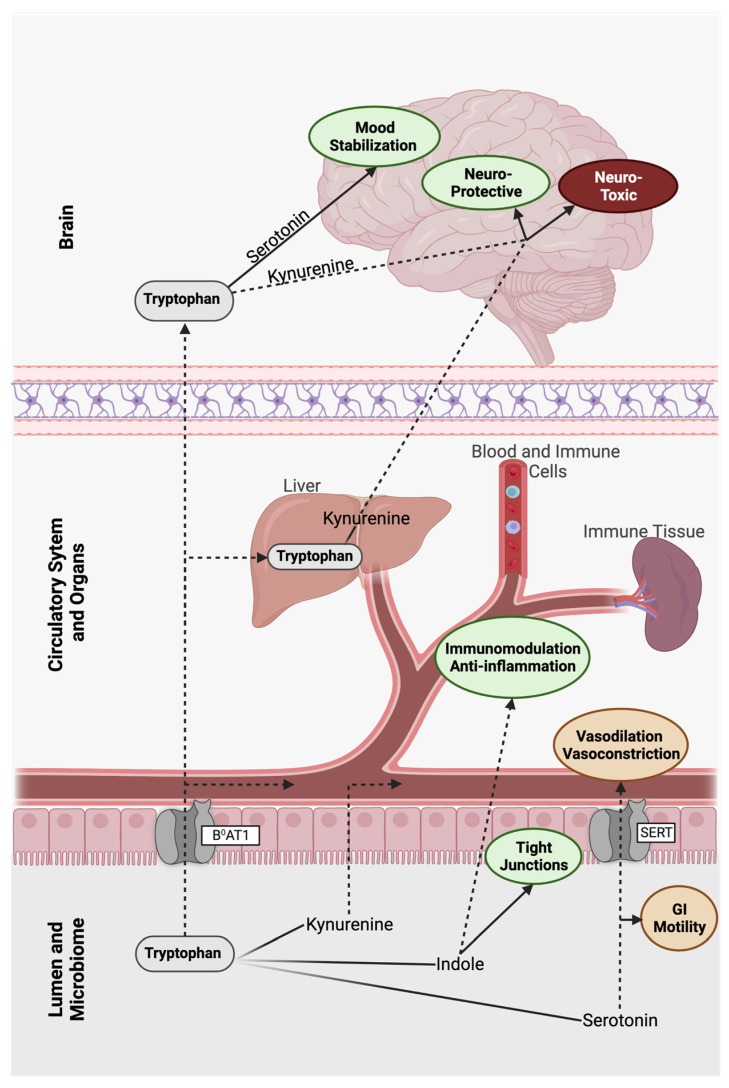
Figure 2.
The three major routes of tryptophan after ingestion, metabolism, and absorption in the human gut. Tryptophan can be absorbed into the blood stream and metabolized via the kynurenine pathway in the liver or via the serotonin or kynurenine pathway in the brain. Within the gut, tryptophan can also be funneled towards the kynurenine, indole, or serotonin pathway. These three metabolic pathways contain neuroactive metabolites that affect host physiology and neurology. Fading lines represent metabolism to a primary compound, dotted lines represent metabolism to secondary or downstream metabolites, green text ovals represent positive effects, red ovals represent negative effects, and orange ovals represent neutral outcomes.