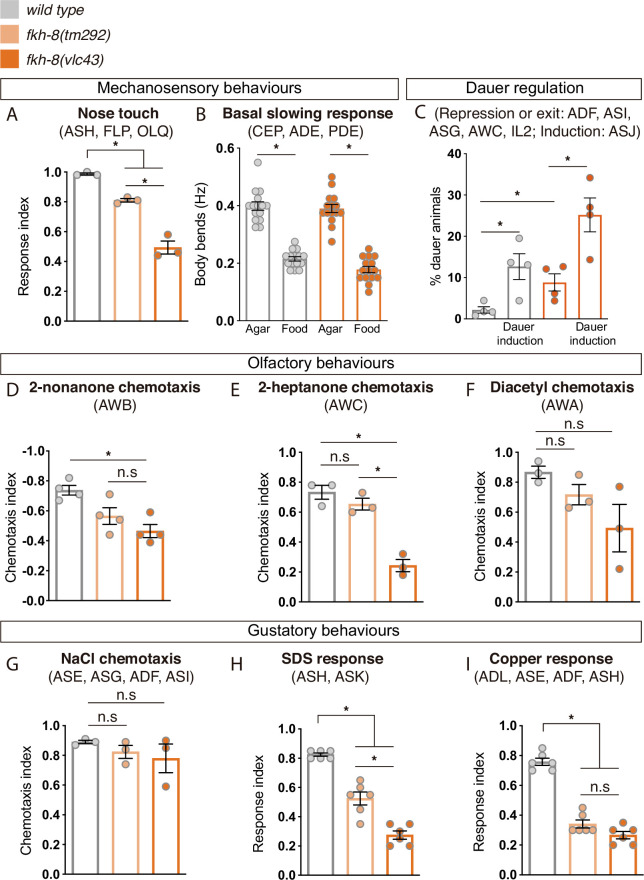
Figure 6. FKH-8 is required for the correct display of several sensory mediated behaviors.
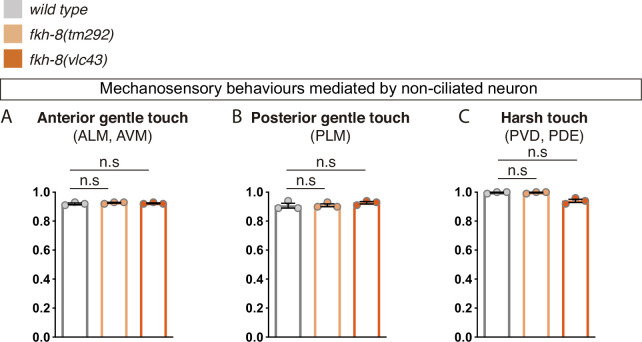
(A) Mutations in fkh-8 significantly impair appropriate backward response to nose touch, revealing functionality defects for the ASH, FLP and/or OLQ ciliated neurons. This phenotype is stronger in fkh-8(vlc43) null mutants than in the hypomorphic tm292 allele. n=20 animals per replicate, three biological replicates per genotype. (B) Decrease in locomotory rate upon re-entering a bacterial lawn is unaffected in fkh-8 mutants. n=15 worms per genotype and condition. (C) fkh-8 null mutants significantly fail to prevent dauer entry. Pheromones induce dauer in fkh-8 mutants, albeit less efficiently than in controls. Four biological replicates n>295 per replicate and genotype. (D to F) Lack of fkh-8 significantly impairs olfaction-mediated behaviors. Defects are observed for 2-nonanone repulsion mediated by AWB [Wild type n=59, 128, 114, 165; fkh-8(tm292) n=76, 123, 129, 209 and fkh-8(vlc43) n=82, 92, 130, 139] and 2-heptanone attraction mediated by AWC neurons [Wild type n=124, 129, 133; fkh-8(tm292) n=68, 94, 102 and fkh-8(vlc43) n=87, 83, 85]. Diacetyl response, mediated by AWA, is affected but not to a significant level due to high variability in the response [Wild type n=168, 69, 103; fkh-8(tm292) n=57, 85, 110 and fkh-8(vlc43) n=115, 107, 74]. (G to I) Attractive chemotaxis towards NaCl is unaffected in fkh-8 mutant animals. [Wild type n=62, 78, 72; fkh-8(tm292) n=105, 116, 106 and fkh-8(vlc43) n=111, 52, 78]. Avoidance behavior towards toxic SDS and copper anions is significantly impaired. [Six biological replicates, 5 worms per replicate and genotype, 4 tests per worm]. Mean and standard error are represented in all graphs. See Figure 6—figure supplement 1 for quantification of non-cilia mediated behaviors and Figure 6—source data 1 for raw data and statistics.