Abstract
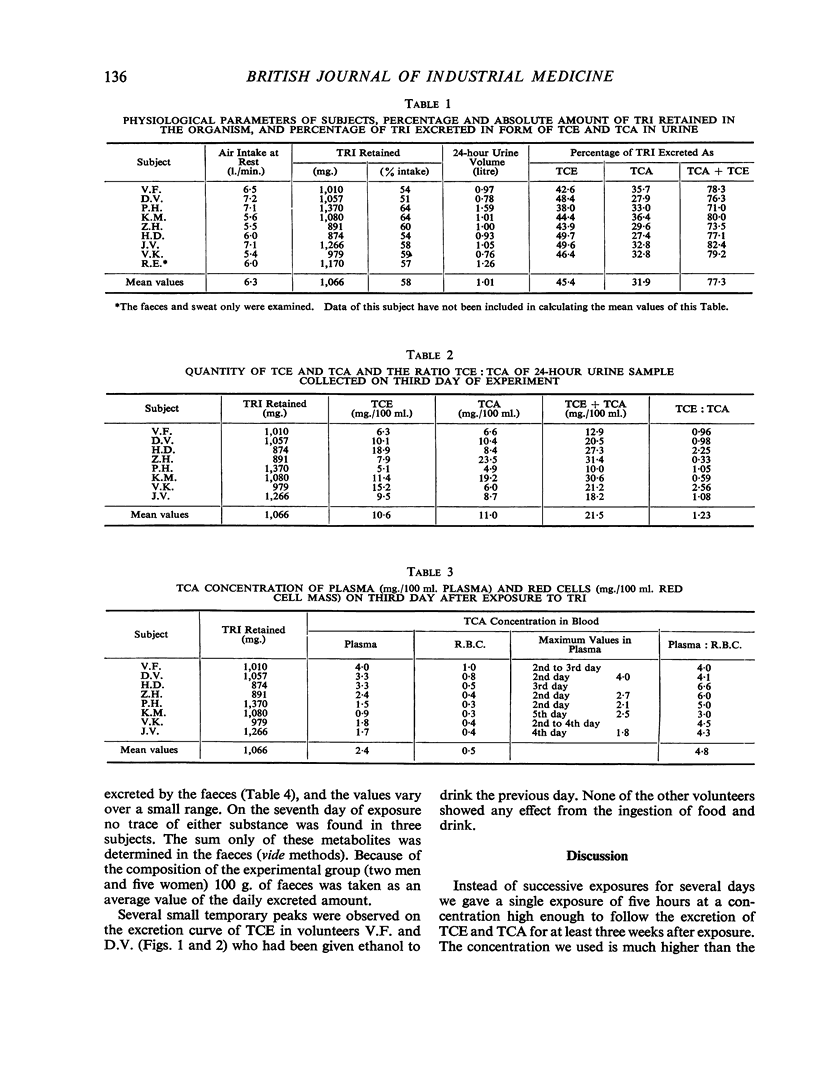
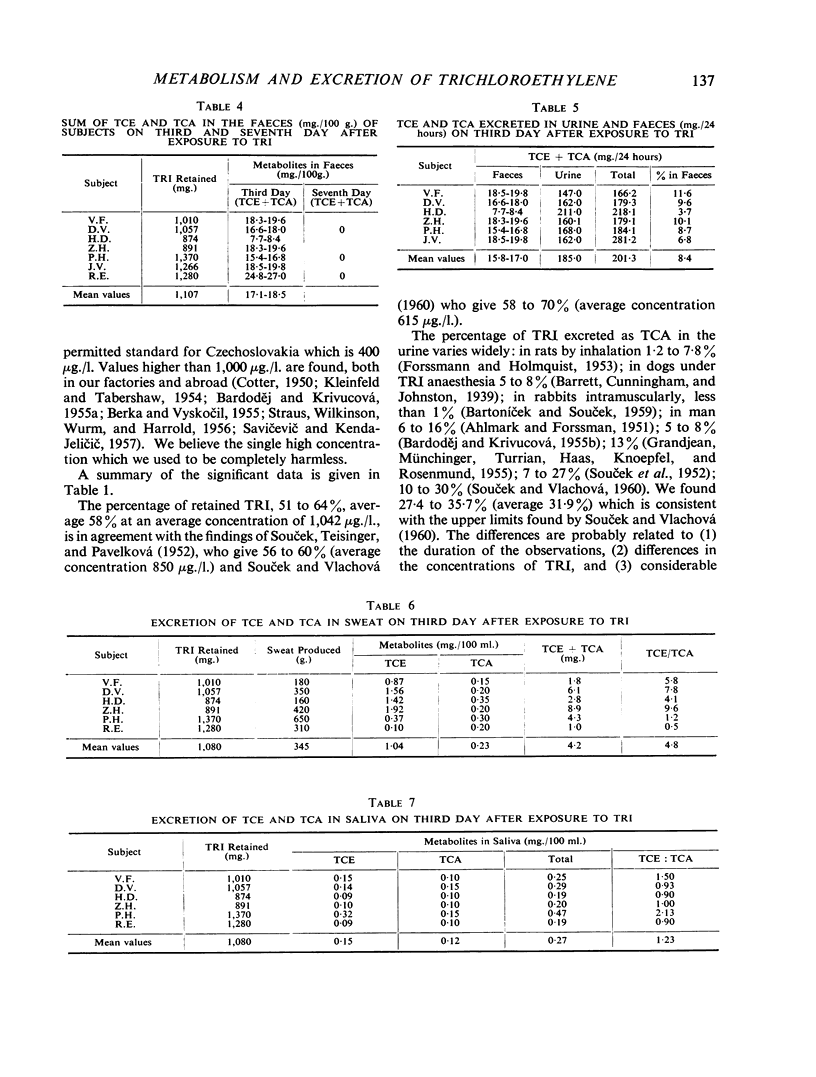
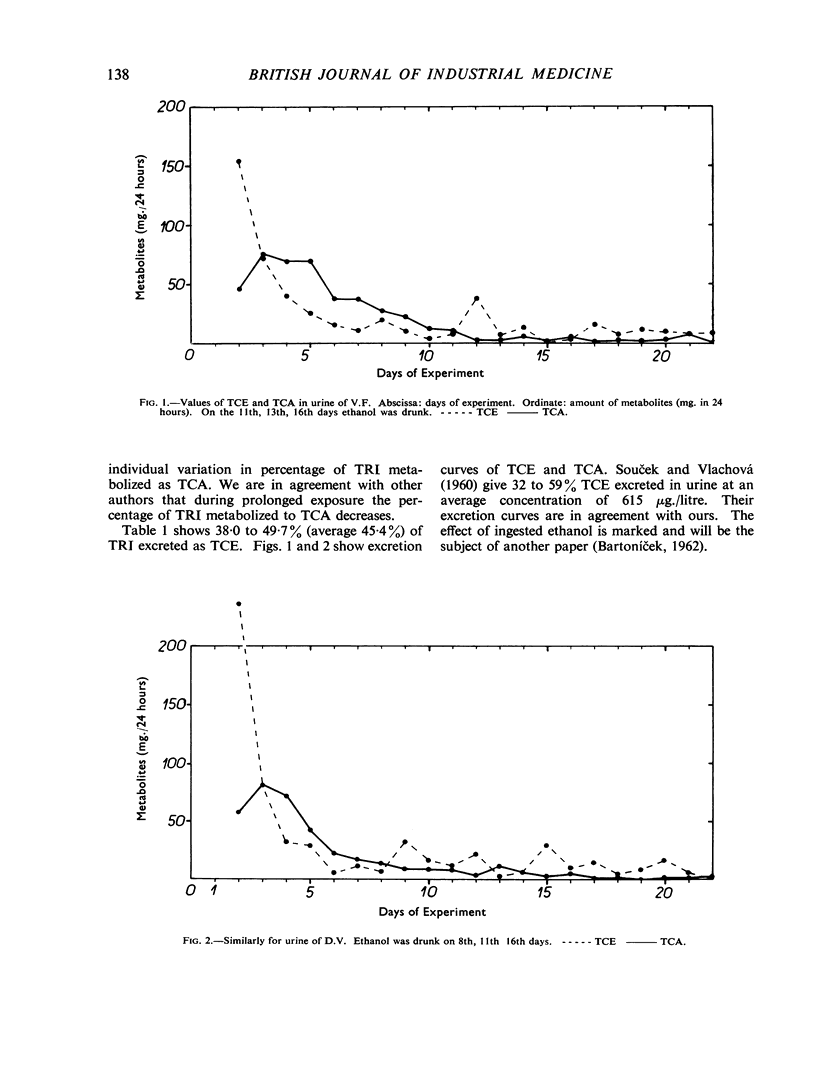
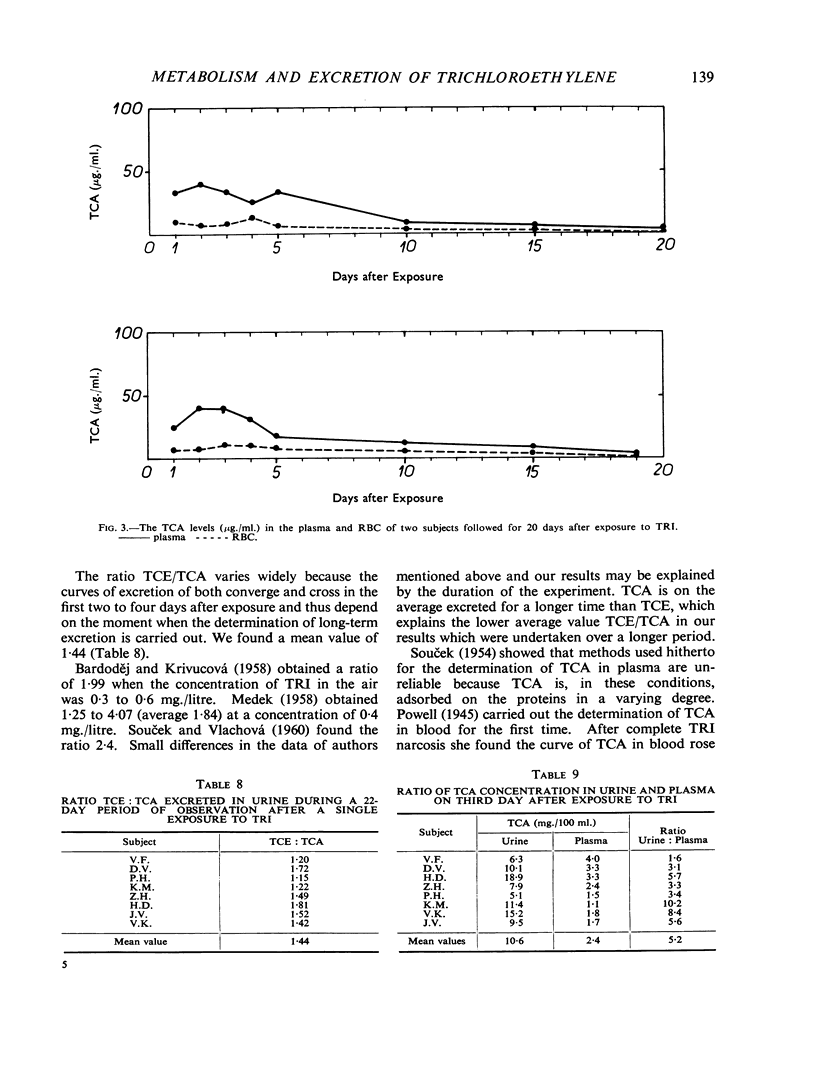
Eight volunteers were exposed to trichloroethylene vapour (1,042 μg./l.) for five hours; 51 to 64% of the inhaled trichloroethylene was retained. The concentration of trichloroethanol and trichloroacetic acid in the urine was studied daily for a three-week period; on the third day both metabolites were determined in faeces, sweat, and saliva. The concentration of trichloroacetic acid in plasma and red blood cells was studied on alternate days. Of the trichloroethylene retained, 38·0 to 49·7% was excreted in the urine as trichloroethanol and 27·4 to 35·7% as trichloroacetic acid. Of both metabolites 8·4% was excreted in the faeces. Sweat collected on the third day of the experiment contained 0·10 to 1·92 mg./100 ml. trichloroethanol and 0·15 to 0·35 mg./100 ml. trichloroacetic acid. In saliva the concentrations were 0·09 to 0·32 mg./100 ml. trichloroethanol and 0·10 to 0·15 mg./100 ml. trichloroacetic acid. The value of the expression trichloroethanol/trichloroacetic acid calculated in the urine within 22 days was within the range 1·15 to 1·81.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COTTER L. H. Trichloroethylene poisoning. Arch Ind Hyg Occup Med. 1950 Mar;1(3):319–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORSSMANN S., HOLMQUIST C. E. The relation between inhaled and exhaled trichlorethylene and trichloracetic acid excreted in the urine of rats exposed to trichlorethylene. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1953;9(3):235–244. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1953.tb02950.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANDJEAN E., MUNCHINGER R., TURRIAN V., HASS P. A., KNOEPFEL H. K., ROSENMUND H. Investigations into the effects of exposure to trichlorethylene in mechanical engineering. Br J Ind Med. 1955 Apr;12(2):131–142. doi: 10.1136/oem.12.2.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OWENS A. H., Jr, MARSHALL E. K., Jr Further studies on the metabolic fate of chloral hydrate and trichloroethanol. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1955 Oct;97(4):320–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRAUS R., WILKINSON A., WURM M., HARROLD B. D. Mass trichlorethylene intoxication masked as isoamyl alcohol intoxication. Ind Med Surg. 1956 Apr;25(4):151–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VLACHOVA D. An easy method for the determination of trichlorethanol in the urine after exposure of trichlorethylene. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1957;1(2):225–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


