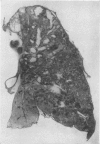
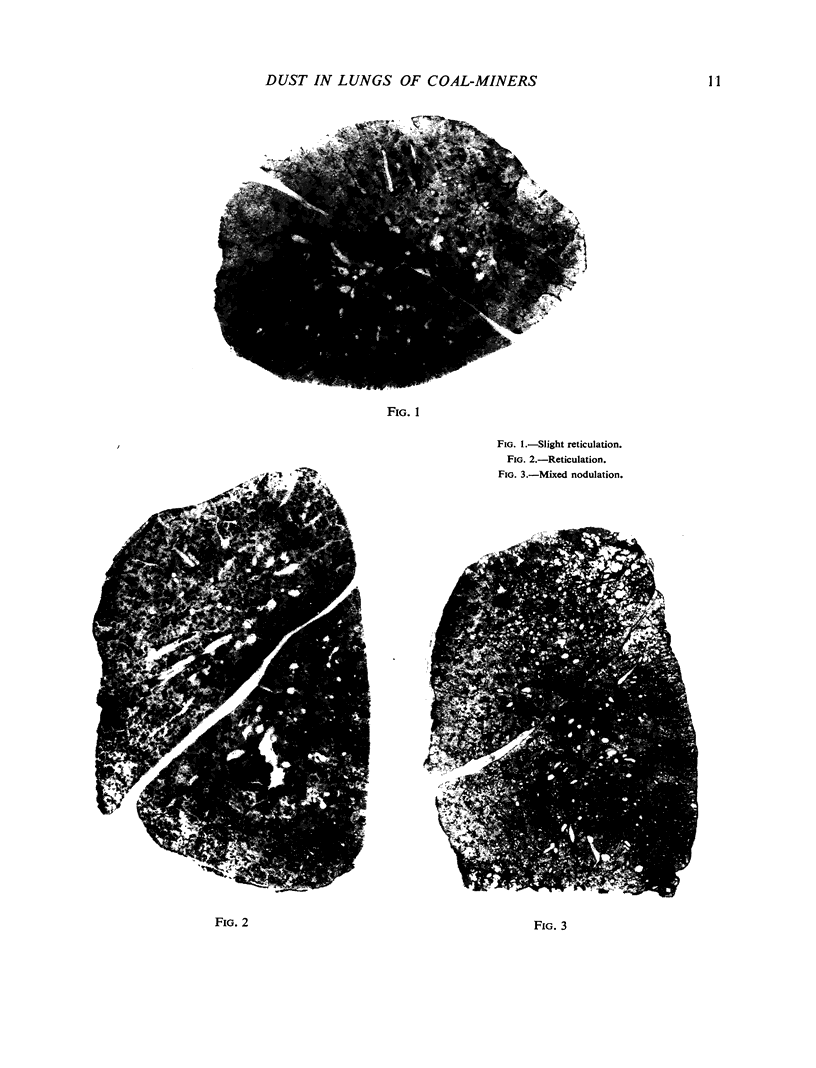
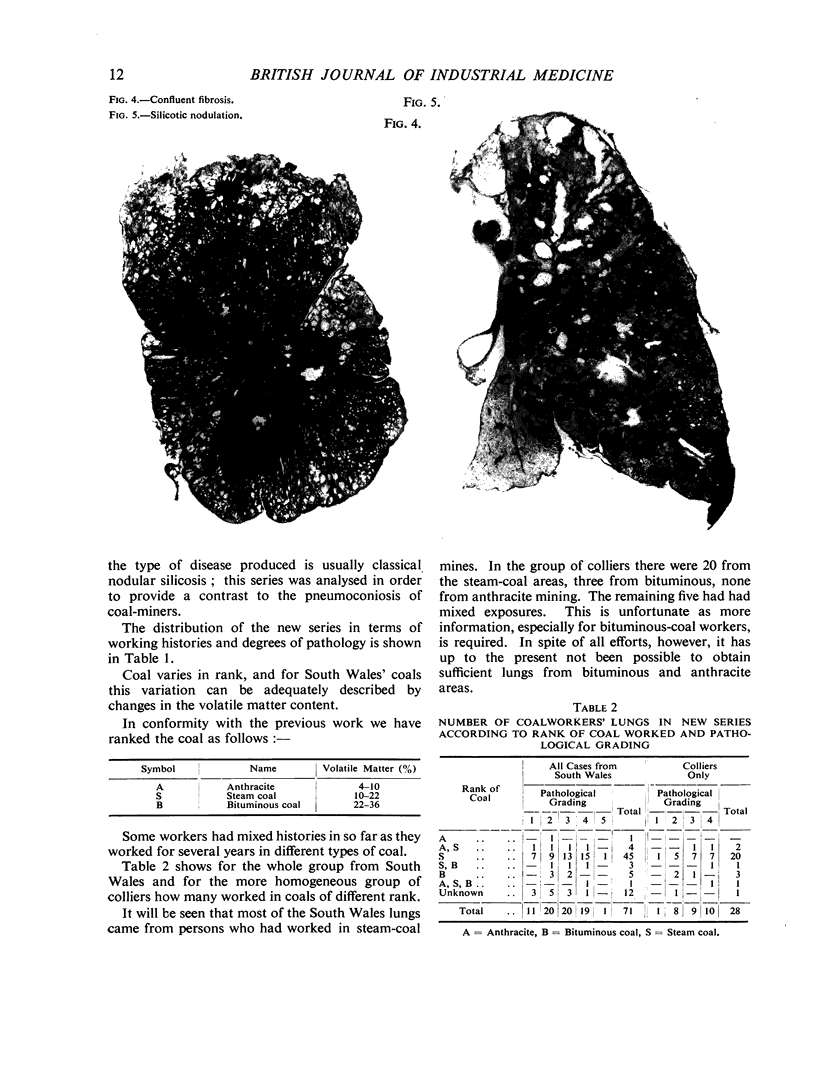
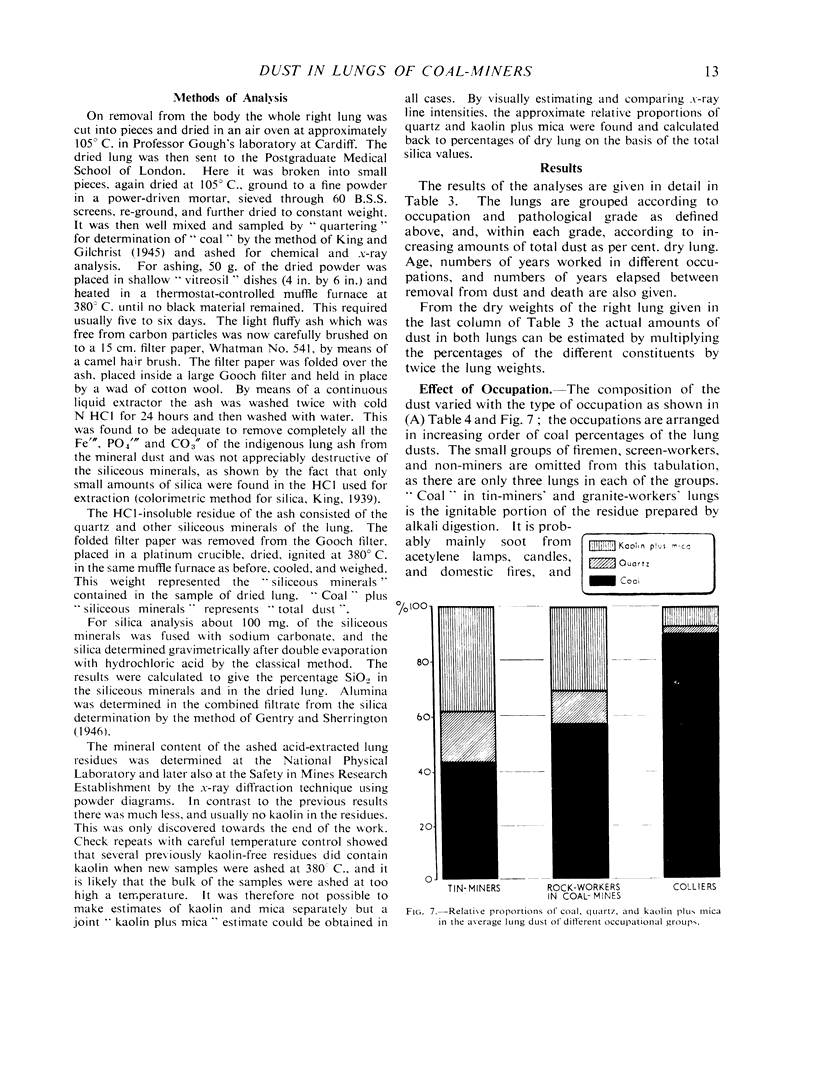
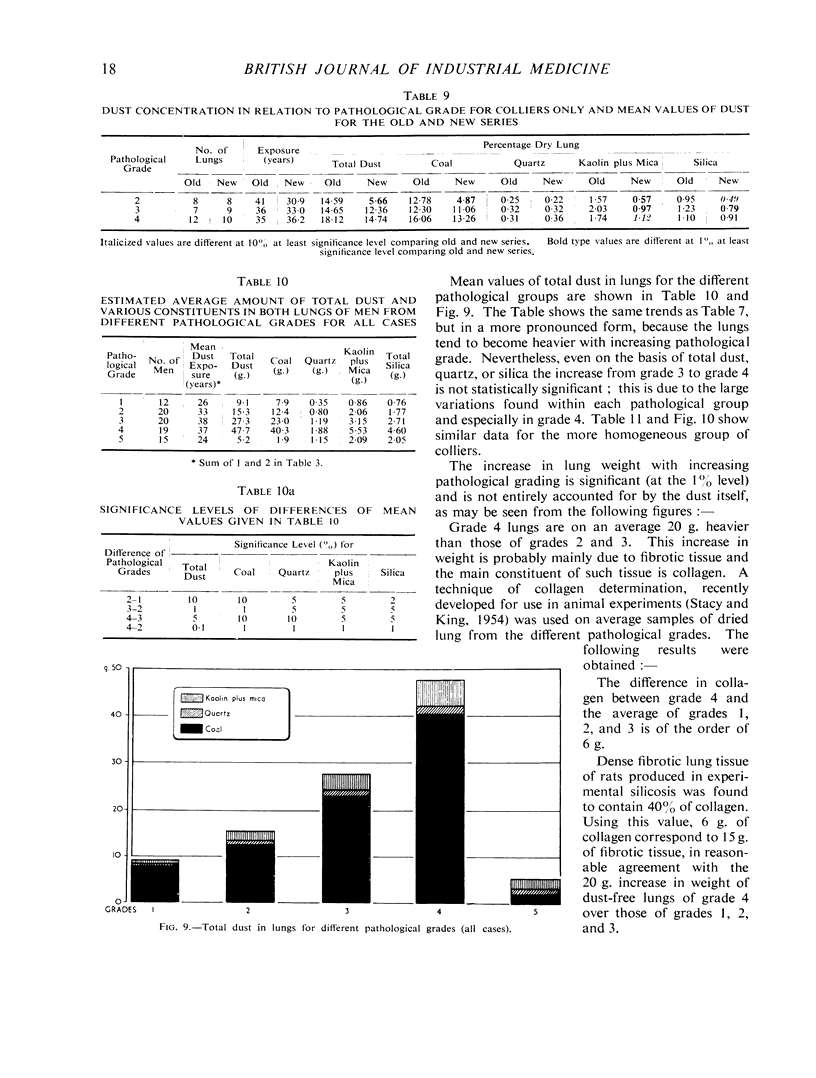
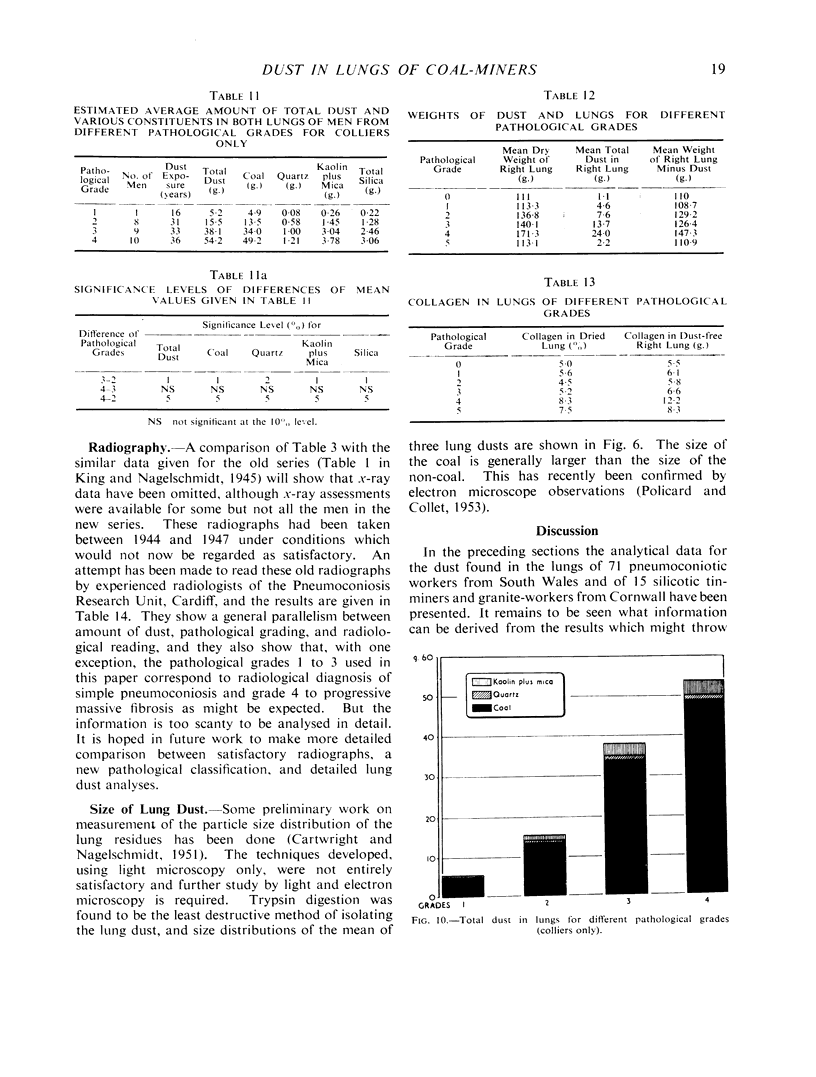
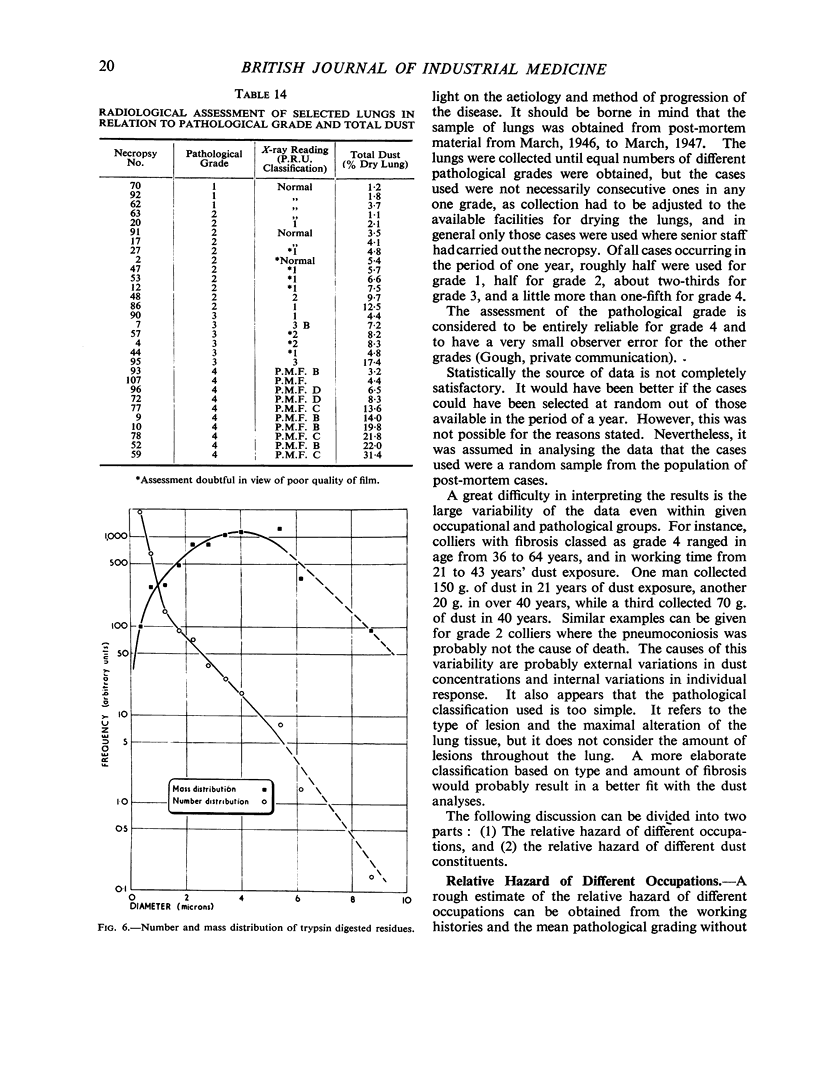
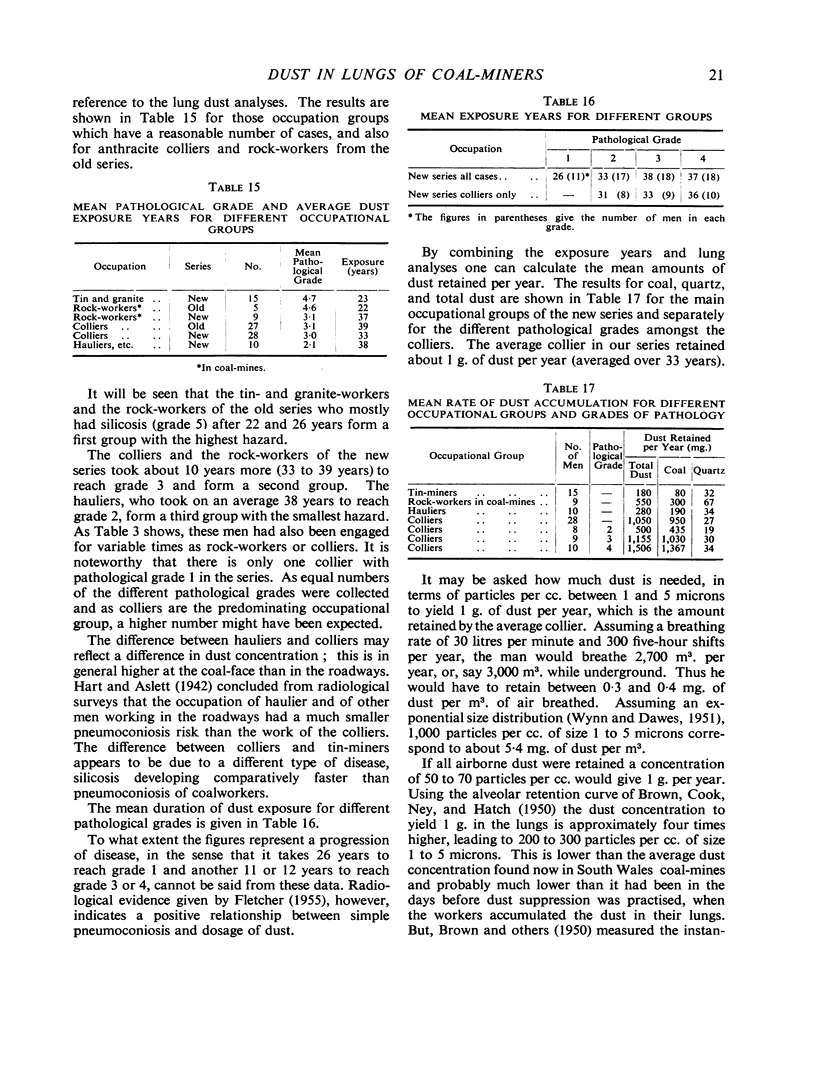
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLACKLOCK J. W., KENNAWAY E. L., LEWIS G. M., URQUHART M. E. The carbon content of human lungs and bronchial glands. Br J Cancer. 1954 Mar;8(1):40–55. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1954.4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. H., Cook K. M., Ney F. G., Hatch T. Influence of Particle Size upon the Retention of Particulate Matter in the Human Lung. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1950 Apr;40(4):450–480. doi: 10.2105/ajph.40.4.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COCHRANE A. L., DAVIES I., FLETCHER C. M. "Entente radiologique": a step towards international agreement on the classification of radiographs in pneumoconiosis. Br J Ind Med. 1951 Oct;8(4):244–255. doi: 10.1136/oem.8.4.244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COCHRANE A. L. Tuberculosis and coalworkers' pneumoconiosis. Br J Tuberc Dis Chest. 1954 Oct;48(4):274–285. doi: 10.1016/s0366-0869(54)80127-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEPPLESTON A. G. Coal workers' pneumoconiosis; pathological and etiological considerations. AMA Arch Ind Hyg Occup Med. 1951 Sep;4(3):270–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAMES W. R. The relationship of tuberculosis to the development of massive pneumokoniosis in coal workers. Br J Tuberc Dis Chest. 1954 Apr;48(2):89–96. doi: 10.1016/s0366-0869(54)80062-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King E. J. The biochemistry of silicic acid: The determination of silica. Biochem J. 1939 Jun;33(6):944–954. doi: 10.1042/bj0330944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLICARD A., COLLET A. Le problème des poussières ultra-fines et son importance en pathologie industrielle. Arch Mal Prof. 1953;14(4):337–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAY S. C., KING E. J., HARRISON C. V. The action of variable amounts of quartz on the lungs of rats; the extent of pathological change in relation to the amount injected. Br J Ind Med. 1951 Apr;8(2):62–67. doi: 10.1136/oem.8.2.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUTTNER J. R., BOVET P., AUFDERMAUR M. Graphit, carborund, Staublunge. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1952 Nov 7;77(45):1413–1415. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1117258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STACY B. D., KING E. J. Silica and collagen in the lungs of silicotic rats treated with cortisone. Br J Ind Med. 1954 Jul;11(3):192–197. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]