Abstract
Introduction
Regardless corticosteroids are recommended for the treatment of organizing pneumonia there is limited evidence supporting this practice. Thus, we performed a systematic review of the literature on systemic corticosteroid treatment for organizing pneumonia.
Methods
A search was implemented in the PubMed database (Medline) for articles published in the last 20 years. Those studies with incomplete or insufficient data and case reports were excluded. We collected data including: demographics, clinical data, diagnostic procedures, aetiology, treatment regimen (drug, posology, duration, response) and evolution.
Results
A total of 135 publications were selected and finally 13 studies with 849 patients were included in the review: 12 retrospective observational studies and a single prospective observational study. Most of the patients were started on treatment with systemic corticosteroids – a total of 627 (30–100% depending on the series), but there was a great heterogeneity regarding drug, doses and duration. On those that started treatment, 226 (36%) presented a relapse of the disease during follow-up. Only one study provided information regarding treatment side-effects.
Conclusion
The findings of this systematic review show the low quality data supporting the use of corticosteroids for the treatment of organizing pneumonia. This highlights a need to undertake appropriately designed studies to investigate which is the most appropriate treatment regimen that trades off benefits and risks of prolonged corticosteroid administration.
Keywords: Organizing pneumonia, Corticosteroids, Steroids, Treatment
Abstract
Introducción
Aunque los corticosteroides están recomendados para tratar la neumonía organizada, hay pocos datos que respalden esta práctica, por lo cual efectuamos una revisión sistemática de la bibliografía sobre el tratamiento con corticosteroides sistémicos para la neumonía organizada.
Métodos
Se hizo una búsqueda en la base de datos PubMed (Medline) de artículos publicados en los últimos 20 años. Se descartaron los estudios con datos y casos clínicos incompletos o insuficientes. Los datos que recabamos abarcaron: datos demográficos, datos clínicos, técnicas diagnósticas, etiología, pauta terapéutica (fármaco, posología, duración, respuesta) y evolución.
Resultados
Se eligieron 135 publicaciones en total y se incorporaron finalmente a la revisión 13 estudios con 849 pacientes: 12 estudios observacionales retrospectivos y un solo estudio observacional prospectivo. La mayor parte de los pacientes habían comenzado el tratamiento con corticosteroides sistémicos, un total de 627 (30%-100% en función de la serie), pero la duración, las dosis y el fármaco manifestaron una gran heterogeneidad. Entre los que habían empezado el tratamiento, 226 (36%) presentaron una recidiva de la enfermedad durante el seguimiento. Solo en un estudio se ofreció información sobre los efectos adversos del tratamiento.
Conclusión
Los resultados de esta revisión ponen de manifiesto la escasa calidad de los datos sobre el tratamiento de la neumonía organizada con corticosteroides. Este hecho destaca la necesidad de emprender estudios diseñados correctamente para investigar la pauta terapéutica más adecuada que compense los riesgos y beneficios de la administración prolongada de corticosteroides.
Palabras clave: Neumonía organizada, Corticosteroides, Esteroides, Tratamiento
Introduction
Organizing pneumonia (OP) is an interstitial lung disease (ILD) initially described as bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia,1 a label currently in disuse because the bronchiolitis is a minor finding.2 OP is histologically characterized by intra-alveolar buds of granulation tissue composed of myofibroblasts and fibroblasts intermixed with connective tissue.3 It is thought of as a nonspecific response to a local or distant injury triggered in the lung.4, 5 Clinical manifestations include an influenza-like syndrome – consisting of fever, cough, asthenia, and weight loss – that evolves to dyspnoea and different degrees of hypoxaemia. The typical clinical picture is non-specific, so a delay in diagnosis is frequent.2, 6
Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP) is the idiopathic form of OP, while OP with a known trigger is referred to as secondary organizing pneumonia (SOP). Triggers for SOP include systemic autoimmune disease (SAD), infection, malignancy, drug, radiation, transplant, and aspiration. COP is diagnosed after ruling out known causes of OP in a compatible clinical, radiological, and histopathological setting.3 While there is no evidence of histological differences between COP and SOP,7 classification is important because appropriate management requires identification of the underlying cause or trigger of SOP.3 Pharmacological treatment for OP is based on the use of systemic corticosteroids, mainly – given the possibility of spontaneous remission – for symptomatic and progressive forms of OP.8 Corticosteroid treatment rapidly improves the clinical and radiological picture. However, dosage and treatment duration are not well established and relapse is common.5 Therapeutic recommendations vary widely between studies, which highlights the great heterogeneity in OP management.
In this study, we performed a systematic review of the evidence on systemic corticosteroid treatment for OP in the last 20 years.
Materials and methods
Search strategy
A systematic literature search was implemented in May 2020 in the PubMed database (Medline) for articles published between January 1st 2000 and May 31st 2020. We decided to set our start date agreeing with the publication of international guidelines that specified the definition of OP in the context of other ILD.9, 10 Articles were limited to those published in English and Spanish. The MeSH terms used for the search were “cryptogenic organizing pneumonia” (which includes the term “organizing pneumonia” and “bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia”) and “corticosteroids”. Additional articles were sought in the reference lists of articles retrieved from PubMed. We followed the PRISMA guidelines for reporting systematics reviews.11
Data extraction
Retrieved publications on OP treated with systemic corticosteroids were evaluated for inclusion in this systematic review by two authors (LC and AR). Due to the heterogeneity of the information retrieved, we excluded from the analysis those studies with incomplete or insufficient data and case reports.
Data analysis
Data extracted from the selected articles and compiled in a Microsoft Excel 2010 document included: demographics (age, sex), clinical data (comorbidities, symptoms, OP extension), procedures performed to obtain the diagnosis, suspected cause/s, treatment (drug, posology, duration, response), and relapse.
Results
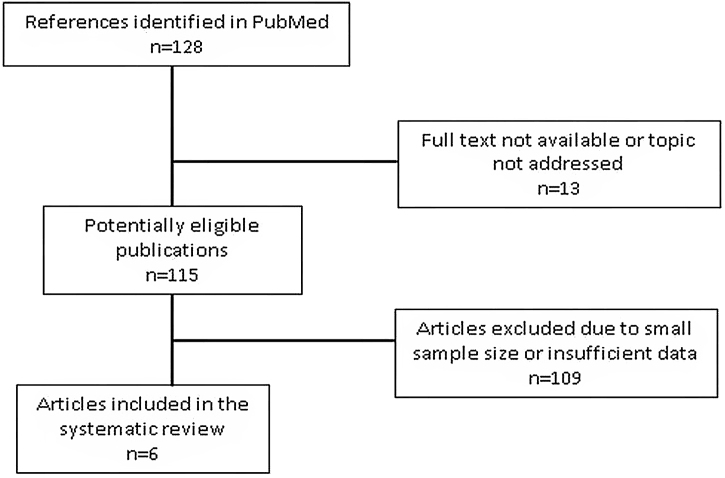
The bibliography search flowchart is depicted in Fig. 1. The systematic search resulted in 135 publications. Of these, 13 were not included in the study because either the full text was unavailable or they were unrelated to the aim of the review. Then 122 articles were selected for reading.2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89, 90, 91, 92, 93, 94, 95, 96, 97, 98, 99, 100, 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107, 108, 109, 110, 111, 112, 113, 114, 115, 116, 117, 118, 119, 120, 121, 122, 123, 124, 125, 126 The most frequent exclusion criterion was sample size, as most publications were case reports. Finally 13 studies with 849 patients were included in the review: 12 retrospective observational studies and a single prospective observational study (Table 1).2, 6, 12, 13, 14, 54, 120, 121, 122, 123, 124, 125, 126 Sample size ranged between 19 and 176 patients. Clinical findings are summarized in Table 2. Radiological and laboratory data and diagnostic procedures are shown in the supplementary data (Tables A1 and A2).
Fig. 1.
Study selection flowchart.
Table 1.
Articles included in the systematic review.
| Author, year | Country | Patients | Design | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cazzato, 200054 | Italy | 78 | Retrospective observational |
| 2 | Lazor, 200013 | France | 48 | Retrospective observational |
| 3 | Basarakodu, 200712 | USA | 57 | Retrospective observational |
| 4 | Barroso, 2007120 | Spain | 33 | Retrospective observational |
| 5 | Drakopanagiotakis, 20116 | Greece/USA | 61 | Prospective observational |
| 6 | Yoo, 2011121 | South Korea | 100 | Retrospective observational |
| 7 | Nishino, 2014122 | USA | 26 | Retrospective observational |
| 8 | Okada, 201614 | Japan | 19 | Retrospective observational |
| 9 | Onishi, 2016123 | Japan | 75 | Retrospective observational |
| 10 | Baha, 20182 | Turkey | 56 | Retrospective observational |
| 11 | Saito, 2019124 | Japan | 33 | Retrospective observational |
| 12 | Zhou, 2019125 | China | 87 | Retrospective observational |
| 13 | Zhang, 2020126 | China | 176 | Retrospective observational |
| Total patients | 849 | |||
Table 2.
Characteristics and symptoms of patients with organizing pneumonia (n = 849).
| Cazzato, 2000,54n = 78 | Lazor, 2000,13n = 48 | Basarakodu, 2007,12n = 57 | Barroso, 2007,120n = 33 | Yoo, 2011,121n = 100 | Drakopanagiotakis, 2011,6n = 61 | Nishino, 2014,122n = 26 | Onishi, 2016,123n = 75 | Okada, 2016,14n = 19 | Baha, 2018,2n = 56 | Saito, 2019,124n = 33 | Zhou, 2019,125n = 87 | Zhang, 2020,126n = 176 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) age (years) |
61 ± 12 | 61 ± 11 | 63 ± 15 (COP) 59 ± 15 (SOP) |
62 ± 10 | 54.8 ± 12.3 (CTD-OP)/56.0 ± 11.5 (COP) | 60.5 ± 13.6 | 62.5 (39–78) | 69.9 ± 10.3 | 61.9 ± 8 | 57.1 ± 12.7 | Relapse: 71 ± 10; No relapse: 74 ± 14 |
56.1 ± 10.4 (31–75) | Unilateral 55.9 ± 9.4 Bilateral 55.8 ± 10.0 |
| Sex (F) | 36 (46%) | 31 (65%) | 26 (46%) | 18 (55%) | 65 (65%) | 34 (56%) | 8 (31%) | 32 (43%) | 12 (63%) | 27 (48%) | 15 (45%) | 42 (48%) | 73 (41%) |
| Smokers | 53 (68%) | 14 (29%) | – | 10 (30%) | 15 (15%) | 33 (54%) | 1 (4%) | – | 7 (37%) | 33 (59%) | 14 (42%) | 24 (28%) | 55 (31%) |
| Lung disease | – | – | 12 (21%) | – | – | – | – | – | 4 (21%) | – | – | – | – |
| Fever | 49 (63%) | – | 16 (28%) | 26 (76%) | – | 39 (64%) | – | 42 (56%) | 15 (79%) | 24 (43%) | 22 (67%) | 40 (46%) | – |
| Cough | 41 (53%) | – | 26 (46%) | 29 (88%) | – | 40 (66%) | – | 44 (59%) | 8 (42%) | 40 (71%) | 27 (82%) | 73 (84%) | – |
| Dyspnoea | 45 (58%) | – | 45 (79%) | 19 (58%) | 85 (85%) | 38 (62%) | – | 17 (23%) | 6 (32%) | 37 (66%) | 20 (61%) | 54 (32%) | – |
| Asthenia | 30 (38%) | – | 16 (28%) | – | – | 44 (72%) | – | – | – | 36 (64%) | – | – | – |
| Weight loss | 10 (13%) | – | 8 (14%) | 14 (42%) | – | 17 (28%) | – | – | – | 14 (25%) | – | 9 (10%) | – |
| Flu-like symptoms | 21 (27%) | – | 2 (3.5%) | 7 (21%) | – | 15 (26%) arthralgia | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Chest pain | 2 (3%) | – | 16 (28%) | 18 (52%) | – | 18 (30%) | – | – | – | 7 (12.5%) | 1 (3%) | 4 (5%) | – |
| Haemoptysis | 1 (1%) | – | – | 12% | – | – | – | – | – | 4 (7%) | – | 5 (6%) | – |
| Asymptomatic | 10 (13%) | – | – | – | – | – | 7 (9%) | – | – | – | – | ||
| Aetiology | 53 (68%) COP 25 (32%) SOP: 7 (9%) drugs 5 (6%) radiotherapy 5 (6%) CTD |
48 (100%) COP | 30 (53%) COP 27 (47%) SOP: 8 (14%) infections 7 (12%) CTD 7 (12%) drugs |
33 (100%) COP | 76 (76%) COP 24 (24%) CTD–OP. 7 (7%) RA 6 (6%) SS 3 (3%) PM |
40 (66%) COP 21 (34%) SOP: 6 (10%) drugs 5 (8%) solid tumours 4 (7%) CTD |
26 (100%) COP | 40 (53%) COP; 35 (47%) SOP: 18 (24%) SAD, 6 (8%) infections, 11 (15%) others |
19 (100%) SOP: 18 (95%) RA 1 (5%) bacterial infection |
37 (66%) COP 19 (34%) SOP: 4 (7%) RA, 3 (5%) SS, 1 (4%) SLE, 2 (4%) lymphoma |
33 (100%) COP | 87 (100%) COP | 176 (100%) COP |
COP: cryptogenic organizing pneumonia; COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; CTD: connective tissue disease; F, female; HBV: hepatitis B virus; IBD: inflammatory bowel disease; ILD: interstitial lung disease; M, male; OSAS: obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome; PMR: polymyalgia rheumatica; POEMS: peripheral neuropathy, organomegaly, endocrinopathy, monoclonal plasma-cells proliferative disorder and skin change syndrome; RA: rheumatoid arthritis; SAD: systemic autoimmune disease; SS: Sjögren syndrome; PM: polymyositis; SLE: systemic lupus erythematosus; SOP: secondary organizing pneumonia.
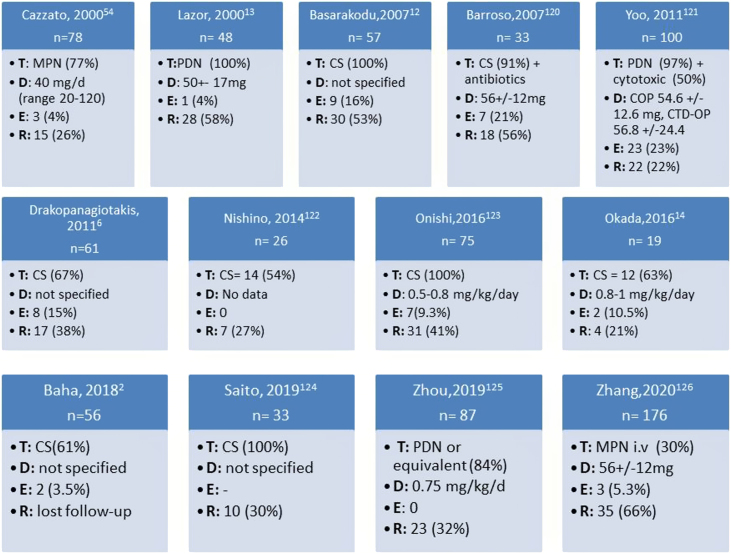
Most of the 849 patients were started on treatment, 627 (74%) with systemic corticosteroids (30–100% depending on the series) (Fig. 2). A detail review of each study is shown in the supplementary data (Table A2). Overall, the studies reported a favourable initial response to the treatment in the majority of cases, including partial or complete resolution. Basarakodu et al.12 found full resolution in 38 cases (67%), Yoo et al. in 40 cases (40%),121 while Okada et al. reported completed resolution in all patients treated with CS.14
Fig. 2.
Summary of corticosteroids prescription and response for the treatment of organizing pneumonia. T: therapy; D: initial dose; E: death; R: relapse; CS: corticosteroids; PDN: prednisone; MTP: methylprednisolone; COP: cryptogenic organizing pneumonia; CTD-OP: connective tissue disease-organizing pneumonia.
The most widely prescribed corticosteroid was prednisone (5 studies), followed by methylprednisolone, although the corticosteroid type was not specified in 6 studies. Moreover, as the majority of the studies were retrospective the period of treatment and the timing of steroid tapering were not unified, which resulted in a huge variability regarding CS total dose and duration (Fig. 2). Altogether, patients were treated initially with high CS doses, with regimens superior to 0.5 mg/kg/day, at least 4 weeks, followed by gradual tapering in the following 6–12 months (Table A2).
About other therapies, spontaneous OP resolution was observed in 31 patients (3.6%), reported as asymptomatic or mild involvement cases, who received no specific treatment. Lung resection surgery was the only treatment in 99 cases (11.6%), while antibiotics (anti-inflammatory treatment with macrolides) were used in 14 cases (1.6%). Information regarding other cytotoxic drugs is very limited, as only in one study half of the patients were under this regimen.121
Among the 849 patients included in the analysis, 66 deaths (7.7%) were reported. In 9 cases were documented as in-hospital, whereas for the remaining occurred during follow-up. The relation of this event with the diagnosis of OP was not described in all studies. Yoo et al. showed 23 deaths among 100 cases (23%), while disease-related was limited to 14 patients (14%).121
A non-negligible number of patients (240 of 849) experienced one or more relapses at some point during their follow-up: 28% of patients with OP, and 36% of patients treated with corticosteroids. Most relapses occurred when corticosteroids were tapered or suspended. The period of time until the event was wide. In Okada et al. relapses occurred at between 3 months and 14 years (mean 5.3 years) after OP diagnosis,14 and in Lazor et al. at between 2 and 46 months (mean 5 months) after starting treatment for the first OP episode.13 In this study, the subgroup with multiple relapses (≥3) was characterized by delayed treatment of the first OP episode and mild cholestasis in laboratory tests.13 Saito et al. found that radiographic findings, such as bilateral shadow pattern, traction bronchiectasis, and partial remission, may have possibility of predictive factors for COP relapse.124 Zhou et al. showed that fever was more common (65% vs 32%, p = 0.04), serum CRP higher (31.5 ± 39.4 mg/L vs 17.5 ± 32.2 mg/L, p = 0.038) and DLCO lower (45.9 ± 14.2% vs 57.6 ± 18.5%, p = 0.05) in the relapse group.125 In other study, BAL neutrophilia (OR 1.07, CI 1.02–1.13, p = 0.012) and high levels of fibrin deposits (OR 17.4, CI 1.89–160.9, p = 0.012) were independent predictors of relapse.123
With reference to CS side effects, it was not described in the majority of studies. Lazor et al. reported a rate of adverse effects as high as 25%,13 Barroso et al. up to 17 of 32 cases (53%),120 while Onishi et al. described one or more adverse effects of corticosteroid therapy in 39 of the 75 patients (52%).123 The most frequent side-effects were weight gain, myopathy, osteoporosis, hypertension, or systemic infection.
Discussion
The thirteen studies analyzed in this systematic review reveal a widespread use of systemic corticosteroids to treat OP, with most of the 849 patients responding favourably in terms of their symptoms and radiological abnormalities. However, our analysis also shows that there is currently no consensus regarding the most appropriate corticosteroid, its dose, and the duration of treatment. A significant number of relapses were reported during follow-up, even in those that had been treated with CS. However, key clinical questions as causes of non-response to steroids, recurrence and the usefulness of other drugs in OP remain answered with the information derived from these articles.
Based on the reviewed studies, OP is characterized by a non-specific clinical picture with respiratory and constitutional symptoms, radiological images of bilateral multifocal lung consolidation, and in the absence of any infectious processes. For diagnostic purposes as a first option, before considering more invasive techniques such as surgical biopsy, most authors used a combination of BAL (which typically shows lymphocyte predominance) and transbronchial biopsy. In most cases, a triggering factor was not detected and the condition was classified as COP.
The studies showed that most patients with organizing pneumonia respond favourably to corticosteroids in the short-term, which support the value of this therapy for this entity. This correlates with current clinical practise and guidelines.10 Some authors have proposed a regimen based on oral prednisone at a dose of 1 mg/kg/day, tapered off over 12 months, given the risk of relapse after dose reduction or treatment discontinuation.127, 128, 129, 130 However, the interpretation of the efficacy is limited because the heterogeneity of the data collected, as each study assesses different outcomes. Prednisone is the most widely used corticosteroid for treatment of OP. There is less experience with other drugs, like methylprednisolone, and none of the reviewed studies used dexamethasone. This is probably due to the safety profile of prednisone and its common use in other chronic respiratory diseases. Regarding the dose, the majority of the studies used a regimen higher than 0.5 mg/kg/day, but with a high variability within the same studies. The doses might have been adjusted based on patient's comorbidities and weight, but this was not clearly stated in the study methods. This highlights the significant heterogeneity in the corticosteroids regimens to treat OP in clinical practise.
An issue of interest is that the prolonged corticosteroid use has traditionally been justified by the risk of relapse. Treatment regimens tended to last at least 6 months and corticosteroid dose was progressively tapered off to minimize the risk of relapse. This is confirmed by the reviewed studies, which reported relapse rates as high as 21–66% depending on the study. Lazor et al. concluded that a delay in initiating treatment increased the risk of relapse, although prolonged treatment did not seem to have any effect on the incidence of relapses.13
There is a scarcity of data to identify patients at greater risk of experiencing a relapse. In Lazor et al.,13 the relapse rate was 68% during treatment (primarily (96%) with prednisone at doses of ≤20 mg/day) and 32% after treatment discontinuation. In Drakopanagiotakis et al.,6 the relapse rate was 37.8%, with no differences between COP and SOP, and with no correlation with hypoxaemia, hypoalbuminemia, BAL lymphocytosis, or a reticulonodular pattern on high-resolution CT. In another study, radiographic findings were not independently associated with the risk of relapse in multivariate analysis.124 Conversely, 90% of patients in Baha et al. achieved complete remission, mostly patients with ground glass opacity on high-resolution CT.2 Some authors, including Cazzato et al.,54 have suggested that elevated BAL lymphocytosis might predict a good response to corticosteroid treatment, although subsequent studies have reported different results.6, 13 In short, although relapse is clinically crucial in the natural history of OP, to date no clinical data enables identification of treatment responders. This would avoid potential adverse effects of unnecessary corticosteroid treatment.
Surprisingly, the issue of the adverse effects of corticosteroid treatment was only reflected in a minority of studies, that reported a rate of adverse effects as high as 53%, mainly weight gain, myopathy, and osteoporosis. Undoubtedly, in addition to avoidance of relapse, reduced mortality may be a justification for the acceptance of such high adverse effect rates. In the reviewed studies, while mortality ranged between 0% and 23%, it is not known which patient profiles was associated with a poorer response to corticosteroids and worse outcomes.
The conclusions of this review of OP studies are clearly limited by the poor quality of currently available studies. Indeed, most existing studies are case reports, while larger studies have limitations in terms of the reported data, with insufficient details on the drugs used, effectiveness, treatment duration, and rates of adverse effects. There is both a lack of studies specifically designed to evaluate this issue and a large heterogeneity in treatment, irrespective of OP aetiology (cryptogenic or secondary). All these unanswered questions highlight the need to undertake appropriately designed studies and to develop a consensus on the most appropriate treatment regimen for patients with OP that trades off benefits (reduced risk of pulmonary sequelae, relapses, and mortality) and risks (side effects) of prolonged corticosteroid administration.
Corticosteroids are widely used to treat OP, despite the lack of clinical trials specifically designed to support this practice. This systematic review of the literature points to an urgent need to implement appropriate studies aimed at developing treatment protocols with regard to compounds, dosage and duration, identifying factors associated with relapse and prognosis, and adequately monitoring adverse effects.
Authors’ contributions
All authors contributed to the manuscript. Laia Cendon, Albert Rafecas and Diego Castillo were responsible for study design, analysis of data and manuscript draft. Laia Cendon and Albert Rafecas did the literature search and data collection. All the authors contributed to the interpretation of the results and the proof reading of the manuscript.
Ethical approval
Due the characteristic of the study, that is a systematic review of previous literature, ethical approval was waived.
Funding
There was no funding source for this article.
Conflicts of interest
LC, AR, DR have nothing to disclose. IC reports grants from Health Department (Generalitat de Catalunya), personal fees from Boeringher-Ingelheim, personal fees from Bristol Myers Squibb, personal fees from Roche, personal fees from Janssen-Cilag, outside the submitted work; PS reports grants, personal fees and non-financial support from Roche, grants, personal fees and non-financial support from PPM Services, personal fees from Red X Pharma, personal fees from Galapagos, personal fees from Chiesi, grants, personal fees and non-financial support from Boehringer-Ingelheim, personal fees from Lupin Pharmaceuticals, outside the submitted work; and Wife employee of Novartis. DC reports personal fees and non-financial support from Roche, personal fees and non-financial support from Boehringer-Ingelheim, grants from Fujirebio, outside the submitted work. Diego Castillo is part of the Editorial board of Open Respiratory Archives and declares that they have remained outside the evaluation and decision-making process in relation to this article.
Acknowledgement
Mrs. Ailish for English editing.
Footnotes
Supplementary data associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at doi:10.1016/j.opresp.2022.100211.
Appendix A. Supplementary data
The following are the supplementary data to this article:
References
- 1.Epler G.R., Colby T.V., McLoud T.C., Carrington C.B., Gaensler E.A. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 1985;312:152–158. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501173120304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Baha A., Yildirim F., Kokturk N., Galata Z., Akyurek N., Demirci N.Y., et al. Cryptogenic and secondary organizing pneumonia: clinical presentation, radiological and laboratory findings, treatment, and prognosis in 56 cases. Turk Thorac J. 2018;19:201–208. doi: 10.5152/TurkThoracJ.2018.18008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cordier J.F. Cryptogenic organising pneumonia. Eur Respir J. 2006;28:422–446. doi: 10.1183/09031936.06.00013505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Arays R., Wang P. A case of pembrolizumab-induced localized organizing pneumonia. Scand J Immunol. 2018;88:e12677. doi: 10.1111/sji.12677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chee C.B., Da Costa J.L., Sim C.S. A female with dry cough, progressive dyspnoea and weight loss. Eur Respir J. 2005;25:206–209. doi: 10.1183/09031936.04.00053504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Drakopanagiotakis F., Paschalaki K., Abu-Hijleh M., Aswad B., Karagianidis N., Kastanakis E., et al. Cryptogenic and secondary organizing pneumonia: clinical presentation, radiographic findings, treatment response, and prognosis. Chest. 2011;139:893–900. doi: 10.1378/chest.10-0883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bissoli L., Di Francesco V., Valbusa F., Zivelonghi A., Fantin F., Zamboni M. A case of bronchiolitis obliterans organising pneumoniae (BOOP) after nine months post-operative irradiation for breast cancer. Age Ageing. 2008;37:235. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afn010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Piciucchi S., Dubini A., Tomassetti S., Casoni G., Ravaglia C., Poletti V. A case of amiodarone-induced acute fibrinous and organizing pneumonia mimicking mesothelioma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015;191:104–106. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201405-0844IM. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.King T.E., Costabel U., Cordier J.F., Dopico G.A., Du Bois R., Lynch D., et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: diagnosis and treatment: international consensus statement. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;161:646–664. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.161.2.ats3-00. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.American Thoracic Society, European Respiratory Society American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. This joint statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) was adopted by the ATS board of directors, June 2001 and by the ERS Executive Committee, June 2001. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165:277–304. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.165.2.ats01. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Page M.J., McKenzie J.E., Bossuyt P.M., Boutron I., Hoffmann T.C., Mulrow C.D., et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Basarakodu K.R., Aronow W.S., Nair C.K., Lakkireddy D., Kondur A., Korlakunta H., et al. Differences in treatment and in outcomes between idiopathic and secondary forms of organizing pneumonia. Am J Ther. 2007;14:422–426. doi: 10.1097/01.pap.0000249905.63211.a1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lazor R., Vandevenne A., Pelletier A., Leclerc P., Court-Fortune I., Cordier J.F. Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia. Characteristics of relapses in a series of 48 patients. The Groupe d’Etudes et de Recherche sur les Maladles “Orphelines” Pulmonaires (GERM“O”P) Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;162:571–577. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.162.2.9909015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Okada H., Kurasawa K., Yamazaki R., Tanaka A., Arai S., Owada T., et al. Clinical features of organizing pneumonia associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2016;26:863–868. doi: 10.3109/14397595.2016.1153217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Katikireddy C.K., Krishna G., Berry G., Faul J., Kuschner W. A 24-year-old woman with bilateral pulmonary infiltrates, pericardial effusion, and bilateral pleural effusions. Chest. 2005;128:4013–4017. doi: 10.1378/chest.128.6.4013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sato H., Yokoe I., Nishio S., Onishi T., Takao T., Kobayashi Y., et al. A case of adult onset Still's disease complicated with cryptogenic organizing pneumonia. Intern Med. 2011;50:247–251. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.50.4180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Al-Khouzaie T.H., Dawamneh M.F., Hazmi A.M. Acute fibrinous and organizing pneumonia. Ann Saudi Med. 2013;33:301–303. doi: 10.5144/0256-4947.2013.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Goncalves J.R., Marques R., Serra P., Cardoso L. Acute fibrinous and organising pneumonia. BMJ Case Rep. 2017:2017. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2016-218802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Guimaraes C., Sanches I., Ferreira C. Acute fibrinous and organising pneumonia. BMJ Case Rep. 2012:2012. doi: 10.1136/bcr.01.2011.3689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lu J., Yin Q., Zha Y., Deng S., Huang J., Guo Z., et al. Acute fibrinous and organizing pneumonia: two case reports and literature review. BMC Pulm Med. 2019;19:141. doi: 10.1186/s12890-019-0861-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Heo J.Y., Song J.Y., Noh J.Y., Yong H.S., Cheong H.J., Kim W.J. Acute fibrinous and organizing pneumonia in a patient with HIV infection and Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia. Respirology. 2010;15:1259–1261. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1843.2010.01845.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Yamamoto M., Murata K., Kiriu T., Kouzai Y., Takamori M. Acute fibrinous and organizing pneumonia with myelodysplastic syndrome: corticosteroid monotherapy led to successful ventilator weaning. Intern Med. 2016;55:3155–3159. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.55.6864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Iwanaga T., Hirota T., Ikeda T. Air leak syndrome as one of the manifestations of bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia. Intern Med. 2000;39:163–165. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.39.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kato T., Ubara Y., Sawa N., Tagami T., Katori H., Takemoto F., et al. An abrupt onset of seropositive polyarthritis with prominent distal tenosynovitis concomitant with bronochiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP): consideration of the relationship with RS3PE syndrome. Intern Med. 2004;43:143–147. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.43.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Agrawal S., Gupta N., Kumar R., Sen M.K., Chakrabarti S., Suri J.C. An unusual case of idiopathic inflammatory myopathy presenting with organizing pneumonia as cavitary lesions. Adv Respir Med. 2019;87:243–246. doi: 10.5603/ARM.2019.0041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Fruchter O., Solomonov A., Guralnik L., Naroditsky I., Yigla M. An unusual radiographic manifestation of bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia. J Thorac Imaging. 2007;22:263–264. doi: 10.1097/01.rti.0000213592.75214.b1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Laszlo A., Espolio Y., Auckenthaler A., Michel J.P., Janssens J.P. Azathioprine and low-dose corticosteroids for the treatment of cryptogenic organizing pneumonia in an older patient. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2003;51:433–434. doi: 10.1046/j.1532-5415.2003.51126.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kroegel C., Reibetaig A., Hengst U., Mock B., Hafner D., Grahmann P.R. Bilateral symmetrical upper-lobe opacities: an unusual presentation of bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia. Chest. 2000;118:863–865. doi: 10.1378/chest.118.3.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hooi L.N. Bronchiolitis obliterans organising pneumonia: a treatable condition. Med J Malaysia. 2005;60:222–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ruth-Sahd L.A., White K.A. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia. Dimens Crit Care Nurs. 2009;28:204–208. doi: 10.1097/DCC.0b013e3181ac49ce. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Guzman E.J., Smith A.J., Tietjen P.A. Bronchiolitis obliterans-organizing pneumonia after coronary artery bypass graft surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2000;119:382–383. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5223(00)70197-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kute V.B., Patel M.P., Patil S.B., Shah P.R., Vanikar A.V., Gumber M.R., et al. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP) after renal transplantation. Int Urol Nephrol. 2013;45:1517–1521. doi: 10.1007/s11255-012-0182-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Biehn S.E., Kirk D., Rivera M.P., Martinez A.E., Khandani A.H., Orlowski R.Z. Bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia after rituximab therapy for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Hematol Oncol. 2006;24:234–237. doi: 10.1002/hon.799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Fanetti G., Bazzani F., Ferrari A., Alterio D., Donghi S.M., Pounou Kamga F.A., et al. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia after stereotactic ablative radiation therapy for lung cancer: a case report. Cancer Radiother. 2018;22:57–61. doi: 10.1016/j.canrad.2017.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Takada H., Saito Y., Nomura A., Ohga S., Kuwano K., Nakashima N., et al. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia as an initial manifestation in systemic lupus erythematosus. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2005;40:257–260. doi: 10.1002/ppul.20224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Fawcett I.W., Ibrahim N.B. BOOP associated with nitrofurantoin. Thorax. 2001;56:161. doi: 10.1136/thorax.56.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Almaslmani M., Derbala M.F., Albozom I., Khattab M., Chacko K., Alani A. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia associated with Pneumocystis jiroveci infection in orthotopic liver transplantation. Transpl Infect Dis. 2008;10:339–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3062.2008.00300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ulubas B., Sahin G., Ozer C., Aydin O., Ozgur E., Apaydin D. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia associated with sulfasalazine in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2004;23:249–251. doi: 10.1007/s10067-003-0848-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Cameron R.J., Kolbe J., Wilsher M.L., Lambie N. Bronchiolitis obliterans organising pneumonia associated with the use of nitrofurantoin. Thorax. 2000;55:249–251. doi: 10.1136/thorax.55.3.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Cheng T.H., Ko F.C., Chang J.L., Wu K.A. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia due to titanium nanoparticles in paint. Ann Thorac Surg. 2012;93:666–669. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2011.07.062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Garibaldi B.T., West N.E., Illei P.B., Terry P.B. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia following a jalapeno grease fire. Chest. 2015;147:e31–e33. doi: 10.1378/chest.14-1338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ning-Sheng L., Chun-Liang L., Ray-Sheng L. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia in a patient with Behcet's disease. Scand J Rheumatol. 2004;33:437–440. doi: 10.1080/03009740410006187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Macartney C., Burke E., Elborn S., Magee N., Noone P., Gleadhill I., et al. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia in a patient with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma following R-CHOP and pegylated filgrastim. Leukemia Lymphoma. 2005;46:1523–1526. doi: 10.1080/10428190500144615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.DeAngelo A.J., Ouellette D. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia in an orthotopic liver transplant patient. Transplantation. 2002;73:544–546. doi: 10.1097/00007890-200202270-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Kaushik P., Cooper E.S., Banda V.R., Vatsavai S.R., Kaushik R. Bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia in rheumatoid arthritis – a fatal case and short review of literature. Rheumatol Int. 2005;25:391–393. doi: 10.1007/s00296-004-0514-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Aguiar Bujanda D., Aguiar Morales J., Bohn Sarmiento U. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia induced by chemotherapy. Arch Bronconeumol. 2004;40:290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Takigawa N., Segawa Y., Saeki T., Kataoka M., Ida M., Kishino D., et al. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia syndrome in breast-conserving therapy for early breast cancer: radiation-induced lung toxicity. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000;48:751–755. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(00)00654-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Mendez M., Barriga F., Garcia C., Holmgren N.L., Gonzalez S., Sanchez I. Bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia secondary to chemotherapy in a child with primary pericardial sarcoma. Rev Med Chil. 2000;128:633–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Cobo Dols M., Gil Calle S., Ales Diaz I., Villar Chamorro E., Alcaide Garcia J., Gutierrez Calderon V., et al. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia simulating progression in bronchioloalveolar carcinoma. Clin Transl Oncol. 2006;8:133–135. doi: 10.1007/s12094-006-0171-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Chiba S., Jinta T., Chohnabayashi N., Fujie T., Sumi Y., Inase N. Bronchiolitis obliterans organising pneumonia syndrome presenting with neutrophilia in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid after breast-conserving therapy. BMJ Case Rep. 2012:2012. doi: 10.1136/bcr.09.2011.4857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Montero C., Brage A., Rodriguez-Trigo G., Verea H. Bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia and primary biliary cirrhosis. Med Clin. 2003;120:37–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Hausler M., Meilicke R., Biesterfeld S., Kentrup H., Friedrichs F., Kusenbach G. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia: a distinct pulmonary complication in cystic fibrosis. Respiration. 2000;67:316–319. doi: 10.1159/000029517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Mohan K., Sayer R., Acharya D. Lessons to be learned: a case study approach. Bronchiolitis obliterans organising pneumonia: a reversible cause of respiratory failure. J R Soc Promot Health. 2004;124:188–190. doi: 10.1177/146642400412400413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Cazzato S., Zompatori M., Baruzzi G., Schiattone M.L., Burzi M., Rossi A., et al. Bronchiolitis obliterans-organizing pneumonia: an Italian experience. Respir Med. 2000;94:702–708. doi: 10.1053/rmed.2000.0805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Weekly clinicopathological exercises. Case 36-2001. Acute febrile respiratory illness in a 57-year-old man with recurrent pulmonary disorders. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:1558–1565. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcpc010036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Heller I., Biner S., Isakov A., Kornitzky Y., Shapira I., Marmor S., et al. TB or not TB: cavitary bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia mimicking pulmonary tuberculosis. Chest. 2001;120:674–678. doi: 10.1378/chest.120.2.674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Garrido M., O’Brien A., Gonzalez S., Clavero J.M., Orellana E. Cryptogenic organizing pneumonitis during oxaliplatin chemotherapy for colorectal cancer: case report. Chest. 2007;132:1997–1999. doi: 10.1378/chest.07-0536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Tzelepis E., Kampolis C.F., Vlachadami I., Moschovi M., Alamani M., Kaltsas G. Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia in Sweet's syndrome: case report and review of the literature. Clin Respir J. 2016;10:250–254. doi: 10.1111/crj.12206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Dinneen H.S., Samiullah S., Lenza C. Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia: a rare extra-intestinal manifestation of Crohn's disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2014;8:177–178. doi: 10.1016/j.crohns.2013.09.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Taniwaki M., Yamasaki M., Matsumoto Y., Matsumoto N., Ohashi N., Hattori N. Corticosteroid therapy for organizing pneumonia in a human T-cell lymphotropic virus type-1 carrier. Pulmonology. 2019;25:193–195. doi: 10.1016/j.pulmoe.2019.02.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Kunal S., Pilaniya V., Jain S., Shah A. ‘Crazy-paving’ pattern: an exceptional presentation of cryptogenic organising pneumonia associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. BMJ Case Rep. 2016:2016. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2016-215445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Kenealy H., Green G. Cryptogenic organising pneumonia in a 92 year old. N Z Med J. 2008;121:81–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Kikuchi N., Nakayama H. Cryptogenic organising pneumonia after radiotherapy. BMJ Case Rep. 2014:2014. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2014-205812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Cottin V., Cordier J.F. Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2012;33:462–475. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1325157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Justet A., Ottaviani S., Dieude P., Taille C. Tocilizumab for refractory organising pneumonia associated with Sjogren's disease. BMJ Case Rep. 2015:2015. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2014-209076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Schlesinger C., Koss M.N. The organizing pneumonias: an update and review. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2005;11:422–430. doi: 10.1097/01.mcp.0000175521.41729.07. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Patel H.C., Lauder N.N. The antisynthetase syndrome. Am J Med. 2011;124:e3–e4. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2011.02.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Kim T.O., Oh I.J., Kang H.W., Chi S.Y., Ban H.J., Kwon Y.S., et al. Temozolomide-associated bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia successfully treated with high-dose corticosteroid. J Korean Med Sci. 2012;27:450–453. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.4.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Ohe M., Shida H., Horita T., Ito K., Sugiura M., Hattori A., et al. Successful treatment of three patients with organizing pneumonia associated with rheumatoid arthritis using clarithromycin and prednisolone. Drug Discov Ther. 2017;11:218–222. doi: 10.5582/ddt.2017.01043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Egerer G., Witzens M., Spaeth A., Breitbart A., Moller P., Goldschmidt H., et al. Successful treatment of bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia with low-dose methotrexate in a patient with Hodgkin's disease. Oncology. 2001;61:23–27. doi: 10.1159/000055348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Koinuma D., Miki M., Ebina M., Tahara M., Hagiwara K., Kondo T., et al. Successful treatment of a case with rapidly progressive Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP) using cyclosporin A and corticosteroid. Intern Med. 2002;41:26–29. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.41.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Chang W.J., Lee E.J., Lee S.Y., In K.H., Kim C.H., Kim H.K., et al. Successful salvage treatment of steroid-refractory bronchiolar COP with low-dose macrolides. Pathol Int. 2012;62:144–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.2011.02766.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Shitenberg D., Fruchter O., Fridel L., Kramer M.R. Successful rituximab therapy in steroid-resistant, cryptogenic organizing pneumonia: a case series. Respiration. 2015;90:155–159. doi: 10.1159/000430100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Wantke F., Kneussl M., Hubner M., Derfler K., Brucke T., Schmaldienst S. Signal recognition particle (SRP) positive myositis in a patient with cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP) Rheumatol Int. 2010;30:1361–1365. doi: 10.1007/s00296-009-1059-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Martinez-Gallo M., Puy C., Ruiz-Hernandez R., Rodriguez-Arias J.M., Bofill M., Nomdedeu J.F., et al. Severe and recurrent episodes of bronchiolitis obliterans organising pneumonia associated with indolent CD4+ CD8+ T-cell leukaemia. Eur Respir J. 2008;31:1368–1372. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00061907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Bhatti S., Hakeem A., Torrealba J., McMahon J.P., Meyer K.C. Severe acute fibrinous and organizing pneumonia (AFOP) causing ventilatory failure: successful treatment with mycophenolate mofetil and corticosteroids. Respir Med. 2009;103:1764–1767. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2009.07.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Schiappacasse G., Acevedo A., Martinez R., Escobar J., Hernandez A., Pires Y. Reversed halo sign as an unusual manifestation of cryptogenic organized pneumonia. Report of one case. Rev Med Chil. 2019;147:663–667. doi: 10.4067/S0034-98872019000500663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Carreno C.A., Gadea M. Case report of a kidney transplant recipient converted to everolimus due to malignancy: resolution of bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia without everolimus discontinuation. Transplant Proc. 2007;39:594–595. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2006.12.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Deeren D., Lammertijn L., Van Dorpe J. Relapsing infiltrates after pneumocystis pneumonia in stem cell transplant patients: think about BOOP! Acta Clin Belg. 2010;65:200–201. doi: 10.1179/acb.2010.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Shimizu Y., Tsukagoshi H., Nemoto T., Honma M., Nojima Y., Mori M. Recurrent bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia in a patient with limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis. Rheumatol Int. 2002;22:216–218. doi: 10.1007/s00296-002-0230-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Zappasodi P., Dore R., Castagnola C., Astori C., Varettoni M., Mangiacavalli S., et al. Rapid response to high-dose steroids of severe bortezomib-related pulmonary complication in multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:3380–3381. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.10.0164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Dalle S., Skowron F., Ronger-Savle S., Balme B., Thomas L. Pseudosclerodermatous panniculitis after irradiation and bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia: simultaneous onset suggesting a common origin. Dermatology. 2004;209:138–141. doi: 10.1159/000079599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Robinson C., Nyi P.P. Probable nitrofurantoin-induced bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2009;66:1919–1922. doi: 10.2146/ajhp090403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Sakurai A., Yanai H., Ishida T., Kuwata H., Kamei K., Izumi S. Possible relationship between organizing pneumonia and chronic pulmonary aspergillosis: a case report and literature review. Respir Invest. 2017;55:74–78. doi: 10.1016/j.resinv.2016.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Tageja N., Nagi J., Valent J., Zonder J. Plasma cell leukemia presenting as organizing pneumonia refractory to high-dose steroid therapy. South Med J. 2010;103:706–710. doi: 10.1097/SMJ.0b013e3181e206da. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Lee W.S., Choi K.H. Organizing pneumonia with atypical computed tomography findings in Sjogren's syndrome. Int J Rheum Dis. 2015;18:482–484. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.12523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Natori H., Koga T., Fujimoto K., Taguchi J., Kamimura T., Nishimura M. Organizing pneumonia associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Jpn J Radiol. 2010;28:688–691. doi: 10.1007/s11604-010-0473-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Deegan A.P., Kirby B., Rogers S., Crotty T.B., McDonnell T.J. Organising pneumonia associated with fumaric acid ester treatment for psoriasis. Clin Respir J. 2010;4:248–251. doi: 10.1111/j.1752-699X.2009.00180.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Fertl A., Menzel M., Hofer T.P., Morresi-Hauf A., Ziegler-Heitbrock L., Frankenberger M. Monitoring of glucocorticoid therapy by assessment of CD14(+)CD16(+) monocytes: a case report. Immunobiology. 2008;213:909–916. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2008.07.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Sohn D.I., Laborde H.A., Bellotti M., Seijo L. Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and bronchiolitis obliterans organized pneumonia. Clin Rheumatol. 2007;26:247–250. doi: 10.1007/s10067-005-0126-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Staud R., Ramos L.G. Influenza A-associated bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia mimicking Wegener's granulomatosis. Rheumatol Int. 2001;20:125–128. doi: 10.1007/s002960000095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Benzo R., Sahn S.A. Fever, pleuritic chest pain, and a lung mass in a 43-year-old man. Chest. 2000;118:542–544. doi: 10.1378/chest.118.2.542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Duvic C., Desrame J., Leveque C., Nedelec G. Retroperitoneal fibrosis, sclerosing pancreatitis and bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004;19:2397–2399. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfh050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Lee Y.H., Choi S.J., Ji J.D., Shim J.J., Kang K.H., Cho H.D., et al. Dermatomyositis without elevation of creatine kinase presented as bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia. Korean J Intern Med. 2000;15:85–88. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2000.15.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Pantalone A., Abate M., D’Ovidio C., Carnevale A., Salini V. Diagnostic failure of ciprofloxacin-induced spontaneous bilateral Achilles tendon rupture: case-report and medical-legal considerations. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2011;24:519–522. doi: 10.1177/039463201102400227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Pierce L., Lewin A., Abdel-Wahab M., Elsayyad N. Early radiation-induced lung injury in a patient with prior diagnosis of bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonitis. J Natl Med Assoc. 2008;100:1474–1476. doi: 10.1016/s0027-9684(15)31551-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Tomonari A., Tsukada N., Takahashi S., Ooi J., Konuma T., Kobayashi T., et al. Early-onset pulmonary complication showing organizing pneumonia pattern following cord blood transplantation in adults. Int J Hematol. 2007;85:364–366. doi: 10.1532/IJH97.07016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Matsuno O., Okubo F., Masutomo K., Yoshida F., Okubo T., Miyazaki E., et al. Elevated concentrations of soluble IL-2 receptor in both bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and serum in a patient with BOOP. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2003;201:61–65. doi: 10.1620/tjem.201.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Ryerson C.J., Olsen S.R., Carlsten C., Donagh C., Bilawich A.M., Field S.K., et al. Fibrosing bronchiolitis evolving from infectious or inhalational acute bronchiolitis. a reversible lesion. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015;12:1323–1327. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201504-234BC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Yoshida-Hiroi M., Koizumi M., Oka R., Mitsuda A., Hiroi N. First case report of acquired pure red cell aplasia associated with micafungin. Intern Med. 2011;50:1051–1054. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.50.4303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Liu H., Li J., Chen M., Su J. Glucocorticoid treatment of suspected organizing pneumonia after H7N9 infection: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore) 2019;98:e16839. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Onishi Y., Kawamura T., Kagami R., Nakahara Y., Yoshiro M. IgG4-related lung disease with organizing pneumonia effectively treated with azathioprine. Intern Med. 2014;53:2701–2704. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.53.2564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Flora A.S., Simo H., Assaly R. Increasing role of macrolide anti-inflammatory therapy in secondary organizing pneumonia. Am J Ther. 2017;24:e495. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0000000000000550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Torrego A., Pajares V., Mola A., Lerma E., Franquet T. Influenza A (H1N1) organising pneumonia. BMJ Case Rep. 2010:2010. doi: 10.1136/bcr.12.2009.2531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Kashiwada T., Minegishi Y., Saito Y., Kato T., Atsumi K., Seike M., et al. Organizing pneumonia after nivolumab treatment in a patient with pathologically proven idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Nippon Med Sch. 2019;86:43–47. doi: 10.1272/jnms.JNMS.2019_86-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Penizzotto M., Retegui M., Arrien Zucco M.F. Organizing pneumonia associated with psoriasis. Arch Bronconeumol. 2010;46:210–211. doi: 10.1016/j.arbres.2009.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Imai R., Jinta T. Organizing pneumonia in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis with progression to usual interstitial pneumonia. QJM. 2019;112:37–38. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcy230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Daniels C.E., Myers J.L., Utz J.P., Markovic S.N., Ryu J.H. Organizing pneumonia in patients with hematologic malignancies: a steroid-responsive lesion. Respir Med. 2007;101:162–168. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2006.03.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Cornejo R., Llanos O., Fernandez C., Carlos Diaz J., Cardemil G., Salguero J., et al. Organizing pneumonia in patients with severe respiratory failure due to novel A (H1N1) influenza. BMJ Case Rep. 2010:2010. doi: 10.1136/bcr.02.2010.2708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Hegade V.S., Sood R., Saralaya D., Moreea S. Pulmonary complications of treatment with pegylated interferon for hepatitis C infection – two case reports. Ann Hepatol. 2013;12:629–633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Munteanu O., Chesov D., Rusu D., Lange C., Botnaru V. Pulmonary erythema migrans? Respiration. 2014;87:252–253. doi: 10.1159/000357323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Husain S.J., Irfan M., Zubairi A.S., Salahuddin N. Rapidly-progressive bronchiolitis obliterans organising pneumonia. Singapore Med J. 2004;45:283–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Kako S., Izutsu K., Oshima K., Sato H., Kanda Y., Motokura T., et al. Regression of the tumor after withdrawal of cyclosporine in relapsed extranodal natural killer/T cell lymphoma following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Am J Hematol. 2007;82:937–939. doi: 10.1002/ajh.20943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Cai M., Bonella F., Dai H., Sarria R., Guzman J., Costabel U. Macrolides inhibit cytokine production by alveolar macrophages in bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia. Immunobiology. 2013;218:930–937. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2012.10.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Patriarca F., Skert C., Sperotto A., Damiani D., Cerno M., Geromin A., et al. Incidence, outcome, and risk factors of late-onset noninfectious pulmonary complications after unrelated donor stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2004;33:751–758. doi: 10.1038/sj.bmt.1704426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Lee P.C., Lin J.H., Lin C.H., Chien S.T., Hsu J.Y., Feng N.H. Spontaneous pneumothorax after steroid treatment in a patient with bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia. J Formos Med Assoc. 2005;104:190–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Kobayashi I., Yamada M., Takahashi Y., Kawamura N., Okano M., Sakiyama Y., et al. Interstitial lung disease associated with juvenile dermatomyositis: clinical features and efficacy of cyclosporin A. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2003;42:371–374. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keg040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Ishii T., Manabe A., Ebihara Y., Ueda T., Yoshino H., Mitsui T., et al. Improvement in bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia in a child after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation by a combination of oral prednisolone and low dose erythromycin. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2000;26:907–910. doi: 10.1038/sj.bmt.1702642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Majeski E.I., Paintlia M.K., Lopez A.D., Harley R.A., London S.D., London L. Respiratory reovirus 1/L induction of intraluminal fibrosis, a model of bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia, is dependent on T lymphocytes. Am J Pathol. 2003;163:1467–1479. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63504-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Barroso E., Hernandez L., Gil J., Garcia R., Aranda I., Romero S. Idiopathic organizing pneumonia: a relapsing disease. 19 years of experience in a hospital setting. Respiration. 2007;74:624–631. doi: 10.1159/000103240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Yoo J.W., Song J.W., Jang S.J., Lee C.K., Kim M.Y., Lee H.K., et al. Comparison between cryptogenic organizing pneumonia and connective tissue disease-related organizing pneumonia. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2011;50:932–938. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keq410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Nishino M., Mathai S.K., Schoenfeld D., Digumarthy S.R., Kradin R.L. Clinicopathologic features associated with relapse in cryptogenic organizing pneumonia. Human Pathol. 2014;45:342–351. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2013.09.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Onishi Y., Kawamura T., Nakahara Y., Kagami R., Sasaki S., Takahashi S., et al. Factors associated with the relapse of cryptogenic and secondary organizing pneumonia. Respir Invest. 2017;55:10–15. doi: 10.1016/j.resinv.2016.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Saito Z., Kaneko Y., Hasegawa T., Yoshida M., Odashima K., Horikiri T., et al. Predictive factors for relapse of cryptogenic organizing pneumonia. BMC Pulm Med. 2019;19:10. doi: 10.1186/s12890-018-0764-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Zhou Y., Wang L., Huang M., Ding J., Jiang H., Zhou K., et al. A long-term retrospective study of patients with biopsy-proven cryptogenic organizing pneumonia. Chron Respir Dis. 2019;16 doi: 10.1177/1479973119853829. 1479973119853829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Zhang Y., Li N., Li Q., Zhou Y., Zhang F., Chen T., et al. Analysis of the clinical characteristics of 176 patients with pathologically confirmed cryptogenic organizing pneumonia. Ann Transl Med. 2020;8:763. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-4490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Drakopanagiotakis F., Polychronopoulos V., Judson M.A. Organizing pneumonia. Am J Med Sci. 2008;335:34–39. doi: 10.1097/MAJ.0b013e31815d829d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.King T.E., Jr., Mortenson R.L. Cryptogenic organizing pneumonitis. The North American experience. Chest. 1992;102:8S–13S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Epler G.R. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia. Arch Int Med. 2001;161:158–164. doi: 10.1001/archinte.161.2.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Wells A.U. Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;22:449–460. doi: 10.1055/s-2001-17387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.