Abstract
A method of bio-assay of the fibrogenicity of respirable dust is described. Quartz, coal, and quartz-coal dust mixtures were administered to mice via the tail vein, and liver collagen was estimated chemically. Groups of mice that had received doses of 10, 15, and 20 mg. of these dusts were killed at intervals of 10, 20, and 30 weeks after injection.
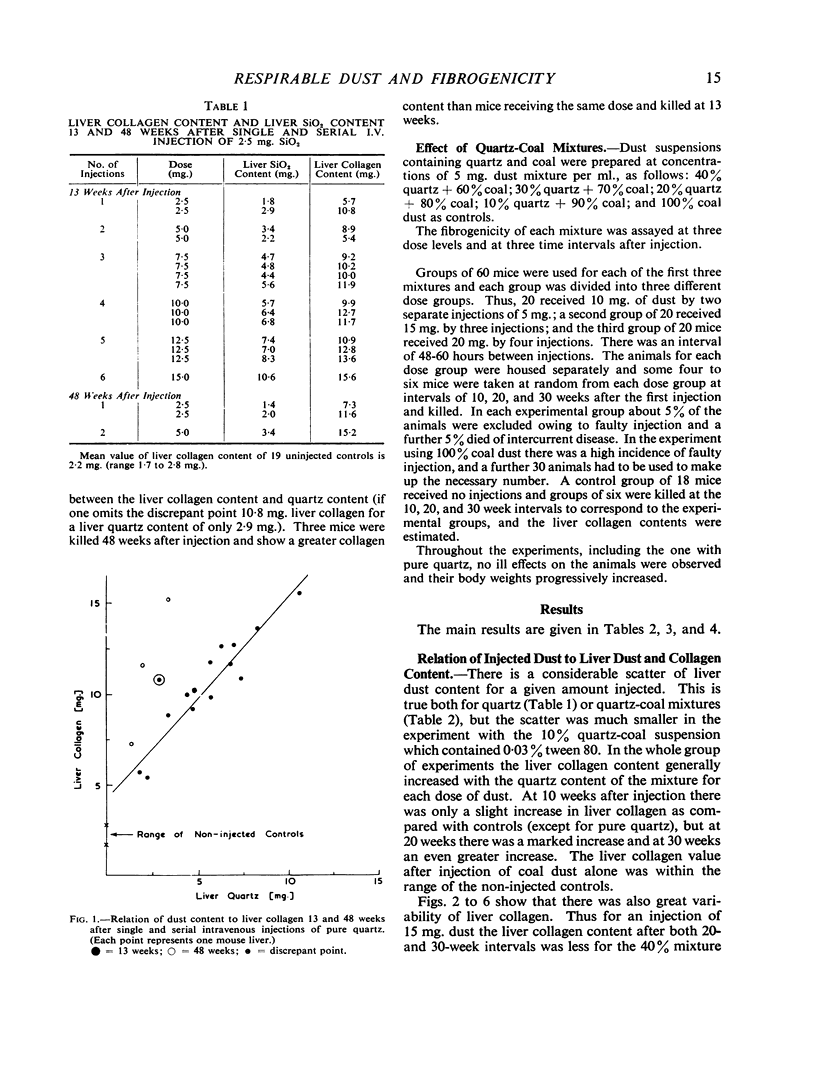
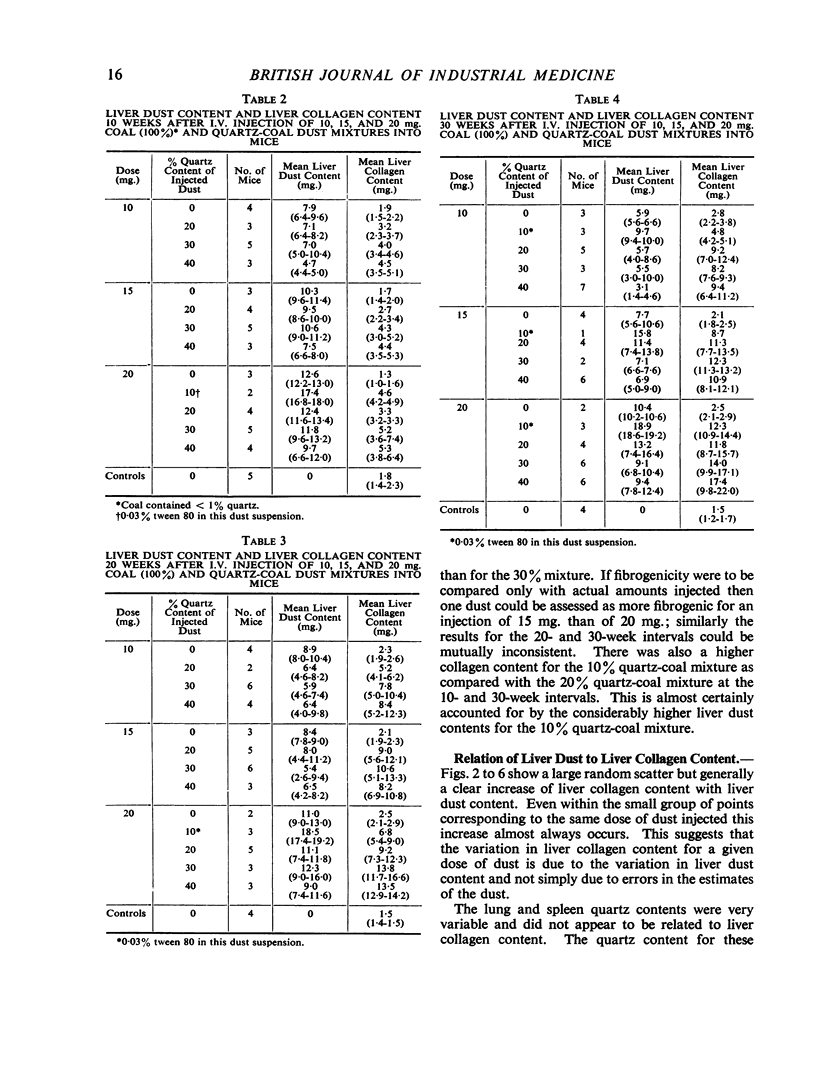
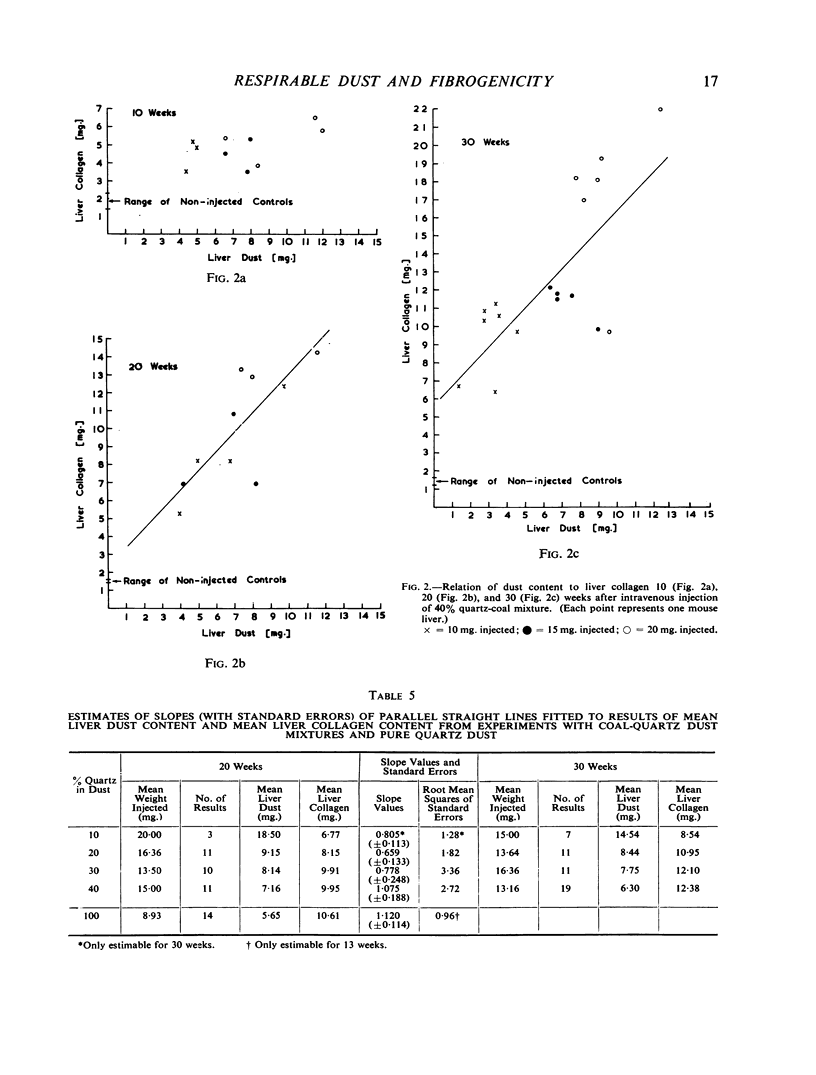
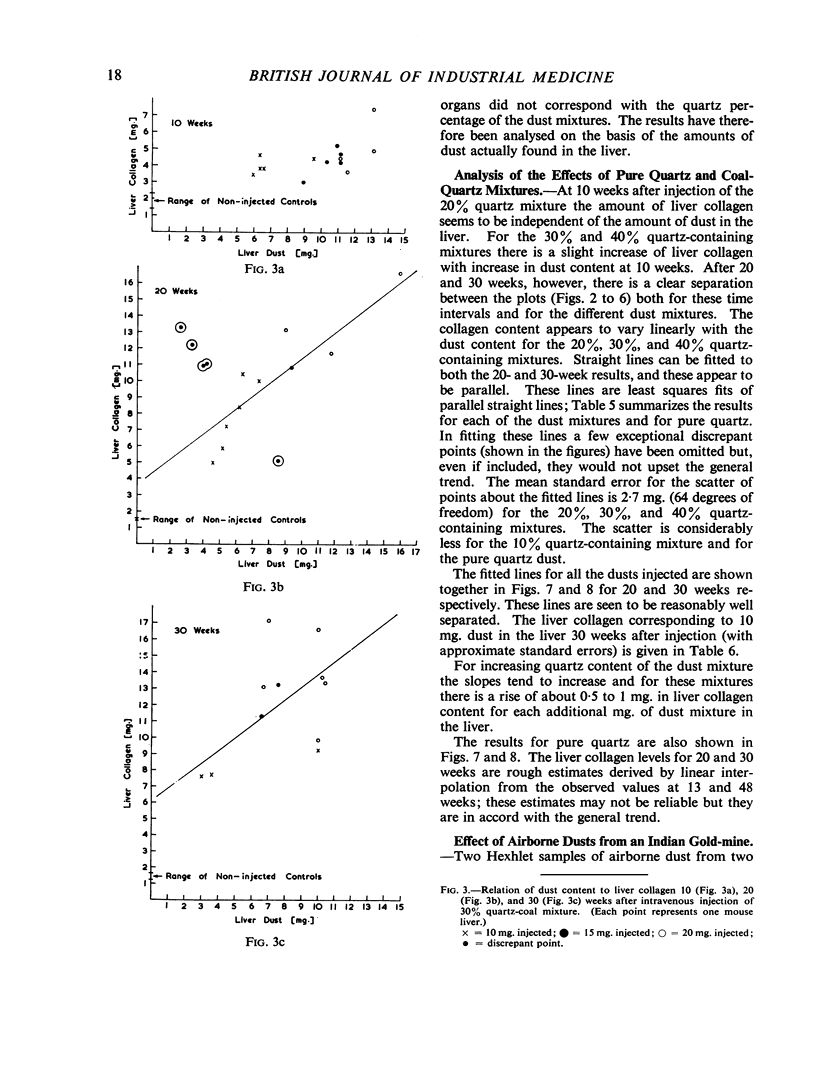
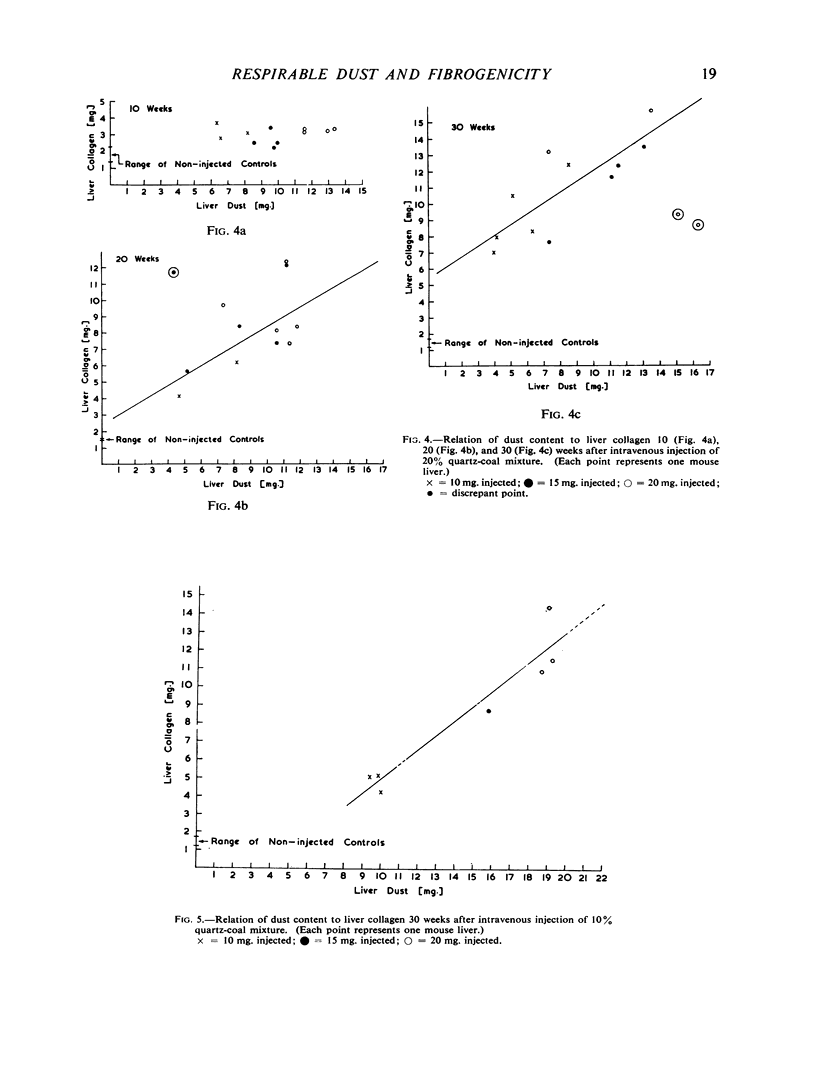
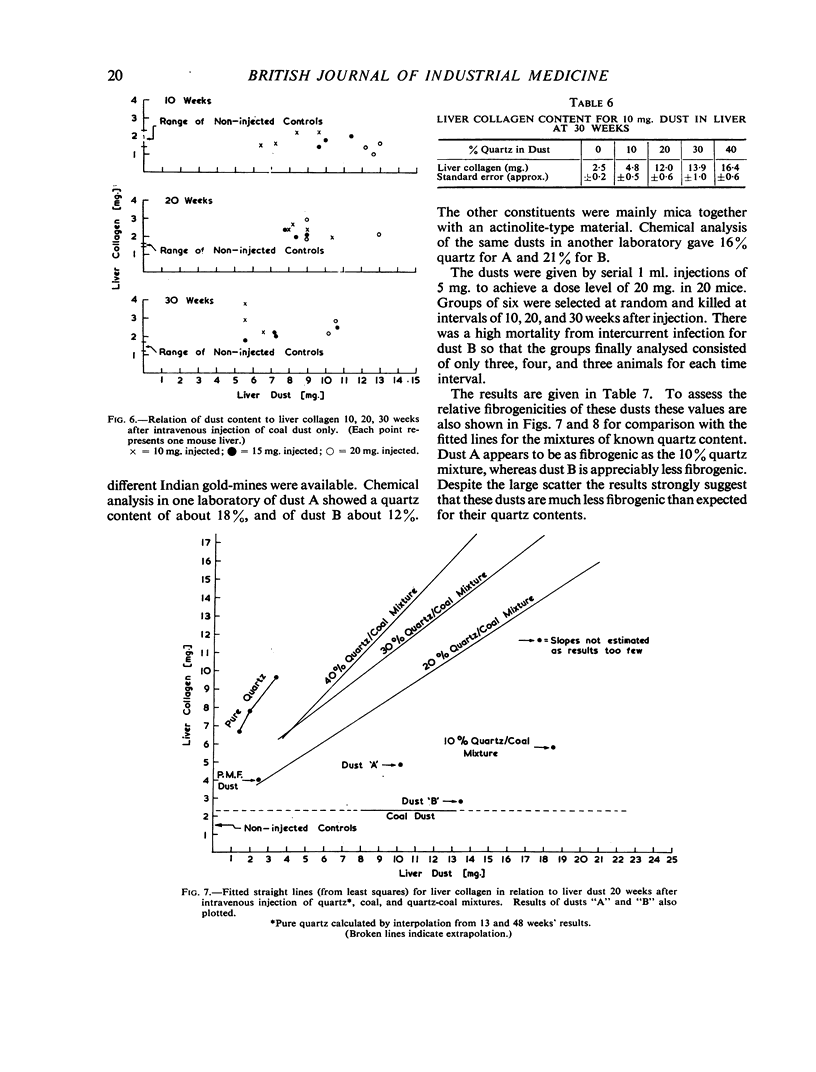
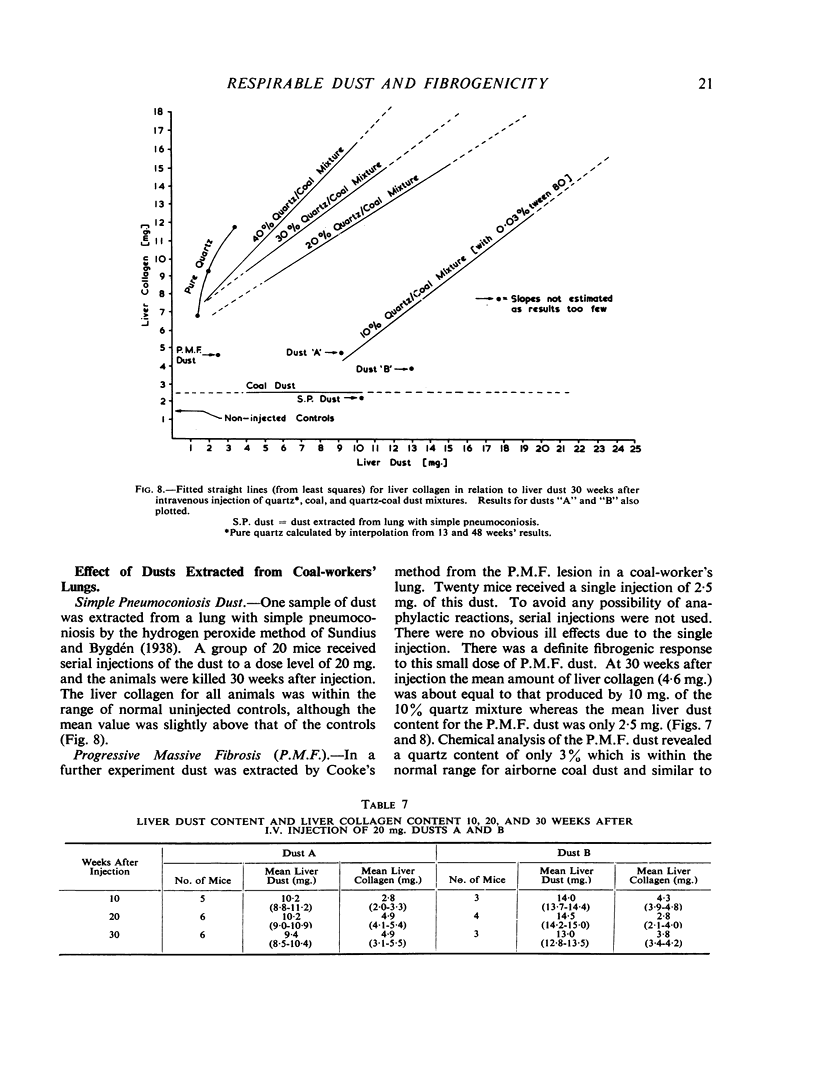
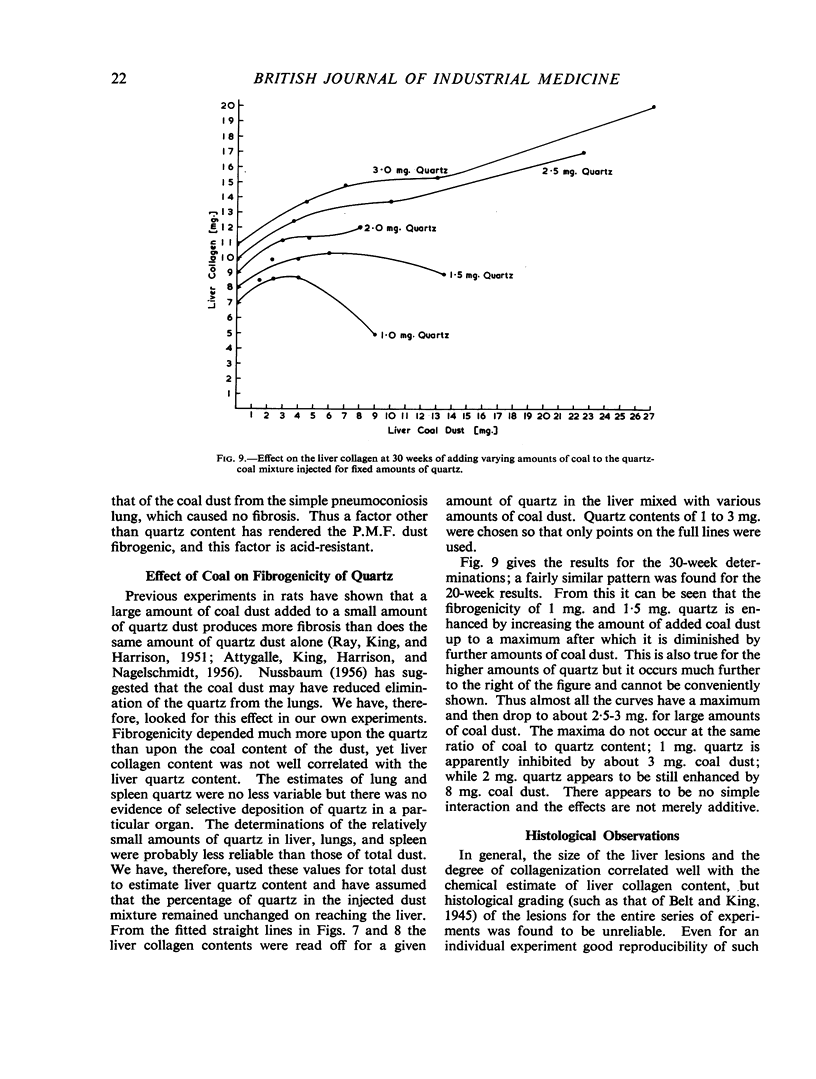
There was, in general, a linear relation between liver dust and collagen content, and a higher liver collagen the greater the quartz content of injected dust. At 30 weeks after injection there was good differentiation of the collagen response of liver to dust mixtures of different quartz content. These provide standard curves with which liver collagen response to any unknown dust can be compared. The fibrogenicity of two samples of respirable gold-mine dust was less than would be expected from the quartz content. Dust extracted from a region of massive fibrosis in a coal-miner's lung was more fibrogenic than dust from a lung with simple pneumoconiosis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATTYGALLE D., KING E. J., HARRISON C. V., NAGELSCHMIDT G. The action of variable amounts of tridymite, and of tridymite combined with coal, on the lungs of rats. Br J Ind Med. 1956 Jan;13(1):41–50. doi: 10.1136/oem.13.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOOM W. L. Disposition of dextran following intravenous injection. J Lab Clin Med. 1956 Jun;47(6):938–949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny J. J., Robson W. D., Irwin D. A. The Prevention of Silicosis by Metallic Aluminum : I. A Preliminary Report. Can Med Assoc J. 1937 Jul;37(1):1–11. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANDJEAN E., NICOD J. L., TURRIAN H. The fibrogenic action of quartz dusts; biological methods for their quantitative evaluation in rats. AMA Arch Ind Health. 1956 Nov;14(5):426–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLNER A., CORRELL J. W., LADD A. T. Sustained hyperlipemia induced in rabbits by means of intravenously injected surface-active agents. J Exp Med. 1951 Apr 1;93(4):373–384. doi: 10.1084/jem.93.4.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING E. J., HARRISON C. V., MOHANTY G. P., YOGANATHAN M. The effect of aluminium and of aluminium containing 5 per cent. of quartz in the lungs of rats. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1958 Apr;75(2):429–434. doi: 10.1002/path.1700750222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKS J., JAMES D. M. The measurement of dust toxicity in vitro. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1959 Apr;77(2):401–406. doi: 10.1002/path.1700770210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN C. J., AXELROD A. E. A modified method for determination of hydroxyproline. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Jul;83(3):461–462. doi: 10.3181/00379727-83-20386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEUMAN R. E., LOGAN M. A. The determination of hydroxyproline. J Biol Chem. 1950 May;184(1):299–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NUSSBAUM Réflexions sur la silicose dans les chantiers d'équipement hydroélectrique. Arch Mal Prof. 1956 Jul-Aug;17(4):350–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAY S. C., KING E. J., HARRISON C. V. The action of small amounts of quartz and larger amounts of coal and graphite on the lungs of rats. Br J Ind Med. 1951 Apr;8(2):68–73. doi: 10.1136/oem.8.2.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STACY B. D., KING E. J. Silica and collagen in the lungs of silicotic rats treated with cortisone. Br J Ind Med. 1954 Jul;11(3):192–197. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZAIDI S. H., KING E. J., HARRISON C. V., NAGELSCHMIDT G. Fibrogenic activity of different forms of free silica; the action of fused silica, quartz, cristobalite, and tridymite on the livers of mice. AMA Arch Ind Health. 1956 Feb;13(2):112–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


