Abstract
BACKGROUND:
Axitinib is approved by the FDA for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) after failure of 1 previous systemic therapy and is distributed primarily through specialty pharmacies. Although the efficacy and safety of axitinib have been established in clinical trials, information from real-world populations will help to elucidate patients' clinical profiles and utilization patterns. Prescription records alone provide limited information on patient characteristics and other treatment experiences. Expansion of these data with information from medical claims databases should yield observational real-world data that may help to optimize therapy for patients with advanced RCC.
OBJECTIVE:
To link information from a specialty pharmacy database with information from medical and pharmacy claims databases to characterize real-world treatment patterns of axitinib as subsequent systemic therapy in patients with RCC in the United States.
METHODS:
This retrospective, observational, cohort study linked de-identified patient-level data from 22 specialty pharmacies that dispense axitinib with databases of longitudinal medical and pharmacy claims. Eligible patients had a diagnosis of RCC (> 1 claim for RCC defined as ICD-9-CM code 189.0), previously received > 1 systemic therapy, had the first prescription for axitinib dispensed between May 2012 and April 2013 (index), and had consistent claims reporting by pharmacies and physicians. All treatment data were used to calculate cycle, line of therapy, and duration of therapy; prescription data were used to determine axitinib dose modifications. Multivariate and logistic regression analyses were conducted to assess the effect of patient/prescriber characteristics on duration of axitinib therapy and dose modifications, respectively.
RESULTS:
In all, 1,175 patients met the study inclusion criteria and had data present in specialty pharmacy and claims databases. Most patients (74%) were male, and 68% were aged 55-74 years. Mean (SD) Charlson Comorbidity Index score was 2.7 (± 1.1); the most common comorbidity was hypertension (in 199 patients, 17%). Based on Rx-Risk-V, the most frequent concomitant conditions were pain (40%) and ischemic heart disease/hypertension (30%); the most frequent concomitant medications were antihypertensive medications (46%) and opiates (40%). Most prescribers (63%) were affiliated with an academic center, and all U.S. geographic regions were represented. In all, 847 patients (72%) had commercial insurance. Axitinib was prescribed as second-line therapy in 659 patients (56%), as third-line therapy in 326 patients (28%), and as fourth-line or later therapy in 190 patients (16%). In the overall population, mean (SD) duration of axitinib therapy was 168.6 (± 148.4) days. Axitinib treatment duration was 21 days longer in males than females (P = 0.013); 28 days longer in patients in the Northeast than in the Midwest or West (P = 0.010 and P = 0.016, respectively); and 26 days longer in patients receiving baseline hypothyroidism treatment (P = 0.004). In patients receiving second-line axitinib, the most common first-line therapy was sunitinib (56%), followed by pazopanib (16%) and everolimus (12%). Mean (SD) duration of second-line axitinib treatment was 172.3 (± 150.6) days and ranged from 127 days in patients who previously received temsirolimus to 196 days in those who previously received sorafenib. Of 1,025 patients who initiated axitinib at the standard 5 mg twice daily starting dose, 70% remained at this dose throughout treatment, whereas 10% had a dose increase. Younger age and gender (male) were associated with dose increases (OR = 0.958, 95% CI = 0.941-0.975 and OR = 0.573, 95% CI = 0.364-0.903, respectively). Baseline hypothyroidism treatment was associated with dose decreases and increases (OR = 1.662, 95% CI = 1.088-2.539 and OR = 2.149, 95% CI = 1.353-3.413, respectively).
CONCLUSIONS:
This analysis demonstrates the feasibility and utility of linking specialty pharmacy data to other longitudinal databases to better understand patient, provider, and reimbursement characteristics. These data provide insight into routine clinical use of axitinib as subsequent RCC therapy in the United States in the period following FDA approval, as well as additional information on sequencing of targeted agents in patients with advanced RCC.
What is already known about this subject
Axitinib is approved in the United States for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) after failure of 1 previous systemic treatment.
The standard starting dose of axitinib is 5 mg orally twice daily (BID); dose adjustments below or above the starting dose (to a maximum 10 mg BID) may be made based on individual safety and tolerability and are supported by retrospective and prospective studies.
Many patients with advanced RCC have disease progression or become resistant to targeted agents; however, few observational studies have examined treatment patterns beyond first-line systemic therapy.
What this study adds
Given the increasing distribution of oncology drugs through specialty pharmacies in the United States and the limited information in prescription records, this observational study demonstrates the feasibility and utility of linking de-identified specialty pharmacy data to other longitudinal databases to enrich our understanding of patient and provider characteristics.
Treatment patterns among patients who received axitinib as subsequent therapy indicate that axitinib was initiated most commonly in the second-line setting following first-line treatment with sunitinib; pazopanib and everolimus were also prescribed as first-line therapy.
Most patients initiated axitinib at the recommended 5 mg BID starting dose and remained on this dose throughout treatment; dose modifications were less frequent than in the pivotal phase III AXIS trial of axitinib versus sorafenib.
An estimated 62,700 individuals will be diagnosed with kidney or renal pelvis cancer in the United States in 2016, and 14,240 deaths because of this disease are predicted.1 Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) accounts for approximately 90% of renal tumors.2 The median age at diagnosis is approximately 64 years, and RCC occurs more commonly in males.1 Approximately 25%-30% of patients with RCC present with metastatic disease (mRCC) at diagnosis, and 20%-30% of patients with localized disease experience relapse with metastases following resection.2,3 In the United States during the years 2004-2010, the 5-year relative survival rates were 91.8% for localized disease, 64.6% for regional disease, and 12.1% for distant disease.4
Since their introduction in 2005, targeted agents acting on the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) pathway or the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway have revolutionized the treatment of mRCC and improved clinical outcomes compared with cytokine-based regimens,5 which were historically used to treat this disease. Presently, there are 7 targeted agents approved in the United States for clear-cell mRCC: VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs; i.e., sunitinib, sorafenib, pazopanib, and axitinib); monoclonal antibody to VEGF (i.e., bevacizumab); and mTOR inhibitors (i.e., evero-limus and temsirolimus). Based on high-level evidence, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) issued category 1 recommendations for sunitinib, pazopanib, or beva-cizumab (combined with interferon-a) as first-line therapy in patients with mRCC, as well as temsirolimus, specifically for those with poor prognosis.2 However, patients with mRCC may not respond to first-line treatment or may develop resistance to these drugs and require subsequent therapies to control their disease.6,7 Consequently, optimizing treatment sequences in patients with mRCC is an important area of investigation.7
Axitinib (Inlyta) was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2012 for the treatment of advanced RCC after failure of 1 previous systemic therapy.8 In the pivotal phase III AXIS trial, axitinib significantly prolonged progression-free survival versus sorafenib and was well tolerated in previously treated patients with advanced RCC.9 As a result, axitinib has NCCN category 1 designation as subsequent therapy for advanced RCC after previous treatment with a TKI or cytokines.2 Axitinib dosing recommendations permit titration below or above the starting dose of 5 mg twice daily (BID) based on patient tolerability and clinician judgment. Patients who tolerate the axitinib 5 mg BID dose for > 2 consecutive weeks with no adverse reactions above grade 2 (according to Common Toxicity Criteria for Adverse Events), and who are normotensive and not receiving antihypertension medication, may have their dose increased stepwise to 7 mg BID and then to a maximum of 10 mg BID.8 This dose-titration strategy has been supported by retrospective analyses and a phase II clinical trial.10,11
Although positive outcomes with targeted agents in phase III clinical trials have transformed the care of patients with mRCC worldwide, the strict patient eligibility criteria and short-term follow-up in these studies may limit the applicability of these clinical findings to routine patient care. Assessment of real-world use of targeted agents, including sequencing of therapies, may help to optimize treatment of patients with mRCC. The objective of this study was to link information from specialty pharmacy databases with information from databases of medical and pharmacy claims to characterize real-world treatment patterns of axitinib as subsequent systemic therapy in patients with RCC in the United States.
Methods
Study Design and Data Sources
This retrospective observational cohort study utilized the Specialty Pharmacy Data Mart, an IMS-managed database containing data from a limited distribution network of 22 specialty pharmacies (regional and national) that dispense axitinib. Data from the specialty pharmacy database were linked to information in the IMS Health medical and pharmacy claims databases via IMS de-identified unique patient identifiers. These identifiers enable IMS to track patients anonymously and longitudinally over time and between datasets and are not dependent on insurance carrier, pharmacy, or employer. The IMS Health pharmacy claims database includes claims (National Council for Prescription Drug Programs, version 5.2) submitted for patients receiving a prescription via retail and specialty pharmacies (> 1.8 billion prescriptions dispensed annually). The medical claims database includes more than 1 billion annual claims that contain diagnosis and visit information and represents activity of more than 870,000 practitioners per month. The data available in these databases represent patients regardless of age, gender, or insurance type from all 50 states and comply with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
This study was conducted in accordance with legal and regulatory requirements and research practices and standards
established by the International Society for Pharmacoepidemiology, International Society for Pharmacoeconomics and Outcomes Research, and Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers Association. This study was exempt from institutional review board approval because it was retrospective, noninterventional, and used anonymized data.
Study Sample Selection
This study evaluated linked claims data between April 2009 and February 2014. Patients with a claim for their first axitinib prescription (index) between May 2012 and April 2013 were included. Treatment histories were assessed using data from April 2009 through April 2012 (3-year look back period). Discontinuation or maintenance of axitinib treatment was determined based on data through December 2013 and confirmed using data from January and February 2014 (washout period).
Patients included in this analysis were required to have a diagnosis of RCC (defined as> 1 claim, International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification [ICD-9-CM] code 189.0) or receipt of previous treatment for RCC (Appendix A, available in online article). In addition, patients were required to have > 1 prescription for axitinib (first prescription received between May 2012 and April 2013), > 1 previous systemic therapy, care from an end-treating physician, and consistent reporting of prescription data by pharmacies (reporting > 50% of all claims for that pharmacy per month) and all medical claims (office-based claims) by providers, respectively, during the study period. Patients who paid in cash for oncology services or participated in a clinical trial were excluded, since these data are not collected as part of the medical claims dataset.
Claims 2 and 4 years before the index date were examined to ensure that patients had office visits or prescriptions. Those patients with missing data from the 3-month period beginning 2 or 4 years before the index date were excluded to ensure that patients had treatment/visits in the look back period.
Study Measures
The primary objective of this study was to describe characteristics of axitinib-treated patients and axitinib-prescribing providers using linked datasets. Patient characteristics included age, gender, Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) score and groups,12,13 Rx-Risk-V score and categories,14 and payer type. The CCI score is calculated by identifying comorbidities in the 12 months before the index prescription. Weights are assigned to the 17 CCI comorbidity categories and the CCI score is cal-culated.12,13 Metastatic cancer was not included in the calculation of CCI scores because all patients had metastatic disease. The Rx-Risk-V score was calculated by identifying specific concomitant prescription categories for the patients in the 60 to 120 days before the axitinib index prescription. Each category was summed for the total patient score.14 Provider characteristics included geographic region per U.S. census and affiliation. Provider affiliations were determined using the IMS Healthcare Organization Services; providers with designations for both academic centers and community practices were counted only as affiliated with the academic center.
The secondary objectives were to describe and evaluate treatment patterns, dosing, treatment line, and duration of therapy. Dispensed drugs were identified using National Drug Code numbers and Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System J codes (Appendix B, available in online article), and systemic therapies before axitinib prescription were ascertained from the 3-year look back period; these data were used to calculate cycle, line, duration of therapy, and axitinib dose modifications (defined in Table 1).
TABLE 1.
Study Measure Definitions and Calculations
| Cycles of therapy |
|
| Lines of therapy |
|
| Duration of therapy |
|
| Axitinib dose modifications |
|
Statistical Analysis
Patient and provider characteristics, as well as treatment and dosing patterns are summarized descriptively. Numeric values and percentages are presented for categorical data; means, standard deviations (SDs), medians, and ranges are presented for continuous data. For some results, continuous variables were categorized into intervals and reported as numeric values and percentages. Inferential statistical tests were not performed to evaluate differences between the axitinib line of therapy subgroups.
The effect of patient/prescriber characteristics on duration of axitinib therapy and dose modifications were evaluated by multivariate and logistic regression analyses, respectively. Covariates included age, gender, prescriber geographic region, payer type, CCI score, prior treatment regimen, affiliation and specialty of axitinib-prescribing physician, concomitant medication classes (based on Rx-Risk-V categories), and line of axitinib therapy. Results were summarized by coefficient estimates for multivariate regression analyses and odds ratios (ORs) with Wald 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for logistic regression analyses. All statistical analyses were performed with 2-sided tests at the 5% significance level using SAS, version 9.3 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC).
Results
Patient and Provider Characteristics
This study included 1,175 patients (Figure 1). Most patients (74%) were male, and mean (SD) age was 63.6 (± 10.1) years (Table 2). Mean (SD) CCI score was 2.7 (± 1.1); the largest proportion of patients (64%) had a score of 2; and the most common comorbidity was hypertension (n = 199, 17%). The most frequently observed Rx-Risk-V categories were pain (40%) and ischemic heart disease/hypertension (30%). The most common concomitant medications were antihypertensive medications (46%) and opiates (40%). Most prescribers (63%) were affiliated with an academic center; 48% were hematology/oncology specialists; all U.S. geographic regions were represented; and 847 (72%) patients had commercial insurance.
FIGURE 1.
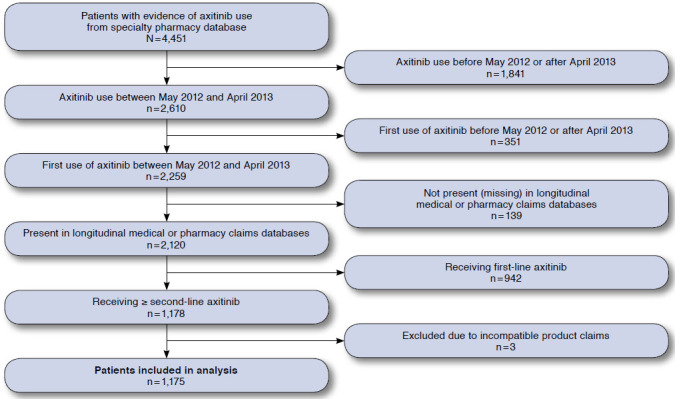
Selection of Study Patients
TABLE 2.
Patient Demographics and Clinical Characteristics
| Characteristic | Total (N = 1,175) | Second Line (n = 659) | Third Line (n = 326) | > Fourth Line (n = 190) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | ||||||||
| Mean (SD) | 63.6 (± 10.1) | 63.6 (± 10.0) | 62.9 (± 10.0) | 64.5 (± 10.3) | ||||
| Median (range) | 64 (23-85) | 64 (29-85) | 63 (23-85) | 65 (28-85) | ||||
| Age group, years, n(%) | ||||||||
| < 45 | 35 | (3) | 18 | (3) | 11 | (3) | 6 | (3) |
| 45-54 | 170 | (14) | 98 | (15) | 50 | (15) | 22 | (12) |
| 55-64 | 424 | (36) | 240 | (36) | 116 | (36) | 68 | (36) |
| 65-74 | 371 | (32) | 205 | (31) | 110 | (34) | 56 | (29) |
| > 75 | 175 | (15) | 98 | (15) | 39 | (12) | 38 | (20) |
| Gender, n (%) | ||||||||
| Male | 865 | (74) | 487 | (74) | 244 | (75) | 134 | (71) |
| Female | 310 | (26) | 172 | (26) | 82 | (25) | 56 | (29) |
| Charlson Comorbidity Indexa | ||||||||
| Mean (SD) | 2.7 (± 1.1) | 2.7 (± 1.0) | 2.7 (± 1.1) | 2.7 (± 1.1) | ||||
| Median (range) | 2 | (2-9) | 2 | (2-7) | 2 | (2-9) | 2 | (2-6) |
| Score, n (%) | ||||||||
| 2 | 749 | (64) | 424 | (64) | 203 | (62) | 122 | (64) |
| 3 | 194 | (17) | 105 | (16) | 55 | (17) | 34 | (18) |
| 4 | 129 | (11) | 76 | (12) | 38 | (12) | 15 | (8) |
| 5-8 | 103 | (9) | 54 | (8) | 30 | (9) | 19 | (10) |
| Comorbid groups,b n (%) | ||||||||
| No comorbidity | 418 | (36) | 252 | (38) | 99 | (30) | 67 | (35) |
| Hypertension | 199 | (17) | 115 | (17) | 58 | (18) | 26 | (14) |
| Diabetes ± acute complications | 171 | (15) | 103 | (16) | 49 | (15) | 19 | (10) |
| Renal disease | 162 | (14) | 88 | (13) | 46 | (14) | 28 | (15) |
| Moderate/severe chronic kidney disease | 108 | (9) | 62 | (9) | 32 | (10) | 14 | (7) |
| Chronic pulmonary disease | 81 | (7) | 42 | (6) | 24 | (7) | 15 | (8) |
| Cardiovascular disease | 65 | (6) | 37 | (6) | 21 | (6) | 7 | (4) |
| Congestive heart failure | 60 | (5) | 32 | (5) | 17 | (5) | 11 | (6) |
| Rx-Risk-V Index | ||||||||
| Score, n (%) | ||||||||
| 0 | 361 | (31) | 211 | (32) | 98 | (30) | 52 | (27) |
| 1 | 109 | (9) | 66 | (10) | 23 | (7) | 20 | (11) |
| 2-3 | 239 | (20) | 133 | (20) | 71 | (22) | 35 | (18) |
| 4-5 | 221 | (19) | 133 | (20) | 57 | (17) | 31 | (16) |
| 6-9 | 228 | (19) | 107 | (16) | 73 | (22) | 48 | (25) |
| 10+ | 17 | (1) | 9 | (1) | 4 | (1) | 4 | (2) |
| Rx-Risk-V categories, n (%) | ||||||||
| No Rx-Risk-V categories | 361 | (31) | 211 | (32) | 98 | (30) | 52 | (27) |
| Pain | 474 | (40) | 263 | (40) | 138 | (42) | 73 | (38) |
| Ischemic heart disease/hypertension | 348 | (30) | 182 | (28) | 102 | (31) | 64 | (34) |
| Congestive heart failure/hypertension | 285 | (24) | 153 | (23) | 84 | (26) | 48 | (25) |
| Gastric acid disorder | 275 | (23) | 154 | (23) | 81 | (25) | 40 | (21) |
| Hyperlipidemia | 250 | (21) | 125 | (19) | 78 | (24) | 47 | (25) |
| Hypothyroidism | 247 | (21) | 129 | (20) | 67 | (21) | 51 | (27) |
| Hypertension | 198 | (17) | 102 | (15) | 53 | (16) | 43 | (23) |
| Anxiety and tension | 189 | (16) | 92 | (14) | 63 | (19) | 34 | (18) |
| Depression | 187 | (16) | 99 | (15) | 56 | (17) | 32 | (17) |
| All others | 573 | (49) | 304 | (46) | 170 | (52) | 99 | (52) |
| Prescriber geographic region, n (%) | ||||||||
| South | 420 | (36) | 234 | (36) | 114 | (35) | 72 | (38) |
| Midwest | 285 | (24) | 162 | (25) | 83 | (25) | 40 | (21) |
| Northeast | 245 | (21) | 153 | (23) | 64 | (20) | 28 | (15) |
| West | 224 | (19) | 109 | (17) | 65 | (20) | 50 | (26) |
| Unknown | 1 | (< 1) | 1 | (<1) | 0 | 0 | ||
| Prescriber affiliation, n (%) | ||||||||
| Academic center | 743 | (63) | 419 | (64) | 211 | (65) | 113 | (59) |
| Community practice | 227 | (19) | 124 | (19) | 62 | (19) | 41 | (22) |
| Unknown | 205 | (17) | 116 | (18) | 53 | (16) | 36 | (19) |
| Payer type,c n (%) | ||||||||
| Commerciald | 847 | (72) | 474 | (72) | 236 | (72) | 137 | (72) |
| Medicare | 252 | (21) | 138 | (21) | 72 | (22) | 42 | (22) |
| Medicaid | 24 | (2) | 17 | (3) | 5 | (2) | 2 | (1) |
| Other | 52 | (4) | 30 | (5) | 13 | (4) | 9 | (5) |
aMetastatic diagnosis excluded from Charlson Comorbidity Index.
bIncludes conditions occurring in > 5% of patients.
cBased on index prescription.
dIncludes Medicare Advantage.
SD = standard deviation.
In total, 659 (56%) patients received axitinib as second-line therapy; 326 (28%) patients received it as third-line therapy; and 190 (16%) patients received it as fourth-line or later therapy (Table 2). Demographics and clinical characteristics did not appear to differ by line of therapy; however, inferential statistical test were not performed. Patient characteristics, including comorbidity profiles, appeared to be similar between those treated by prescribers affiliated with academic centers versus community practices (data not shown).
Treatment Patterns
Sunitinib (38%) was the systemic therapy most frequently prescribed directly before axitinib was initiated in any line of therapy, followed by everolimus (22%) and pazopanib (21%; Table 3). In the overall population, mean (SD) duration of axitinib therapy was 168.6 (± 148.4) days, and 937 (80%) patients discontinued axitinib treatment as of December 2013. Mean and median duration of therapy did not appear to differ substantially between lines of therapy (Table 3).
TABLE 3.
Treatment Patterns and Axitinib Dosing Patterns
| Characteristic | Total (N = 1,175) | Second Line (n = 659) | Third Line (n = 326) | > Fourth Line (n = 190) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duration of axitinib therapy, days | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 168.6 (±148.4) | 172.3 (±150.6) | 169.2 (±146.9) | 154.6 (± 142.8) |
| Median (range) | 115 (7-688) | 114 (8-688) | 122 (7-644) | 111(10-642) |
| Therapy received directly before axitinib, n (%) | ||||
| Sunitinib | 446 (38) | 368 (56) | 51 (16) | 27 (14) |
| Everolimus | 259 (22) | 78 (12) | 142 (44) | 39 (21) |
| Pazopanib | 244 (21) | 106 (16) | 65 (20) | 73 (38) |
| Temsirolimus | 83 (7) | 56 (8) | 17 (5) | 10 (5) |
| Sorafenib | 44 (4) | 19 (3) | 15 (5) | 10 (5) |
| Bevacizumab | 31 (3) | 12 (2) | 13 (4) | 6 (3) |
| Other | 68 (6) | 20 (3) | 23 (7) | 25 (13) |
| Axitinib daily dose,a mg | ||||
| Mean (SD) | 10.3 (3) | 10.3 (3) | 10.5 (3) | 10.2 (3) |
| Median (range) | 10.0 (2.0-31.5) | 10.0 (2.0-31.5) | 10.0 (3.5-21.4) | 10.0 (2.0-20.0) |
| Axitinib dose modifications,a n (%) | ||||
| No change | 789 (67) | 445 (68) | 213 (66) | 131 (69) |
| Decrease | 161 (14) | 90 (14) | 43 (13) | 28 (15) |
| Increase | 141 (12) | 79 (12) | 44 (14) | 18 (10) |
| Increase then decrease | 83 (7) | 45 (7) | 25 (8) | 13 (7) |
aA total of 1,174 patients were evaluated for axitinib dosing patterns; 1 patient whose titration patterns could not be determined and did not follow expected clinical patterns was excluded.
SD = standard deviation.
For the 659 patients prescribed second-line axitinib, mean (SD) duration of axitinib treatment was 172.3 (± 150.6) days and ranged from 127 days in patients previously administered temsirolimus to 196 days in those previously prescribed sorafenib (Table 3 and Figure 2A). The most common first-line treatments in these patients were sunitinib (56%), pazopanib (16%), and everolimus (12%), after which mean (SD) duration of second-line axitinib treatment was 184 (± 156), 154 (± 125), and 189 (± 180) days, respectively. In all, 80% of patients completed second-line axitinib treatment as of December 2013. In patients who received first-line sunitinib or pazopanib, baseline patient and prescriber characteristics were generally similar (data not shown), although a higher proportion of patients prescribed first-line pazopanib had no Rx-Risk-V categories (40% vs. 28%, respectively); statistical significance is unknown.
FIGURE 2.
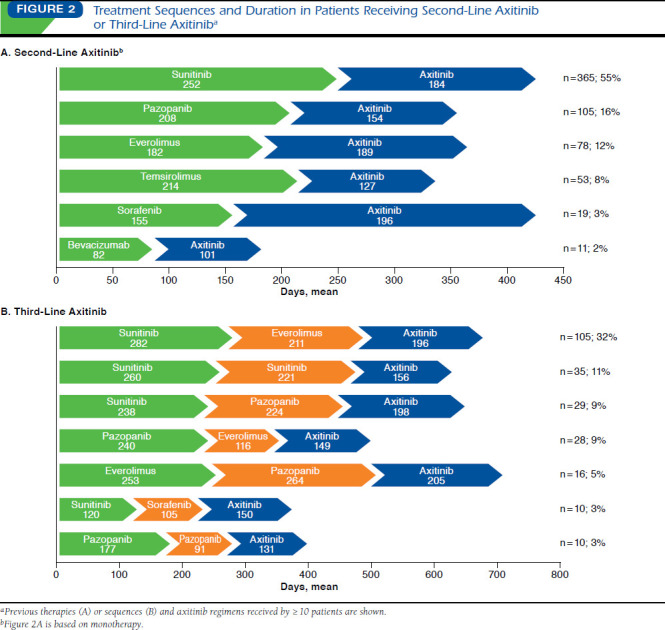
Treatment Sequences and Duration in Patients Receiving Second-Line Axitinib or Third-Line Axitinib
For the 326 patients prescribed third-line axitinib, mean (SD) duration of axitinib treatment was 169.2 (± 146.9) days, ranging from 131 days in patients who received first- and second-line pazopanib to 205 days in patients who received first-line everolimus and second-line pazopanib (Table 3 and Figure 2B). The most common (32%) prior treatment sequence was sunitinib followed by everolimus; mean (SD) duration of axitinib treatment in these patients was 196 (± 165) days. In all, 79% of patients completed third-line axitinib treatment as
Multivariate regression analysis revealed several patient characteristics associated with duration of axitinib therapy (Appendix C, available in online article). Longer axitinib treatment duration was observed in males versus females (21 days longer, P = 0.013); in patients in the Northeast (28 days longer) versus the Midwest or West (P = 0.010 and P = 0.016, respectively); and in patients receiving baseline hypothyroid-ism treatment (26 days longer, P = 0.004). Compared with sunitinib, prior bevacizumab and prior temsirolimus were associated with shorter treatment duration (50 days and 31 days shorter, P = 0.028 and P = 0.034, respectively). Neither the line of axitinib therapy nor the prescriber's affiliation was associated with duration of axitinib treatment (Table 3 and data not shown).
Axitinib Dosing Patterns
In the overall population, 67% of patients remained on the same axitinib dose during the entire course of therapy, whereas 14% had dose decreases; 12% had increases; and 7% had increases followed by decreases (Table 3). A total of 1,025 (87%) patients initiated axitinib at the standard 5 mg BID starting dose. Of these, 715 (70%) patients remained on 5 mg BID throughout treatment, whereas 138 (14%) had dose decreases; 107 (10%) had increases; and 65 (6%) had increases followed by decreases. Axitinib dose modifications did not appear to vary by line of therapy (Table 3).
Baseline hypothyroidism treatment was associated with dose increases (OR = 2.149, 95% CI = 1.353-3.413); dose decreases
(OR = 1.662, 95% CI = 1.088-2.539); and dose increases followed by decreases (OR = 2.381, 95% CI = 1.396-4.060).
Results of multivariate logistic regression (Table 4) indicated that younger age (OR = 0.958, 95% CI = 0.941-0.975); male gender (OR = 0.573, 95% CI = 0.364-0.903); and lack of concomitant medication as described by Rx Risk V (OR = 0.468, 95% CI = 0.314-0.697) were associated with an increase in dose.
TABLE 4.
Logistic Regression of Key Patient Characteristics on Axitinib Dose Modifications
| Variable | Odds Ratio | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|
| Dose decrease | ||
| Age | 1.015 | 0.998-1.033 |
| Gender (female vs. male) | 0.695 | 0.462-1.047 |
| Baseline hypothyroidism treatment (yes vs. no) | 1.662 | 1.088-2.539 |
| Other baseline treatment (yes vs. no) | 0.913 | 0.639-1.306 |
| Dose increase only | ||
| Age | 0.958 | 0.941-0.975 |
| Gender (female vs. male) | 0.573 | 0.364-0.903 |
| Baseline hypothyroidism treatment (yes vs. no) | 2.149 | 1.353-3.413 |
| Other baseline treatment (yes vs. no) | 0.468 | 0.314-0.697 |
| Dose increase then decrease | ||
| Age | 0.989 | 0.967-1.012 |
| Gender (female vs. male) | 1.033 | 0.627-1.702 |
| Baseline hypothyroidism treatment (yes vs. no) | 2.381 | 1.396-4.060 |
| Other baseline treatment (yes vs. no) | 0.762 | 0.469-1.237 |
| CI = confidence interval. | ||
Discussion
The benefits of targeted agents in patients with mRCC have been demonstrated in numerous clinical studies. However, development of drug resistance and/or refractory disease in patients receiving these treatments necessitates administration of subsequent therapies. Although current guidelines from NCCN recommend use of consecutive targeted agents,2 an optimal sequencing strategy has not yet been determined from prospective clinical trial data. Observational studies in patients with mRCC treated with targeted therapies, including the present analysis, provide insight into real-world sequencing patterns, as well as patient, provider, and reimbursement characteristics.
Coincident with the shift from cytokine-based therapies to targeted agents to treat mRCC has been an expansion of oncology drug distribution via specialty pharmacies.15 However, pharmacy records provide limited information with regard to patient and provider characteristics. Linking independent databases in a HIPAA-compliant manner is a growing method to enrich these datasets. This retrospective, observational study demonstrates the feasibility of matching de-identified specialty pharmacy data to other longitudinal databases, as is evidenced by 94% of patients with their first axitinib prescriptions dispensed by specialty pharmacies from May 2012 to April 2013 also having information in the medical and pharmacy claims databases (Figure 1). With a study population of 1,175 patients, this methodology yields one of the largest sample sizes in observational studies examining mRCC treatment patterns in the United States.16-27
Baseline demographics of the patient population evaluated here were consistent with the known epidemiology of kidney cancer in the United States, including a higher prevalence in males versus females and in patients aged 55-74 years versus other age groups, and with hypertension as a comorbidity.1,4,28 Patient characteristics in this analysis were also generally consistent with other retrospective studies in patients with mRCC treated with targeted agents.16-27 Whereas the majority of previous observational studies used data from community or tertiary oncology practices in the United States,16-18,21,23 the present study evaluated patients treated by physicians affiliated with both academic centers and community practices, of which the proportions of prescribers were similar to those reported in a retrospective study of patients receiving first-line targeted therapy for mRCC.22 Although we found that patient characteristics, including comorbidity profiles, were similar regardless of prescriber affiliation (data not shown), patients seeking care in community settings have characteristics that might restrict their ability to travel to academic centers (e.g., advanced age and/or a greater degree of comorbidity). The present analysis may be limited by classification of physicians associated with both academic centers and community practices as affiliated with academic centers only. The affiliation describes provider characteristics but does not necessarily describe where patient treatments took place.
In this study, the majority of patients (56%) were treated with axitinib in the second line of therapy. Evaluation of real-world treatment patterns in patients receiving axitinib as second-line therapy revealed that sunitinib was the most common first-line therapy, but other targeted agents, including pazopanib (16%) and everolimus (12%), were also prescribed.
Prior retrospective analyses in previously treated patients with mRCC also reported sunitinib as the most commonly administered first-line therapy.16,19,21,24,27 Similar proportions of patients received first-line sunitinib in the present analysis versus the AXIS trial (56% vs. 54%), whereas proportions of patients who received first-line temsirolimus (8% vs. 3%) or bevacizumab (2% vs. 8%) varied slightly.9 There were very few patients treated with cytokines in the current study, whereas 35% of patients in the AXIS trial were cytokine-refractory.9 The AXIS trial did not restrict the number of patients enrolled for each first-line therapy; therefore, the population was expected to parallel real-world treatment trends for mRCC at the time of trial initiation—these trends may have evolved since 2008 when enrollment began.
Few retrospective studies have evaluated treatment for mRCC beyond second-line therapy. Harrison et al. (2013, 2014) assessed up to 3 lines of treatment for mRCC from a joint community-academic registry.19,20 For patients receiving 3 subsequent targeted agents, TKI to mTOR inhibitor to another TKI was a more common treatment sequence than switching from one TKI to another TKI followed by an mTOR inhibitor.20 Likewise, in a review of medical records from oncology practices in the United States, Jonasch et al. (2014) found that the most common 3-line targeted therapy sequence was a VEGF inhibitor to an mTOR inhibitor to another VEGF inhibitor, with sunitinib, everolimus, and bevacizumab, respectively, the most frequently used treatments in this sequence.21 In the present analysis, the most common previous therapy sequence in patients prescribed third-line axitinib was also first-line sunitinib followed by second-line everolimus. Because axitinib was not approved in the United States until 2012 (sorafenib and sunitinib were approved in 2005 and 2006, respectively), axitinib was not frequently reported as second- or third-line therapy in earlier retrospective studies.
For patients receiving second-line axitinib in this study, mean duration of first-line therapy ranged from 82 days to 252 days and was longest in patients who previously received sunitinib. Mean duration of second-line axitinib varied somewhat by first-line therapy, ranging from 127 days to 196 days for therapies received by ≥ 10 patients. However, it cannot be determined if duration of first-line therapy influenced duration of second-line axitinib. Moreover, because reasons for treatment discontinuation (e.g., disease progression or adverse events) were not assessed, duration of treatment cannot be considered a surrogate for efficacy.
Our results indicate that duration of axitinib treatment was not affected by the affiliation of the prescriber (data not shown). In contrast, previous studies reported that median duration of sunitinib and sorafenib was shorter in patients with mRCC treated at community practices versus tertiary oncology centers.17,18 These authors speculated that community oncologists may have less experience in the use of targeted agents to treat mRCC, which resulted in more frequent dose modifications and change in therapy.17
Analysis of dosing patterns indicated that most patients (87%) initiated axitinib at the recommended starting dose of 5 mg BID, and of these patients, the majority (70%) remained on that dose throughout treatment. This is consistent with previous analyses of axitinib-dispensing data from specialty pharmacies.29,30 The frequency of axitinib dose modifications in the current analysis was lower (14% of patients in the overall population had a dose decrease; 12% had a dose increase; and 7% had a dose increase followed by a decrease) than in the AXIS trial (31% had dose decreases and 37% had dose increases).9 This disparity may reflect differences in real-world management of patients with mRCC compared with management in the clinical trial setting, for instance, in terms of physician consideration of patient-specific factors such as performance status, comorbidities, and age. Although up titration in patients who tolerate the starting dose of axitinib is supported by results of a prospective, randomized phase II study,11 drug exposure does not appear to be the sole determinant of clinical response. Identification of pharmacodynamic factors contributing to axitinib efficacy may help to personalize treatment.31 Similarly, for other oncology drugs, efforts are underway to determine optimal dosing to balance safety and efficacy according to individual patient characteristics.32
The experience of patients and prescribers in clinical practice likely differs from the highly controlled setting of a clinical trial. Results from this analysis provide insight into routine clinical use of axitinib as subsequent therapy for mRCC in the United States in the period following FDA approval and complement information derived from clinical trials. The findings from this study also further expand the knowledge base of real-world treatment patterns of targeted agents for mRCC.
Limitations
This study used data from medical and pharmacy claims, which have inherent limitations. Because claims data are collected for billing and reimbursement purposes, rather than research objectives, causality (e.g., reason for change in therapy) cannot be inferred. In addition, data entry errors at sites of care cannot be detected or corrected in data analysis. There is potential for misclassification of treatment sequence because regimens may not be identified if a patient received treatment from a pharmacy/prescriber whose data are not included in the IMS database—for instance, the database may not include a patient's actual first line of therapy. Clinical outcomes (such as survival) were not addressed. In addition, the affiliation describes provider characteristics but does not necessarily describe where patient treatments took place. Although data used in this study were collected from all states, because of geographic biases, any unprojected geographic information may not be representative of the true distribution. Finally, the small number of patients in many subgroups evaluated (e.g., previous therapy or treatment sequence) preclude comparisons by statistical analysis, so results are descriptive in nature.
Conclusions
This retrospective, observational study, which linked data from specialty pharmacies with data from medical and pharmacy claims, evaluated patient, prescriber, and reimbursement characteristics associated with use of axitinib as subsequent therapy for mRCC in the United States. Of 1,175 patients analyzed, axitinib was prescribed as second-line therapy in 56% of patients and as third-line therapy in 28% of patients. The most common treatment before second-line axitinib was sunitinib, followed by pazopanib and everolimus. In contrast with results from the phase III AXIS trial,9 real-world dosing patterns for axitinib in the current analysis found that 70% of patients who started at the standard 5 mg BID dose remained on that regimen. Further investigation of real-world axitinib use in patients with mRCC through review of medical records, which have greater detail regarding disease characteristics, is warranted.
Acknowledgments
Medical writing support was provided by Joanna Bloom, PhD, of Engage Scientific Solutions and was funded by Pfizer.
Appendix A. ICD-9-CM Codes Used to identify Comorbidities and GPi-14 Codes Used to identify Rx-Risk-V Drugs
| Comorbidities | ICD-9-CM Code |
|---|---|
| AIDS/HIV | 042, 079.53, V08 |
| Cancer | 140.x, 141.x, 142.x, 143.x, 144.x, 145.x, 146.x, 147.x, 148.x, 149.x, 150.x, 151.x, 152.x, 153.x, 154.x, 155.x, 156.x, 158.x, 158.x, 159.x, 160.x, 161.x, 162.x, 163.x, 164.x, 165.x, 170.x, 171.x, 172.x, 174.x, 175.x, 176.x, 179, 180.x, 181, 182.x, 183.x, 184.x, 185, 186.x, 187.x, 188.x, 189.x, 190.x, 191.x, 192.x, 193, 194.x, 195.x, 200.x, 201.x, 202.x, 203.x, 204.x, 205.x, 206.x, 207.x, 208.x, 209.x, 235.x, 236.x, 237.x, 238.x, 239.x |
| Congestive heart failure | 398.91, 404.x, 425.x, 428.x |
| Chronic pulmonary disease | 490, 491.x, 492.x, 493.x, 494.x, 495.x, 496, 500, 501, 502, 503, 504, 505, 506.4 |
| Cardiovascular disease | 430, 431, 432.x, 433.x, 434.x, 435.x, 436, 437.x, 438.x |
| Dementia | 290.x, 331.x |
| Diabetes with chronic complications | 249.x, 250.x |
| Diabetes with or without acute complications | 249.x, 250.x |
| Metastatic carcinoma | 196.x, 197.x, 198.x, 199.x |
| Mild liver disease | 571.x |
| Moderate to severe liver disease | 456.x, 572.x |
| Myocardial infarction | 410.x, 412 |
| Paraplegia/hemiplegia | 342.x, 344.1 |
| Peptic ulcer disease | 531.x, 532.x, 533.x, 534.x |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 441.x, 443.9, 785.4, V434 |
| Renal disease | 582.x, 583.x, 585.x, 586, 588.xm |
| Rheumatologic disease | 710.x, 714.x, 725 |
| Rx-Risk-V Drugs | GPI-14 Code |
| Abacavir sulfate | 1210500510* |
| Abacavir sulfate-lamivudine | 1210990220* |
| Abacavir sulfate-lamivudine-zidovudine | 1210990320* |
| Abciximab | 8515301000* |
| Acarbose | 2750001000* |
| Acebutolol HCl | 3320001010* |
| Acetaminophen w/codeine | 6599100205* |
| Acetaminophen-caffeine-dihydrocodeine | 6599130305* |
| Acetaminophen-codeine & dietary management product | 6599700310* |
| Acetaminophen-isometheptene-caffeine | 6799000307* |
| Acetaminophen-isometheptene-dichloralphenazone | 6799000310* |
| Acetohexamide | 2720001000* |
| Acitretin | 9025051000* |
| Acitretin w/moisturizer | 9025051030* |
| Aclidinium bromide | 44100007108020 |
| Adalimumab | 6627001500* |
| Adenosine | 3550001000* |
| Albiglutide | 2717001000* |
| Albuterol | 4420101000* |
| Albuterol sulfate | 4420101010* |
| Alclometasone dipropionate | 9055000510* |
| Alefacept | 9025051500* |
| Alendronate sodium | 3004201010* |
| Alendronate sodium-cholecalciferol | 3004201020* |
| Alfentanil | 6510001500* |
| Alfuzosin HCl | 5685201010* |
| Aliskiren fumarate | 3617001010* |
| Aliskiren-amlodipine | 3699670210* |
| Aliskiren-amlodipine-hydrochlorothiazide | 3699680320* |
| Aliskiren-hydrochlorothiazide | 3699600215* |
| Aliskiren-valsartan | 3699650215* |
| Allopurinol | 6800001000* |
| Allopurinol sodium | 6800001010* |
| Almotriptan malate | 6740601010* |
| Alogliptin benzoate | 2755001010* |
| Alogliptin-metformin HCl | 2799250210* |
| Alogliptin-pioglitazone | 2799400210* |
| Alosetron HCl | 5255401510 |
| Alprazolam | 5710001000* |
| Alprazolam-dietary management product | 5799900210* |
| Amantadine HCl | 7320001010* |
| Amcinonide | 9055001000* |
| Amiloride HCl | 3750001010* |
| Aminosalicylic acid | 0900001000* |
| Amitriptyline HCl | 5820001010* |
| Amitriptyline HCl & dietary management product | 5899870210* |
| Amiodarone HCl | 3540000500* |
| Amiodarone HCl in dextrose | 3540000511* |
| Amlodipine besylate | 3400000310* |
| Amlodipine besylate-benazepril HCl | 3699150220* |
| Amlodipine besylate-olmesartan medoxomil | 3699300205* |
| Amlodipine besylate-valsartan | 3699300210* |
| Amlodipine-valsartan-hydrochlorothiazide | 3699450320* |
| Ammoniated mercury-salicylic acid | 90259902104110 |
| Amobarbital sodium | 6010001010* |
| Amoxapine | 5820002000* |
| Amprenavir | 1210451000* |
| Amyl nitrite | 3210005000* |
| Amylase-lipase-protease | 5199000320* |
| Amylase-lipase-protease w/ca carb | 5199000420* |
| Anagrelide HCl | 8515601010* |
| Anisindione | 8330001000* |
| Anthralin | 9025002000* |
| Acetaminophen w/butalbital & codeine | 6599100310* |
| Apixaban | 8337001000* |
| Apomorphine HCl | 7320301010* |
| Apraclonidine HCl | 8660201010* |
| Arformoterol tartrate | 4420101210* |
| Argatroban | 8333701500* |
| Argatroban in NaCl | 8333701520* |
| Aripiprazole | 5925001500* |
| Asenapine maleate | 5915501510* |
| Aspirin buffered-pravastatin sodium | 3940990215* |
| Aspirin w/codeine | 6599100210* |
| Aspirin-acetaminophen-salicyl-caffeine w/codeine | 6599100510* |
| Aspirin-caffeine-dihydrocodeine bitartrate | 6599130310* |
| Aspirin-dipyridamole | 8515990220* |
| Astemizole | 4155001000* |
| Atazanavir sulfate | 1210451520* |
| Atenolol | 3320002000* |
| Atenolol & chlorthalidone | 3699200210* |
| Atorvastatin calcium | 3940001010* |
| Azatadine maleate | 4150001015* |
| Azathioprine | 9940601000* |
| Azathioprine sodium | 9940601010* |
| Azelastine HCl-fluticasone propionate | 4299550215* |
| Azilsartan medoxomil | 3615001020* |
| Azilsartan medoxomil-chlorthalidone | 3699400210* |
| Beclomethasone diprop monohyd | 4220001032* |
| Beclomethasone dipropionate (nasal) | 4220001030* |
| Bedaquiline fumarate | 0900001510* |
| Belatacept | 9940802000* |
| Benazepril HCl | 3610000510* |
| Benazepril & hydrochlorothiazide | 3699180215* |
| Bendroflumethiazide | 3760001000* |
| Bendroflumethiazide/rauwolfia | 3699100210* |
| Benzthiazide | 3760001500* |
| Benztropine mesylate | 7310001010* |
| Bepridil HCl | 3400000510* |
| Betamethasone benzoate | 9055002020* |
| Betamethasone dipropionate (topical) | 9055002000* |
| Betamethasone dipropionate augmented | 9055002005* |
| Betamethasone valerate | 9055002010* |
| Betaxolol HCl | 3320002110* |
| Betaxolol HCl (ophth) | 8625001010* |
| Bimatoprost | 8633001500* |
| Biperiden HCl | 7310002010* |
| Bisoprolol & hydrochlorothiazide | 3699200213* |
| Bisoprolol fumarate | 3320002210* |
| Bitolterol mesylate | 4420102010* |
| Bivalirudin | 8333402000* |
| Bretylium tosylate | 3540001010* |
| Brimonidine tartrate | 8660202010* |
| Brimonidine tartrate-timolol maleate | 8625990215* |
| Brinzolamide | 8680232000* |
| Brinzolamide-brimonidine tartrate | 8660990220* |
| Bromfenac sodium | 6610000510* |
| Bromocriptine mesylate | 7320002010* |
| Bromocriptine mesylate (diabetes) | 2757402010* |
| Brompheniramine maleate | 4110001015* |
| Brompheniramine tannate | 4110001040* |
| Brompheniramine-diphenhydramine | 4199100215* |
| Budesonide (nasal) | 4220001500* |
| Budesonide-formoterol fumarate dihydrate | 4420990241* |
| Bumetanide | 3720001000* |
| Buprenorphine | 6520001000* |
| Buprenorphine HCl | 6520001010* |
| Buprenorphine HCl-naloxone HCl dihydrate | 6520001020* |
| Bupropion HCl | 5830004010* |
| Bupropion HCl (smoking deterrent) | 6210000210* |
| Bupropion HCl-dietary management product | 5899900220* |
| Bupropion hydrobromide | 5830004020* |
| Butabarbital sodium | 6010002510* |
| Butalbital-acetaminophen-caffeine w/codeine | 6599100410* |
| Butalbital-aspirin-caffeine w/codeine | 6599100430* |
| Butorphanol tartrate | 6520002010* |
| Calcifediol | 7720203400* |
| Calcipotriene | 9025002500* |
| Calcipotriene-betamethasone dipropionate | 9055990232* |
| Calcitriol | 3090503000* |
| Calcitriol (topical) | 9025002800* |
| Canagliflozin | 2770002000* |
| Candesartan cilexetil | 3615002010* |
| Candesartan cilexetil-hydrochlorothiazide | 3699400220* |
| Capreomycin sulfate | 0900002010* |
| Captopril | 3610001000* |
| Captopril & hydrochlorothiazide | 3699180225* |
| Carbachol (ophth) | 8650102000* |
| Carbamazepine | 7260002000* |
| Carbamazepine (antipsychotic) | 5940001500* |
| Carbidopa | 7340303000* |
| Carbidopa-levodopa | 7320990210* |
| Carbidopa-levodopa-entacapone | 7320990330* |
| Carbinoxamine maleate | 4120001015* |
| Carbinoxamine maleate-carbinoxamine tannate | 4199100230* |
| Carbinoxamine tannate | 4120001025* |
| Carteolol HCl (ophth) | 8625001210* |
| Celecoxib | 6610052500* |
| Cerivastatin sodium | 3940002010* |
| Cetirizine HCl | 4155002010* |
| Chlordiazepoxide | 5710002000* |
| Chlordiazepoxide HCl | 5710002010* |
| Chlorpheniramine maleate | 4110002015* |
| Chlorpheniramine maleate tannate | 4110002017* |
| Chlorpheniramine tannate | 4110002025* |
| Chlorpheniramine tannate-methscopolamine | 4199200225* |
| Chlorpheniramine-methscopolamine | 4199200220* |
| Chlorpropamide | 2720002000* |
| Chlorpromazine | 5920001500* |
| Chlorpromazine HCl | 5920001510* |
| Chlorothiazide | 3760002000* |
| Chlorothiazide sodium | 3760002010* |
| Chlorthalidone | 3760002500* |
| Cholestyramine | 3910001000* |
| Cholestyramine light | 3910001010* |
| Choline fenofibrate | 3920000600* |
| Ciclesonide (nasal) | 4220001800* |
| Cilostazol | 8515551600* |
| Cimetidine | 4920001000* |
| Cimetidine HCl | 4920001010* |
| Cimetidine in saline | 4920001100* |
| Citalopram & dietary management product | 5899850220* |
| Citalopram hydrobromide | 5816002010* |
| Clemastine fumarate | 4120002040* |
| Clevidipine butyrate | 3400000710* |
| Clobazam | 7210000700* |
| Clobetasol propionate | 9055002510* |
| Clobetasol propionate & clobetasol propionate emulsion | 9055002550* |
| Clobetasol propionate cream & coal tar solution | 9055990235* |
| Clobetasol propionate emollient base | 9055002515* |
| Clobetasol propionate emulsion | 9055002520* |
| Clobetasol propionate ointment & coal tar solution | 9055990236* |
| Clocortolone pivalate | 9055003010* |
| Clofibrate | 3920001000* |
| Clomipramine HCl | 5820002510* |
| Clonazepam | 7210001000* |
| Clonidine & chlorthalidone | 3699500220* |
| Clonidine HCl | 3620101010* |
| Clopidogrel bisulfate | 8515802010* |
| Clorazepate dipotassium | 5710003010* |
| Clozapine | 5915202000* |
| Coal tar extract | 9052001000* |
| Coal tar-amm mercury-methen sulfosalicylate | 9052990340* |
| Coal tar-salicylic acid | 9052990220* |
| Codeine phosphate | 6510002010* |
| Codeine sulfate | 6510002020* |
| Colchicine | 6800002000* |
| Colchicine w/probenecid | 6899000210* |
| Colesevelam HCl | 3910001610* |
| Colestipol HCl | 3910002010* |
| Cycloserine | 0900003000* |
| Cyclosporine | 9940202000* |
| Cyclosporine modified (for microemulsion) | 9940202030* |
| Cyproheptadine HCl | 4150002010* |
| Dabigatran etexilate mesylate | 8333703020* |
| Dalteparin sodium | 8310101010* |
| Danaparoid sodium | 8310101410* |
| Dapagliflozin propanediol | 2770004020* |
| Dapiprazole HCl | 8650102510* |
| Darbepoetin alfa-albumin (human) | 8240101512* |
| Darbepoetin alfa-polysorbate 80 | 8240101511* |
| Darunavir ethanolate | 1210452010* |
| Delavirdine mesylate | 1210902020* |
| Demecarium bromide | 8650201010* |
| Deserpidine & hydrochlorothiazide | 3699100222* |
| Deserpidine & methyclothiazide | 3699100220* |
| Desipramine HCl | 5820003010* |
| Desirudin | 8333403000* |
| Desloratadine | 4155002100* |
| Desonide | 9055003500* |
| Desonide cream w/moisturizing lotion | 9055003555* |
| Desonide cream w/wound dressing cream | 9055003565* |
| Desonide lotion w/moisturizing cream | 9055003550* |
| Desonide ointment w/moisturizing lotion | 9055003560* |
| Desonide ointment w/wound dressing cream | 9055003568* |
| Desoximetasone | 9055004000* |
| Dexamethasone sodium phosphate | 9055004510* |
| Desvenlafaxine | 5818002000* |
| Desvenlafaxine fumarate | 5818002010* |
| Desvenlafaxine succinate | 5818002020* |
| Dexbrompheniramine tannate-pyrilamine maleate | 4199100240* |
| Dexchlorpheniramine maleate | 4110003015* |
| Dexlansoprazole | 4927002000* |
| Dezocine | 6520002500* |
| Diazepam | 5710004000* |
| Diazepam (anticonvulsant) | 7210003000* |
| Diazepam-dietary management product | 5799900220* |
| Diazoxide | 2730002000* |
| Diazoxide (antihypertensive) | 3660001000* |
| Diclofenac | 6610000700* |
| Diclofenac potassium | 6610000710* |
| Diclofenac potassium (migraine) | 6760004010* |
| Diclofenac sodium | 6610000720* |
| Diclofenac w/misoprostol | 6610990220* |
| Dicumarol | 8320001000* |
| Didanosine | 1210501500* |
| Diflorasone diacetate | 9055005010* |
| Diflorasone diacetate emollient base | 9055005015* |
| Digitoxin | 3120002000* |
| Digoxin | 3120001000* |
| Dihydroergotamine mesylate | 6700003010* |
| Diltiazem HCl | 3400001010* |
| Diltiazem HCl coated beads | 3400001012* |
| Diltiazem HCl extended release beads | 3400001011* |
| Diltiazem malate | 3400001030* |
| Dipivefrin HCl | 8660001000* |
| Dipyridamole | 8515003000* |
| Disopyramide phosphate | 3510001010* |
| Disulfiram | 6280204000*, 6200002000* |
| Divalproex sodium | 7250001010* |
| Dofetilide | 3540002500* |
| Dolutegravir sodium | 1210301510* |
| Donepezil HCl | 6205102510* |
| Dorzolamide HCl | 8680234010* |
| Dorzolamide HCl-timolol maleate | 8625990220* |
| Doxazosin mesylate | 3620200510* |
| Doxazosin mesylate (BPH) | 5685202520* |
| Doxepin HCl | 5820004010* |
| Doxylamine succinate | 4120004010* |
| Doxylamine succinate tannate | 4120004020* |
| Dronedarone HCl | 3540002810* |
| Duloxetine HCl | 5818002510* |
| Dutasteride-tamsulosin HCl | 5685990225* |
| Echothiophate iodide | 8650202010* |
| Efalizumab | 9025052700* |
| Efavirenz | 1210903000* |
| Efavirenz-emtricitabine-tenofovir disoproxil fumarate | 1210990330* |
| Eletriptan hydrobromide | 6740602510* |
| Elvitegravir-cobicistat-emtricitabine-tenofovir | 1210990430* |
| Emtricitabine | 1210603000* |
| Emtricitabine-rilpivirine-tenofovir disoproxil fumarate | 1210990340* |
| Emtricitabine-tenofovir disoproxil fumarate | 1210990230* |
| Enalapril maleate | 3610002010* |
| Enalapril maleate & hydrochlorothiazide | 3699180235* |
| Enalapril maleate-diltiazem malate | 3699150226* |
| Enalapril maleate-felodipine | 3699150230* |
| Enalaprilat | 3610002510* |
| Encainide HCl | 3530000510* |
| Enfuvirtide | 1210253000* |
| Enoxaparin sodium | 8310102010* |
| Entacapone | 7315303000* |
| Epinephrine bitartrate (ophth) | 8660002010* |
| Epinephrine HCl | 4420202020* |
| Epinephrine HCl (ophth) | 8660002020* |
| Epinephryl borate | 8660002030* |
| Eplerenone | 3625003000* |
| Epoetin alfa | 8240102000* |
| Eprosartan mesylate | 3615002420* |
| Eprosartan mesylate-hydrochlorothiazide | 3699400225* |
| Eptifibatide | 8515303000* |
| Ergot w/pentobarb-bella-caffeine | 6799100420* |
| Ergotamine tartrate | 6700002010* |
| Ergotamine w/caffeine | 6799100210* |
| Ergotamine w/pb & belladonna | 6799100320* |
| Escitalopram oxalate | 5816003410* |
| Eslicarbazepine acetate | 7260002410* |
| Esmolol HCl | 3320002510* |
| Esmolol HCl-sodium chloride | 3320002511* |
| Esomeprazole magnesium | 4927002510* |
| Esomeprazole sodium | 4927002520* |
| Esomeprazole strontium | 4927002530* |
| Ethambutol HCl | 0900004010* |
| Etanercept | 6629003000* |
| Ethacrynate sodium | 3720002010* |
| Ethacrynic acid | 3720002000* |
| Ethionamide | 0900005000* |
| Ethosuximide | 7240001000* |
| Ethotoin | 7220001000* |
| Etidronate disodium | 3004204010* |
| Etodolac | 6610000800* |
| Etravirine | 1210903500* |
| Etretinate | 9025003000* |
| Ezetimibe | 3930003000* |
| Ezetimibe-atorvastatin | 3999400220* |
| Ezetimibe-simvastatin | 3999400230* |
| Ezogabine | 7260002600* |
| Famotidine | 4920003000* |
| Famotidine in NaCl | 4920003011* |
| Febuxostat | 6800003000* |
| Felbamate | 7212002000* |
| Felodipine | 3400001300* |
| Fenofibrate | 3920002500* |
| Fenofibrate micronized | 3920002510* |
| Fenofibric acid | 3920002400* |
| Fenoldopam mesylate | 3640203010* |
| Fenoprofen calcium | 6610001010* |
| Fentanyl | 6510002500* |
| Fentanyl citrate | 6510002510* |
| Fentanyl citrate-bupivacaine HCl-NaCl | 6599150330* |
| Fentanyl citrate-ropivacaine HCl-NaCl | 6599150335* |
| Fentanyl citrate-NaCl | 6510002512* |
| Fexofenadine HCl | 4155002410* |
| Flecainide acetate | 3530001010* |
| Fluocinolone acetonide | 9055005510* |
| Fluocinolone acetonide & cleanser | 9055990239* |
| Fluocinolone-emollient | 9055990240* |
| Fluocinonide | 9055006000* |
| Fluocinonide emulsified base | 9055006010* |
| Fluoxetine HCl | 5816004000* |
| Fluoxetine HCl-dietary management product | 5899850245* |
| Fluphenazine decanoate | 5920002530* |
| Fluphenazine enanthate | 5920002520* |
| Fluphenazine HCl | 5920002510* |
| Flurandrenolide | 9055006500* |
| Flurbiprofen | 6610001200* |
| Fluticasone furoate-vilanterol | 4420990275* |
| Fluticasone propionate | 9055006810* |
| Fluticasone-salmeterol | 4420990270* |
| Fluvastatin sodium | 3940003010* |
| Fluvoxamine maleate | 5816004510* |
| Fondaparinux sodium | 8310303010* |
| Formoterol fumarate | 4420102710* |
| Fosamprenavir calcium | 1210452510* |
| Fosinopril sodium | 3610002710* |
| Fosinopril sodium & hydrochlorothiazide | 3699180240* |
| Fosphenytoin sodium | 7220001310* |
| Frovatriptan succinate | 6740603010* |
| Furosemide | 3720003000* |
| Gabapentin | 7260003000* |
| Gabapentin-dietary management product | 7299600230* |
| Gemfibrozil | 3920003000* |
| Glimepiride | 2720002700* |
| Glipizide | 2720003000* |
| Glipizide-metformin HCl | 2799700235* |
| Glyburide | 2720004000* |
| Glyburide-metformin | 2799700240* |
| Glyburide micronized | 2720004010* |
| Golimumab | 6627004000* |
| Guanabenz acetate | 3620102010* |
| Guanadrel sulfate | 3620201010* |
| Guanethidine & hydrochlorothiazide | 3699550230* |
| Guanethidine monosulfate | 3620202010* |
| Guanfacine HCl | 3620102510* |
| Halazepam | 5710005000* |
| Halcinonide | 9055007000* |
| Halobetasol propionate | 9055007310* |
| Halobetasol propionate & ammonium lactate | 9055990247* |
| Halobetasol propionate & lactic acid | 9055990249* |
| Haloperidol | 5910001010* |
| Haloperidol decanoate | 5910001030* |
| Haloperidol lactate | 5910001020* |
| Heparin (porcine) in NaCl | 8310002022* |
| Heparin sod (porcine) in d5w | 8310002025* |
| Heparin sodium (bovine) | 8310002021* |
| Heparin sodium (porcine) | 8310002020* |
| Hydralazine & hydrochlorothiazide | 3699900245* |
| Hydralazine & reserpine & hydrochlorothiazide | 3699100320* |
| Hydralazine HCl | 3640001010* |
| Hydrochlorothiazide | 3760004000* |
| Hydrocodone bitartrate | 6510003010* |
| Hydrocodone-acetaminophen | 6599170210* |
| Hydrocodone-acetaminophen-dietary management product | 6599170210* |
| Hydrocodone-aspirin | 6599170220* |
| Hydrocodone-ibuprofen | 6599170250* |
| Hydrocortisone (intrarectal) | 8915001000* |
| Hydrocortisone & salicylic acid-sulfur & shampoo | 9055990435* |
| Hydrocortisone acetate-aloe vera | 9055990251* |
| Hydrocortisone-salicylic acid-sulfur | 9055990330* |
| Hydromorphone HCl | 6510003510* |
| Hydromorphone HCl-bupivacaine HCl-NaCl | 6599180330* |
| Hydromorphone HCl-NaCl | 6510003512* |
| Ibuprofen | 6610002000* |
| Ibuprofen w/caffeine & vitamins | 6610990328* |
| Ibuprofen w/liniment | 6610002050* |
| Ibuprofen-famotidine | 6610990232* |
| Ibutilide fumarate | 3540005010* |
| Icosapent ethyl | 3950003510* |
| Iloperidone | 5907003500* |
| Imipramine HCl | 5820005010* |
| Imipramine pamoate | 5820005020* |
| Indacaterol maleate | 4420104220* |
| Indapamide | 3760005000* |
| Indinavir sulfate | 1210453020* |
| Indomethacin | 6610003000* |
| Indomethacin sodium | 6610003010* |
| Infliximab | 5250504000* |
| Insulin aspart | 2710400200* |
| Insulin aspart protamine & aspart (human) | 2710407000* |
| Insulin detemir | 2710400600* |
| Insulin glargine | 2710400300* |
| Insulin glulisine | 2710400400* |
| Insulin lispro (human) | 2710400500* |
| Insulin lispro protamine & lispro (human) | 2710408000* |
| Insulin regular (human) | 2710401000* |
| Insulin regular (pork) | 2710301000* |
| Ipratropium bromide | 4410003010* |
| Ipratropium bromide hfa | 4410003012* |
| Ipratropium-albuterol | 4420990201* |
| Irbesartan | 3615003000* |
| Irbesartan-hydrochlorothiazide | 3699400230* |
| Isocarboxazid | 5810001000* |
| Isoetharine HCl | 4420103010* |
| Isoetharine mesylate | 4420103020* |
| Isoflurophate | 8650203000* |
| Isometheptene mucate | 6700005010* |
| Isoniazid | 0900006000* |
| Isoniazid & rifampin | 0999000210* |
| Isoniazid w/B6 | 0999000220* |
| Isoniazid-rifampin w/pyrazinamide | 0999000320* |
| Isoproterenol & phenylephrine | 4420990210* |
| Isoproterenol HCl | 4420104010* |
| Isoproterenol sulfate | 4420104020* |
| Isosorbide dinitrate | 3210002000* |
| Isosorbide mononitrate | 3210002500* |
| Isradipine | 3400001500* |
| Ketoprofen | 6610003500* |
| Ketorolac tromethamine | 6610003710* |
| Labetalol & hydrochlorothiazide | 6992002150* |
| Lacosamide | 7260003600* |
| Lactulose | 4660002000* |
| Lactulose (encephalopathy) | 5240002000* |
| Lamivudine | 1210606000* |
| Lamivudine-zidovudine | 1210990250* |
| Lamotrigine | 7260004000* |
| Lansoprazole | 4927004000* |
| Lansoprazole-naproxen | 6610990242* |
| Latanoprost | 8633005000* |
| Lepirudin | 8333405010* |
| Levalbuterol HCl | 4420104510* |
| Levalbuterol tartrate | 4420104550* |
| Levetiracetam | 7260004300* |
| Levetiracetam in NaCl | 7260004305* |
| Levobunolol HCl | 8625002010* |
| Levocetirizine dihydrochloride | 4155002710* |
| Levodopa | 7320004000* |
| Levomethadyl acetate HCl | 6510003710* |
| Levomilnacipran HCl | 5818005010* |
| Levorphanol tartrate | 6510004010* |
| Levothyroxine sodium | 2810001010* |
| Lidocaine HCl (cardiac) | 3520002010* |
| Lidocaine in d5w | 3520002011* |
| Linaclotide | 5255705000* |
| Linagliptin | 2755005000* |
| Linagliptin-metformin HCl | 2799250240* |
| Liothyronine sodium | 2810002010* |
| Liotrix (t3-t4) | 2810003000* |
| Lisinopril | 3610003000* |
| Lisinopril & hydrochlorothiazide | 3699180255* |
| Lisinopril-dietary management product | 3699850250* |
| Lithium carbonate | 5950001010* |
| Lithium citrate | 5950001020* |
| Lomitapide mesylate | 3948005020* |
| Lopinavir-ritonavir | 1210990255* |
| Loratadine | 4155003000* |
| Lorazepam | 5710006000* |
| Losartan potassium | 3615004020* |
| Losartan potassium & hydrochlorothiazide | 3699400245* |
| Lovastatin | 3940005000* |
| Loxapine | 5915402000* |
| Loxapine HCl | 5940002010* |
| Loxapine succinate | 5940002020* |
| Lurasidone HCl | 5940002310* |
| Maprotiline HCl | 5830001010* |
| Maraviroc | 1210206000* |
| Mecamylamine HCl | 3660002010* |
| Meclofenamate sodium | 6610004010* |
| Mefenamic acid | 6610005000* |
| Meloxicam | 6610005200* |
| Meloxicam w/liniment | 6610005260* |
| Meperidine HCl | 6510004510* |
| Meperidine HCl-NaCl | 6510004512* |
| Meperidine w/promethazine | 6599300220* |
| Mephenytoin | 7220002000* |
| Mephobarbital | 6010004000* |
| Mesoridazine besylate | 5920003010* |
| Metaproterenol sulfate | 4420105020* |
| Metformin HCl | 2725005000* |
| Metformin HCl-dietary management product | 2799900250* |
| Methadone HCl | 6510005010* |
| Methotrexate | 2130005000* |
| Methotrexate (antirheumatic) | 6625005000* |
| Methotrexate sodium | 2130005010* |
| Methotrexate sodium (antirheumatic) | 6625005010* |
| Methoxsalen rapid | 9025056010* |
| Methsuximide | 7240002000* |
| Methyclothiazide | 3760005500* |
| Methyldopa | 3620103000* |
| Methyldopa & chlorothiazide | 3699500260* |
| Methyldopa & hydrochlorothiazide | 3699500270* |
| Methyldopate HCl | 3620103010* |
| Methysergide maleate | 6700001010* |
| Metipranolol | 8625001510* |
| Metolazone | 3760006000* |
| Metoprolol & hydrochlorothiazide | 3699200220* |
| Metoprolol succinate | 3320003005* |
| Metoprolol tartrate | 3320003010* |
| Metoprolol tartrate-dietary management product | 3699880260* |
| Metyrosine | 3630002500* |
| Mexiletine HCl | 3520002510* |
| Mibefradil dihydrochloride | 3400001710* |
| Mifepristone (hyperglycemia) | 2730405000* |
| Miglitol | 2750005000* |
| Minoxidil | 3640002000* |
| Mipomersen sodium | 3950004010* |
| Mirtazapine | 5803005000* |
| Moexipril HCl | 3610003310* |
| Moexipril-hydrochlorothiazide | 3699180260* |
| Molindone HCl | 5916005010* |
| Mometasone furoate | 9055008210* |
| Mometasone furoate-ammonium lactate | 9055990254* |
| Mometasone furoate-formoterol fumarate dihydrate | 4420990290* |
| Montelukast sodium | 4450505010* |
| Moricizine HCl | 3505003010* |
| Morphine sulfate | 6510005510* |
| Morphine sulfate beads | 6510005520* |
| Morphine sulfate for continuous microinfusion | 6510005530* |
| Morphine sulfate in dextrose | 6510005511* |
| Morphine sulfate liposome | 6510005540* |
| Morphine sulfate-NaCl | 6510005515* |
| Morphine-naltrexone | 6510005570* |
| Mycophenolate mofetil | 9940303010* |
| Mycophenolate mofetil HCl | 9940303020* |
| Mycophenolate sodium | 9940303030* |
| Nabumetone | 6610005500* |
| Nadolol & bendroflumethiazide | 3699200230* |
| Nalbuphine HCl | 6520003010* |
| Naltrexone | 9340003000* |
| Naltrexone HCl | 9340003010*, 6540003010* |
| Naproxen | 6610006000* |
| Naproxen sodium | 6610006010* |
| Naproxen w/liniment | 6610006050* |
| Naproxen-esomeprazole magnesium | 6610990244* |
| Naratriptan HCl | 6740605010* |
| Nateglinide | 2728004000* |
| Nebivolol HCl | 3320004010* |
| Nefazodone HCl | 5812005010* |
| Nelfinavir mesylate | 1210454520* |
| Nevirapine | 1210905000* |
| Niacin (antihyperlipidemic) | 3945005000* |
| Niacin-lovastatin | 3940990245* |
| Niacin-simvastatin | 3940990270* |
| Nicardipine HCl | 3400001810* |
| Nicardipine HCl in dextrose | 3400001812* |
| Nicardipine HCl in NaCl | 3400001814* |
| Nicotine | 6210000500* |
| Nicotine polacrilex | 6210001000* |
| Nifedipine | 3400002000* |
| Nimodipine | 3400002200* |
| Nisoldipine | 3400002400* |
| Nitroglycerin | 3210003000* |
| Nitroglycerin in d5w | 3210003010* |
| Nitroprusside sodium | 3640004010* |
| Nizatidine | 4920004000* |
| Nortriptyline HCl | 5820006010* |
| Olanzapine | 5915706000* |
| Olanzapine pamoate | 5915706010* |
| Olmesartan medoxomil | 3615005520* |
| Olmesartan medoxomil-amlodipine-hydrochlorothiazide | 3699450345* |
| Olmesartan medoxomil-hydrochlorothiazide | 3699400250* |
| Omega-3-acid ethyl esters | 3950004520* |
| Omeprazole | 4927006000* |
| Omeprazole magnesium | 4927006010* |
| Oxaprozin | 6610006500* |
| Oxazepam | 5710007000* |
| Oxcarbazepine | 7260004600* |
| Oxycodone HCl | 6510007510* |
| Oxycodone w/acetaminophen | 6599000220* |
| Oxycodone-aspirin | 6599000222* |
| Oxycodone-ibuprofen | 6599000226* |
| Oxymorphone HCl | 6510008010* |
| Paliperidone | 5907005000* |
| Paliperidone palmitate | 5907005010* |
| Pancreatin | 5120001000* |
| Pancrelipase | 5120002000* |
| Pancrelipase (lipase-protease-amylase) | 5120002400* |
| Pantoprazole sodium | 4927007010* |
| Paramethadione | 7230001000* |
| Paroxetine HCl | 5816006000* |
| Paroxetine mesylate | 5816006030* |
| Pegloticase | 6800005000* |
| Pentaerythritol tetranitrate | 3210004000* |
| Pentazocine lactate | 6520004020* |
| Pentazocine w/aspirin | 6599400220* |
| Pentazocine w/naloxone | 6520004030* |
| Pentazocine-acetaminophen | 6599400210* |
| Pentobarbital | 6010005500* |
| Pentobarbital sodium | 6010005510* |
| Perampanel | 7255006000* |
| Pergolide mesylate | 7320005000* |
| Perindopril erbumine | 3610003510* |
| Perphenazine | 5920004500* |
| Phenacemide | 7260005000* |
| Phenelzine sulfate | 5810002010* |
| Pheniramine-phenyltoloxamine-pyrilamine | 4199100310* |
| Phenobarbital | |
| Phenobarbital sodium | 6010006010* |
| Phenoxybenzamine HCl | 3630001010* |
| Phentolamine mesylate | 3630002010* |
| Phenylbutazone | 6610101000* |
| Phenytoin | 7220003000* |
| Phenytoin sodium | 7220003005* |
| Phenytoin sodium extended | 7220003020* |
| Phenytoin sodium prompt | 7220003010* |
| Phenytoin w/phenobarbital | 7260990210* |
| Physostigmine sulfate | 8650204020* |
| Pilocarpine & epinephrine | 8650990210* |
| Pilocarpine HCl | 8650103010* |
| Pilocarpine nitrate | 8650103020* |
| Pioglitazone HCl | 2760705010* |
| Pioglitazone HCl-glimepiride | 2799780240* |
| Pioglitazone HCl-metformin HCl | 2799800240* |
| Pirbuterol acetate | 4420105500* |
| P irox icam | 6610007000* |
| Pitavastatin calcium | 3940005810* |
| Polythiazide | 3760006500* |
| Pramipexole dihydrochloride | 73203060100305 |
| Prasugrel HCl | 8515806010* |
| Pravastatin sodium | 3940006510* |
| Prazepam | 5710008000* |
| Prazosin HCl | 3620203010* |
| Prazosin & polythiazide | 3699550270* |
| Prednicarbate | 9055008300* |
| Pregabalin | 7260005700* |
| Primidone | 7260006000* |
| Probenecid | 6810001000* |
| Probucol | 3950005500* |
| Procainamide HCl | 3510002010* |
| Prochlorperazine | 5920005500* |
| Prochlorperazine edisylate | 5920005520* |
| Prochlorperazine maleate | 5920005510* |
| Procyclidine HCl | 7310006000* |
| Promazine HCl | 5920006010* |
| Promethazine HCl | 4140002010* |
| Propafenone HCl | 3530005000* |
| Propoxyphene compound | 6599200210* |
| Propoxyphene HCl | 6510008510* |
| Propoxyphene HCl w/acetaminophen | 6599200220* |
| Propoxyphene napsylate | 6510008520* |
| Propoxyphene w/aspirin | 6599200230* |
| Propoxyphene-n w/acetaminophen | 6599200240* |
| Propoxyphene-n w/acetaminophen & dietary management product | 6599800250* |
| Propranolol & hydrochlorothiazide | 3699200240* |
| Protriptyline HCl | 5820007010* |
| Pyrazinamide | 0900007000* |
| Pyrilamine tannate | 4130001040* |
| Quetiapine fumarate | 5915307010* |
| Quinapril HCl | 3610004010* |
| Quinapril-hydrochlorothiazide | 3699180265* |
| Quinidine gluconate | 3510003010* |
| Quinidine polygalacturonate | 3510003020* |
| Quinidine sulfate | 3510003030* |
| Rabeprazole sodium | 4927007610* |
| Raltegravir potassium | 1210306010* |
| Ramipril | 3610005000* |
| Ranitidine bismuth citrate | 4920002005* |
| Ranitidine HCl | 4920002010* |
| Ranitidine HCl in NaCl | 4920002011* |
| Rasagiline mesylate | 7330002520* |
| Remifentanil HCl | 6510008710* |
| Repaglinide | 2728006000* |
| Repaglinide-metformin HCl | 2799500270* |
| Reserpine | 3620304000* |
| Reserpine & chlorothiazide | 3699100232* |
| Reserpine & hydrochlorothiazide | 3699100234* |
| Reserpine & hydroflumethiazide | 3699100235* |
| Reserpine & methyclothiazide | 3699100236* |
| Reserpine & polythiazide | 3699100237* |
| Reserpine & trichlormethiazide | 3699100239* |
| Ribavirin-interferon alfa-2b | 1299500260* |
| Rifabutin | 0900007500* |
| Rifampin | 0900008000* |
| Rifapentine | 0900008500* |
| Rilpivirine HCl | 1210908010* |
| Risperidone | 5907007000* |
| Risperidone microspheres | 5907007010* |
| Ritonavir | 1210456000* |
| Rivaroxaban | 8337006000* |
| Rizatriptan benzoate | 6740606010* |
| Rofecoxib | 6610056500* |
| Ropinirole HCl | 7320307010* |
| Rosiglitazone maleate | 2760706010* |
| Rosiglitazone maleate-glimepiride | 2799780260* |
| Rosiglitazone maleate-metformin HCl | 2799800260* |
| Rosuvastatin calcium | 3940006010* |
| Rotigotine | 7320307500* |
| Rufinamide | 7260006500* |
| Saquinavir | 1210458000* |
| Saquinavir mesylate | 1210458020* |
| Sacrosidase | 5120006000* |
| Salmeterol xinafoate | 4420105810* |
| Saxagliptin HCl | 2755006510* |
| Saxagliptin-metformin HCl | 2799250260* |
| Secobarbital sodium | 6010007010* |
| Selegiline | 5810002700* |
| Selegiline HCl | 7330003010* |
| Sertraline HCl | 5816007010* |
| Sevelamer carbonate | 5280007005* |
| Sevelamer HCl | 5280007010* |
| Silodosin | 5685206000* |
| Simvastatin | 3940007500* |
| Sirolimus | 9940407000* |
| Sitagliptin phosphate | 2755007010* |
| Sitagliptin-metformin HCl | 2799250270* |
| Sitagliptin-simvastatin | 2799300270* |
| Sodium polystyrene sulfonate | 9945001000* |
| Spironolactone | 3750002000* |
| Stavudine | 1210807000* |
| Sufentanil citrate | 6510009010* |
| Sulfinpyrazone | 6810002000* |
| Sulindac | 6610008000* |
| Sumatriptan | 6740607000* |
| Sumatriptan succinate | 6740607010* |
| Sumatriptan-naproxen sodium | 6799200260* |
| Tacrine HCl | 6205105010* |
| Tacrolimus | 9940408000* |
| Tafluprost | 8633006500* |
| Tamsulosin HCl | 5685207010* |
| Tapentadol HCl | 6510009110* |
| Tazarotene | 9025007000* |
| Tegaserod maleate | 5255506020* |
| Telmisartan | 3615007000* |
| Telmisartan-amlodipine | 3699300270* |
| Telmisartan-hydrochlorothiazide | 3699400260* |
| Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate | 1210857010* |
| Terazosin HCl | 3620204010* |
| Terbutaline sulfate | 4420106020* |
| Terfenadine | 4155004000* |
| Thioridazine HCl | 5920008010* |
| Thiothixene | 5930002010* |
| Thiothixene HCl | 5930002020* |
| Thyroglobulin | 2810004000* |
| Thyroid | 2810005000* |
| Thyroid (pork) | 2810008000* |
| Thyroid strong | 2810006000* |
| Tiagabine HCl | 7217007010* |
| Ticagrelor | 8515847000* |
| Ticlopidine HCl | 8515808010* |
| Timolol | 8625003000* |
| Timolol & hydrochlorothiazide | 3699200250* |
| Timolol maleate (ophth) | 8625003010* |
| Tinzaparin sodium | 8310108010* |
| Tiotropium bromide monohydrate | 4410008010* |
| Tipranavir | 1210458500* |
| Tirofiban HCl | 8515306010* |
| Tirofiban HCl in NaCl | 8515306011* |
| Tocainide HCl | 3520003010* |
| Tolazamide | 2720005000* |
| Tolazoline HCl | 3660003010* |
| Tolbutamide | 2720006000* |
| Tolcapone | 7315207000* |
| Tolmetin sodium | 6610009010* |
| Topiramate | 7260007500* |
| Torsemide | 3720008000* |
| Tramadol HCl | 6510009510* |
| Tramadol HCl-dietary management product | 6599850250* |
| Tramadol-acetaminophen | 6599500220* |
| Trandolapril | 3610006000* |
| Trandolapril-verapamil HCl | 3699150270* |
| Tranylcypromine sulfate | 5810003010* |
| Travoprost | 8633007000* |
| Trazodone HCl | 5812008010* |
| Trazodone HCl-dietary management product | 5899800275* |
| Triamterene | 3750003000* |
| Trichlormethiazide | 3760007500* |
| Trifluoperazine HCl | 5920008510* |
| Trihexyphenidyl HCl | 7310007010* |
| Trimeprazine tartrate | 4140003010* |
| Trimethadione | 7230002000* |
| Trimipramine maleate | 5820008010* |
| Tripelennamine HCl | 4130002010* |
| Triprolidine HCl | 4110004010* |
| Triprolidine tannate | 4110004030* |
| Troglitazone | 2760707000* |
| Umeclidinium-vilanterol | 4420990295* |
| Unoprostone isopropyl | 8633008510* |
| Urea-hc acetate | 9055990285* |
| Ustekinumab | 9025058500* |
| Valdecoxib | 6610057500* |
| Valproate sodium | 7250002010* |
| Valproic acid | 7250003000* |
| Valsartan | 3615008000* |
| Valsartan-hydrochlorothiazide | 3699400270* |
| Varenicline tartrate | 6210008020* |
| Venlafaxine HCl | 5818009010* |
| Verapamil HCl | 3400003010* |
| Vigabatrin | 7217008500* |
| Vilazodone HCl | 5812008810* |
| Vorapaxar sulfate | 8515578030* |
| Vortioxetine HBr | 5812009310* |
| Warfarin sodium | 8320003020* |
| Zafirlukast | 4450508000* |
| Zalcitabine | 1210608500* |
| Zidovudine | 1210808500* |
| Ziprasidone HCl | 5940008510* |
| Ziprasidone mesylate | 5940008520* |
| Zolmitriptan | 6740608000* |
| Zonisamide | 7260009000* |
Note: The asterisk * represents a wild card. The first 10 digits of the GPI define the therapeutic class code (Drug Group, Drug Class, Drug sub-class, Drug name, Drug name extension), and the last 4 digits define route, dosage, or strength. Use of the wild card is a shorthand for reporting a large number of unique GPI codes belonging to the same category.
D5W = 5% dextrose in water; GPI = Generic Product Identifier; HCl = hydrochloride; ICD-9-CM = International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification; NaCl = sodium chloride; ophth = ophthalmic solution.
Appendix B. NDC Numbers and HCPCS/J Codes Used to Identify Treatments
| Drug | NDC Numbera | HCPCS/J Code |
|---|---|---|
| Ado-trastuzumab | C9131,J9354 | |
| Ado-trastuzumab emtansine | 5024200 | |
| Alemtuzumab | 5846803, 5041903 | S0087, J9010, C9110 |
| Afatinib dimaleate | 0059701 | |
| Aldesleukin | 6548301, 5390509, 0007804, 5486855 | J9015 |
| Alitretinoin | 6436505, 6285606 | |
| Arsenic trioxide | 6055301, 6345906 | J9017, C9012 |
| Asparaginase | 6738604, 0000646, 0024712 | C9289,J9020 |
| Asparaginase erwinia chrysanthemi | 5790202 | |
| Axitinib | 0006901 | |
| Azacitidine | 4359803, 0078132, 0078192, 5957201, 6721101 | J9025, C9218, S0168 |
| BCG vaccine | 1179308 | |
| Bevacizumab | 5024200 | C9214, S0116, J9035 |
| Bexarotene oral | 6285606, 0018755, 6436505 | |
| Bexarotene topical | 6436505, 6285606 | |
| Bosutinib | 0006901 | |
| Brentuximab | 5114400 | C9287, J9042 |
| Busulfan | 0017307, 6728600, 5914800, 7638807, 6216100, 0008107 | C1178,J8510,J0594 |
| Cabazitaxel | 0002458 | J9043, C9276 |
| Cabozantinib | 4238800 | |
| Carboplatin | 0001532, 2502102, 6170303, 6675800, 1013900, 1521000, 0059134, 0070332, 0070342, 5539001, 6781700, 6686001, 5539002, 6332301, 5011109, 1001909, 0059136, 0059133, 0040911, 0059122 | J9045 |
| Carfilzomib | 7607501 | C9295, J9047 |
| Carmustine | 0001530, 2315502 | C9437, J9050 |
| Carmustine in polifeprosan intracranial implant | 6285601, 6137901, 5806301 | |
| Cetuximab | 6673309 | C9215,J9055 |
| Chlorambucil | 5486811, 0017306, 0008106, 7638806 | S0172 |
| Cisplatin | 5539004, 0070357, 0001532, 6332301, 5539001, 4456705, 1001909, 0001530, 0006900, 5539000 | J9062, C9418, J9060 |
| Cladribine | 6332301, 5539001, 5967602, 0006900, 0006902 | C9419, J9065 |
| Clofarabine | 5846801 | J9027, C9129 |
| Crizotinib | 0006981 | |
| Cyclophosphamide | 1001909, 5456903, 0005441, 0001505, 0001356, 0008705, 5486850, 5486852, 5456957, 0005481, 0064122, 0005480 | C9420, J9096, J9092, J9070, J9080, J9093, J9097, C9421, J9090, J9094, J8530, J9091, J9095 |
| Cytarabine | 0000903, 0006901, 0036424, 6332301, 5539001, 5539008, 6170303, 0000904, 0000930, 0070351, 6745704, 0000932,5390501 | J9098, C9422, J9110, J9100 |
| Cytarabine liposome | 5766503, 5390503 | C1166 |
| Dabrafenib | 0017308 | |
| Dactinomycin | 0000632, 5529208, 6738608, 5539003 | J9120 |
| Dasatinib | 0000308, 0000305, 5486857 | |
| Daunorubicin citrate liposome | 5614603, 6195803, 1088500 | J9151 |
| Daunorubicin HCl | 6332301, 0070352, 5539001, 5539008, 5539002, 0070350 | C9424, J9150 |
| Decitabine | 5511105, 4359803, 6285606, 5806306 | C9231, J0894 |
| Denileukin diftitox | 6436505, 6285606 | C1084, J9160 |
| Docetaxel | 0007580, 0040902, 0095510, 1672902, 6050560, 2502102, 4733502, 6675800, 1672901 | J9170,J9171 |
| Doxorubicin HCl | 0001311, 0001533, 0018615, 0046988, 1001909, 5390502,5390508,5539002,0001312, 0001310, 0007450, 0006930, 0006901, 0070350, 0006940, 5315003, 2502102, 6745703, 6332308, 6275608, 6332301, 6745704, 0070202 | Q2048, J9000, C9415 |
| Epirubicin HCl | 6170303, 5992307, 6332301, 1051801, 5315002, 6675800, 5539002,0059134,1013900, 2502102, 0000950,5976250, 0070330 | J9178,J9180, C1167 |
| Eribulin | 6285603 | C9280, J9179 |
| Erlotinib | 5024200, 5456958, 5486854, 5486852 | |
| Etoposide | 0001530, 0007414, 0020930, 0070356, 1001909, 5539002, 584 0 607, 6332301, 00 07456, 0001373, 0036430, 5107909, 5539 004, 0018615, 0037832, 5390502, 5456957, 5486853, 1672901, 0001534 | C9414, J9182, C9425, J8560, J9181 |
| Everolimus | 0007805, 0007806 | J7527 |
| Floxuridine | 5539004, 6170303, 0000419, 6332301, 5539001 | C9426, J9200 |
| Fludarabine | Q2025, J9185, C9262 | |
| Fludarabine phosphate | 0006993, 5041905, 5846801, 6332301, 0070348, 0070358, 6170303, 0002458, 6745702, 2502102, 6675800 | |
| Fluorouracil | 1672902, 0001310, 0070330, 3976900, 6332301, 6170304, 1013900, 0046917, 0006901, 0070217, 1001909, 6675800, 0000419, 0018739, 0018230 | J9190 |
| Gefitinib | 0031004 | J8565 |
| Gemcitabine | 6332301, 5511106, 0006938, 0040901, 1672901, 2315502, 0000275, 0078132, 0070357, 4733501, 0059135, 2502102, 5539003, 1672900 | J9201 |
| Ibrutinib | 5796201 | |
| Idarubicin HCl | 0001325, 0070341, 5539002, 6332301, 5976225 | C9429, J9211 |
| Ifosfamide & mesna | 0001535, 0070341 | |
| Imatinib mesylate | 5486852, 5486854, 0007804, 6825890, 0007803, 5456958 | S0088 |
| Interferon alfa-2a | 0000419, 0000420, 0000469 | J9213 |
| Interferon alfa-2b | 0033965, 0008501, 5486830, 0008505, 0008506, 0008509, 0008511, 0008512, 0008507, 5486833, 0008502 | J9214 |
| Interferon alfa-n3 | 5474600, 0003410 | J9215 |
| Ipilimumab | 0000323 | C9284,J9228 |
| Ixabepilone | 0001519 | C9240,J9207 |
| Lapatinib ditosylate | 0017307 | |
| Lenalidomide | 5957204 | |
| Levamisole HCl | 5045802 | S0177 |
| Lomustine | 0001530, 5818130 | C9017, S0178 |
| Mechlorethamine | 0000677, 6738609, 5529209 | J9230 |
| Melphalan | 5260930, 6745701, 5486843,0017300, 5957203, 5456903, 0017301, 0008100, 5260900, 6745702 | J8600, J9245 |
| Mercaptopurine | 0037835, 6808403, 0008108, 5784405, 0005445, 5486852, 6825891, 0017308, 4988409, 0009355 | S0108 |
| Mesna | 0001535, 2502102, 6710835, 0033813, 6745701, 6332307, 5539000, 5539002, 1001909, 0070348, 5539003 | |
| Methotrexate | J9250,J8610,J9260 | |
| Mitomycin | 1672901, 0001530, 5390502, 1672902, 5539002, 5539004, 6332301, 6270100, 6170303 | J9290, J9280, C9432, J9291 |
| Mitoxantrone HCl | 0020593, 1051801, 4408715, 5539000, 6170303, 6332301, 1521004, 0070346, 5840606 | J9293 |
| Nelarabine | 0000744 | J9261 |
| Nilotinib | 0007805 | |
| Obinutuzumab | 5024200 | |
| Ofatumumab | 0017308 | C9260, J9302 |
| Omacetaxine mepesuccinate | 6345901 | |
| Paclitaxel | 5107909, 0007443, 5539003, 1051801, 6675800, 0070347, 0001534, 6332307, 2502102, 0006900, 0017237, 5539001, 6170303, 5539005, 0055519 | C9431, J9265 |
| Pazopanib | 0017308 | |
| Pegaspargase | 0007506, 5448203, 5766500 | J9266 |
| Peginterferon alfa-2a | 0000403, 5486848 | S0145 |
| Peginterferon alfa-2b | 0008512, 0008513, 5486850 | S0146 |
| Pentostatin | 5539002, 0040908, 6270108 | J9268 |
| Pertuzumab | 5024201 | C9292, J9306 |
| Plicamycin | J9270 | |
| Pomalidomide | 5957205 | |
| Ponatinib | 7618905 | |
| Porfimer sodium | 5891415, 0002415, 7612801, 5891401 | J9600 |
| Pralatrexate | 4881800 | C9259, J9307 |
| Procarbazine | S0182 | |
| Procarbazine HCl | 5486813, 5448200, 0000400 | |
| Regorafenib | 5041901 | |
| Rituximab | 5024200 | J9310 |
| Romidepsin | 5957209, 4602609 | J9315, C9265 |
| Ruxolitinib | 5088100 | |
| Sipuleucel-t | 3023789 | C9273, Q2043 |
| Sorafenib tosylate | 0002684, 5041904 | |
| Streptozocin | 0000908, 0024713, 0070346 | J9320 |
| Sunitinib malate | 0006907, 0006909, 5456959, 0006905, 5486855 | |
| Temozolomide | 0078126, 0008513, 0008530, 0008515, 5486853, 0008514, 0008512, 5456958, 5486841, 4733509, 4733508, 0009376, 6726305, 5486859, 0009375 | C1086, C9253, J8700, J9328 |
| Temsirolimus | 0000811 | J9330, C9239 |
| Teniposide | 0001530, 4456705 | Q2017 |
| Thalidomide | 5957202, 5957201 | |
| Thioguanine | 0008108, 7638808, 0017308 | |
| Thiotepa | 5840606, 0000546, 0070343, 5539000 | J9340, C9433 |
| Topotecan | J9351, J8705, J9350 | |
| Tositumomab | 6780001, 0000732 | G3001 |
| Trametinib | 0985008, 0017308 | |
| Tretinoin | 6808400, 0000402, 0055508, 1037002 | S0117 |
| Uracil mustard | 0000909 | |
| Valrubicin | 5301402, 6797900 | J9357 |
| Vandetanib | 0031078 | |
| Vemurafenib | 5024200 | |
| Vincristine sulfate | 0001374, 0070344, 0036424, 0000271, 6170303, 0030421, 0046935, 5130902, 0040210 | J9380, J9370, J9375 |
| Vincristine sulfate liposome | 2053603 | |
| Vismodegib | 5024201 | |
| Vorinostat | 0000605 | |
| Ziv-aflibercept | 0002458 | C9296, J9400 |
a Concatenated NDC number to numbers 1-7 to include multiple subcodes at NDC11 level.
BCG = Bacillus Calmette—Guérin; HCl = hydrochloride; HCPCS = Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System; NDC = National Drug Code.
Appendix C. Multivariate Regression of Key Patient Characteristics on Duration of Axitinib Therapy
| Variable | Estimate | Standard Error | T Value | P Value |
| Intercept | 164.054 | 9.316 | 17.61 | < 0.0001 |
| Gender (female vs. male) | -20.628 | 8.251 | -2.500 | 0.013 |
| Geography | ||||
| Midwest vs. Northeast | -27.978 | 10.763 | -2.60 | 0.010 |
| West vs. Northeast | -27.710 | 11.456 | -2.42 | 0.016 |
| South vs. Northeast | -10.709 | 9.959 | -1.08 | 0.282 |
| Unknown vs. Northeast | 156.946 | 122.997 | 1.28 | 0.202 |
| Prior regimen | ||||
| Everolimus vs. sunitinib | 18.188 | 9.619 | 1.890 | 0.059 |
| Pazopanib vs. sunitinib | -2.983 | 9.865 | -0.300 | 0.762 |
| Temsirolimus vs. sunitinib | -31.320 | 14.791 | -2.120 | 0.034 |
| Other vs. sunitinib | -46.400 | 16.075 | -2.890 | 0.004 |
| Sorafenib vs. sunitinib | -3.385 | 19.412 | -0.170 | 0.862 |
| Bevacizumab vs. sunitinib | -50.226 | 22.874 | -2.200 | 0.028 |
| Baseline hypothyroidism treatment (yes vs. no) | 25.538 | 8.927 | 2.860 | 0.004 |
References
- 1.Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A.. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(1):7-30. Available at: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.3322/caac.21332/epdf. Accessed May 10, 2016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology (NCCN Guidelines): kidney cancer version 3. 2015. Available at: http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/f_guidelines.asp. Accessed April 28, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Motzer RJ, Bander NH, Nanus DM.. Renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1996;335(12):865-75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al., eds.. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2011. National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute; December 17, 2014. Available at: http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2011/. Accessed April 28, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Shek D, Tomlinson B, Brown M, Brunson A, Pan CX, Lara PN Jr.. Epidemiologic trends in renal cell carcinoma in the cytokine and post-cytokine eras: a registry analysis of 28,252 patients. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2012;10(2):93-98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Heng DY, Mackenzie MJ, Vaishampayan UN, et al. Primary anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-refractory metastatic renal cell carcinoma: clinical characteristics, risk factors, and subsequent therapy. Ann Oncol. 2012;23(6):1549-55. Available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3858023/. Accessed April 28, 2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hudes GR, Carducci MA, Choueiri TK, et al. NCCN Task Force report: optimizing treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma with molecular targeted therapy. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2011;9(Suppl 1):S1-29. Available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4659363/. Accessed April 28, 2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Inlyta (axitinib) tablets for oral administration. Pfizer. August 2014. Available at: http://labeling.pfizer.com/ShowLabeling.aspx?id=759. Accessed April 28, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Rini BI, Escudier B, Tomczak P, et al. Comparative effectiveness of axitinib versus sorafenib in advanced renal cell carcinoma (AXIS): a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2011;378(9807):1931-39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rini BI, Garrett M, Poland B, et al. Axitinib in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: results of a pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic analysis. J Clin Pharmacol. 2013;53(5):491-504. Available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4175417/. Accessed April 28, 2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Rini BI, Melichar B, Ueda T, et al. Axitinib with or without dose titration for first-line metastatic renal-cell carcinoma: a randomised double-blind phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14(12):1233-42. Available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4120767/. Accessed April 28, 2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR.. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis. 1987;40(5):373-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Deyo RA, Cherkin DC, Ciol MA.. Adapting a clinical comorbidity index for use with ICD-9-CM administrative databases. J Clin Epidemiol. 1992;45(6):613-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Clark DO, Von Korff M, Saunders K, Baluchi WM, Simon GE.. A chronic disease score with empirically derived weights. Med Care. 1995;33(8):783-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Schwartz RN, Eng KJ, Frieze DA, et al. NCCN Task Force report: specialty pharmacy. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2010;8(Suppl 4):S1-12. Available at: http://www.jnccn.org/content/8/Suppl_4/S-1.full.pdf+html. Accessed April 28, 2016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Signorovitch JE, Vogelzang NJ, Pal SK, et al. Comparative effectiveness of second-line targeted therapies for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: synthesis of findings from two multi-practice chart reviews in the United States. Curr Med Res Opin. 2014;30(11):2343-53. Available at: http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1185/03007995.2014.949645. April 28, 2016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Feinberg BA, Jolly P, Wang ST, et al. Safety and treatment patterns of angiogenesis inhibitors in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: evidence from US community oncology clinics. Med Oncol. 2012;29(2):786-94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Choueiri TK, Duh MS, Clement J, et al. Angiogenesis inhibitor therapies for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: effectiveness, safety and treatment patterns in clinical practice-based on medical chart review. BJU Int. 2010;105(9):1247-54. Available at: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2009.08972.x/abstract. Accessed April 28, 2016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Harrison MR, George DJ, Walker MS, et al. "Real world" treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma in a joint community-academic cohort: progression-free survival over three lines of therapy. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2013;11(4):441-50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Harrison MR, Hirsch BR, George DJ, et al. Real-world outcomes in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: insights from a Joint Community-Academic Registry. J Oncol Pract. 2014;10(2):e63-72. Available at: http://jop.ascopubs.org/content/10/2/e63.long. Accessed April 28, 2016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Jonasch E, Signorovitch JE, Lin PL, et al. Treatment patterns in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a retrospective review of medical records from US community oncology practices. Curr Med Res Opin. 2014;30(10):2041-50 Available at: http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1185/03007995.2014.938730. Accessed April 28, 2016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hess G, Borker R, Fonseca E.. Treatment patterns: targeted therapies indicated for first-line management of metastatic renal cell carcinoma in a real-world setting. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2013;11(2):161-67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Vogelzang NJ, Hackshaw MD, Hutson TE, et al. First-line and sequentia use of pazopanib followed by mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor thei apy among patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma in a US community oncology setting. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2015;13(3):210-17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hackshaw MD, Nagar SP, Parks DC, Miller LA.. Persistence and compliance with pazopanib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma within a U.S. administrative claims database. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2014;20(6):603-10. Available at: http://www.jmcp.org/doi/abs/10.18553/jmcp.2014.20.6.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hirsch BR, Harrison MR, George DJ, et al. Use of “real-world” data to describe adverse events during the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma in routine clinical practice. Med Oncol. 2014;31(9):156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Filson CP, Redman BG, Dunn RL, Miller DC.. Initial patterns of care with oral targeted therapies for patients with renal cell carcinoma. Urology. 2011;77(4):825-30.e1. Available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3074053/. Accessed April 28, 2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wong MK, Yang H, Signorovitch JE, et al. Comparative outcomes of everolimus, temsirolimus and sorafenib as second targeted therapies for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a U.S. medical record review. Curr Med Res Opin. 2014;30(4):537-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ridge CA, Pua BB, Madoff DC.. Epidemiology and staging of renal cell carcinoma. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2014;31(1):3-8. Available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3930658/. Accessed April 28, 2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chen C, Assang M, Cisar L.. Axitinib real-world dose titration experienc from U.S. specialty pharmacy data. J Manag Care Pharm. 2013;19(8):659. [Abstract]. Available at: http://www.amcp.org/WorkArea/DownloadAsset.aspx?id=17207. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Borst DL, Arruda LS, MacLean E, Pithavala YK, Morgado JE.. Common questions regarding clinical use of axitinib in advanced renal cell carcinom Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2014;71(13):1092-96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Rini BI, Melichar B, Fishman MN, et al. Axitinib dose titration: analyses of exposure, blood pressure and clinical response from a randomized phase II study in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Ann Oncol. 2015;26(7):1372-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Minasian L, Rosen O, Auclair D, Rahman A, Pazdur R, Schilsky RL.. Optimizing dosing of oncology drugs. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2014;96(5):572-79 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


