Abstract
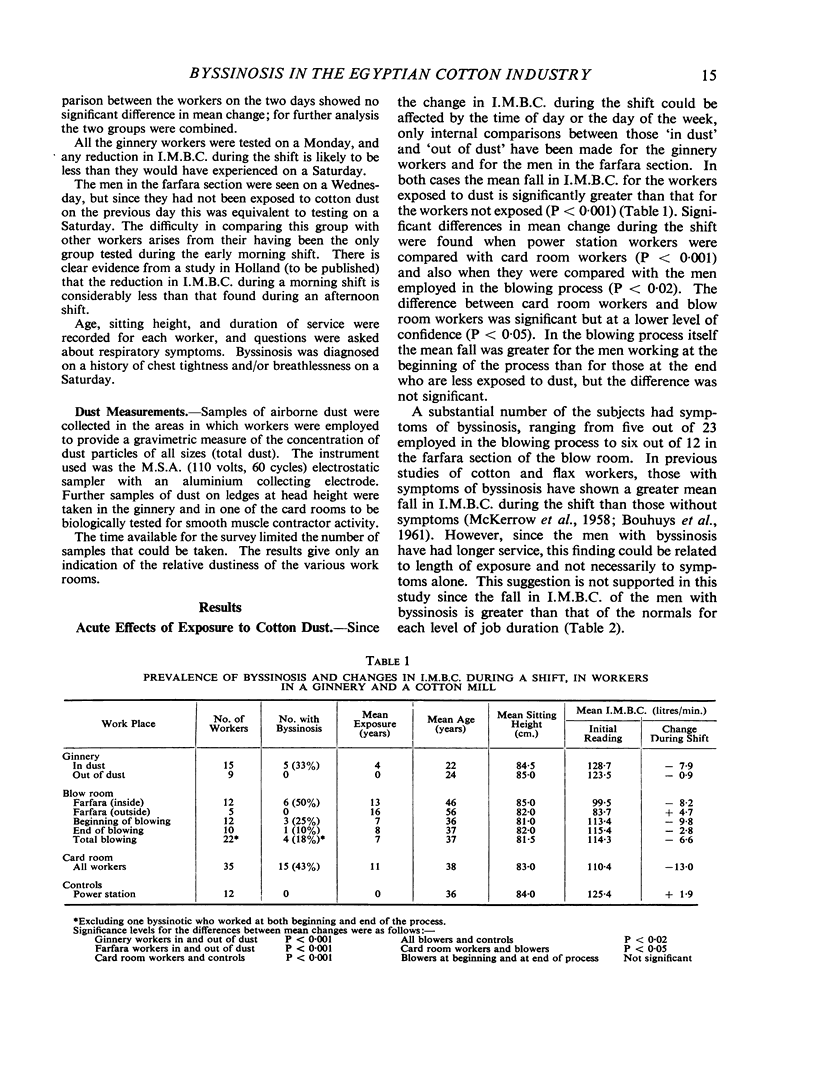
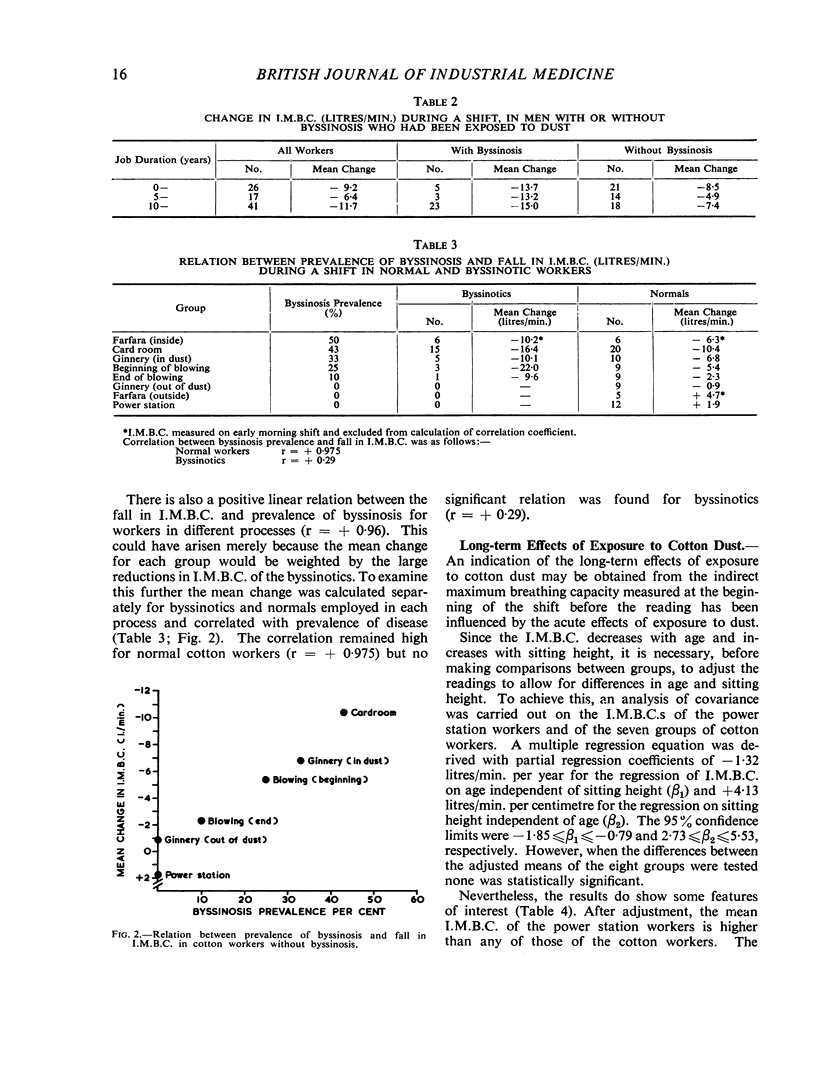
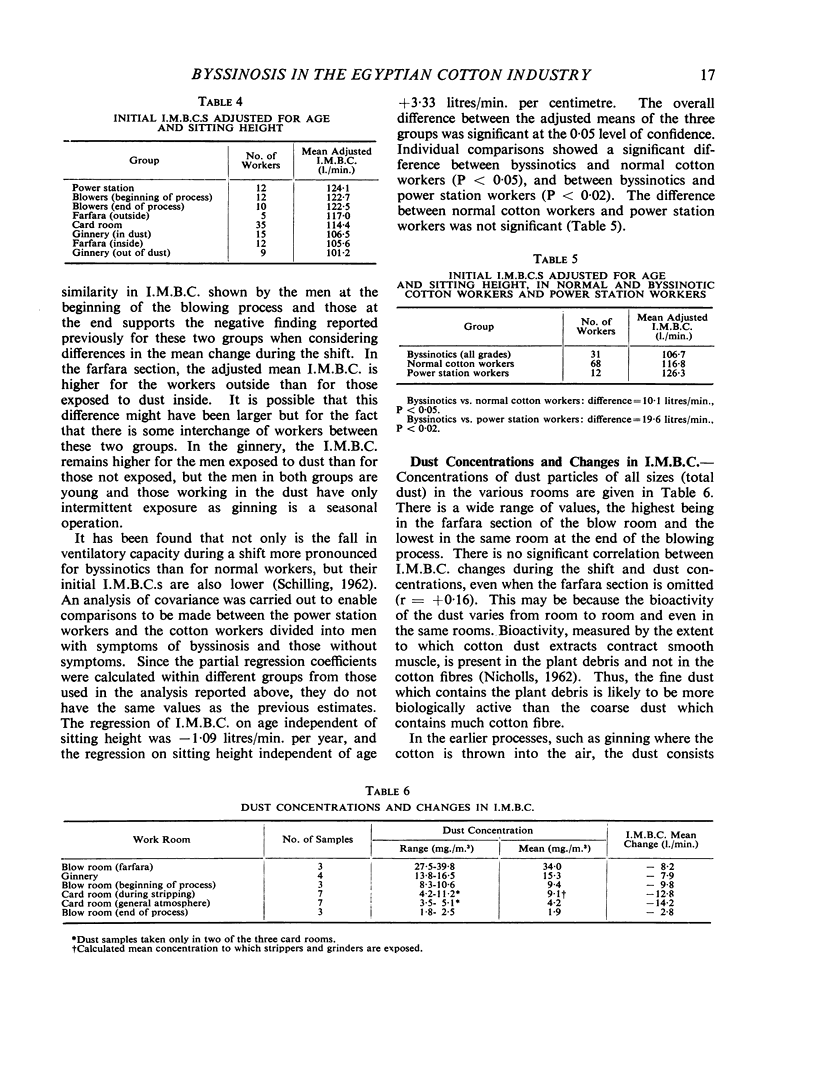
A study in Egypt of 99 male cotton workers in a cotton ginnery and spinning mill, and of a control group of 12 power station workers, showed that the groups exposed to cotton dust had significantly greater falls in indirect maximum breathing capacity (I.M.B.C.) during the shift than groups not exposed to dust. Long-term effects of exposure to cotton dust were studied by examining the I.M.B.C.s measured at the beginning of the shift after adjustment to allow for differences in age and sitting height. The adjusted mean value for those with byssinosis was 10·1 litres/min. lower than for normal cotton workers and 19·6 litres/min. lower than for the power station workers. Four men were judged by their breathlessness on slight exertion and low ventilatory capacities to be seriously disabled with byssinosis.
In four other mills, all spinning similar types of cotton, changes in I.M.B.C. during the shift correlated highly with dust concentrations and indicated a safe level of dustiness of 1 mg./m.3 (total dust) at which the effects on ventilatory capacity were minimal.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOUHUYS A., LINDELL S. E., LUNDIN G. Experimental studies on byssinosis. Br Med J. 1960 Jan 30;1(5169):324–326. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5169.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOUHUYS A., van DUYN, van LENNEP H. Byssinosis in flax workers. Arch Environ Health. 1961 Nov;3:499–509. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1961.10663061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EL BATAWI M. A. Byssinosis in the cotton industry of Egypt. Br J Ind Med. 1962 Apr;19:126–130. doi: 10.1136/oem.19.2.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROACH S. A., SCHILLING R. S. A clinical and environmental study of byssinosis in the Lancashire cotton industry. Br J Ind Med. 1960 Jan;17:1–9. doi: 10.1136/oem.17.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHILLING R. Case study. 2. Field studies of byssinosis. J Occup Med. 1962 Oct;4:627–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



