Abstract
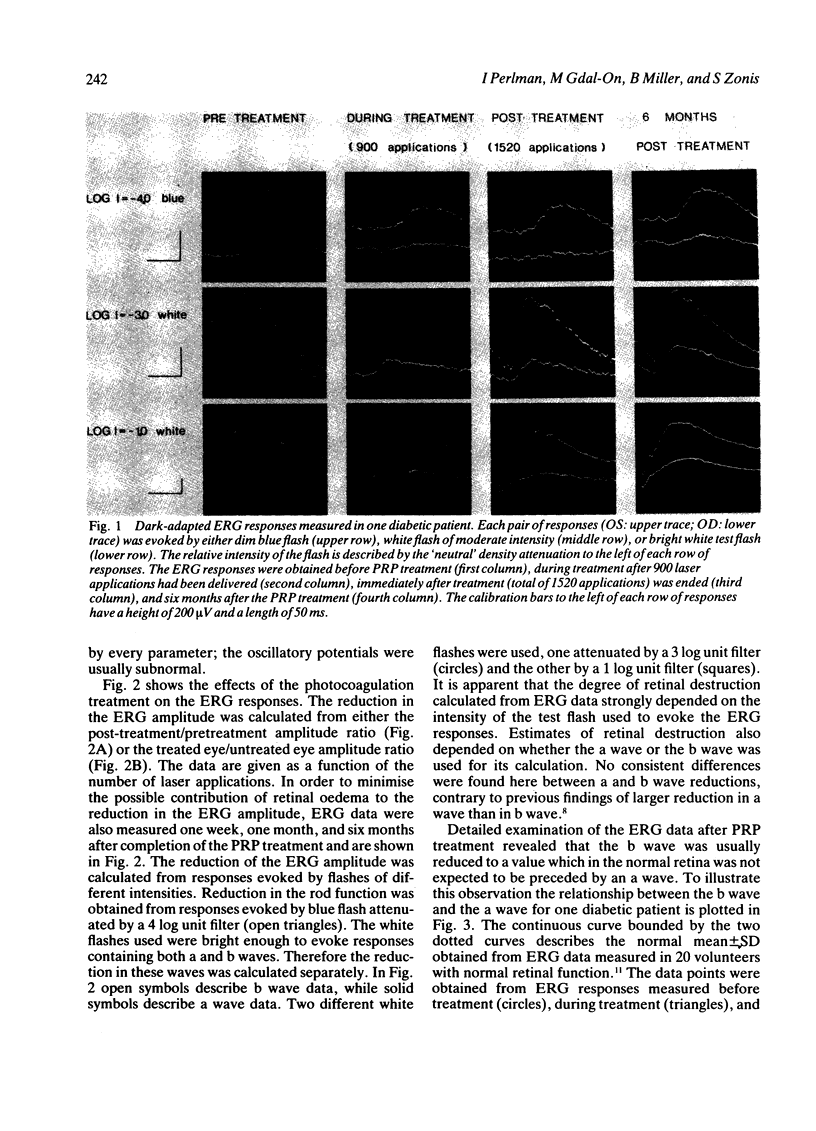
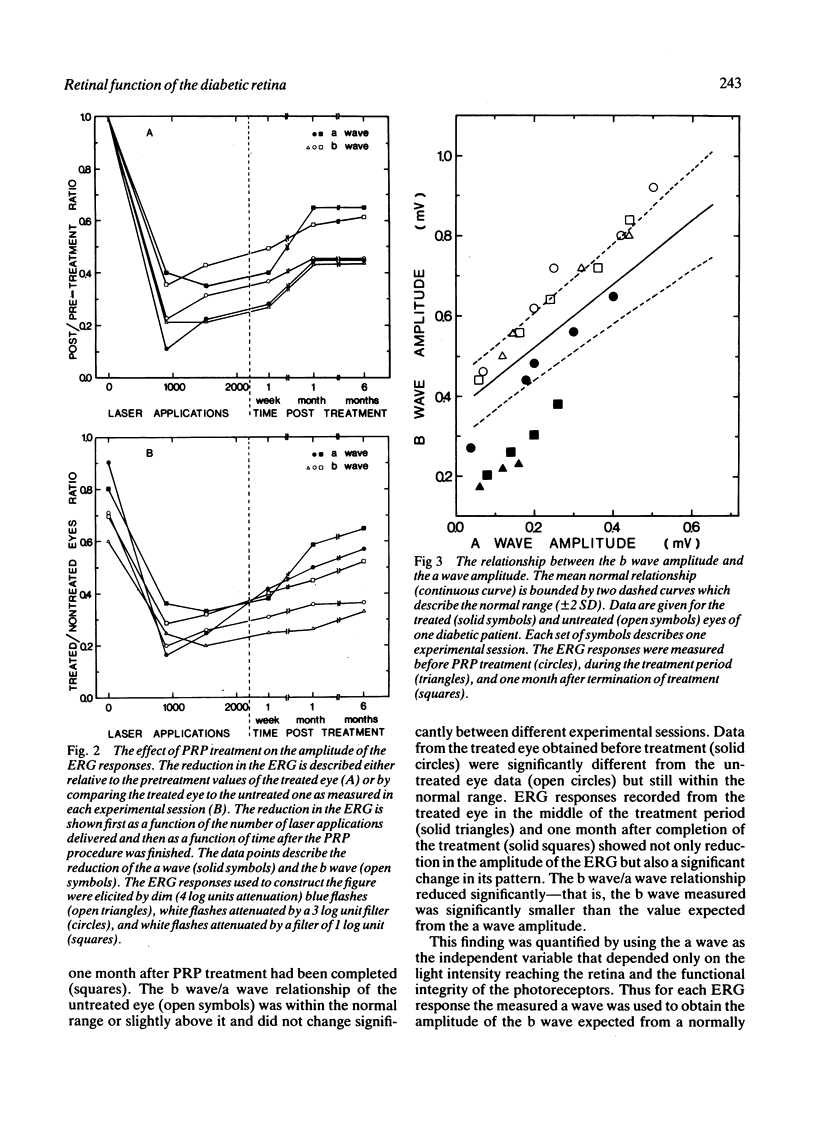
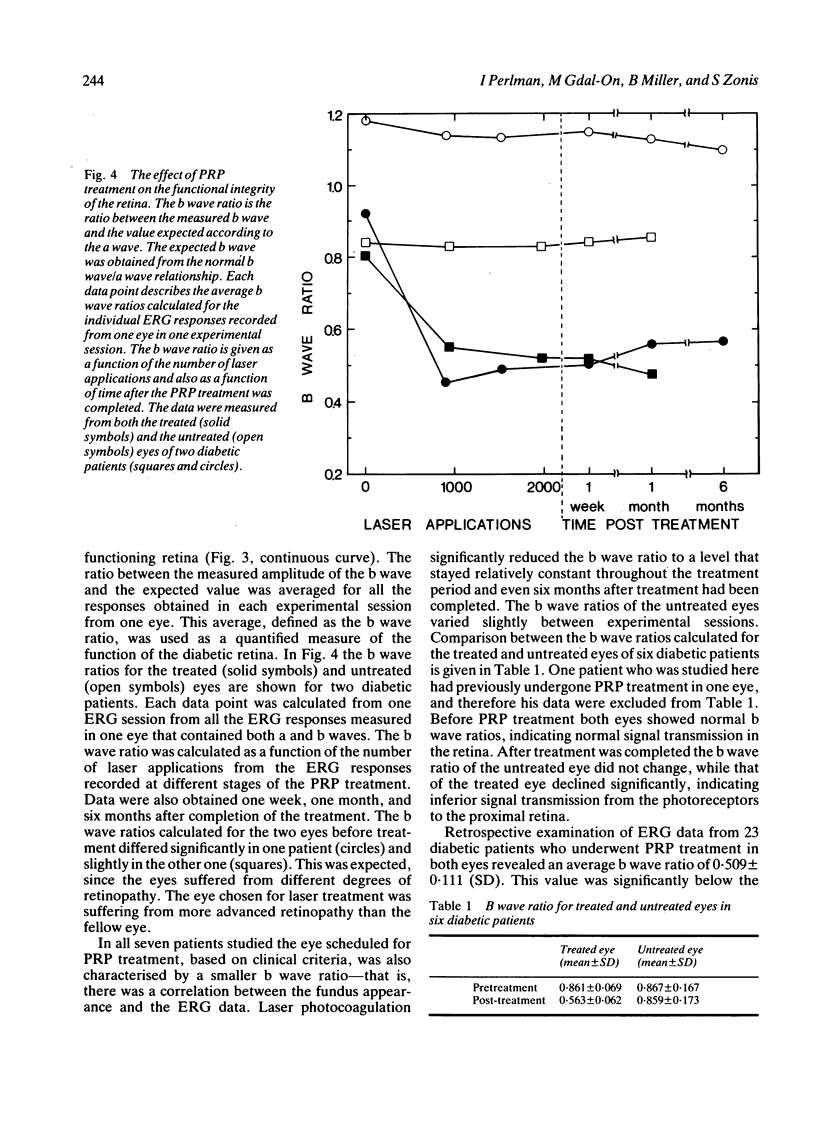
Electroretinographic (ERG) responses were measured in diabetic patients before, during, and after panretinal photocoagulation treatment with argon laser. The laser applications reduced considerably the amplitudes of the a and b waves of the ERG. Moreover, the relationship between the amplitude of the b wave and that of the a wave was severely affected, resulting in ERG responses of abnormal pattern. The b waves were smaller than expected from the a waves. These findings indicated that the photocoagulation treatment not only destroyed the retinal areas directly illuminated by the laser beam, but also affected the functional integrity of adjacent areas. These additional effects resulted in subnormal signal transmission from the photoreceptors to the proximal retina.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Frank R. N. Visual fields and electroretinography following extensive photocoagulation. Arch Ophthalmol. 1975 Aug;93(8):591–598. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1975.01010020575004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- François J., De Rouck A., Cambie E., Castanheira-Dinis A. Electrophysiological studies before and after argon-laser photocoagulation in diabetic retinopathy. Ophthalmologica. 1977;176(3):133–144. doi: 10.1159/000308705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krill A. E., Archer D. B., Newell F. W., Chishti M. I. Photocoagulation in diabetic retinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1971 Aug;72(2):299–321. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(71)91300-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang J. C., Fishman G. A., Huamonte F. U., Anderson R. J. Comparative electroretinograms in argon laser and xenon arc panretinal photocoagulation. Br J Ophthalmol. 1983 Aug;67(8):520–525. doi: 10.1136/bjo.67.8.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden T. E., Callahan F., Riekhof F. T. The electroretinogram after peripheral retinal ablation in diabetic retinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1976 Apr;81(4):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(76)90293-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman I. Relationship between the amplitudes of the b wave and the a wave as a useful index for evaluating the electroretinogram. Br J Ophthalmol. 1983 Jul;67(7):443–448. doi: 10.1136/bjo.67.7.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuurmans R. P., Lege W. A., Lith G. H., Oosterhuis J. A. The influence of photocoagulation of the retina on the electroretinogram. Doc Ophthalmol. 1977 Feb 28;42(2):369–373. doi: 10.1007/BF02742250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



