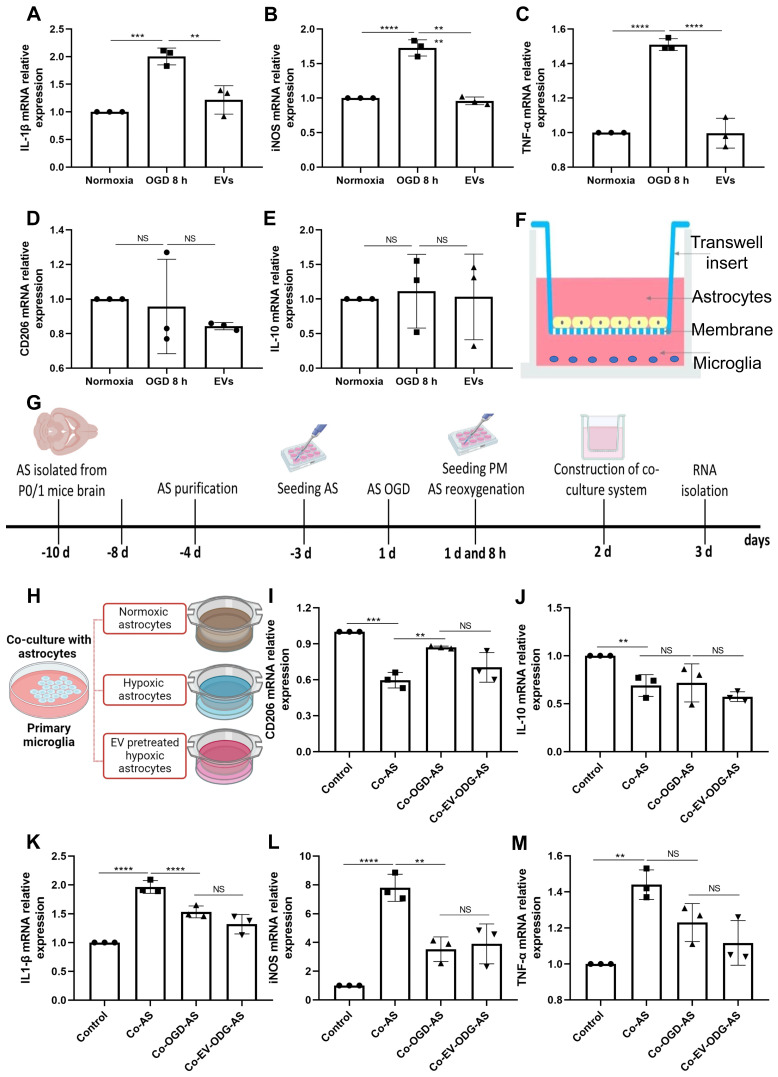
Figure 6.
EVs derived from hypoxic microglia shift inflammation in primary astrocytes exposed to hypoxia. (A-E) RT-qPCR assay of IL-1β, iNOS, TNF-α, IL-10, and CD206 mRNA levels in primary astrocytes in the three groups: normoxic astrocytes and 8 h of OGD followed by 24-h reoxygenation in untreated astrocytes or astrocytes treated with EVs (n = 3). (F) The construction of the co-culture system of astrocyte-microglia communication. Astrocytes and microglia were respectively seeded on the upper and lower compartment. (G) Experimental paradigm summarizing the in vitro communication co-culture model. (H) Microglia were exposed to co-culture with astrocytes under three statuses: normoxia, 8 h of OGD followed by 24-h reoxygenation, and 8 h of OGD followed by 24-h reoxygenation with EV treatment. (I-M) An alteration of AQP4 level in modulating astrocyte-to-microglia communication in terms of neuroinflammation. Secreted anti-inflammatory cytokines (CD206 and IL-10 mRNA) and pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, iNOS, and TNF-α mRNA) in primary microglia were measured using RT-qPCR (n = 3). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001; NS, not statistically significant; OGD, oxygen-glucose deprivation; EVs, extracellular vesicles; AQP4, Aquaporin 4; PM, primary microglia; AS; astrocytes; RT-qPCR, quantitative real-time PCR analysis; IL, Interleukin; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase.