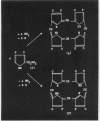
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASKEVOLD R. Routine analysis of porphyrines in urine. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1951;3(4):318–319. doi: 10.3109/00365515109060622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASKEVOLD R. Routine analysis of porphyrines in urine. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1951;3(4):318–319. doi: 10.3109/00365515109060622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHU T. C., SISTER A A GREEN, CHU E. J. Paper chromatography of methyl esters of porphyrins. J Biol Chem. 1951 Jun;190(2):643–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COMFORT A., MOORE H., WEATHERALL M. Normal human urinary porphyrins. Biochem J. 1954 Oct;58(2):177–182. doi: 10.1042/bj0580177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOKSON G. H., RIMINGTON C. Porphobilinogen. Biochem J. 1954 Jul;57(3):476–484. doi: 10.1042/bj0570476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERIKSEN L. A coproporphyrin excreted in normal and pathological urine. Nature. 1951 Apr 28;167(4252):691–691. doi: 10.1038/167691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERIKSEN L. The extraction of the urinary coproporphyrin chromogen and the conversion of the chromogen to porphyrin. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1952;4(1):55–62. doi: 10.3109/00365515209060633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FALK J. E., DRESEL E. I., BENSON A., KNIGHT B. C. Studies on the biosynthesis of blood pigments. 4. The nature of the porphyrins formed on incubation of chicken erythrocyte preparations with glycine, delta-aminolaevulic acid or porphobilinogen. Biochem J. 1956 May;63(1):87–94. doi: 10.1042/bj0630087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBERG A. Fate of porphobilinogen, administered enterally or parenterally, in the rat. Biochem J. 1955 Jan;59(1):37–44. doi: 10.1042/bj0590037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFFBAUER F. W., WATSON C. J., SCHWARTZ S. Urinary and fecal coproporphyrin excretion in rats. III. Excretion of injected coproporphyrin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Jun;83(2):238–242. doi: 10.3181/00379727-83-20318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jope E. M., O'brien J. R. Spectral absorption and fluorescence of coproporphyrin isomers I and III and the melting-points of their methyl esters. Biochem J. 1945;39(3):239–244. doi: 10.1042/bj0390239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENCH J. E., LANE R. E., VARLEY H. Urinary coproporphyrins in lead poisoning. Br J Ind Med. 1952 Apr;9(2):133–137. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICHOLAS R. E. H., RIMINGTON C. Paper chromatography of porphyrins; some hitherto unrecognized porphyrins and further notes on the method. Biochem J. 1951 Mar;48(3):306–309. doi: 10.1042/bj0480306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIMINGTON C., SVEINSSON S. L. The spectrophotometric determination of uroporphyrin. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1950;2(3):209–216. doi: 10.3109/00365515009049872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ S., ZIEVE L., WATSON C. J. An improved method for the determination of urinary coproporphyrin and an evaluation of factors influencing the analysis. J Lab Clin Med. 1951 Jun;37(6):843–859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON C. J., PIMENTA de MELLO R., SCHWARTZ S., HAWKINSON V. E., BOSSENMAIER I. Porphyrin chromogens or precursors in urine, blood, bile, and feces. J Lab Clin Med. 1951 Jun;37(6):831–842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON C. J., PIMENTA de MELLO R., SCHWARTZ S., HAWKINSON V. E., BOSSENMAIER I. Porphyrin chromogens or precursors in urine, blood, bile, and feces. J Lab Clin Med. 1951 Jun;37(6):831–842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEATHERALL M. The fate of intravenously administered coproporphyrin III in normal and lead-treated rabbits. Biochem J. 1952 Dec;52(4):683–690. doi: 10.1042/bj0520683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]