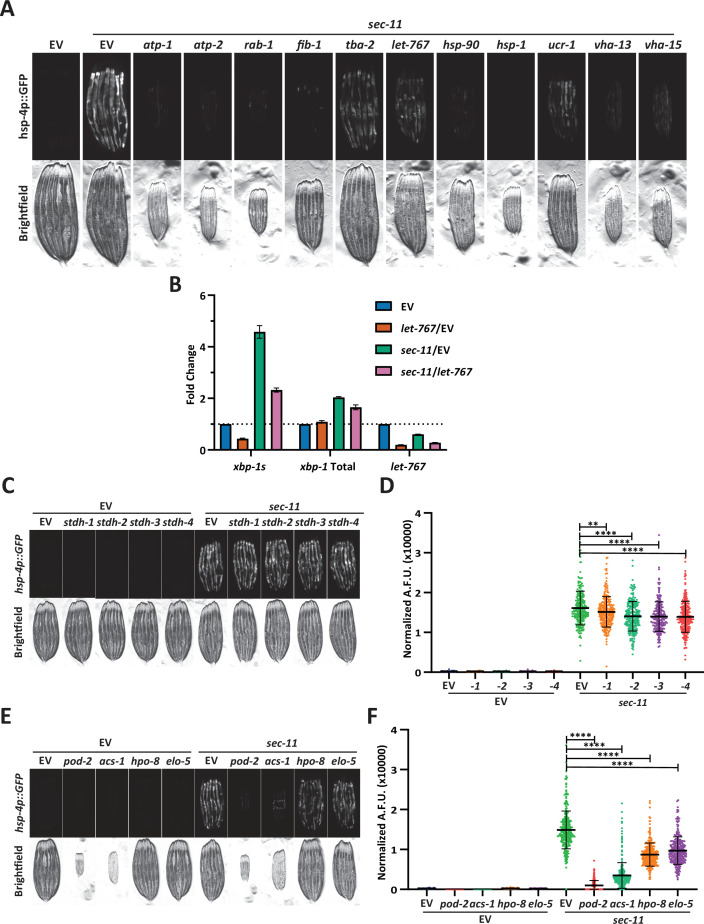
Figure 1. Knockdown of let-767 specifically suppresses the UPRER.
(A) Schematic for screening method used to identify UPRER modulators from candidate genes. Animals expressing hsp-4p::GFP were grown from L1 on candidate RNAi mixed in a 1:1 Ratio with ER stress inducing sec-11 RNAi. Animals were then screened at day 1 of adulthood and scored for changes in fluorescence compared to the sec-11/Empty Vector (EV) control. (B) Fluorescent micrographs of day 1 adult transgenic animals expressing hsp-4p::GFP grown from L1 on EV, sec-11, or tag-335 RNAi combined in a 1:1 ratio with either EV or let-767 RNAi to assay effects on UPRER induction. (C) Quantification of (B) normalized to size using a BioSorter. Lines represent mean and standard deviation. n=500. Mann-Whitney test p-value ****<0.0001. Representative data shown is one of three biological replicates. (D) Fluorescent micrographs of day 1 adult transgenic animals expressing hsp-16.2p::GFP grown from L1 on EV or let-767 RNAi with or without 2 hr 34 °C heat-shock treatment to assay heat shock response. Animals imaged 2 hr after recovery at 20 °C. (E) Quantification of (D) normalized to size using a BioSorter. Lines represent mean and standard deviation. n=400. Mann-Whitney test n.s.=not significant. Representative data shown is 1 of 3 biological replicates. (F) Fluorescent micrographs of day 1 adult transgenic animals expressing hsp-6p::GFP, grown from L1 on EV or cco-1 RNAi combined in a 1:1 ratio with either EV or let-767 RNAi to assay effects on UPRmt induction. (G) Quantification of (F) normalized to size using a BioSorter. Lines represent mean and standard deviation. n=431. Mann-Whitney test p-value ****<0.0001. Representative data shown is one of three biological replicates.