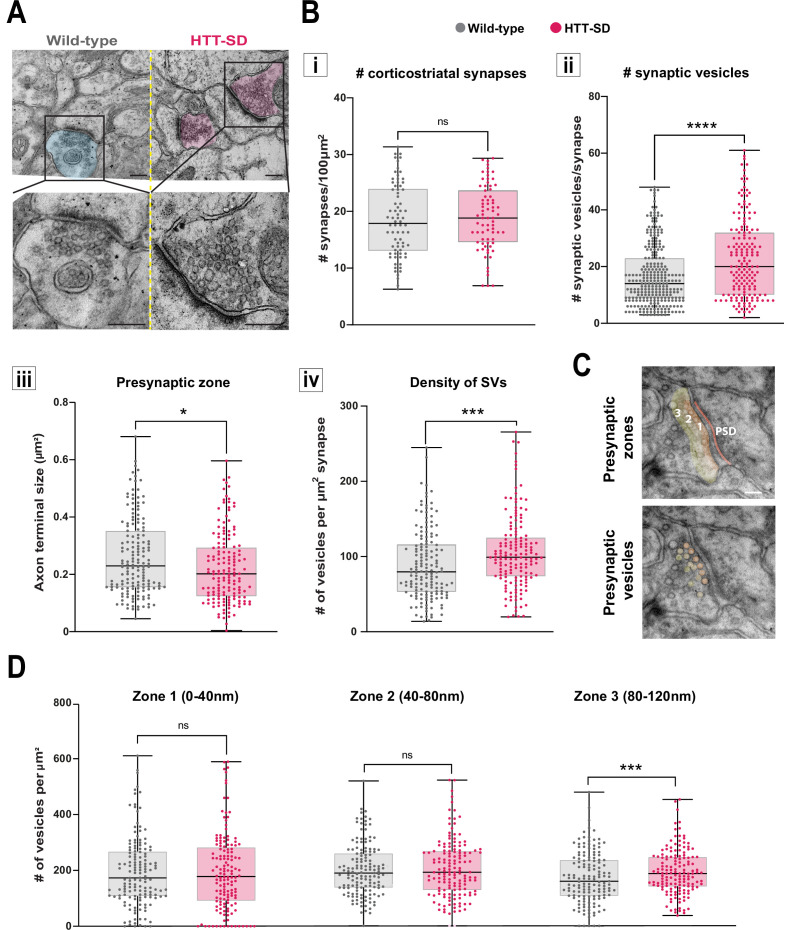
Figure 4. HTT phosphorylation increases the number of synaptic vesicles (SVs) distally to the presynaptic active zone.
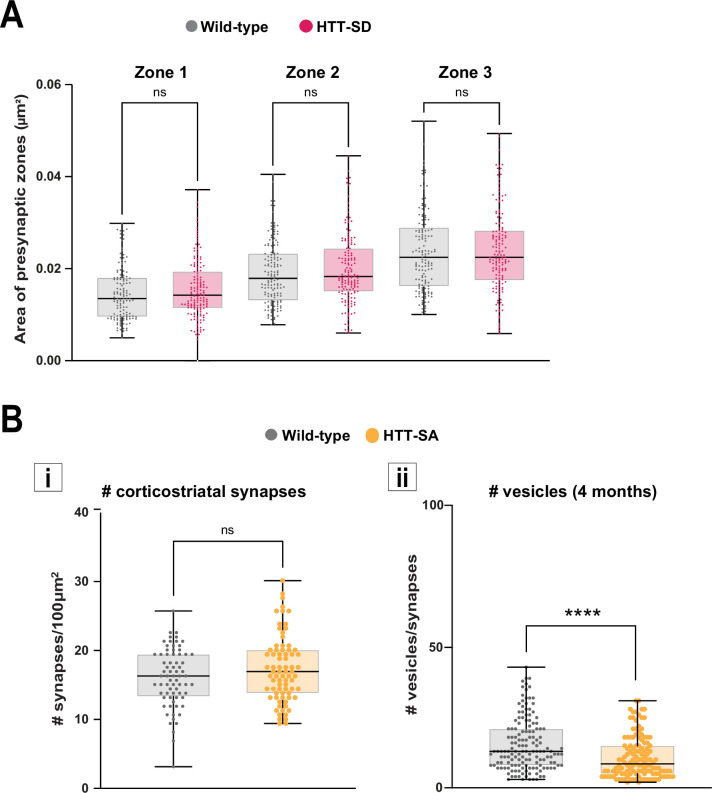
(A) Representative images of SVs at the corticostriatal synapse, obtained by electronic microscopy, in dorsolateral striatum (DLS) slices from three wild-type (WT) and HTT-SD mice 3-month-old male. Scale = 200 nm. (B) Quantification of (i) the number of synapses at the corticostriatal synapse per 100 µm2 in DLS on n=74 WT and 74 HTT-SD striatal areas (ns: non-significant), (ii) the number of SVs per corticostriatal synapse from five WT and three HTT-SD mouse brains (N=279 WT and 171 HTT-SD axon terminals; ****p<0.0001), (iii) size of the cortical axon terminal in 158 WT and 156 HTT-SD corticostriatal synapses (*p<0.05), and (iv) the density of SVs within these axon terminals (number of vesicles per μm2) in N=157 WT and 162 HTT-SD corticostriatal synapses (***p<0.001). (C) Representative images showing the 40-nm-wide zones in the axon terminal. Zone 1 is the closest to the synaptic cleft and contains the active zone. Zone 2 (40–80 nm) is adjacent to zone 1, and zone 3 (80–120 nm) is farthest from the active zone. Dark orange denotes the PSD within the striatal postsynaptic element. Scale = 100 nm. (D) The number of SVs per zone within the distal 120 nm of the axon terminal in at least 149±2 axon terminals (ns: non-significant, *p<0.05). The box-whisker plots show the median, the 25th and the 75th percentiles, the smallest and the largest value from at least three brains for each condition. Significances were determined using the Mann-Whitney test.