Abstract
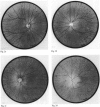
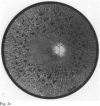
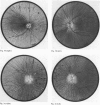
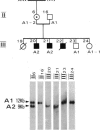
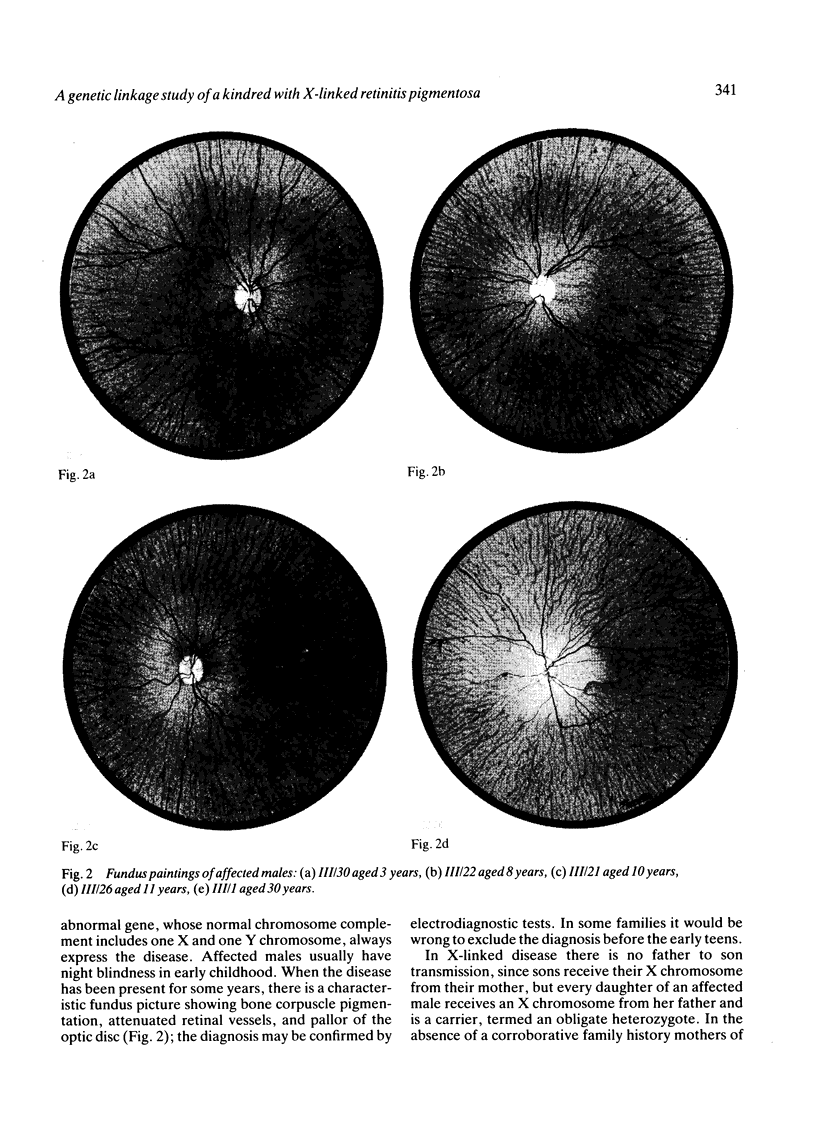
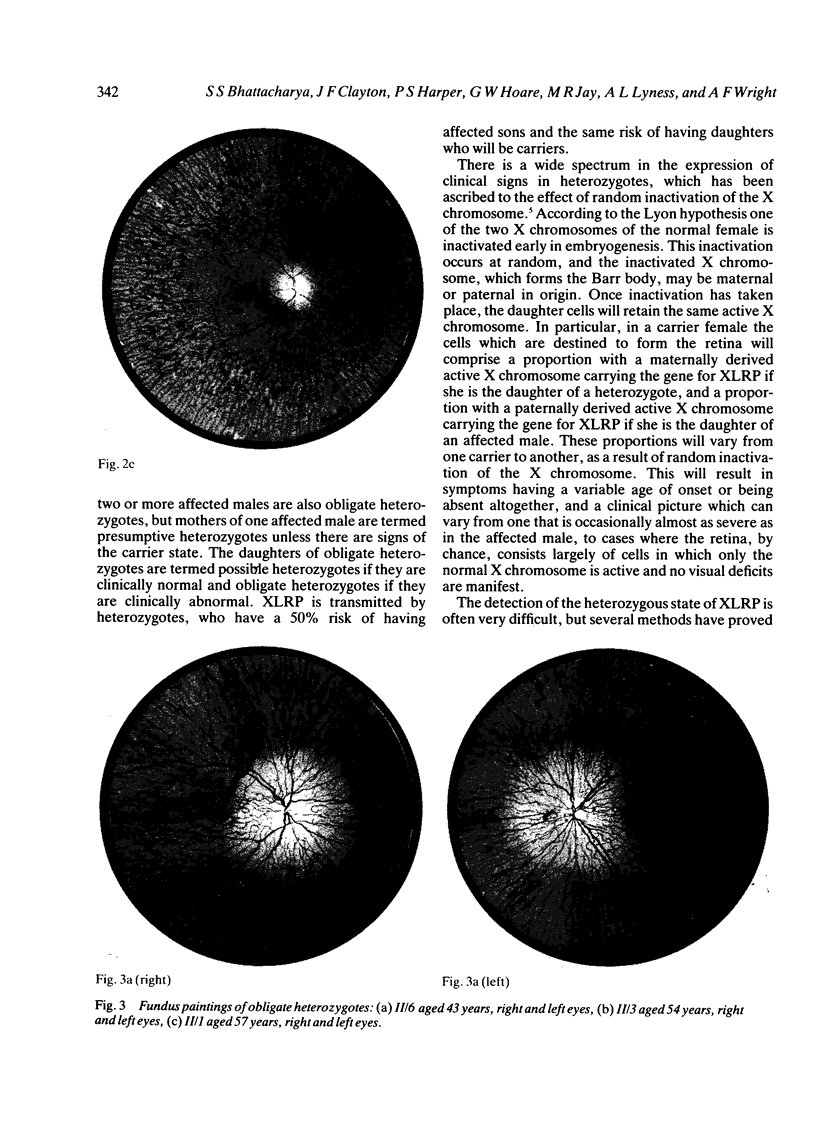
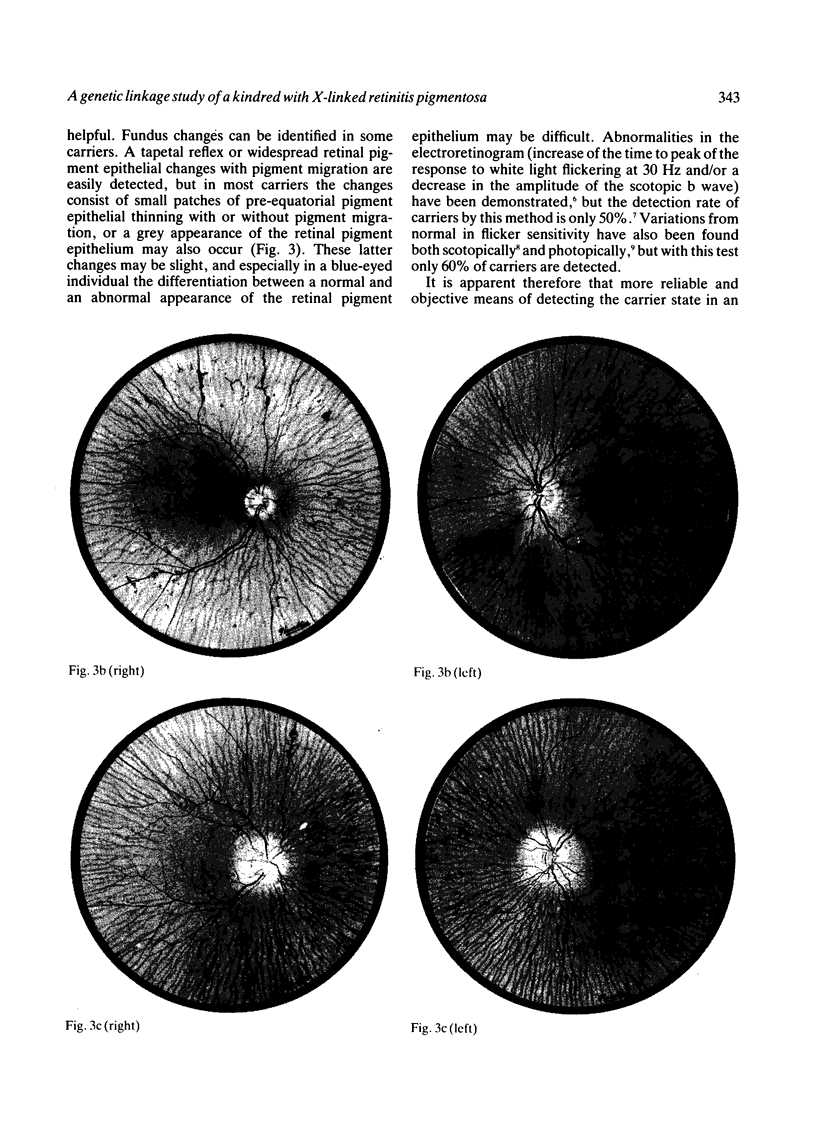
A large kindred with X-linked retinitis pigmentosa (XLRP) was investigated clinically and by means of genetic linkage with a view to developing methods of carrier detection and early diagnosis. A restriction fragment length polymorphism, identified by recombinant DNA probe L1.28, showed close genetic linkage to XLRP in this kindred and is a potentially useful marker for the purposes of genetic counselling.
Full text
PDF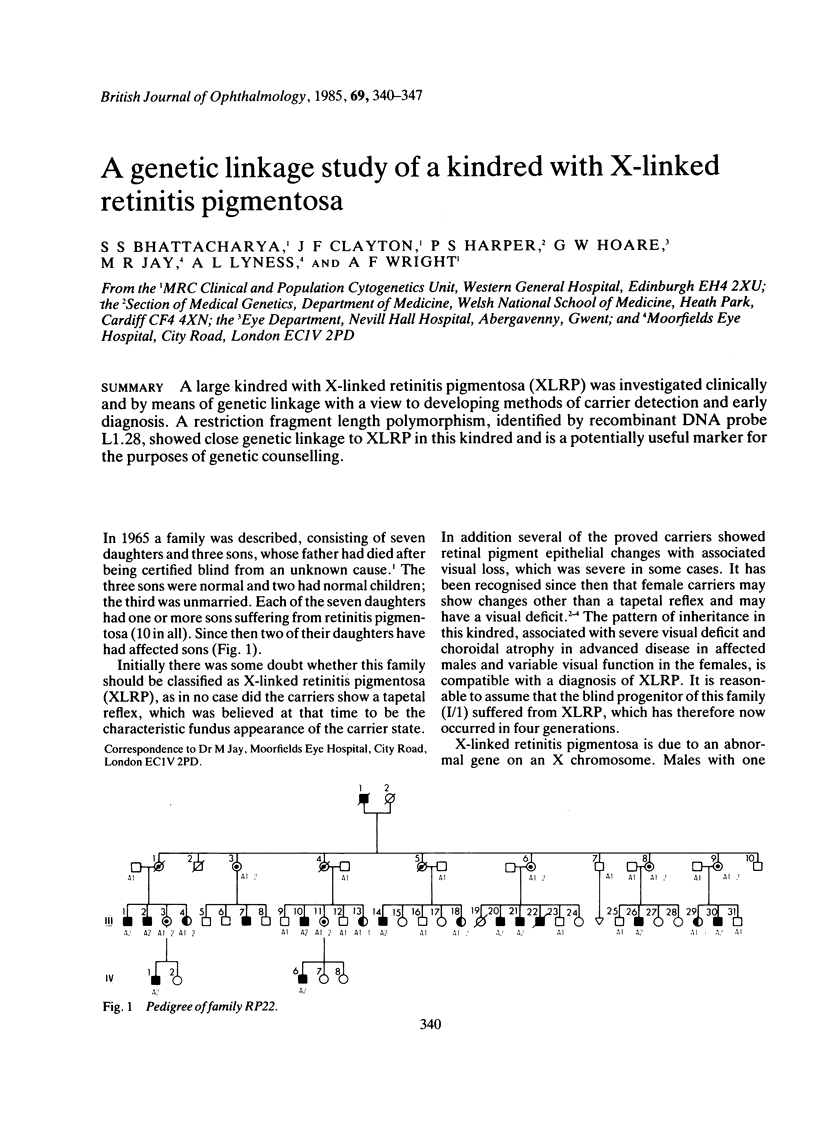




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arden G. B., Carter R. M., Hogg C. R., Powell D. J., Ernst W. J., Clover G. M., Lyness A. L., Quinlan M. P. A modified ERG technique and the results obtained in X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Br J Ophthalmol. 1983 Jul;67(7):419–430. doi: 10.1136/bjo.67.7.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berson E. L., Gouras P., Gunkel R. D., Myrianthopoulos N. C. Rod and cone responses in sex-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Arch Ophthalmol. 1969 Feb;81(2):215–225. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1969.00990010217012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya S. S., Wright A. F., Clayton J. F., Price W. H., Phillips C. I., McKeown C. M., Jay M., Bird A. C., Pearson P. L., Southern E. M. Close genetic linkage between X-linked retinitis pigmentosa and a restriction fragment length polymorphism identified by recombinant DNA probe L1.28. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):253–255. doi: 10.1038/309253a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. C. X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Br J Ophthalmol. 1975 Apr;59(4):177–199. doi: 10.1136/bjo.59.4.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst W., Clover G., Faulkner D. J. X-linked retinitis pigmentosa: reduced rod flicker sensitivity in heterozygous females. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1981 Jun;20(6):812–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoare G. W. Choroido-retinal dystrophy. Br J Ophthalmol. 1965 Sep;49(9):449–459. doi: 10.1136/bjo.49.9.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Tantravahi U., Eisenhard M., Latt S. A. Regional localization on the human X of DNA segments cloned from flow sorted chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1557–1578. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYON M. F. Gene action in the X-chromosome of the mouse (Mus musculus L.). Nature. 1961 Apr 22;190:372–373. doi: 10.1038/190372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. Estimation of the recombination fraction in human pedigrees: efficient computation of the likelihood for human linkage studies. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Sep;26(5):588–597. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ropers H. H., Wieacker P., Wienker T. F., Davies K., Williamson R. On the genetic length of the short arm of the human X chromosome. Hum Genet. 1983;65(1):53–55. doi: 10.1007/BF00285028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler C. W. Specific deficits of flicker sensitivity in glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1981 Feb;20(2):204–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A. F., Bhattacharya S., Price W. H., Phillips C. I., McKeown C., Crews S. J., Jay M., Bird A. C. DNA probes in X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Trans Ophthalmol Soc U K. 1983;103(Pt 4):467–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]