Full text
PDF


























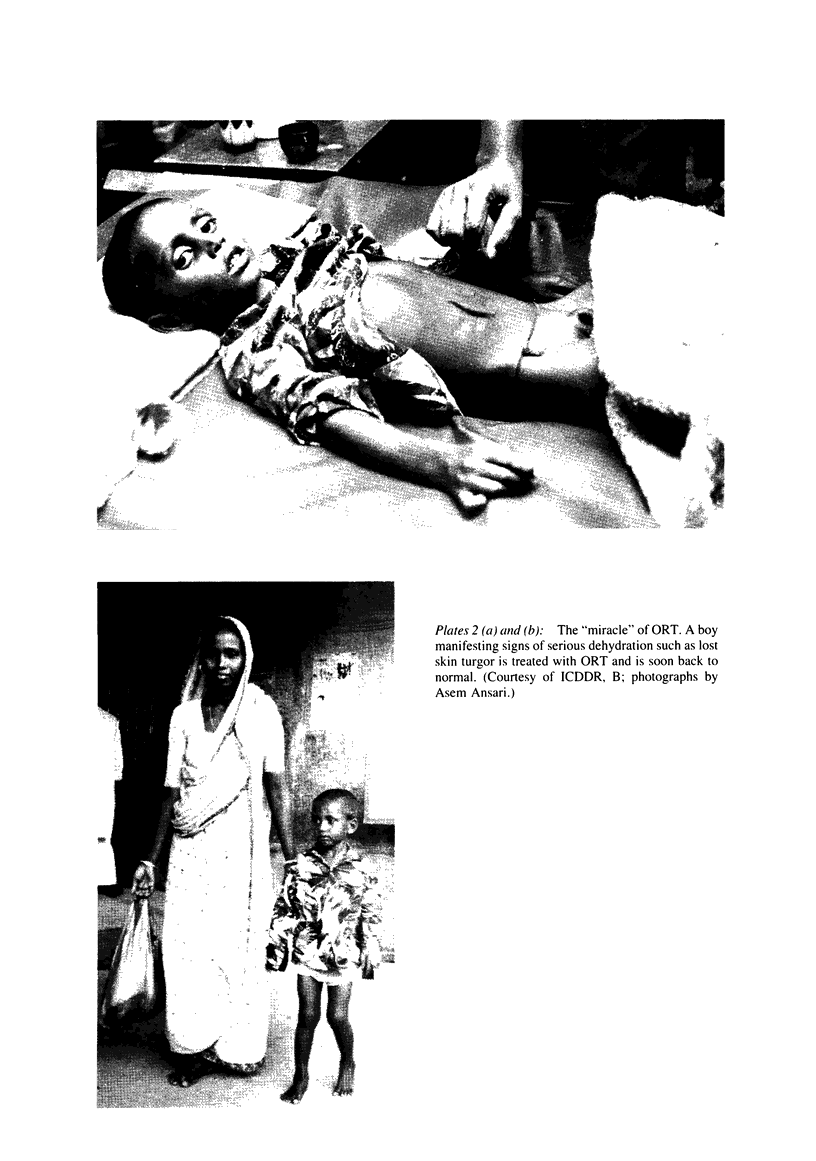











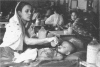
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARNESS L. A., YOUNG L. N. A SIMPLIFIED VIEW OF FLUID THERAPY. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1964 Feb;11:3–15. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)31512-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett R. G., Greenough W. B., 3rd Approach to acute diarrhea in the elderly. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1993 Sep;22(3):517–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHATTERJEE H. N. Control of vomiting in cholera and oral replacement of fluid. Lancet. 1953 Nov 21;265(6795):1063–1063. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(53)90668-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLE E., AYOUB E., RAILE R. Hypertonic dehydration (hypernatremia): the role of feedings high in solutes. Pediatrics. 1958 Jul;22(1 Pt 1):5–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRANE R. K. Hypothesis for mechanism of intestinal active transport of sugars. Fed Proc. 1962 Nov-Dec;21:891–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURRAN P. F. Na, Cl, and water transport by rat ileum in vitro. J Gen Physiol. 1960 Jul;43:1137–1148. doi: 10.1085/jgp.43.6.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cash R. A., Forrest J. N., Nalin D. R., Abrutyn E. Rapid correction of acidosis and dehydration of cholera with oral electrolyte and glucose solution. Lancet. 1970 Sep 12;2(7672):549–550. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91350-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cash R. A., Nalin D. R., Rochat R., Reller L. B., Haque Z. A., Rahman A. S. A clinical trial of oral therapy in a rural cholera-treatment center. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1970 Jul;19(4):653–656. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1970.19.653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DARROW D. C., WELSH J. S. Recent experience in the treatment of diarrhea in infants. J Pediatr. 1960 Feb;56:204–210. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(60)80120-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEIG M. Diarrhea, dysentery, food poisoning, and gastroenteritis; a study of 926 outbreaks and 49,879 cases reported to the United States Public Health Service (1945-1947). Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1950 Nov;40(11):1372–1394. doi: 10.2105/ajph.40.11.1372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER R. B., PARSONS D. S. Glucose movements across the wall of the rat small intestine. J Physiol. 1953 Feb 27;119(2-3):210–223. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRADKIN W. Z. The dietary treatment of diarrheal diseases. Am J Dig Dis. 1953 Jul;20(7):208–210. doi: 10.1007/BF02881322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIES J. H., CHIARA N. J., WALDRON R. J. Dehydrated banana in the dietetic management of diarrheas of infancy. J Pediatr. 1950 Sep;37(3):367–372. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(50)80156-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENE D. C., ALBRECHT R. M. Recent developments in diarrhea of the newborn. N Y State J Med. 1955 Oct 1;55(19):2764–2768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRISON H. E. The treatment of diarrhea in infancy. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1954 May;:335–348. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)30071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMES C. A. Diarrhea with dehydration in infants; a simple treatment. Ariz Med. 1955 May;12(5):195–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn N., Cash R. A., Woodward W. E., Spivey G. H. Oral fluid therapy of Apache children with acute infectious diarrhoea. Lancet. 1972 Jul 1;2(7766):15–18. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91277-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn N., Kinzie J. L., Sachar D. B., Northrup R. S., Taylor J. O., Ahmad S. Z., Phillips R. A. Decrease in net stool output in cholera during intestinal perfusion with glucose-containing solutions. N Engl J Med. 1968 Jul 25;279(4):176–181. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196807252790402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn N., McCarthy B. J., Ranney B., Hirschhorn M. A., Woodward S. T., Lacapa A., Cash R. A., Woodward W. E. Ad libitum oral glucose-electrolyte therapy for acute diarrhea in Apache children. J Pediatr. 1973 Oct;83(4):562–571. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn N. The treatment of acute diarrhea in children. An historical and physiological perspective. Am J Clin Nutr. 1980 Mar;33(3):637–663. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/33.3.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahalanabis D., Choudhuri A. B., Bagchi N. G., Bhattacharya A. K., Simpson T. W. Oral fluid therapy of cholera among Bangladesh refugees. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1973 Apr;132(4):197–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalin D. R., Cash R. A., Islam R., Molla M., Phillips R. A. Oral maintenance therapy for cholera in adults. Lancet. 1968 Aug 17;2(7564):370–373. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90591-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalin D. R., Cash R. A. Oral or nasogastric maintenance therapy for diarrhoea of unknown aetiology resembling cholera. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1970;64(5):769–771. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(70)90020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalin D. R., Cash R. A., Rahman M. Oral (or nasogastric) maintenance therapy for cholera patients in all age-groups. Bull World Health Organ. 1970;43(3):361–363. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS R. A. WATER AND ELECTROLYTE LOSSES IN CHOLERA. Fed Proc. 1964 May-Jun;23:705–712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Banwell J. G., Rupak D. M., Mitra R. C., Caranasos G. J., Keimowitz R. I., Mondal A., Manji P. M. Effect of intragastric glucose-electrolyte infusion upon water and electrolyte balance in Asiatic cholera. Gastroenterology. 1968 Sep;55(3):333–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Sack R. B., Mitra R. C., Banwell J. G., Brigham K. L., Fedson D. S., Mondal A. Replacement of water and electrolyte losses in cholera by an oral glucose-electrolyte solution. Ann Intern Med. 1969 Jun;70(6):1173–1181. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-70-6-1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIKLIS E., QUASTEL J. H. Effects of cations on sugar absorption by isolated surviving guinea pig intestine. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1958 Mar;36(3):347–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELANDER P. Carrot soup in the treatment of infantile diarrhea. J Pediatr. 1950 Jun;36(6):742–745. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(50)80228-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEPHENS L. J., HENRICKSON W. E. Mild diarrhea in children; clinical evaluation of oral electrolyte therapy with a nonabsorbable sulfonamide for treatment. Mo Med. 1954 Feb;51(2):105–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachar D. B., Taylor J. O., Saha J. R., Phillips R. A. Intestinal transmural electric potential and its response to glucose in acute and convalescent cholera. Gastroenterology. 1969 Mar;56(3):512–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATTEN R. H., PHILLIPS R. A. Potassium in the treatment of cholera. Lancet. 1960 Nov 5;2(7158):999–1001. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(60)92078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Awqati Q. S., Mekkiya M., Thamer M. Establishment of a cholera treatment unit under epidemic conditions in a developing country. Lancet. 1969 Feb 1;1(7588):252–253. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91254-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]