Abstract
The main purpose of this bibliometric analysis is to conduct a quantitative and qualitative analysis of the publications on dental caries. Research productivity can be measured with the use of bibliometric analysis. In this study, we conducted a bibliometric analysis using the Scopus database to identify dental caries research trends and patterns over the years. The search yielded 1630 scientific articles. The data was analysed using bibliometric indicators such as the h-index, the total number of citations and the number of publications. An analysis of the data highlighted that the United States of America (USA) and Brazil have the highest number of single-country publications. Top authors were listed based on the h-index and the total number of citations. Top cited countries, institutions etc. were also analysed using this bibliometric study. This bibliometric evaluation provides a wide area of literature carried out to date. The existing knowledge can be used to direct future research.
Keywords: dental caries, risk factors, etiology, dentistry, h index
Introduction and background
Dental caries, also known as cavities or tooth decay, is a significant public health issue affecting individuals of all ages worldwide. Despite the widespread availability of preventive measures, the prevalence of dental caries remains high in many populations [1]. To address this challenge, a current understanding of the dental caries knowledge that exists, including the risk factors, preventive strategies, and management is paramount. Bibliometrics is a method for quantitatively analysing the literature in a specific field, such as dental caries, and providing valuable insights into the distribution, frequency, and patterns of research activities. Bibliometric studies can help identify the most productive authors, institutions and countries, as well as reveal trends and gaps in the research landscape.
This bibliometric analysis of the scientific literature on dental caries aimed to provide a comprehensive overview of the current knowledge and research trends in this field. The study encompassed an extensive literature search and analysis of relevant studies published in the past decade that covered various aspects of dental caries including its aetiology, risk factors, prevention and management. The findings of this bibliometric analysis may provide valuable insights into the current state of knowledge about dental caries including critical public health issues and highlight areas for future research. The findings of the study may be used as a valuable resource for researchers, practitioners, and policy-makers in dental health.
Review
Methodology
Bibliometric analysis is a valuable tool for identifying trends and patterns in research. Briefly, it involved the quantitative analysis of publication data. Insights, such as productivity, impact, and the collaborative networks of researchers and institutions were extracted. In this study, the Scopus database was used to identify the trends and patterns in dental caries research over the years.
Data extraction
We conducted a comprehensive search of the Scopus database using relevant keywords, such as "dental caries, tooth decay", “dental caries epidemiology", "dental caries prevention" and "dental caries treatment." The search was limited to published articles, reviews, and conference papers. The search yielded 1630 scientific articles.
Data analysis
The data was analysed using bibliometric indicators, such as the h-index, the total number of citations and the number of publications. The data was also visualised using VOSviewer and Biblioshiny, with the help of R-studio software (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria).
Results
Most Cited Local Documents
The identified articles were analysed to determine the top eight locally cited articles. The top eight articles are listed below (Table 1). According to the citation criteria, Lussi (1999) [2] has the highest number of citations compared to the other articles. Lussi, published in the journal Caries Research, has been cited approximately 115 times (Table 1).
Table 1. Most locally cited documents .
| Authors | Citations | Year | Title | Journal |
| Lussi A [2] | 115 | 1999 | Performance and reproducibility of a laser fluorescence system for detection of occlusal caries in vitro. | Caries Research |
| Lussi A [3] | 95 | 2001 | Clinical performance of a laser fluorescence device for detection of occlusal caries lesions. | European Journal of Oral Sciences |
| Bader JD [4] | 89 | 2004 | A systematic review of the performance of a laser fluorescence device for detecting caries. | The Journal of the American Dental Association |
| Jablonski-Momeni A [5] | 86 | 2008 | Reproducibility and accuracy of the ICDAS-II for detection of occlusal caries in vitro. | Caries Research |
| Shi X-Q [6] | 81 | 2000 | Occlusal caries detection with KaVo DIAGNOdent and radiography: an in vitro comparison. | Caries Research |
| Ekstrand KR [7] | 71 | 2007 | Detection and activity assessment of primary coronal caries lesions: a methodologic study. | Operative Dentistry |
| Lussi A [8] | 60 | 2004 | DIAGNOdent: an optical method for caries detection. | Journal of Dental Research |
| Ekstrand KR [9] | 60 | 1998 | Detection, diagnosing, monitoring and logical treatment of occlusal caries in relation to lesion activity and severity: an in vivo examination with histological validation. | Caries Research |
Most Cited Global Documents
Based on the global citation criteria, the identified articles were analysed to determine the top eight global-cited articles. The result highlighted that Ismail (2007) [10], published in Community Dentistry and Oral Epidemiology, has the highest number of citations, with approximately 831 citations (Table 2).
Table 2. Most globally cited documents .
| Author | Citations | Year | Title | Journal |
| Ismail AI [10] | 831 | 2007 | The international caries detection and assessment system (ICDAS): an integrated system for measuring dental caries. | Community Dentistry and Oral Epidemiology |
| Pinheiro ET [11] | 375 | 2003 | Microorganisms from canals of root-filled teeth with periapical lesions. | International Endodontic Journal |
| Lussi A [2] | 349 | 1999 | Performance and reproducibility of a laser fluorescence system for detection of occlusal caries in vitro. | Caries Research |
| Pitts N [12] | 315 | 2004 | The dental caries experience of 14-year-old children in England and Wales. Surveys co-ordinated by the British Association for the Study of Community Dentistry in 2002/2003. | Community Dental Health |
| Lussi A [3] | 289 | 2001 | Clinical performance of a laser fluorescence device for detection of occlusal caries lesions. | European Journal of Oral Sciences |
| Lee JH [13] | 287 | 2018 | Detection and diagnosis of dental caries using a deep learning-based convolutional neural network algorithm. | Journal of Dentistry |
| Shi X-Q [6] | 261 | 2000 | Occlusal caries detection with KaVo DIAGNOdent and radiography: an in vitro comparison. | Caries Research |
| Frencken JE [14] | 251 | 2012 | Minimal intervention dentistry for managing dental caries – a review: report of a FDI task group. | International Dental Journal |
Top Cited Countries
The top cited articles were analysed using Biblioshiny based on the countries affiliated with the published studies. The United States was involved in the most dental caries research studies compared with the rest of the world, with a massive 7511 citations. This was followed by the United Kingdom with 3703 citations and Brazil with 3686. Australia ranked 10th, with only 15 cited articles (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Most cited countries .
Institutions With the Most Relevant Articles
Based on the bibliometric analysis, the top 10 universities with the most relevant articles on dental caries were listed. The University of São Paulo published the highest number of articles on dental caries (a total of 178 articles), followed by the University of Bern in the second position with 86 articles and Indiana University in the third position with 75 articles (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Institutions with the most relevant articles .
Keyword Analysis
The top 10 most relevant keywords were evaluated. The most frequently used keyword was “Dental caries” with an occurrence of 2603. Other frequently mentioned keywords included “humans” with 1492 occurrences. The other most relevant keywords are listed in Figure 3.
Figure 3. Most relevant keywords .
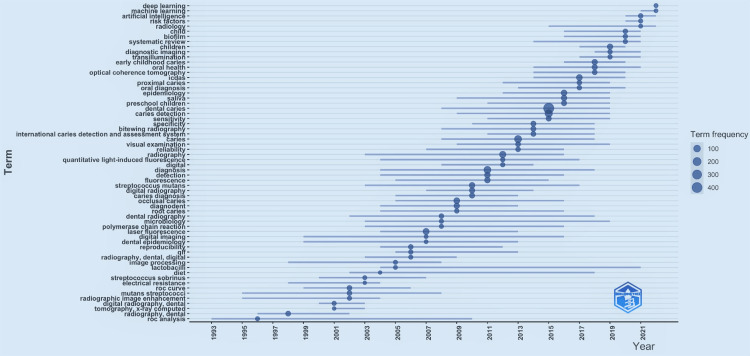
Trending Topics Over Time
From the time research started on the detection of dental caries till the middle of the 1990s, terms such as receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis were the most trended topics. In the early 2000s, the most trended topics were “tomography” and “x-ray computer”. After 2020, the top trending topics were “artificial intelligence”, “machine learning” and “deep learning”. These topics are also the presently trending topics related to dental caries. All the trending topics are listed in Figure 4.
Figure 4. Trending topics over time .
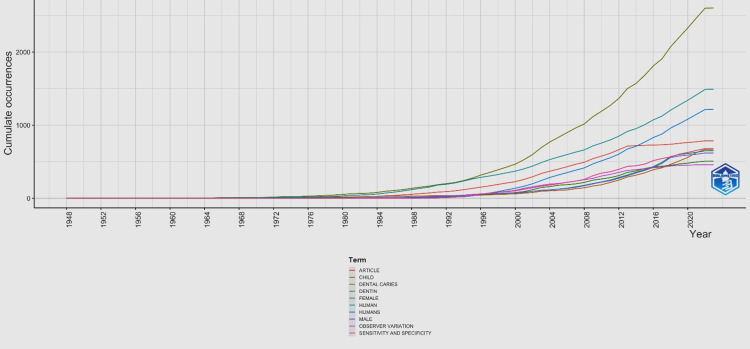
Frequency of Words Used Over Time
The top 10 most frequently used words related to dental caries are listed in Figure 5. Most of these words have started to peak. The most frequent terms used after 1988 included “dentin”, which has gradually reached the highest position over recent years, with a cumulative occurrence of over 2000. In recent years after 2020, other words were also mentioned as shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5. Frequency of words used over time .
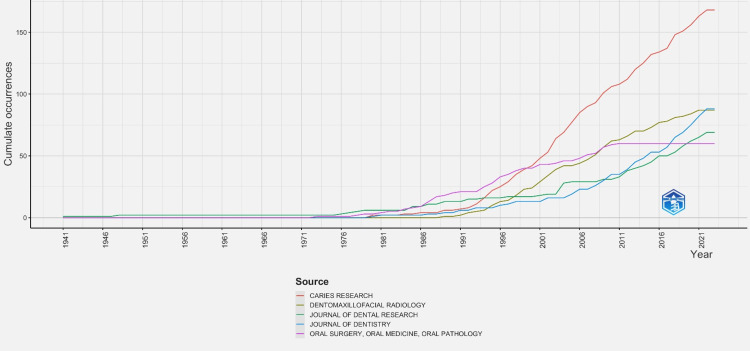
Journals Production Over Time
The top five journals that published dental caries research over time are listed in Figure 6.
Figure 6. Sources production over time .
On close examination of the analysed data, there were no journals with dental caries publications over time before the year 1975. From 1995 to 2000, there was a close competition between the top five journals. In more recent years, caries research journals have significantly impacted dental caries research, with a massive cumulative occurrence of more than 150 publications.
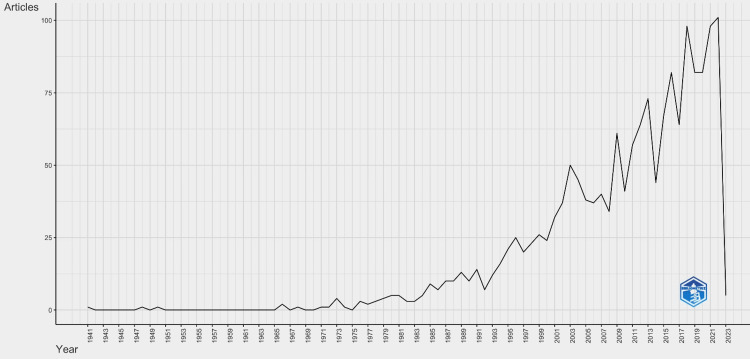
Annual Scientific Production
On analysing the data over time, the top five highest numbers of articles published in a particular year are listed in Table 3. The highest number of articles published among all journals occurred in 2022, with a massive number of 101 dental caries publications (Figure 7).
Table 3. The top five highest numbers of articles published in a particular year .
| Year | Total no of dental caries articles published in that year |
| 2022 | 101 |
| 2021,2018 | 98 |
| 2020,2019,2016 | 82 |
| 2013 | 73 |
| 2017& 2012 | 64 |
Figure 7. Annual scientific production .
H-index
The h-index, or Hirsch index, measures the impact of a particular scientist rather than a journal. The h-index is “defined as the highest number of publications of a scientist that received h or more citations each while the other publications have not more than h citations each” [15]. Based on the data analysis, the top five authors with the highest h-index were identified (Table 4). The top 10 authors based on the h-index are listed in Figure 8.
Table 4. Top five authors with highest h-index .
| AUTHOR NAME | H-INDEX |
| WENZEL A | 28 |
| LUSSI A | 23 |
| EKSTRAND KR | 21 |
| PITTS NB | 21 |
| MENDES FM | 19 |
Figure 8. Top 10 authors based on h-index .
Discussion
This bibliometric analysis is the first of its kind. It aimed to identify and quantitatively evaluate scientific research articles on dental caries detection methods. An analysis of the data highlighted that the United States of America and Brazil have the highest number of single-country publications (Figure 9).
Figure 9. Corresponding authors and their affiliated countries .
The citations are seen in Figure 1. This was attributed to the finding that the majority of publications were from the University of São Paulo in Brazil and Indiana University in the USA (Figure 2).
The two top highly cited authors globally (Table 2), namely, Ismail [10] and Pinheiro [11], were affiliated with the University of Michigan (USA) and the State University of Campinas, Brazil, respectively. Interestingly, the majority of the top 10 journals on dental caries belong to the United Kingdom, the USA, or Switzerland. This indicates that developed countries make significant contributions to this field of research.
Although in recent years, journals such as Caries Research have published more than 150 articles (Figure 6) and these can be correlated with the top eight locally cited publications (Table 1). For example, articles were published by authors, such as Lussi et al. 1999 [2], Jablonski Momeni et al. 2008 [5], and Shi et al. 2000 [6]. Moreover, among the top eight globally cited publications (Table 2), articles included those written by Lussi et al. 1999 [2] and Shi et al. 2000 [6]. Hence, caries research journals significantly contribute to the publication of dental caries research. It was also found that among the top eight globally cited articles (Table 2), Lussi et al. had multiple publications in the years 1999, [2] 2001 [3] and 2004 [8]. The authors were affiliated with the University of Bern, which ranked second among the top 10 universities with most relevant dental caries research articles (Figure 2). This shows that the authors made a significant contribution to their university’s research output.
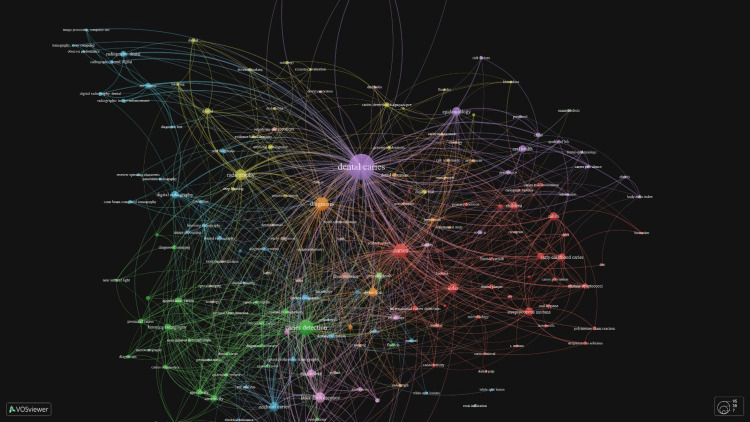
Keyword co-occurrence was also analysed. It is said that keywords with the relevance rate are closer the keywords to each other [16]. Our findings determined that the keywords, “dental caries”, “human”, “humans”, and “articles” had the highest co-occurrence (Figure 10).
Figure 10. Keywords with the most co-occurrence .
Co-occurrence of Author Keywords
The incidence of co-occurrence of author keywords was investigated and it was considered in terms of the relationship between their research. "DENTAL CARIES”, “CARIES DETECTION”, “CARIES” and “DIAGNOSIS & RADIOGRAPHY" were the most frequently co-occurring terms (Figure 11).
Figure 11. Image obtained from the vos-viewer denotes the co-occurrence of author keywords of different domains .
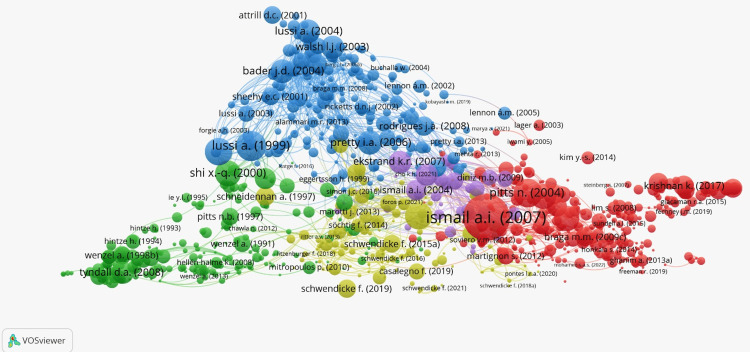
Author Bibliographic Coupling
Author bibliographic coupling is an extension of bibliographic coupling, and refers to the phenomenon when two authors cite the same article(s) in their publications [17]. For example, an article published by Ismail (2007) [10] dominated the author bibliographic coupling, as seen in Figure 12.
Figure 12. Author Bibliographic Coupling.
Advancements
In recent years, there have been significant advancements in caries treatment through research. These improvements have aimed to provide more effective, minimally invasive, and patient-friendly approaches to managing dental caries. Here are some notable advancements:
Early detection techniques: Research has focused on developing more accurate and efficient methods to detect caries at their earliest stages. Technologies like laser fluorescence, digital imaging, and fluorescence-based diagnostic tools have improved the detection of hidden and early caries lesions, enabling timely intervention.
Remineralization therapies: Researchers have explored various remineralization strategies to reverse early-stage caries. The development of remineralizing agents containing calcium, phosphate, and fluoride ions, as well as bioactive materials like casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate (CPP-ACP), has shown promising results in promoting remineralization and halting the progression of caries.
Minimal intervention techniques: The concept of minimal intervention dentistry has gained traction, aiming to preserve as much healthy tooth structure as possible. Advances in adhesive technologies and dental materials have facilitated minimally invasive approaches such as micro-invasive and non-invasive techniques, including resin infiltration, sealing of occlusal surfaces, and selective removal of carious tissue.
Antibacterial agents: Research has focused on developing effective antibacterial agents that can selectively target cariogenic bacteria while preserving the natural oral microbiota. Innovations include antimicrobial peptides, nanoparticles, and photodynamic therapy, which show promise in reducing cariogenic bacteria and preventing caries progression.
Biomaterials for restoration: Researchers have explored novel biomaterials to improve the longevity and performance of dental restorations. Advances in resin-based composites, glass ionomer cements, and bioactive materials have resulted in improved aesthetic properties, enhanced bonding strength, and increased resistance to wear and secondary caries.
Regenerative approaches: Regenerative dentistry aims to promote the regeneration of damaged dental tissues. Researchers are investigating techniques such as tissue engineering, stem cell therapy, and growth factors to facilitate the regeneration of dentin, enamel, and the pulp-dentin complex, which could potentially lead to non-invasive or less invasive treatments for caries.
Digital dentistry: Technological advancements in digital dentistry have revolutionized caries treatment planning and restoration procedures. Digital imaging, computer-aided design and manufacturing (CAD/CAM), and 3D printing enable precise and efficient restoration fabrication, resulting in better-fitting restorations with reduced chairside time.
These advancements in caries treatment through research offer promising possibilities for improved prevention, detection, and management of dental caries. However, it's important to note that while research is advancing, regular dental check-ups, proper oral hygiene practices, and a healthy diet remain crucial in preventing caries.
Limitations
One of the limitations of this bibliometric analysis is using a single Scopus database. However, the journals in the Scopus database are audited annually to ensure they adhere to higher standards. It is the largest abstract and citation database of peer-reviewed scientific journals, books and conference proceedings. The Scopus database was therefore used in the current study to retrieve data and analyze using software.
Conclusions
The findings of this review indicated a development in detection of dental caries literature over eight decades. A lack of well-designed clinical research persists involving substances like liquid crystalline systems, polymer-based nanoparticles, lipid-based nanoparticles and inorganic nanoparticles. These lacunae lay the groundwork for future research improvements in the field of dental caries management.
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
References
- 1.Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2017;390:1211–1259. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32154-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Performance and reproducibility of a laser fluorescence system for detection of occlusal caries in vitro. Lussi A, Imwinkelried S, Pitts N, Longbottom C, Reich E. Caries Res. 1999;33:261–266. doi: 10.1159/000016527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Clinical performance of a laser fluorescence device for detection of occlusal caries lesions. Lussi A, Megert B, Longbottom C, Reich E, Francescut P. Eur J Oral Sci. 2001;109:14–19. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0722.2001.109001014.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.A systematic review of the performance of a laser fluorescence device for detecting caries. Bader JD, Shugars DA. J Am Dent Assoc. 2004;135:1413–1426. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.2004.0051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Reproducibility and accuracy of the ICDAS-II for detection of occlusal caries in vitro. Jablonski-Momeni A, Stachniss V, Ricketts DN, Heinzel-Gutenbrunner M, Pieper K. Caries Res. 2008;42:79–87. doi: 10.1159/000113160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Occlusal caries detection with KaVo DIAGNOdent and radiography: an in vitro comparison. Shi XQ, Welander U, Angmar-Månsson B. https://doi.org/10.1159/000016583. Caries Res. 2000;34:151–158. doi: 10.1159/000016583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Detection and activity assessment of primary coronal caries lesions: a methodologic study. Ekstrand KR, Martignon S, Ricketts DJ, Qvist V. Oper Dent. 2007;32:225–235. doi: 10.2341/06-63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.DIAGNOdent: an optical method for caries detection. Lussi A, Hibst R, Paulus R. J Dent Res. 2004;83 Spec No C:0–3. doi: 10.1177/154405910408301s16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Detection, diagnosing, monitoring and logical treatment of occlusal caries in relation to lesion activity and severity: an in vivo examination with histological validation. Ekstrand KR, Ricketts DN, Kidd EA, Qvist V, Schou S. Caries Res. 1998;32:247–254. doi: 10.1159/000016460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.The International Caries Detection and Assessment System (ICDAS): an integrated system for measuring dental caries. Ismail AI, Sohn W, Tellez M, Amaya A, Sen A, Hasson H, Pitts NB. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0528.2007.00347.x. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2007;35:170–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0528.2007.00347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Microorganisms from canals of root-filled teeth with periapical lesions. Pinheiro ET, Gomes BP, Ferraz CC, Sousa EL, Teixeira FB, Souza-Filho FJ. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2591.2003.00603.x. Int Endod J. 2003;36:1–11. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2591.2003.00603.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.The dental caries experience of 14-year-old children in England and Wales. Surveys co-ordinated by the British Association for the Study of Community Dentistry in 2002/2003. Pitts NB, Boyles J, Nugent ZJ, Thomas N, Pine CM. https://www.unboundmedicine.com/medline/citation/15074872/The_dental_caries_experience_of_14_year_old_children_in_England_and_Wales__Surveys_co_ordinated_by_the_British_Association_for_the_Study_of_Community_Dentistry_in_2002/2003_. Caries Res. 2004;21:45–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Detection and diagnosis of dental caries using a deep learning-based convolutional neural network algorithm. Lee JH, Kim DH, Jeong SN, Choi SH. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdent.2018.07.015. J Dent. 2018;77:106–111. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2018.07.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Minimal intervention dentistry for managing dental caries - a review: report of a FDI task group. Frencken JE, Peters MC, Manton DJ, Leal SC, Gordan VV, Eden E. https://doi.org/10.1111/idj.12007. Int Dent J. 2012;62:223–243. doi: 10.1111/idj.12007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.An empirical investigation of the g-index for 26 physicists in comparison with the h-index, the A-index, and the R-index. Schreiber M. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/asi.20856 J Am Soc Inf Sci Technol. 2008;59:1513. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Visualizing the context of citations referencing papers published by Eugene Garfield: a new type of keyword co-occurrence analysis. Bornmann L, Haunschild R, Hug SE. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-017-2591-8. Scientometrics. 2018;114:427–437. doi: 10.1007/s11192-017-2591-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Author bibliographic coupling analysis: a test based on a Chinese academic database. Ruimin MA. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2012.04.006 J Informetr. 2012;6:532–542. [Google Scholar]