Abstract
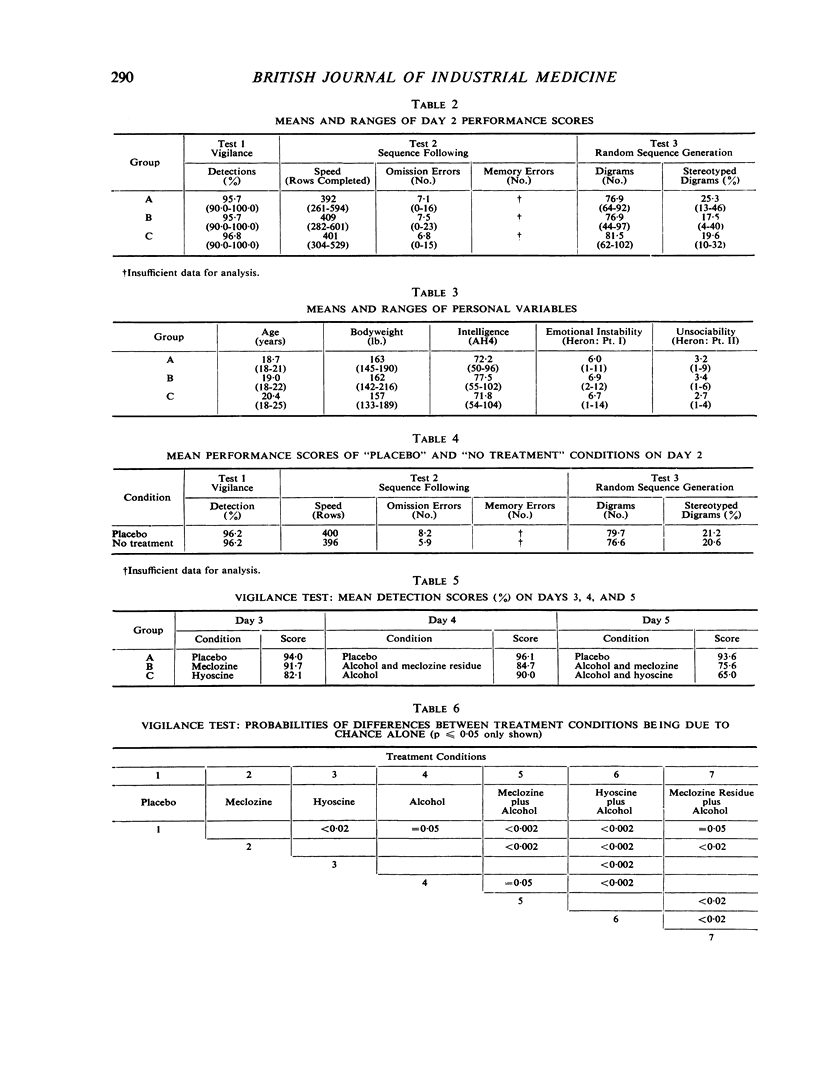
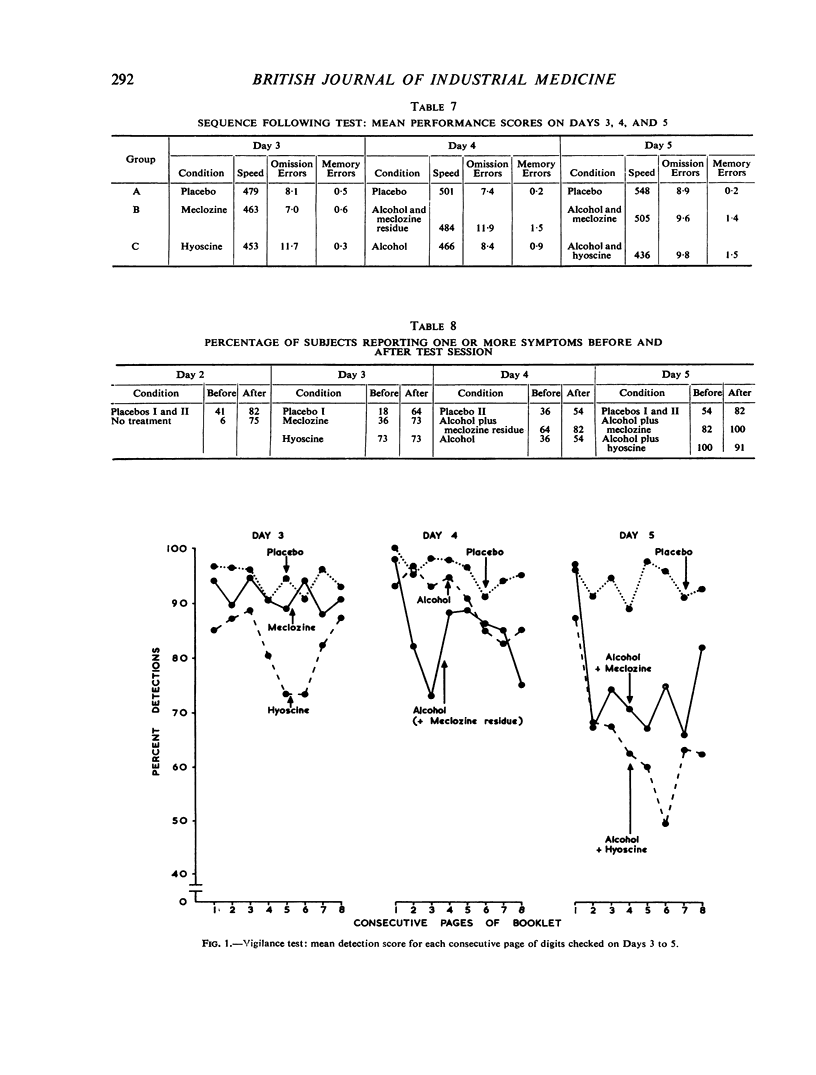
An investigation was made of the effects of 1 mg. hyoscine hydrobromide and of 50 mg. meclozine hydrochloride on the performance of tasks of vigilance and short-term memory. In further trials the effects of these drugs were measured after ingestion of 32 g. ethyl alcohol. Efficiency was impaired by hyoscine taken alone, but meclozine alone had no significant effect. The effect of hyoscine was substantially increased by the presence of alcohol and under these conditions the effect of meclozine was equally great. The vigilance task appeared to be more sensitive to the effects of the drugs than the memory task, and possible reasons for this are considered in the discussion.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROADBENT D. E., HERON A. Effects of a subsidiary task on performance involving immediate memory by younger and older men. Br J Psychol. 1962 May;53:189–198. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8295.1962.tb00825.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLASER E. M., McCANCE R. A. Effect of drugs on motion sickness produced by short exposures to artificial waves. Lancet. 1959 Apr 25;1(7078):853–856. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)91937-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLASER E. M. Prevention and treatment of motion sickness. Proc R Soc Med. 1959 Nov;52:965–972. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLASER E. M., WHITTOW G. C. Experimental errors in clinical trials. Clin Sci. 1954 May;13(2):199–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERON A. A two-part personality measure for use as a research criterion. Br J Psychol. 1956 Nov;47(4):243–251. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8295.1956.tb00586.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPPAUF W. E., POWE W. E. Performance decrement at an audio-visual checking task. J Exp Psychol. 1959 Jan;57(1):49–56. doi: 10.1037/h0043436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAYNE R. B., MOORE E. W. The effects of some analeptic and depressant drugs upon tracking behavior. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1955 Dec;115(4):480–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


