Abstract
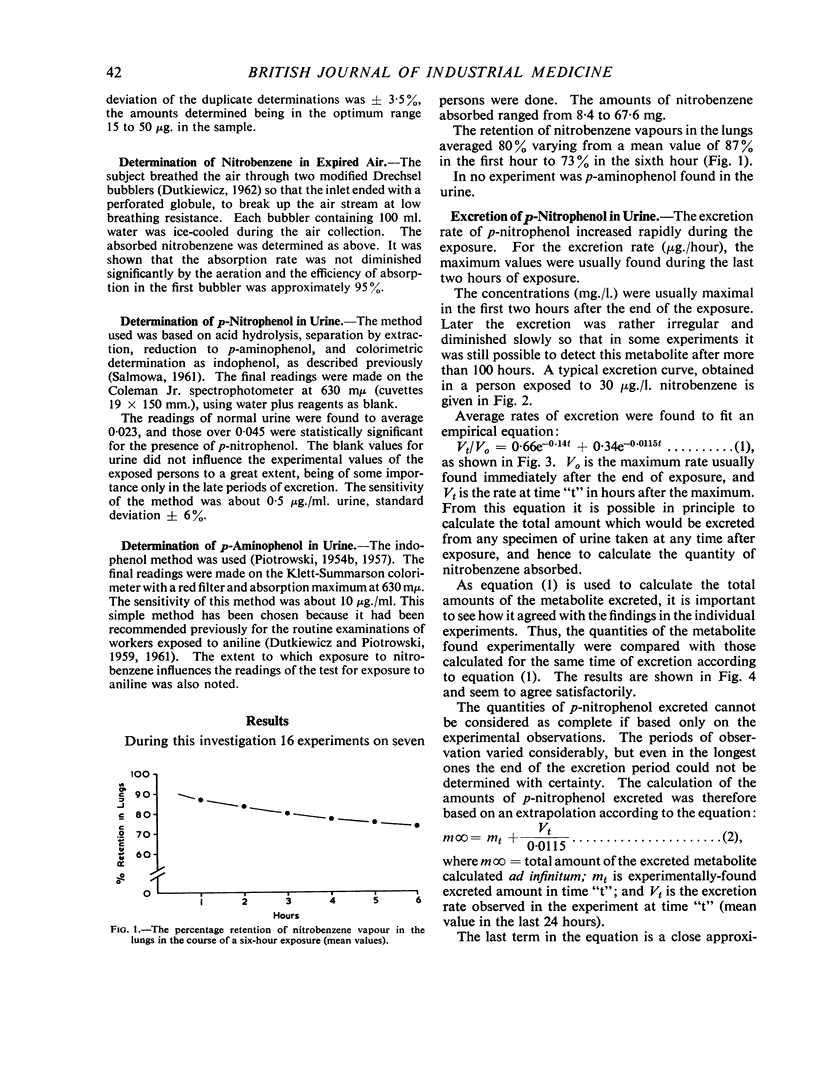
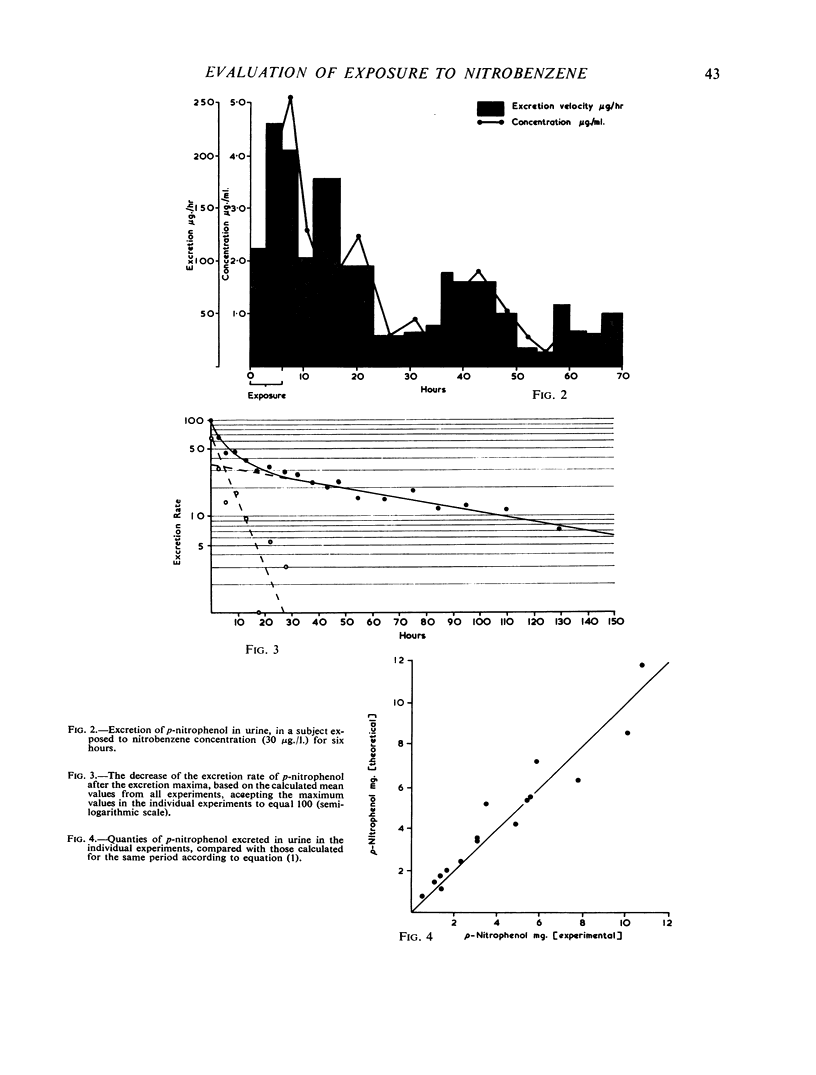
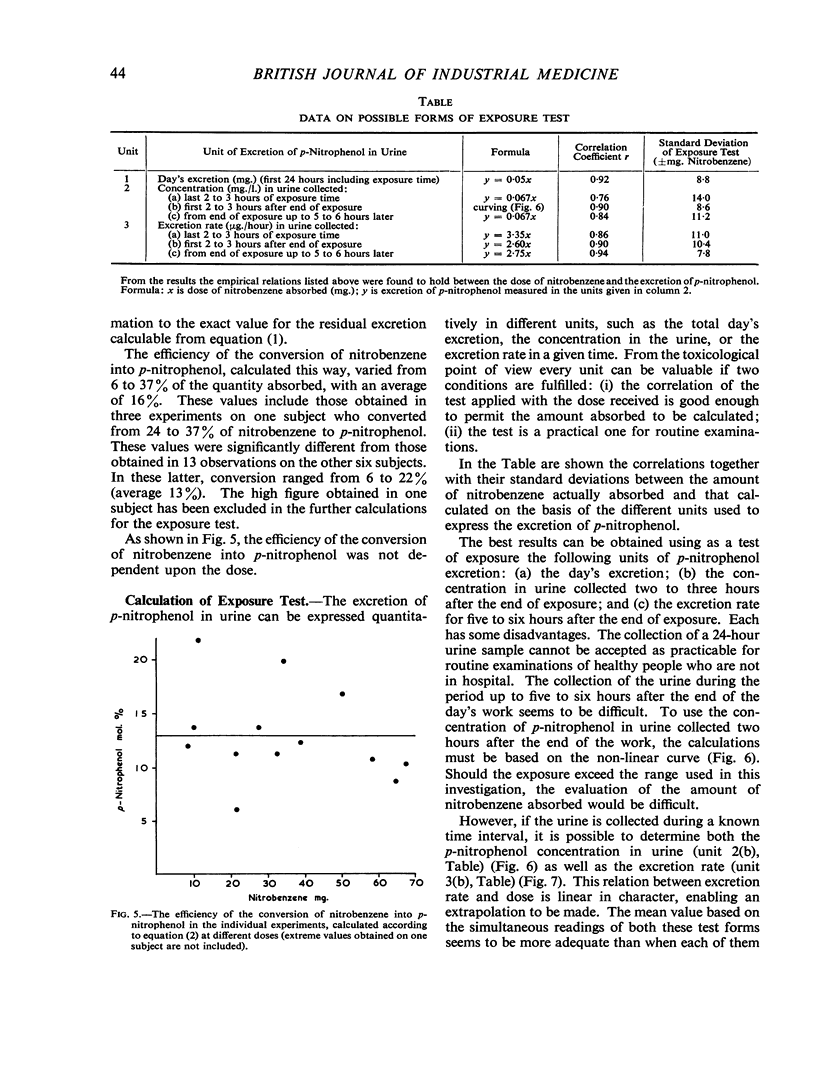
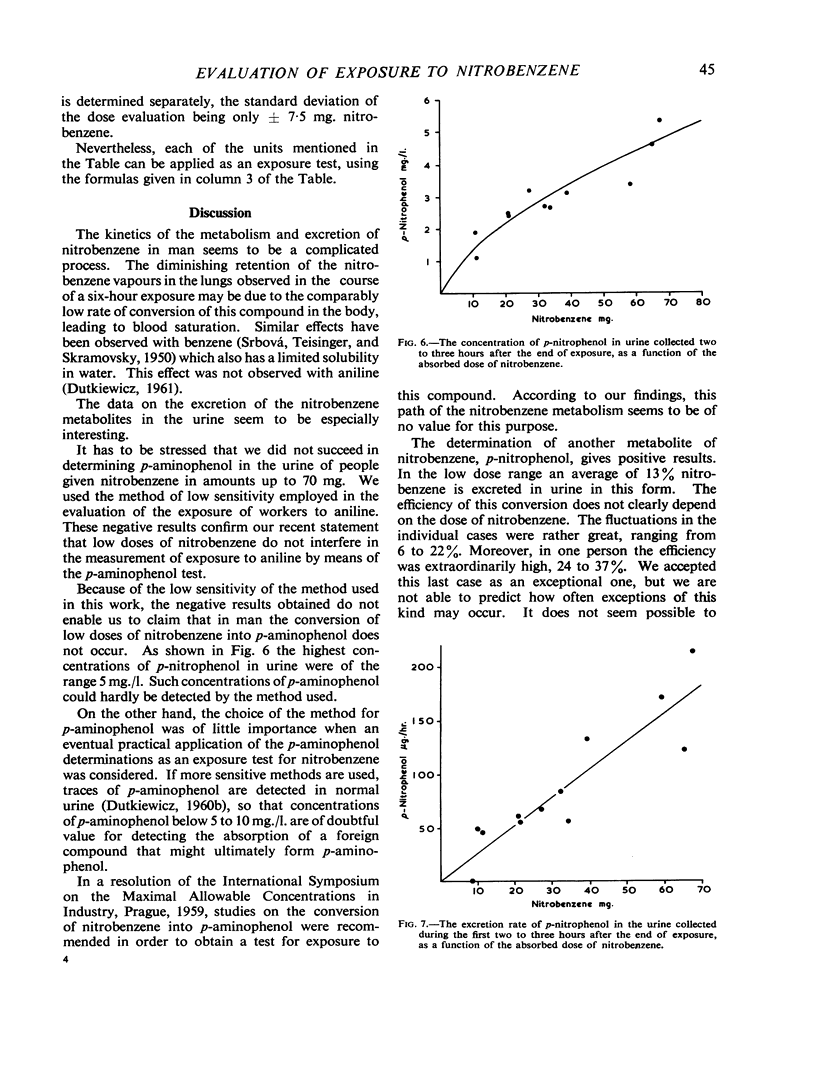
In order to obtain a quantitative test for measuring exposure to nitrobenzene, experiments on men were done, in which nitrobenzene vapours (5 to 30 μg./l.) were absorbed into the lungs only. During an exposure of six hours the retention of nitrobenzene in the lungs diminished from approximately 87 to 73%. p-Aminophenol was not detected in the urine by the method used. Another metabolite, p-nitrophenol, was estimated in the urine of the exposed subjects; the quantities present represented about 13% of the inhaled dose of nitrobenzene. It was found that the determination of p-nitrophenol in urine could be used as a quantitative test when a single exposure to nitrobenzene occurred with a precision of approximately ± 8 mg. nitrobenzene. p-Nitrophenol is excreted in urine very slowly and therefore it may accumulate in the body. To evaluate the results of the proposed test in the case of a repeated exposure further investigations are necessary.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- PIOTROWSKI J. Próby zastosowania biochemicznych wskaźników wchłaniania aniliny, nitrobenzenu i benzenu u pracowników przemysłu barwnikarskiego. Med Pr. 1954;5(4):299–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


