Abstract
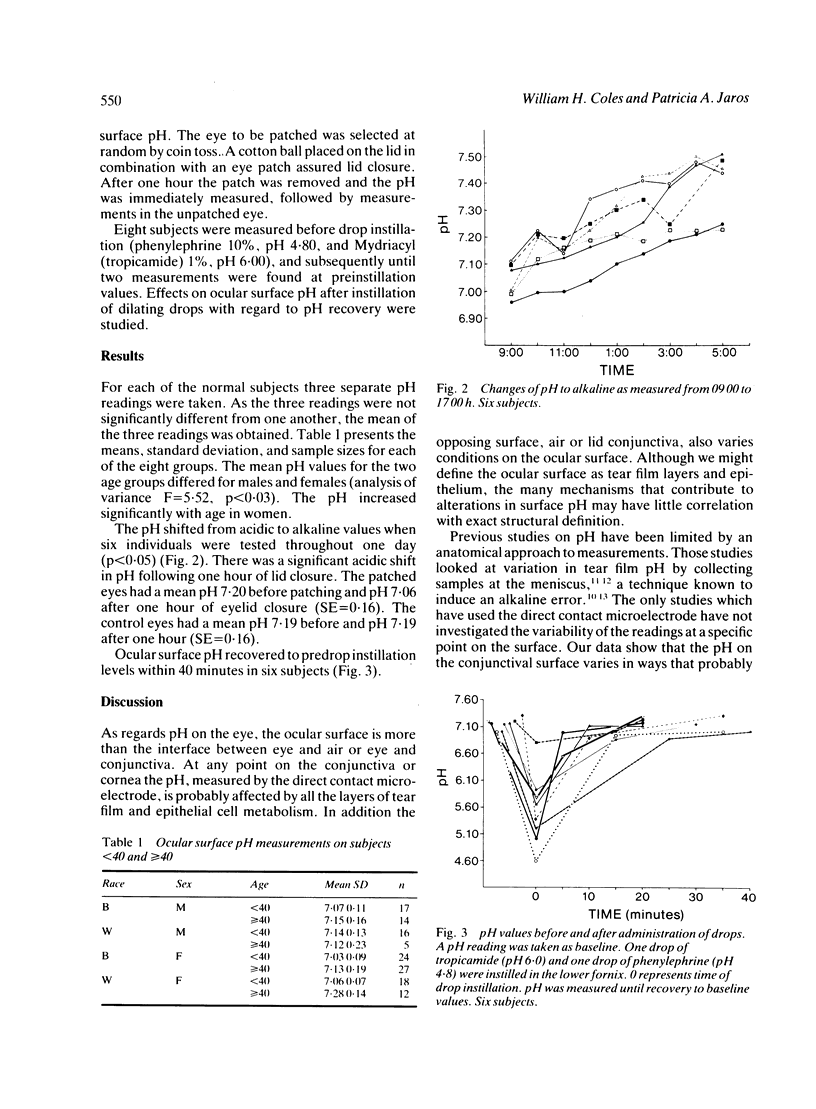
We studied ocular surface pH in 161 subjects. The mean pH for 133 normal volunteers was 7 . 11, SD 1 . 5. We found that older women had a more alkaline pH than other subjects, that the pH shifted from acid to alkaline during the day, that one hour of eyelid closure caused an acid shift in pH, and that pH recovered to baseline values within 40 minutes after acid drop instillation. We explored the mechanism of pH regulation, and we believe that pH changes could affect contact lens toleration, drug effectiveness, and clinical signs in disease processes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abelson M. B., Udell I. J., Weston J. H. Normal human tear pH by direct measurement. Arch Ophthalmol. 1981 Feb;99(2):301–301. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1981.03930010303017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barza M. Principles of tissue penetration of antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Nov;8 (Suppl 100):7–28. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_c.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. I., Dervichian D. G. The oils of the meibomian glands. Physical and surface characteristics. Arch Ophthalmol. 1969 Oct;82(4):537–540. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1969.00990020539019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney L. G., Hill R. M. Human tear pH. Diurnal variations. Arch Ophthalmol. 1976 May;94(5):821–824. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1976.03910030405011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes C. Circadian rhythms in the flow rate and composition of unstimulated and stimulated human submandibular saliva. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(2):535–548. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doroshow J. H., Locker G. Y., Gaasterland D. E., Hubbard S. P., Young R. C., Myers C. E. Ocular irritation from high-dose methotrexate therapy: pharmacokinetics of drug in the tear film. Cancer. 1981 Nov 15;48(10):2158–2162. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19811115)48:10<2158::aid-cncr2820481007>3.0.co;2-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLIOT J. S., SHARP R. F., LEWIS L. Urinary pH. J Urol. 1959 Feb;81(2):339–343. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)66022-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer F. H., Wiederholt M. Human precorneal tear film pH measured by microelectrodes. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1982;218(3):168–170. doi: 10.1007/BF02215658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. M., Carney L. G. Human tear responses to alkali. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1980 Feb;19(2):207–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. M. Laboratory studies. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 1981;21(2):223–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaros P. A., Coles W. H. Ocular surface pH in Rosacea. CLAO J. 1983 Oct-Dec;9(4):333–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarey B. E., Wilson L. A. pH, osmolarity and temperature effects on the water content of hydrogel contact lenses. Contact Intraocul Lens Med J. 1982 Jul-Sep;8(3):158–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norn M. S. Human tear PH. Arch Ophthalmol. 1977 Jan;95(1):170–170. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1977.04450010170031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norn M. S. Hydrogen ion concentration of tear fluid. Estimated on the basis of a bromothymol-blue-dyed lacrimal streak. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1968;46(2):189–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietsch R. L., Pearlman M. E. Human tear lysozyme variables. Arch Ophthalmol. 1973 Aug;90(2):94–96. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1973.01000050096003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon C., Malerczyk V., Klaus M. Absorption of bacampicillin and ampicillin and penetration into body fluids (skin blister fluid, saliva, tears) in healthy volunteers. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1978;(14):228–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentic J. P., Leopold I. H., Dea F. J. Excretion of salicylic acid into tears following oral administration of aspirin. Ophthalmology. 1980 Aug;87(8):815–820. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(80)35157-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



