Abstract
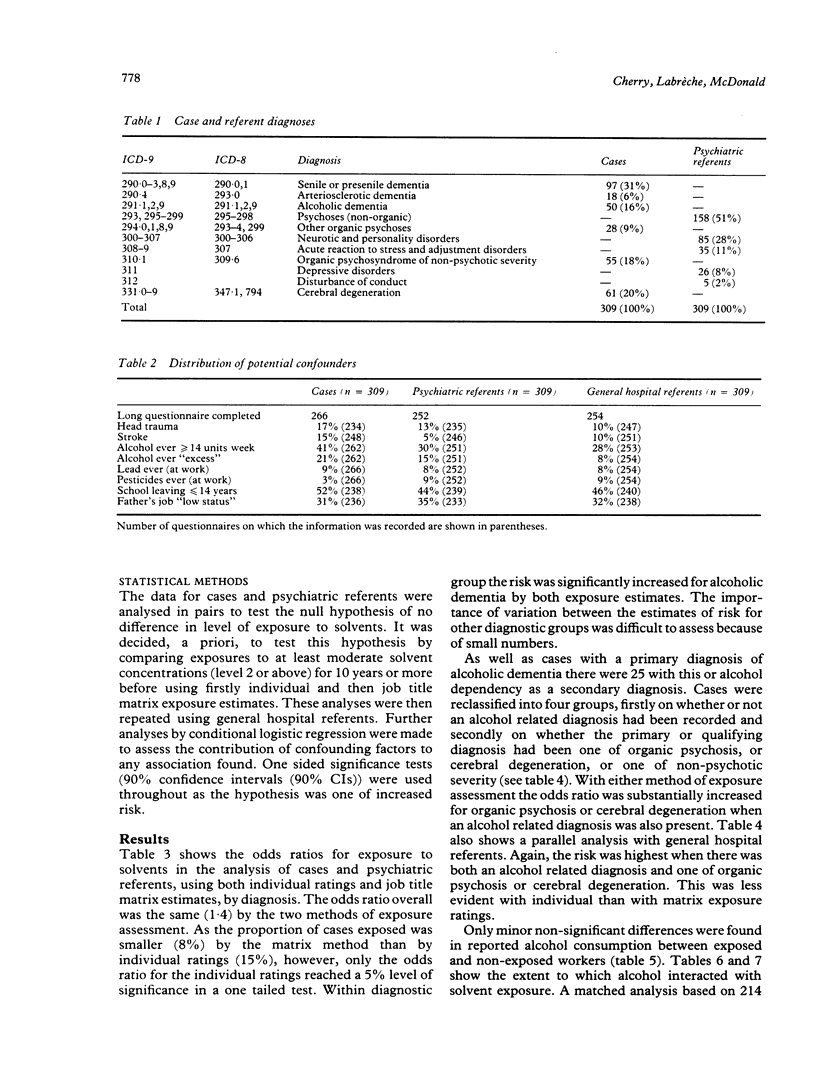
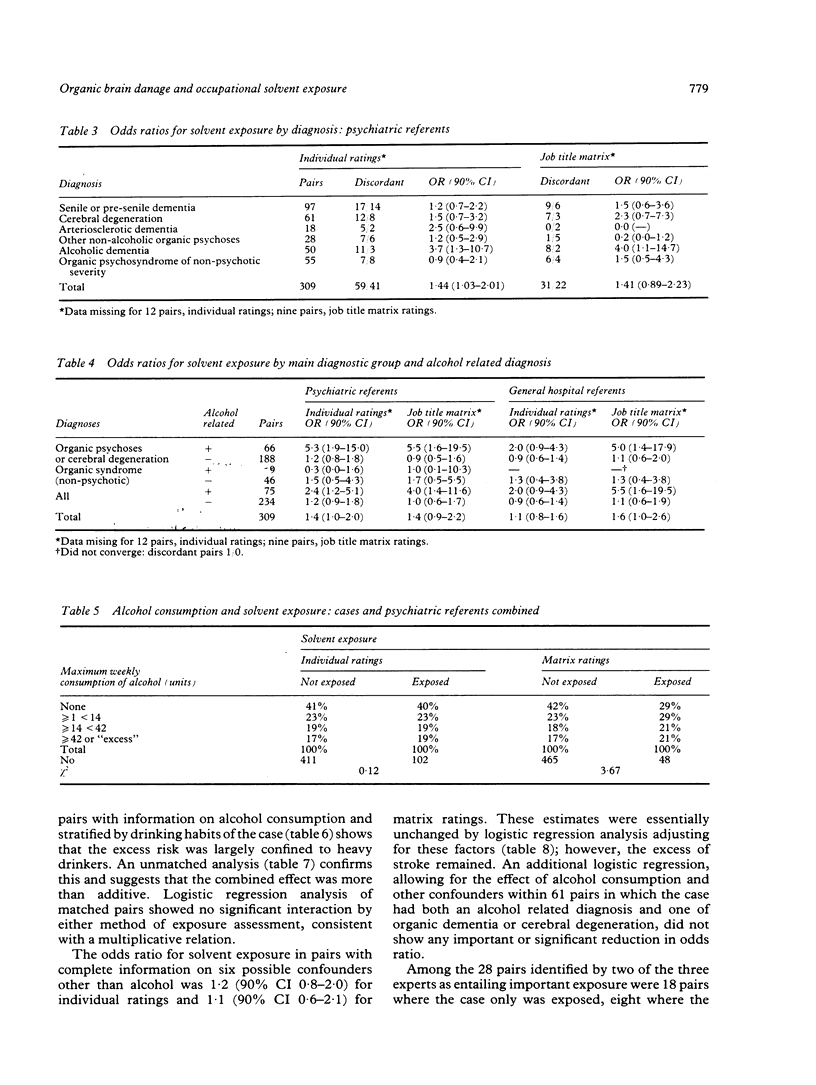
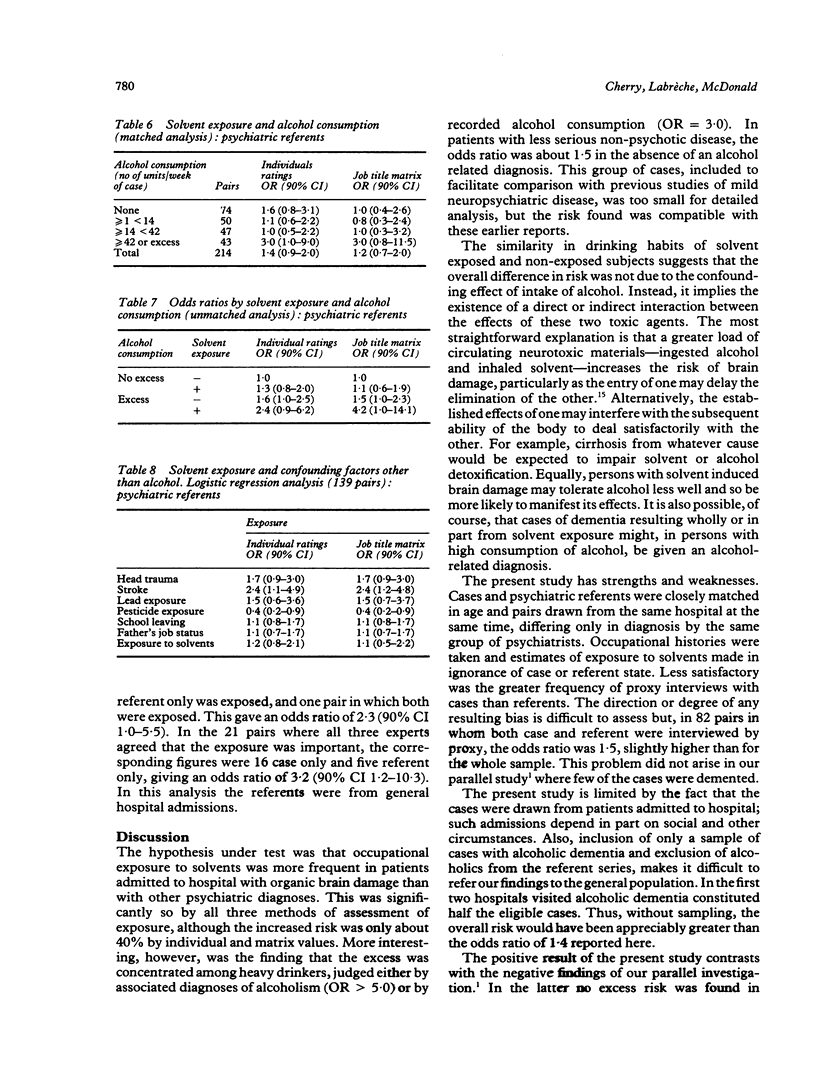
Three hundred and nine men with organic dementia, cerebral atrophy, or psycho-organic syndrome admitted for five nights or more to one of 18 Quebec hospitals were individually matched with patients admitted (1) with some other psychiatric diagnosis and (2) to a general hospital. Lifetime occupational histories were obtained by telephone. Occupational exposure to solvents was assessed blind to type of case by (1) individual ratings and (2) a job exposure matrix; men who worked in moderate or high solvent concentrations for at least 10 years were considered exposed. With the psychiatric referent series, an odds ratio of 1.4 (90% CI 1.0-2.0) was calculated by individual exposure ratings and 1.4 (90% CI 0.9-2.2) by job matrix. Increased risk was mainly in those with organic dementia or cerebral atrophy and an alcohol related diagnosis. The same pattern of risk was found against the general hospital referents. Adjustment for possible confounders did not alter the risk estimates appreciably. Also, lifetime job histories, compared in selected case-referent pairs, gave similar evidence of increased risk (odds ratio 2.3; 90% CI 1.0-5.5). It is concluded that the combined effect of occupational solvent exposure and alcohol intake is probably an important cause of organic brain damage.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelson O., Hane M., Hogstedt C. A case-referent study on neuropsychiatric disorders among workers exposed to solvents. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1976 Mar;2(1):14–20. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brackbill R. M., Maizlish N., Fischbach T. Risk of neuropsychiatric disability among painters in the United States. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1990 Jun;16(3):182–188. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.1796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubéran E., Usel M., Raymond L., Tissot R., Sweetnam P. M. Disability, mortality, and incidence of cancer among Geneva painters and electricians: a historical prospective study. Br J Ind Med. 1989 Jan;46(1):16–23. doi: 10.1136/oem.46.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labrèche F. P., Cherry N. M., McDonald J. C. Psychiatric disorders and occupational exposure to solvents. Br J Ind Med. 1992 Dec;49(12):820–825. doi: 10.1136/oem.49.12.820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindström K., Riihimäki H., Hänninen K. Occupational solvent exposure and neuropsychiatric disorders. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1984 Oct;10(5):321–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelsen S. A cohort study of disability pension and death among painters with special regard to disabling presenile dementia as an occupational disease. Scand J Soc Med Suppl. 1980;16:34–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flynn R. R., Monkman S. M., Waldron H. A. Organic solvents and presenile dementia: a case referent study using death certificates. Br J Ind Med. 1987 Apr;44(4):259–262. doi: 10.1136/oem.44.4.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen H., Olsen J., Lauritsen J. Risk of encephalopathia among retired solvent-exposed workers. A case-control study among males applying for nursing home accommodation or other types of social support facilities. J Occup Med. 1985 Aug;27(8):561–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalat S. L., Seltzer B., Baker E. L., Jr Occupational risk factors and Alzheimer's disease: a case-control study. J Occup Med. 1988 Dec;30(12):934–936. doi: 10.1097/00043764-198812000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson H. K., Robertson S. M., Waldron H. A., Gompertz D. Effect of alcohol on the kinetics of mandelic acid excretion in volunteers exposed to styrene vapour. Br J Ind Med. 1983 Feb;40(1):75–80. doi: 10.1136/oem.40.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Vliet C., Swaen G. M., Volovics A., Tweehuysen M., Meijers J. M., de Boorder T., Sturmans F. Neuropsychiatric disorders among solvent-exposed workers. First results from a Dutch case-control study. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1990;62(2):127–132. doi: 10.1007/BF00383589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


