |
| Cytokine and antibody therapy | |||||
| Kunwar et al. Single injection of (2010)50 IL13-Pe38QQR via CED vs carmustine wafers | Phase III | Recurrent glioblastoma (n = 296) | Median OS, 9.1 months in IL13-Pe38QQR group vs 8.8 months in controls | Increased incidence of pulmonary embolism in IL13-Pe38QQR group (16 vs 2 patients) | |
| Immunostimulating oligodeoxynucleotides | |||||
| Carpentier et al. (2010)111 | Single stereotactic injection of CpG-O DN | Phase II | Recurrent glioblastoma (n = 31) | One partial response and three minor responses; median OS, 6.4 months; median PFS, 2.1 months | Transient worsening of neurological deficits (22), death owing to haemorrhage (1) |
| Ursu et al. (2017)112 | CpG-ODN injected into resection cavity wall followed by standard of care vs standard of care only | Phase II | Primary glioblastoma (n = 81) | Median OS, 17 months in CpG-ODN group vs 18 months in controls; median PFS, 9 months in both groups | Increased occurrence of fever and postoperative haemorrhage |
BBB, blood–brain barrier; CED, convection-enhanced delivery; CpG-ODN, oligodeoxynucleotides containing unmethylated cytosine–guanosine motifs; OS, overall survival; PFS, progression-free survival; PVSRIPO, recombinant non-pathogenic polio–rhinovirus chimaera.
Another gene therapy approach uses the replication-defective adenoviral Ad-RTS-hIL-12 vector, which encodes a human IL12 transgene under the control of a ligand-inducible expression switch89 (FIG.3). The vector is injected into the tumour site after resection, and the activator ligand, veledimex, is administered orally. IL-12 is thought to have potent anticancer potential via stimulation of T cells to produce IFNγ, thereby creating a more inflammatory tumour microenvironment90. However, systemic IL-12 administration or direct local injection of IL-12-producing lymphocytes causes severe adverse events91,92. The switch method enables transcription and expression of IL-12 to be regulated, and the levels of this factor decrease rapidly when veledimex administration ceases, thereby allowing rapid correction if adverse effects occur93. A phase I dose-escalation trial demonstrated the safety of this approach, with increased inflammation and infiltration of PD1-expressing CD8+ T cells being noted on re-resection89 (TABLE 3). This result, combined with improved OS after IL-12 therapy, led to the initiation of new phase I trials (NCT03636477 and NCT04006119), which are studying IL-12 viral therapy in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors (nivolumab or cemiplimab) in an effort to further improve efficacy (Supplementary Table 3).
Toca 511 is a retroviral therapy that is designed to induce expression of cytosine deaminase in tumour cells via a retroviral replicating vector. This enzyme converts the prodrug 5-fluorocytosine to 5-fluorouracil, a potent chemotherapeutic that has shown efficacy against glioma94. A phase I trial showed promising responses in 45 patients with recurrent glioblastoma95, but a subsequent phase III trial (NCT02414165) was terminated by the company after failing to show any improvements over standard of care.
Oncolytic therapy.
PVSRIPO is a recombinant, replication-competent oncolytic polio–rhinovirus chimaera that has been tested in recurrent glioblastoma96. Infection with PVSRIPO requires expression of CD155, which is abundant on glioblastoma and, to a lesser extent, on antigen-presenting cells (FIG.3). PVSRIPO infection of the tumour cells halts protein synthesis and induces oncolysis, whereas infection of non-tumour antigen-presenting cells leads to interferon-dominant activation of the tumour microenvironment and an enhanced T cell response97. After patients received PVSRIPO via CED, a strong inflammatory response was observed, which necessitated surgery in 4 of 61 individuals96 (TABLE 3). Later in the study, the addition of lomustine seemed to be beneficial when treating recurrence: about one-third of patients who also received this drug showed radiographic signs of cystic tumour degradation and a rapid decline in tumour volume. OS was not improved compared with historical controls. A phase II trial in patients with recurrent glioblastoma is now underway (NCT02986178), and the use of PVSRIPO is also being explored in paediatric patients with recurrent high-grade glioma (NCT03043391) (Supplementary Table 3).
Another replication-competent oncolytic adenovirus is DNX-2401 (REF.98). This vector is designed to enter cells that express high levels of αvβ3 and αvβ5 integrins, such as glioma stem cells, but it cannot replicate when a functional retinoblastoma (Rb) pathway is present. The Rb pathway regulates the G1 checkpoint of the cell cycle, and this pathway is frequently inactivated in cancers, including gliomas99,100. Consequently, replication of DNX-2401 is limited to tumour cells100 (FIG.3). DNX-2401 kills tumour cells by direct oncolysis, which also induces an inflammatory response. A phase I trial demonstrated that stereotactic injection of DNX-2401 into the tumour or the resection cavity wall is safe98 (TABLE 3). Tumour reduction was observed in 72% of patients, with a median OS of 13.0 months. Three patients showed more than 95% tumour reduction after injection and were alive 3 years after the start of treatment. Data are currently awaited from a recently completed phase II trial, combining DNX-2401 with the anti-PD1 monoclonal antibody pembrolizumab (NCT02798406). The same group is also investigating intra-arterial injection of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) loaded with DNX-2401 before and after surgery in patients with recurrent glioblastoma (NCT03896568) (Supplementary Table 3).
G207 is a replication-competent oncolytic HSV-1 vector. Deletion of the diploid γ134.5 neurovirulence gene and inactivation of viral ribonucleotide reductase via insertion of Escherichia coli lacZ prevents infection of normal cells while allowing replication in tumour cells101 (FIG.3). A phase I trial in patients with recurrent glioblastoma showed that when administered into the resection bed, G207 is safe, can be combined with radiotherapy and induces a response in the majority of patients102 (TABLE 3). As xenograft studies indicated that paediatric glial tumours have a markedly increased sensitivity to G207, possibly owing to increased expression of CD111 (nectin 1)103, a phase I trial evaluated the safety of this vector in a cohort of paediatric patients with high-grade glioma104 (TABLE 3). No serious adverse events were found, and a response was observed in 11 of 12 patients. Median survival was 12.2 months, which is remarkable for paediatric patients with recurrent high-grade glioma. Combination with radiotherapy was well tolerated and this approach will be studied further in an upcoming phase II trial (NCT04482933) (Supplementary Table 3).
Summary.
Viral therapy in glioblastoma has generated considerable interest and excitement. Some patients have shown remarkable responses to these therapies, with long-term survivors in several studies96,98,104. However, not all patients benefit from these treatments, and further study and analysis of the factors that influence the response is warranted81 (BOX 1). One potential confounding factor is that most of the long-term responders seem to have favourable prognostic factors such as small tumour size, young age, isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) and IDH2 mutations, 6-O-methylguanine–DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter methylation and good performance status81. These observations point to a general problem when studying recurrent glioblastoma: the patient population is usually heterogeneous with regard to age, performance status, molecular subtype, previous therapy and dexamethasone use. In addition, the patients who are selected for these experimental trials are likely to be well-motivated individuals with high socioeconomic status — factors that contribute to improved outcomes in general105.
Box 1 |. Selection bias in early-phase clinical trials.
This Review discusses many phase I and II trials of local therapy for glioblastoma that demonstrate some form of treatment response or efficacy. However, translation of these promising results into successful randomized phase III trials has so far been lacking. Several factors could have contributed to this apparent discrepancy.
Patients selected for phase I and II trials are usually a subset of individuals with good performance status, no comorbidities, relatively young age and high motivation to undergo further treatment. A Swedish study showed that only a minority of patients with glioblastoma meet the current study inclusion criteria, and this group already has significantly improved median overall survival — 16.4 months compared with 7.7 months for patients who do not meet the criteria — regardless of whether additional therapy is administered118. Comparing these patients with historical or non-participating controls will, therefore, bias the data towards favourable outcomes for the study cohort.
Similarly, in several phase I and II trials, some patients showed remarkable long-term survival after treatment81. However, in the Swedish study, 8.6% of the patients who were deemed eligible for study inclusion at diagnosis had an overall survival of more than 5 years118. A retrospective analysis of patients with glioblastoma in Australia also noted that participation in a clinical trial was associated with improved survival, regardless of treatment allocation and independent of performance status, age and tumour location117.
Patients might benefit from participating in clinical trials by having access to better care, including more frequent check-ups, imaging and physician contact. Consequently, disease progression and complications are more closely monitored and potentially treated earlier compared with patients who are not participating in clinical trials. Factors such as socioeconomic status and race could also influence trial participation and survival outcomes, although precise data are currently lacking105,148. In addition, phase I and II studies in recurrent glioblastoma often include patients with a wide range of disease progression, tumour size, previous treatments and dexamethasone usage, all of which can influence survival and response to treatment149,150. Therefore, drawing general conclusions from this patient group is complex and should be done with the utmost caution.
To improve generalizability and applicability, large, multicentre, randomized clinical trials are necessary. Given the substantial financial and regulatory hurdles, however, this approach is not feasible in the early stages of treatment development. To enable the generalizability of smaller trials to be assessed, these trials must include extensive data on patient characteristics, including not only tumour size, location, steroid use and previous treatments, but also socioeconomic background, race and education. Immune and genetic profiling of tumours is becoming more accessible and should be included in the patient data and outcome analyses wherever possible.
The literature on viral therapies for glioblastoma currently consists largely of phase I and II trials106, and phase III trials in large patient cohorts will be essential to determine the true value of these therapies. At present, however, no such trials are registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (Supplementary Table 3).
Cytokine therapy
Systemically administered cytokines can induce an immune response against cancer but also carry a large risk of toxicity and adverse events92. Consequently, strategies are being developed to localize the release of cytokines to induce local inflammation while avoiding a systemic response.
The PRECISE trial utilized expression of IL-13 by glioblastoma cells to facilitate entry of exotoxin A, a cytotoxin derived from Pseudomonas aeruginosa50. By fusing IL-13 to this exotoxin, the researchers created a recombinant chimaeric cytotoxin known as IL13-PE38QQR, which inhibits protein synthesis and induces apoptosis107. A randomized phase III trial was performed in 296 patients with recurrent glioblastoma50. After gross total resection of the tumour, the participants were randomly assigned to receive either IL13-P E38QQR via CED or implantation of carmustine wafers. No difference in OS was found, but the incidence of pulmonary embolism was significantly higher in the those treated with IL13-PE38QQR, possibly owing to prolonged hospital stay and additional surgery (TABLE 3). As discussed previously, appropriate placement of the catheters was challenging, with less than 70% of catheters adequately positioned. Despite efforts to optimize delivery of IL13-PE38QQR, these results were disappointing and no new trials with this cytotoxin are currently planned.
To date, local injection of cytokines has shown limited promise. The rise of gene therapies such as Ad-RTS-hIL-12 with veledimex89, which can regulate delivery of cytokines over time without the need for CED or repeated surgery, might limit the role of direct injection of cytokines into the tumour. However, new gene therapies require careful design and testing, with a long developmental trajectory to reach the clinic. Direct injection could serve as a first-line method to evaluate the functionality of the cytokine, before developing more suitable methods of delivery. Currently, CED of various cytokines and antibodies is being tested in phase I trials, including 124I-omburtamab (NCT01502917), anti-C D26 (NCT04608812), anti-C D40 (NCT04547777) and bone morphogenetic protein 4 (NCT02869243) (Supplementary Table 3).
Immunostimulatory oligodeoxynucleotides
To enhance the immune response to tumour cells, immunostimulatory oligodeoxynucleotides containing unmethylated cytosine–guanosine motifs (CpG-ODN) have been developed to activate Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9)108. As TLR9 is mainly expressed by antigen-presenting cells, such as plasmacytoid dendritic cells and microglia109, CpG-O DNs injected into glioblastoma are hypothesized to increase antigen presentation and, consequently, improve the immune response. Promising responses to CpG-ODNs were reported in mice110. However, two phase II trials in which these CpG-ODNs were injected into the tumour cavity wall after resection of primary or recurrent glioblastoma failed to show improvements in outcomes when combined with standard chemoradiotherapy111,112 (TABLE 3). A possible explanation is that antigens presented by microglia or dendritic cells fail to induce an immune response if these antigens are not recognized by T cells as foreign. One of the hallmarks of glioblastoma is immuno suppression, with limited T cell infiltration into the tumour113. This immunosuppression is further aggravated by the use of dexamethasone, and in the phase II trial in recurrent glioblastoma, only four of 34 patients were not receiving this drug111. Minimization of steroid use and/or combination with immune checkpoint inhibi tion might be beneficial for these therapies. No trials are currently studying CpG-ODN in glioblastoma.
Localized radiotherapy
Radiotherapy has been a cornerstone of glioblastoma treatment for many years. Improvements are continually being made to minimize harm to healthy tissue while maximizing the dose administered to the tumour area. The current standard of care involved stereotactic radiotherapy with a total dose of 60 Gy, delivered in 30 fractions of 2 Gy over 6 weeks114. Radiotherapy targets the surgical cavity, often including the margin where peritumoural oedema is seen on fluid-attenuated inversion recovery MRI sequences. Over 80% of glioblastoma recurrences occur within these radiotherapy fields11. In an effort to increase the dose received by the tumour bed while minimizing damage to surrounding tissue, various forms of brachytherapy — a type of radiotherapy in which a radiation source is implanted in or near the tumour — have been investigated, with varying degrees of success115. In this section, we discuss the latest developments.
A 2019 study based on the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results database concluded that OS is improved in patients who have received some form of brachytherapy for glioblastoma116. The study included a total of 60,456 patients who were diagnosed with primary glioblastoma between 1975 and 2015, 362 of whom received brachytherapy. A multivariate Cox regression analysis including age, tumour size, tumour location, extent of resection and chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy treatment showed brachytherapy to be an independent predictor of improved outcome (as were all the other included variables). However, this study had multiple limitations. Most patients were treated before the introduction of the Stupp protocol, patients enrolled in clinical studies were likely to have an improved outcome regardless of treatment group allocation117,118, and no data were available regarding IDH or MGMT aberrations in these groups. Therefore, no firm conclusions can be drawn from these data.
Two studies evaluated low dose-rate brachytherapy involving stereotactic implantation of 125I seeds in patients with inoperable (predominantly recurrent) glioblastoma119,120 (TABLE 4). These studies demonstrated the safety of the procedure, with manageable adverse effects related to postoperative oedema. However, no evidence of improvements in patient outcomes was found in either study. Schwartz et al.119 observed that all instances of tumour progression occurred in the vicinity of the treated area, casting further doubt on the usefulness of low-dose brachytherapy in glioblastoma. A clinical trial is currently evaluating the dose, safety and efficacy of 186Re nanoliposomes delivered by CED in recurrent glioblastoma (NCT01906385). These nanoliposomes have shown promise in preclinical models121, but whether the findings will translate to a clinical response remains to be seen.
Table 4 |.
Clinical trials in high-grade glioma: localized radiotherapy
| Study | Treatment | Study type | Patient cohort | Results | Adverse events (number of patients) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schwartz et al. (2015)119 | Stereotactic implantation of 125I beads | Retrospective cohort | Recurrent high-grade glioma (n = 68) | Median OS, 41.8 months; median PFS, 8.3 months; treatment failure observed in 57 patients | Surgical revision of beads (1), oedema requiring steroids and bevacizumab (6) |
| Kickingereder et al. (2014)120 | Stereotactic implantation of 125I beads vs standard of care only | Retrospective cohort | Inoperable primary or recurrent glioblastoma (n = 201) | Median OS, 11.1 months; median PFS, 6.2 months | Transient oedema treated with corticosteroids (7), persistent neurological deficits owing to oedema (3), cyst requiring stereotactic evacuation (1), abscess requiring stereotactic drainage (1) |
| Sarria et al. (2020)123 | Intraoperative radiotherapy + standard of care | Retrospective cohort | Primary glioblastoma (n = 51) | Median OS, 18.0 months; median PFS, 11.4 months | Radiation necrosis, no intervention required (12) |
OS, overall survival; PFS, progression-free survival.
Another technique in development is intraoperative radiotherapy (IORT), which has shown promise in breast and colon cancer122. A retrospective analysis gathered outcome and toxicity data from 51 patients with primary glioblastoma who were treated with IORT in addition to the Stupp protocol123 (TABLE 4). Most patients received 10 Gy IORT via a spherical applicator in the resection cavity. Toxicities were limited to radiation necrosis in 13 patients, and outcomes were positive (TABLE 4). Of special interest is the finding that tumour progression initiated locally in only 35.5% of patients, compared with the usual 80% in glioblastoma11. A large multicentre phase III trial is attempting to recruit 314 patients to evaluate whether IORT as an addition to first-line treatment can improve outcomes in glioblastoma (NCT02685605) (Supplementary Table 4).
Engineered stem cells and T cells
MSCs and neural stem cells (NSCs) are known to migrate towards damaged tissue and tumours, are able to release bioactive molecules, and can induce positive immunomodulatory effects124. Several studies in mice have shown the potential of modified MSCs and NSCs, injected either intravenously or intracranially, to migrate towards glial tumours and deliver chemotherapy, such as paclitaxel125, or convert a prodrug into a toxic compound124. The latter technique was studied in a phase I trial in patients with recurrent glioblastoma126 (TABLE 5). A human NSC line, HB1.F3, was retrovirally transduced to express cytosine deaminase, which converts 5-fluorocytosine, a non-toxic compound that crosses the BBB, to 5-fluorouracil, a cytotoxic agent. The NSCs were injected into the wall of the resection cavity or into the tumour tissue that remained after resection, and 5-fluorocytosine was administered orally. Three different doses of NSCs were tested, and the six patients who received the highest dose (5 × 107 NSCs) had a median OS of 15.4 months, compared with only 2.9 months in patients who received lower doses. Post-mortem pathological assessment in two patients found injected NSCs in tumour tissue, but also showed migration of NSCs to sites distant from the tumour, crossing the corpus callosum in one patient. Given the deep infiltration of glioblastoma cells throughout the brain, deep spread of NSCs is an important and encouraging finding. One theoretical limitation is the possibility for NSCs to become tumorigenic, as they are immortalized through expression of MYC127, but this phenomenon was not observed in the present study126. Furthermore, not all patients are able to receive this therapy as some express antibodies against class I or II HLA (3 of 18 in this study). A new study is exploring the combination of carboxylesterase-expressing allogeneic NSCs with irinotecan hydrochloride in patients with recurrent glioblastoma (NCT02192359) (Supplementary Table 5).
Table 5 |.
Clinical trials in high-grade glioma: neural stem cell therapy
| Study | Treatment | Study type | Patient cohort | results | Adverse events (number of patients) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Portnow et al. (2017)126 | Neural stem cells expressing cytosine deaminase into resection cavity wall | Phase I | Recurrent high-grade glioma (n = 15) | Median OS, 8.4 months; median PFS, 1.0 month; higher dose correlated with longer survival | Death owing to haemorrhage (1), grade 3 liver toxicity necessitating termination of treatment (1) |
| Fares et al. (2021)128 | Neural stem cells delivering oncolytic adenovirus into resection cavity wall | Phase I | Primary high-grade glioma (n = 12) | Median OS, 18.4 months; median PFS, 9.1 months | Meningitis owing to injection into cerebral ventricle (1) |
OS, overall survival, PFS, progression-free survival.
An interesting pilot study demonstrated the possibility of delivering an oncolytic adenovirus (CRAd-S-pk7) via NSCs in patients with primary glioblastoma128 (TABLE 5). This method combines the tumour-trophic characteristics of NSCs with the sustained oncolytic capabilities of a replication-competent virus, and has produced positive results in animal models129. Injection of these NSCs into the cavity wall after resection induced an influx in CD8+ T cells at the tumour site, and patients who received the treatment had a median OS of 18.4 months. No traces of either NSCs or adenoviral vectors were found on re-resection or autopsy 4–24 months after injection. A phase II trial (NCT03072134) has recently been completed, with results expected soon (Supplementary Table 5).
Chimaeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy has shown impressive results in B cell malignancies and is currently being developed for various solid cancers. A complete overview of the current state of CAR T cell therapy in glioblastoma is provided elsewhere130. The potential to deliver these T cells locally to the tumour has gained attention in recent years. Currently, a phase I study is recruiting patients to receive CAR T cells via a Rickham catheter (NCT02208362) (Supplementary Table 5). In this study, CAR T cells targeting IL-13Rα2 are generated through lentiviral transduction of enriched central memory T cells and are injected into the tumour cavity on a weekly basis. One patient from this study, who had recurrent glioblastoma and multiple lesions in the brain and spinal cord, showed a remarkable response, although the lesions recurred after 8 months131. Many studies are currently testing various forms of CAR T cell therapy, some in combination with checkpoint inhibition (NCT04003649) or temozolomide (NCT04165941) (Supplementary Table 5).
Engineered stem cells and T cells are still in the early stages of development for the treatment of glioblastoma. The tumour-homing abilities of NSCs and T cells are highly relevant in glioblastoma, which has often infiltrated deep into the brain by the time of diagnosis132–134. Local delivery ensures that most cells arrive at the area with the highest number of tumour cells, but this approach might not be amenable to repeated dosing. The presence of NSCs months after administration was noted in one study126 but not in another128. Some questions regarding malignant transformation of NSCs remain and the dynamics and life cycle of NSCs requires further study, but given the aggressive nature of glioblastoma, long-term adverse effects might be less relevant than in some other cancers. A major factor that complicates CAR T cell therapy in glioblastoma is that the T cells are modified to attack tumour cells expressing specific antigens. However, glioblastoma is notoriously heterogeneous and expression profiles can change drastically in response to treatment, which might limit long-term efficacy135,136. The immunosuppressive tumour microenvironment and the frequently observed T cell exhaustion in glioblastoma provide additional challenges for this therapy113,137. Further research is needed in the clinical and preclinical settings to address these issues. Furthermore, CAR T cell therapy is currently highly labour-intensive for clinicians and financially prohibitive for many patients. Although this field is developing rapidly, phase III trials have not yet been planned (Supplementary Table 5).
Conclusions and future prospects
In glioblastoma, most recurrences occur in — or close to — the resection cavity11. Directing therapy to the tumour cavity might, therefore, improve treatment efficacy. Local therapies for glioblastoma are an attractive prospect; however, most novel approaches are still in the developmental phase. Local gene therapy and oncolytic viral therapies show promise and are awaiting further phase II–III trials. A major strength of local therapy lies in minimizing systemic adverse effects and interactions, thereby allowing combinatorial approaches with systemic therapies. Many current clinical trials are evaluating combinations of local and systemic therapy (Supplementary Tables 1–5). Monitoring of systemic levels of locally administered agents has shown that crossing of the BBB is usually minimal104,126, and most trials indicate that systemic adverse effects rarely occur. Therefore, combining local and systemic therapy could be safe, at least in certain cases; however, more studies are necessary.
Although treatment of the surgical cavity might enhance local control of the tumour, it does not attack deeply infiltrated glioblastoma cells. Only NSCs and CAR T cells have been shown to migrate throughout the brain and attack distant foci of tumour cells126,131. To aim to cure glioblastoma, a therapy must have the potential to penetrate deeply into the healthy tissue to selectively kill glioma cells. A deeper understanding of NSC therapy, CAR T cells and the infiltration of glioblastoma itself is needed to increase the potential of these treatments.
Glioblastoma is an immunologically ‘cold’ tumour owing to low infiltration of T cells, and has shown a poor response to immunotherapies78. Aside from the direct antitumour effects, local therapy might induce and enhance a local immune response. Cloughesy et al. showed that neoadjuvant anti-PD1 therapy combined with surgery improved survival outcomes138. Local therapy can further enhance and prolong the inflammatory response after surgery, as seen in magnetic thermotherapy30, PDT43, IL-12 adenoviral therapy89 and G207 therapy104. Combination of these approaches with systemic checkpoint inhibition therapies could produce synergistic effects — a possibility that is being studied in many ongoing phase I and II trials (Supplementary Tables 1–5).
Local therapy could provide a first-line treatment option in patients with limited surgical possibilities. LITT and CED of chemotherapeutics and viral therapies might offer an alternative to surgery, although further optimization of the current high risk of adverse events and worsening of symptoms — albeit often transient — is warranted. At standard doses, brachytherapy does not seem to provide additional benefits, and although higher dosing could be feasible, studies have shown an unacceptable increase in toxicity and adverse events139, without improvements in outcomes140, when large local doses are administered.
Local delivery might also improve the efficacy of therapies such as bevacizumab that have shown limited benefits when administered systemically66. Even the efficacy of current therapeutics such as temozolomide may be improved when delivered locally, and a clinical trial of intra-arterial delivery of this drug (NCT01180816) has recently finished including patients.
In the laboratory, various new techniques and therapies are being developed. New methods of delivery such as hydrogels141, nanoliposomal packaging142, polymeric microspheres143 and cannabinoid microparticles144 have all shown promise for delivering therapeutics to the tumour. The arsenal of therapeutics is also expanding. Bacterial carriers145, RNA interference therapeutics146 and high-frequency irreversible electroporation147 have been tested in preclinical models and are awaiting translation to the clinic.
The preliminary successes of local therapy in patients will hopefully encourage the development of novel techniques and therapeutics. Neurosurgeons, neurologists, oncologists and other clinicians should be involved in the development of new therapies as early as possible to improve applicability to patients with glioblastoma, translation to the clinic and design of phase I and II trials. Although many innovative phase I and II trials are already being conducted, few therapies have been compared with the standard of care in randomized phase III trials. Currently, only one local therapy study, which is evaluating IORT plus standard of care (NCT02685605), is enrolling patients. Recruitment of enough patients to power a phase III trial remains a challenging and lengthy endeavour. Collaboration between governmental institutions, hospitals and countries should be encouraged and established in the early stages of treatment development to smooth the transition to larger cohorts and facilitate rapid expansion to phase III trials.
Glioblastoma remains challenging to treat, and many local therapies are currently in development. The future of glioblastoma treatment is likely to lie not in a singular approach but in combining local and systemic patient-tailored treatments to combat this lethal disease.
Supplementary Material
Key points.
Glioblastoma almost always recurs at or near the resection cavity, within the radiotherapy field.
Local therapy provides a unique opportunity to deliver high doses of therapeutics to the area with the highest concentration of glioblastoma cells, with limited systemic adverse effects.
Many phase I and II trials experimenting with various forms of local therapy have been — and are being — conducted in glioblastoma, with many showing great potential for improving progression-free and overall survival.
Large randomized phase III trials comparing local therapies with standard of care have been hindered by high cost, labour intensity and challenges in patient recruitment.
Close collaboration between clinicians, researchers, companies and governmental institutions is needed to smooth the transition from laboratory to phase I and II trials to large-scale randomized controlled trials.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank M. E. Haeflich for proofreading this manuscript for typographical and grammatical errors; skilled editorial assistance from S. McDavitt; and insights from X. Breakefield. M.L.D.B. is supported by grant NIH NCI R35 CA232103. T.S.v.S. is supported by grants from the Bontius Stichting, the Nijbakker-Morra Fund, Foundation Vrijvrouwe van Renswoude and the Bekker-l a Bastide Fund. T.S.v.S. and E.A.C. are supported by NIH grant P01 CA069246.
Footnotes
Peer review information
Nature Reviews Neurology thanks C. Herold-Mende and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Review criteria
In December 2020, we searched PubMed and Embase for studies utilizing any form of local therapy in glioblastoma. Keywords, Mesh terms and Emtree terms including “glioblastoma”, “glioma”, “local therapy”, “localized therapy”, “convection enhanced delivery”, “thermotherapy”, “wafer”, “brachytherapy”, “photodynamic therapy” and their synonyms were combined to form our search. Titles and abstracts were screened for relevant articles and studies. References from full-t ext articles were screened for additional studies. Articles had to be written in English and published within the past 20 years. Studies performed before implementation of the Stupp protocol were excluded, unless deemed relevant to current studies or patient care. Case reports were also excluded. Additional papers were recommended by all authors. For current clinical trials, ClinicalTrials.gov was searched for disease “glioblastoma” and “glioma”, and all trials with status ‘not yet recruiting’, ‘recruiting’, ‘enrolling by invitation’, ‘active, not recruiting’, or ‘available’.
Supplementary information
The online version contains supplementary material available at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-022-00621-0.
Competing interests
E.A.C. is currently an advisor to Advantagene, Alcyone Biosciences, Insightec, DNAtrix, Immunomic Therapeutics, Seneca Therapeutics, GlaxoSmithKline and Voyager Therapeutics and has equity interest in DNAtrix, Immunomic Therapeutics and Seneca Therapeutics; he has also advised Oncorus, Merck, Tocagen, Ziopharm, Stemgen, NanoTx., Ziopharm Oncology, Cerebral Therapeutics, Genenta. Merck, Janssen, Karcinolysis, Shanghai Biotech and Sangamo Therapeutics. He has received research support from the NIH, the US Department of Defense, the American Brain Tumor Association, the National Brain Tumor Society, the Alliance for Cancer Gene Therapy, the Neurosurgical Research Education Foundation, Advantagene, NewLink Genetics and Amgen. He is also a named inventor on patents related to oncolytic HSV-1 and non-coding RNAs. The other authors declare no competing interests.
References
- 1.Stupp R. et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med 352, 987–996 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zhu P, Du XL, Lu G. & Zhu JJ Survival benefit of glioblastoma patients after FDA approval of temozolomide concomitant with radiation and bevacizumab: a population-based study. Oncotarget 8, 44015–44031 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Stupp R. et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 10, 459–466 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Stupp R. et al. Maintenance therapy with tumor-treating fields plus temozolomide vs temozolomide alone for glioblastoma: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 314, 2535–2543 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Mittal S. et al. Alternating electric tumor treating fields for treatment of glioblastoma: rationale, preclinical, and clinical studies. J. Neurosurg 128, 414–421 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Patel AP et al. Single-cell RNA-s eq highlights intratumoral heterogeneity in primary glioblastoma. Science 344, 1396–1401 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Brennan CW et al. The somatic genomic landscape of glioblastoma. Cell 157, 753 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Broekman ML et al. Multidimensional communication in the microenvirons of glioblastoma. Nat. Rev. Neurol 14, 482–495 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Antunes ARP et al. Understanding the glioblastoma immune microenvironment as basis for the development of new immunotherapeutic strategies. eLife 9, e52176 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Jackson M, Hassiotou F. & Nowak A. Glioblastoma stem-like cells: at the root of tumor recurrence and a therapeutic target. Carcinogenesis 36, 177–185 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Brandes AA et al. Recurrence pattern after temozolomide concomitant with and adjuvant to radiotherapy in newly diagnosed patients with glioblastoma: correlation with MGMT promoter methylation status. J. Clin. Oncol 27, 1275–1279 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.McGirt MJ et al. Independent association of extent of resection with survival in patients with malignant brain astrocytoma: clinical article. J. Neurosurg 110, 156–162 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Duffau H. Long-term outcomes after supratotal resection of diffuse low-grade gliomas: a consecutive series with 11-year follow-up. Acta Neurochir. 158, 51–58 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.De Leeuw CN & Vogelbaum MA Supratotal resection in glioma: a systematic review. Neuro Oncol. 21, 179–188 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Titsworth WL, Murad GJA, Hoh BL & Rahman M. Fighting fire with fire: the revival of thermotherapy for gliomas. Anticancer. Res 34, 565–574 (2014). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Watanabe M, Tanaka R, Hondo H. & Kuroki M. Effects of antineoplastic agents and hyperthermia on cytotoxicity toward chronically hypoxic glioma cells. Int. J. Hyperthermia 8, 131–138 (1992). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Menovsky T, Beek JF, Van Gemert MJC, Roux FX & Bown SG Interstitial laser thermotherapy in neurosurgery: a review. Acta Neurochir. 138, 1019–1026 (1996). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Man J. et al. Hyperthermia sensitizes glioma stem-like cells to radiation by inhibiting AKT signaling. Cancer Res. 75, 1760–1769 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Schildkopf P. et al. Biological rationales and clinical applications of temperature controlled hyperthermia – implications for multimodal cancer treatments. Curr. Med. Chem 17, 3045–3057 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Frey B. et al. Old and new facts about hyperthermia-induced modulations of the immune system. Int. J. Hyperthermia 28, 528–542 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lee I, Kalkanis S. & Hadjipanayis CG Stereotactic laser interstitial thermal therapy for recurrent high-grade gliomas. Clin. Neurosurg 79, S24–S34 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Holste KG & Orringer DA Laser interstitial thermal therapy. Neurooncol Adv. 2, vdz035 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Mohammadi AM et al. Upfront magnetic resonance imaging-guided stereotactic laser-ablation in newly diagnosed glioblastoma: a multicenter review of survival outcomes compared to a matched cohort of biopsy-only patients. Clin. Neurosurg 85, 762–772 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kamath AA et al. Glioblastoma treated with magnetic resonance imaging-guided laser interstitial thermal therapy: safety, efficacy, and outcomes. Clin. Neurosurg 84, 836–843 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mohammadi AM et al. The role of laser interstitial thermal therapy in enhancing progression-free survival of difficult-to-access high-grade gliomas: a multicenter study. Cancer Med. 3, 971–979 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Viozzi I, Guberinic A, Overduin CG, Rovers MM & ter Laan M. Laser interstitial thermal therapy in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma: a systematic review. J. Clin. Med 10, 355 (2021). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Leuthardt EC, Voigt J, Kim AH & Sylvester P. A single-center cost analysis of treating primary and metastatic brain cancers with either brain laser interstitial thermal therapy (LITT) or craniotomy. Pharmacoecon. Open 1, 53–63 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Barnett GH, Voigt JD & Alhuwalia MS A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies examining the use of brain laser interstitial thermal therapy versus craniotomy for the treatment of high-grade tumors in or near areas of eloquence: an examination of the extent of resection and major complication rates associated with each type of surgery. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg 94, 164–173 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Maier-Hauff K. et al. Efficacy and safety of intratumoral thermotherapy using magnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles combined with external beam radiotherapy on patients with recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. J. Neurooncol 103, 317–324 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Grauer et al. Combined intracavitary thermotherapy with iron oxide nanoparticles and radiotherapy as local treatment modality in recurrent glioblastoma patients. J. Neurooncol 141, 83–94 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Brown NF, Carter TJ, Ottaviani D. & Mulholland P. Harnessing the immune system in glioblastoma. Br. J. Cancer 119, 1171–1181 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Meng Y, Hynynen K. & Lipsman N. Applications of focused ultrasound in the brain: from thermoablation to drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Neurol 17, 7–22 (2021). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Bunevicius A, McDannold NJ & Golby AJ Focused ultrasound strategies for brain tumor therapy. Oper. Neurosurg 19, 9–18 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Elias WJ et al. A randomized trial of focused ultrasound thalamotomy for essential tremor. N. Engl. J. Med 375, 730–739 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Guthkelch AN et al. Treatment of malignant brain tumors with focused ultrasound hyperthermia and radiation: results of a phase I trial. J. Neurooncol 10, 271–284 (1991). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Castano AP, Demidova TN & Hamblin MR Mechanisms in photodynamic therapy: part one–photosensitizers, photochemistry and cellular localization. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther 1, 279–293 (2004). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Castano AP, Demidova TN & Hamblin MR Mechanisms in photodynamic therapy: part two–cellular signaling, cell metabolism and modes of cell death. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther 2, 1–23 (2005). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Fingar VH Vascular effects of photodynamic therapy. J. Clin. Laser Med. Surg 14, 323–328 (1996). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Li F. et al. Photodynamic therapy boosts anti-glioma immunity in mice: a dependence on the activities of T cells and complement C3. J. Cell. Biochem 112, 3035–3043 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Bellnier DA et al. Clinical pharmacokinetics of the PDT photosensitizers porfimer sodium (Photofrin), 2-[1-hexyloxyethyl]-2-devinyl pyropheophorbide-a (Photochlor) and 5-ALA-induced protoporphyrin IX. Lasers Surg. Med 38, 439–444 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Stummer W. et al. Fluorescence-guided surgery with 5-aminolevulinic acid for resection of malignant glioma: a randomised controlled multicentre phase III trial. Lancet Oncol. 7, 392–401 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Eljamel MS, Goodman C. & Moseley H. ALA and Photofrin® fluorescence-guided resection and repetitive PDT in glioblastoma multiforme: a single centre phase III randomised controlled trial. Lasers Med. Sci 23, 361–367 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Schipmann S. et al. Combination of ALA-induced fluorescence-g uided resection and intraoperative open photodynamic therapy for recurrent glioblastoma: case series on a promising dual strategy for local tumor control. J. Neurosurg 134, 426–436 (2020). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Linde ME Van et al. Treatment outcome of patients with recurrent glioblastoma multiforme: a retrospective multicenter analysis. J. Neurooncol 135, 183–192 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wang H-W et al. Broadband reflectance measurements of light penetration, blood oxygenation, hemoglobin concentration, and drug concentration in human intraperitoneal tissues before and after photodynamic therapy. J. Biomed. Opt 10, 014004 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Akimoto J. et al. First autopsy analysis of the efficacy of intra-o perative additional photodynamic therapy for patients with glioblastoma. Brain Tumor Pathol. 36, 144–151 (2019). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Vermandel M. et al. Standardized intraoperative 5-ALA photodynamic therapy for newly diagnosed glioblastoma patients: a preliminary analysis of the INDYGO clinical trial. J. Neurooncol 152, 501–514 (2021). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Jain RK Delivery of novel therapeutic agents in tumors: physiological barriers and strategies. J. Natl Cancer Inst 81, 570–576 (1989). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Jahangiri A. et al. Convection-enhanced delivery in glioblastoma: a review of preclinical and clinical studies. J. Neurosurg 126, 191–200 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kunwar S. et al. Phase III randomized trial of CED of IL13-PE38QQR vs Gliadel wafers for recurrent glioblastoma. Neuro. Oncol 12, 871–881 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Jain RK Vascular and interstitial barriers to delivery of therapeutic agents in tumors. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 9, 253–266 (1990). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Smith JH & Humphrey JAC Interstitial transport and transvascular fluid exchange during infusion into brain and tumor tissue. Microvasc. Res 73, 58–73 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Gimenez F. et al. Image-guided convection-enhanced delivery of GDNF protein into monkey putamen. Neuroimage 54 (Suppl. 1), 189–195 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Astary GW, Kantorovich S, Carney PR, Mareci TH & Sarntinoranont M. Regional convection-enhanced delivery of gadolinium-labeled albumin in the rat hippocampus in vivo. J. Neurosci. Methods 187, 129–137 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Sampson JH et al. Colocalization of gadolinium-diethylene triamine pentaacetic acid with high-molecular-weight molecules after intracerebral convection-enhanced delivery in humans. Neurosurgery 69, 668–676 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Saito R. et al. Regression of recurrent glioblastoma infiltrating the brainstem after convection-enhanced delivery of nimustine hydrochloride: case report. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr 7, 522–526 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Saito R. et al. Phase I trial of convection-enhanced delivery of nimustine hydrochloride (ACNU) for brainstem recurrent glioma. Neurooncol. Adv 2, vdaa033 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Haar PJ et al. Modelling convection-enhanced delivery in normal and oedematous brain. J. Med. Eng. Technol 38, 76–84 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.White E. et al. An evaluation of the relationships between catheter design and tissue mechanics in achieving high-flow convection-enhanced delivery. J. Neurosci. Methods 199, 87–97 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Westphal M. et al. A phase 3 trial of local chemotherapy with biodegradable carmustine (BCNU) wafers (Gliadel wafers) in patients with primary malignant glioma. Neuro. Oncol 5, 79–88 (2003). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Bregy A. et al. The role of Gliadel wafers in the treatment of high-grade gliomas. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther 13, 1453–1461 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.De Bonis P. et al. Safety and efficacy of Gliadel wafers for newly diagnosed and recurrent glioblastoma. Acta Neurochir. 154, 1371–1378 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Tsai NM et al. The natural compound n-butylidenephthalide derived from Angelica sinensis inhibits malignant brain tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. J. Neurochem 99, 1251–1262 (2006). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Yang D-Y et al. Enhanced antitumor effects of radiotherapy combined local nimustine delivery rendezvousing with oral temozolomide chemotherapy in glioblastoma patients. J. Cancer Res. Ther 14, 78 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Wilson CB Chemotherapy of brain tumors by continuous arterial infusion. Surgery 55, 640–653 (1964). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.D’Amico RS et al. Super selective intra-arterial cerebral infusion of modern chemotherapeutics after blood–brain barrier disruption: where are we now, and where we are going. J. Neurooncol 147, 261–278 (2020). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Karmur BS et al. Blood–brain barrier disruption in neuro-o ncology: strategies, failures, and challenges to overcome. Front. Oncol 10, 563840 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Boockvar JA et al. Safety and maximum tolerated dose of superselective intraarterial cerebral infusion of bevacizumab after osmotic blood-brain barrier disruption for recurrent malignant glioma: clinical article. J. Neurosurg 114, 624–632 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Galla N. et al. Apparent diffusion coefficient changes predict survival after intra-arterial bevacizumab treatment in recurrent glioblastoma. Neuroradiology 59, 499–505 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Shin BJ, Burkhardt J-K, Riina HA & Boockvar JA Superselective intra-arterial cerebral infusion of novel agents after blood–brain disruption for the treatment of recurrent glioblastoma multiforme: a technical case series. Neurosurg. Clin 23, 323–329 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Chakraborty S. et al. Superselective intraarterial cerebral infusion of cetuximab after osmotic blood/brain barrier disruption for recurrent malignant glioma: phase I study. J. Neurooncol 128, 405–415 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Fortin D, Morin PA, Belzile F, Mathieu D. & Paré FM Intraarterial carboplatin as a salvage strategy in the treatment of recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. J. Neurooncol 119, 397–403 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Petr J. et al. Early and late effects of radiochemotherapy on cerebral blood flow in glioblastoma patients measured with non-invasive perfusion MRI. Radiother. Oncol 118, 24–28 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.. Svensson SF et al. MR elastography-based tissue stiffness in glioblastomas is associated with reduced cerebral blood flow. Preprint at medRxiv 10.1101/2021.06.11.21258742 (2021). [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Chow KL et al. Prognostic factors in recurrent glioblastoma multiforme and anaplastic astrocytoma treated with selective intra-arterial chemotherapy. Am. J. Neuroradiol 21, 471–478 (2000). [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Joshi S. et al. Transient cerebral hypoperfusion assisted intraarterial cationic liposome delivery to brain tissue. J. Neurooncol 118, 73–82 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Riina HA et al. Balloon-assisted superselective intra-arterial cerebral infusion of bevacizumab for malignant brainstem glioma: a technical note. Interv. Neuroradiol 16, 71–76 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Jackson CM, Choi J. & Lim M. Mechanisms of immunotherapy resistance: lessons from glioblastoma. Nat. Immunol 20, 1100–1109 (2019). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.McGranahan T, Therkelsen KE, Ahmad S. & Nagpal S. Current state of immunotherapy for treatment of glioblastoma. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol 20, 24 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Weller M. & Le Rhun E. Immunotherapy for glioblastoma: quo vadis? Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol 16, 405–406 (2019). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Chiocca EA, Nassiri F, Wang J, Peruzzi P. & Zadeh G. Viral and other therapies for recurrent glioblastoma: is a 24-month durable response unusual? Neuro. Oncol 21, 14–25 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Auffinger B, Ahmed AU & Lesniak MS Oncolytic virotherapy for malignant glioma: translating laboratory insights into clinical practice. Front. Oncol 3, 32 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Martikainen M. & Essand M. Virus-based immunotherapy of glioblastoma. Cancers 11, 186 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Harsh GR et al. Thymidine kinase activation of ganciclovir in recurrent malignant gliomas: a gene-marking and neuropathological study. J. Neurosurg 92, 804–811 (2000). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Rainov NG et al. Temozolomide enhances herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase/ganciclovir therapy of malignant glioma. Cancer Gene Ther. 8, 662–668 (2001). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Nestler U. et al. The combination of adenoviral HSV TK gene therapy and radiation is effective in athymic mouse glioblastoma xenografts without increasing toxic side effects. J. Neurooncol 67, 177–188 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Wheeler LA et al. Phase II multicenter study of gene-mediated cytotoxic immunotherapy as adjuvant to surgical resection for newly diagnosed malignant glioma. Neuro. Oncol 18, 1137–1145 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Ji N. et al. Adenovirus-mediated delivery of herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase administration improves outcome of recurrent high-grade glioma. Oncotarget 7, 4369–4378 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Chiocca EA et al. Regulatable interleukin-12 gene therapy in patients with recurrent high-grade glioma: results of a phase 1 trial. Sci. Transl Med 11, eaaw5680 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Trinchieri G. Interleukin-12 and the regulation of innate resistance and adaptive immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol 3, 133–146 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Zhang L. et al. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes genetically engineered with an inducible gene encoding interleukin-12 for the immunotherapy of metastatic melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res 21, 2278–2288 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Car BD, Eng VM, Lipman JM & Anderson TD The toxicology of interleukin-12: a review. Toxicol. Pathol 27, 58–63 (1999). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Cai H. et al. Plasma pharmacokinetics of veledimex, a small-molecule activator ligand for a proprietary gene therapy promoter system, in healthy subjects. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev 6, 246–257 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Ostertag D. et al. Brain tumor eradication and prolonged survival from intratumoral conversion of 5-fluorocytosine to 5-fluorouracil using a nonlytic retroviral replicating vector. Neuro Oncol. 14, 145–159 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Cloughesy TF et al. Phase 1 trial of vocimagene amiretrorepvec and 5-fluorocytosine for recurrent high-grade glioma. Sci. Transl Med 8, 341ra75 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Desjardins A. et al. Recurrent glioblastoma treated with recombinant poliovirus. N. Engl. J. Med 379, 150–161 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Brown MC et al. Cancer immunotherapy with recombinant poliovirus induces IFN-dominant activation of dendritic cells and tumor antigen-specific CTLs. Sci. Transl Med 9, eaan4220 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Lang FF et al. Phase I study of DNX-2401 (delta-24-RGD) oncolytic adenovirus: replication and immunotherapeutic effects in recurrent malignant glioma. J. Clin. Oncol 36, 1419–1427 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Maher EA et al. Malignant glioma: genetics and biology of a grave matter. Genes Dev. 15, 1311–1333 (2001). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Fueyo J. et al. Preclinical characterization of the antiglioma activity of a tropism-enhanced adenovirus targeted to the retinoblastoma pathway. J. Natl Cancer Inst 95, 652–660 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Mineta T, Rabkin SD, Yazaki T, Hunter WD & Martuza RL Attenuated multi-mutated herpes simplex virus-1 for the treatment of malignant gliomas. Nat. Med 1, 938–943 (1995). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Markert JM et al. A phase 1 trial of oncolytic HSV-1, G207, given in combination with radiation for recurrent GBM demonstrates safety and radiographic responses. Mol. Ther 22, 1048–1055 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Friedman GK et al. Enhanced sensitivity of patient-derived pediatric high-grade brain tumor xenografts to oncolytic HSV-1 virotherapy correlates with nectin-1 expression. Sci. Rep 8, 13930 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Friedman GK et al. Oncolytic HSV-1 G207 immunovirotherapy for pediatric high-grade gliomas. N. Engl. J. Med 384, 1613–1622 (2021). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Liu EK, Yu S, Sulman EP & Kurz SC Racial and socioeconomic disparities differentially affect overall and cause-specific survival in glioblastoma. J. Neurooncol 149, 55–64 (2020). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Rainov NG A phase III clinical evaluation of herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase and ganciclovir gene therapy as an adjuvant to surgical resection and radiation in adults with previously untreated glioblastoma multiforme. Hum. Gene Ther 11, 2389–2401 (2000). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Kawakami M, Kawakami K. & Puri RK Intratumor administration of interleukin 13 receptor-targeted cytotoxin induces apoptotic cell death in human malignant glioma tumor xenografts. Mol. Cancer Ther 1, 999–1007 (2002). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Krieg AM Antitumor applications of stimulating Toll-like receptor 9 with CpG oligodeoxynucleotides. Curr. Oncol. Rep 6, 88–95 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Meng Y. et al. Expression of TLR9 within human glioblastoma. J. Neurooncol 88, 19–25 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Andaloussi SEL, Mäger I, Breakefield XO & Wood MJ Extracellular vesicles: biology and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov 12, 347–357 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Carpentier A. et al. Intracerebral administration of CpG oligonucleotide for patients with recurrent glioblastoma: a phase II study. Neuro. Oncol 12, 401–408 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Ursu R. et al. Intracerebral injection of CpG oligonucleotide for patients with de novo glioblastoma–a phase II multicentric, randomised study. Eur. J. Cancer 73, 30–37 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Nduom EK, Weller M. & Heimberger AB Immunosuppressive mechanisms in glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 17 (Suppl. 7), vii9–vii14 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Mann J, Ramakrishna R, Magge R. & Wernicke AG Advances in radiotherapy for glioblastoma. Front. Neurol 8, 748 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Barbarite E. et al. The role of brachytherapy in the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. Neurosurg. Rev 40, 195–211 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Bartek J. et al. Receipt of brachytherapy is an independent predictor of survival in glioblastoma in the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database. J. Neurooncol 145, 75–83 (2019). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Field KM et al. Clinical trial participation and outcome for patients with glioblastoma: multivariate analysis from a comprehensive dataset. J. Clin. Neurosci 20, 783–789 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Skaga E. et al. Real-world validity of randomized controlled phase III trials in newly diagnosed glioblastoma: to whom do the results of the trials apply? Neurooncol. Adv 3, vdab008 (2021). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Schwartz C. et al. Outcome and toxicity profile of salvage low-dose-rate iodine-125 stereotactic brachytherapy in recurrent high-grade gliomas. Acta Neurochir. 157, 1757–1764 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Kickingereder P. et al. Low-dose rate stereotactic iodine-125 brachytherapy for the treatment of inoperable primary and recurrent glioblastoma: single-center experience with 201 cases. J. Neurooncol 120, 615–623 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Phillips WT et al. Rhenium-186 liposomes as convection-enhanced nanoparticle brachytherapy for treatment of glioblastoma. Neuro. Oncol 14, 416–425 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Pilar A, Gupta M, Ghosh Laskar S. & Laskar S. Intraoperative radiotherapy: review of techniques and results. Ecancermedicalscience 11, 750 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Sarria GR et al. Intraoperative radiotherapy for glioblastoma: an international pooled analysis. Radiother. Oncol 142, 162–167 (2020). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Aboody KS et al. Neural stem cell-mediated enzyme/prodrug therapy for glioma: preclinical studies. Sci. Transl Med 5, 184ra59 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Pacioni S. et al. Human mesenchymal stromal cells inhibit tumor growth in orthotopic glioblastoma xenografts. Stem Cell Res. Ther 8, 53 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Portnow J. et al. Neural stem cell-based anticancer gene therapy: a first-in-human study in recurrent high-grade glioma patients. Clin. Cancer Res 23, 2951–2960 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Kim SU Human neural stem cells genetically modified for brain repair in neurological disorders. Neuropathology 24, 159–171 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Fares J. et al. Neural stem cell delivery of an oncolytic adenovirus in newly diagnosed malignant glioma: a first-in-human, phase 1, dose-escalation trial. Lancet Oncol. 22, 1103–1114 (2021). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Ahmed AU et al. A preclinical evaluation of neural stem cell-based cell carrier for targeted antiglioma oncolytic virotherapy. J. Natl Cancer Inst 105, 968–977 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Salinas RD, Durgin JS & O’Rourke DM Potential of glioblastoma-targeted chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-c ell therapy. CNS Drugs 34, 127–145 (2020). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Brown CE et al. Regression of glioblastoma after chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy. N. Engl. J. Med 375, 2561–2569 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Spaeth E, Klopp A, Dembinski J, Andreeff M. & Marini F. Inflammation and tumor microenvironments: defining the migratory itinerary of mesenchymal stem cells. Gene Ther. 15, 730–738 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Choi SH et al. Tumor resection recruits effector T cells and boosts therapeutic efficacy of encapsulated stem cells expressing IFNβ in glioblastomas. Clin. Cancer Res 23, 7047–7058 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Alayo QA et al. Glioblastoma infiltration of both tumor-and virus-antigen specific cytotoxic T cells correlates with experimental virotherapy responses. Sci. Rep 10, 5095 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Neftel C. et al. An integrative model of cellular states, plasticity, and genetics for glioblastoma. Cell 178, 835–849.e21 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Felsberg J. et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor variant III (EGFRvIII) positivity in EGFR-amplified glioblastomas: prognostic role and comparison between primary and recurrent tumors. Clin. Cancer Res 23, 6846–6855 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Chongsathidkiet P. et al. Sequestration of T cells in bone marrow in the setting of glioblastoma and other intracranial tumors. Nat. Med 24, 1459–1468 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Cloughesy TF et al. Neoadjuvant anti-PD-1 immunotherapy promotes a survival benefit with intratumoral and systemic immune responses in recurrent glioblastoma. Nat. Med 25, 477–486 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Chen AM et al. Phase I trial of gross total resection, permanent iodine-125 brachytherapy, and hyperfractionated radiotherapy for newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys 69, 825–830 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Cabrera AR et al. Radiation therapy for glioblastoma: executive summary of an American Society for Radiation Oncology evidence-based clinical practice guideline. Pract. Radiat. Oncol 6, 217–225 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Puente Pdela et al. Injectable hydrogels for localized chemotherapy and radiotherapy in brain tumors. J. Pharm. Sci 107, 922–933 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Chen PY et al. Comparing routes of delivery for nanoliposomal irinotecan shows superior anti-tumor activity of local administration in treating intracranial glioblastoma xenografts. Neuro Oncol. 15, 189–197 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Floyd JA, Galperin A. & Ratner BD Drug encapsulated polymeric microspheres for intracranial tumor therapy: a review of the literature. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev 91, 23–37 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Hernán Pérez de la Ossa D et al. Local delivery of cannabinoid-loaded microparticles inhibits tumor growth in a murine xenograft model of glioblastoma multiforme. PLoS ONE 8, 2–9 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Mehta N. et al. Bacterial carriers for glioblastoma therapy. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 4, 1–17 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Cohen ZR et al. Localized RNAi therapeutics of chemoresistant grade IV glioma using hyaluronan-grafted lipid-based nanoparticles. ACS Nano 9, 1581–1591 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Sharabi S. et al. The application of point source electroporation and chemotherapy for the treatment of glioma: a randomized controlled rat study. Sci. Rep 10, 2178 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Giuliano AR et al. Participation of minorities in cancer research: the influence of structural, cultural, and linguistic factors. Ann. Epidemiol 10, S22–S34 (2000). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Pitter KL et al. Corticosteroids compromise survival in glioblastoma. Brain 139, 1458–1471 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Gorlia T. et al. New prognostic factors and calculators for outcome prediction in patients with recurrent glioblastoma: a pooled analysis of EORTC Brain Tumour Group phase I and II clinical trials. Eur. J. Cancer 48, 1176–1184 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.