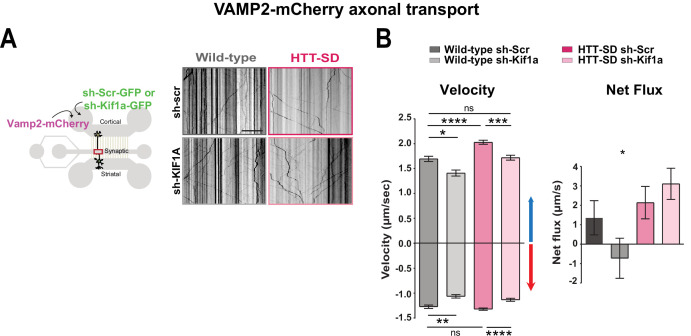
Figure 6. HTT-dependent axonal transport of synaptic vesicle precursors (SVPs) is mediated by KIF1A.
(A) Diagram indicating lentiviral transduction of VAMP2-mCherry and sh-scramble (sh-Scr-GFP) or sh-Kif1a (sh-Kif1a-GFP) lentiviruses at day in vitro (DIV) 8 in the microfluidic device. On the right, representative kymographs of VAMP2-mCherry vesicle transport in axons for each condition. Scale bar = 25 µm. (B) Segmental anterograde and retrograde velocities (anterograde: *p<0.05, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001; N=548 vesicles wild-type [WT] sh-Scr, 318 vesicles WT sh-Kif1a, 1129 vesicles HTT-SD sh-Scr, 628 vesicles HTT-SD sh-Kif1a) (retrograde: *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001; N=583 vesicles WT sh-Scr, 396 vesicles WT sh-Kif1a, 1282 vesicles HTT-SD sh-Scr, 620 vesicles HTT-SD sh-Kif1a) and directional net flux (*p<0.01; N=79 axons WT sh-Scr, 59 axons WT sh-KIFA,112 axons HTT-SD sh-Scr, 89 axons HTT-SD sh-Kif1a; one-way ANOVA test) of VAMP2-mCherry vesicles in WT and HTT-SD neurons transduced with sh-Scr or sh-Kif1a lentiviruses. Histograms represent means ± SEM of three independent experiments. Significance was determined using a one-way ANOVA followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test.