Abstract
患者女,36岁,因“腰部白斑10+年,其上新发环状斑块6+月”来院就诊。入院后完善伍德灯检查示:阳性。右腰部环状隆起边缘处皮肤组织病理示:表皮角化过度,颗粒层楔形增厚,基底层细胞液化变性,真皮浅层淋巴细胞呈带状浸润。诊断:白癜风并发环状扁平苔藓。予以卤米松乳膏治疗,2次/d,治疗1个月后紫红色环状斑块基本消退,随访2个月未见复发。环状扁平苔藓是扁平苔藓的一种少见亚型,迄今国内外尚未见到此病合并白癜风的病例报道。
Keywords: 环状扁平苔藓, 扁平苔藓, 白癜风
Abstract
A 36-year-old female patient came to our hospital with the chief complaint of having white patches on her waist for 10-plus years and having new annular plaques appearing on the white patches for 6-plus months. Wood's lamp examination done in the hospital showed a positive result. Histopathology of skin tissue from the edge of the annular swelling on the right waist revealed epidermal hyperkeratosis, wedge-shaped thickening of the granular layer, liquefactive degeneration of the basal cells, and a band-like infiltration of lymphocytes in the superficial dermis. The patient was diagnosed with vitiligo combined with annular lichen planus (ALP). The patient was treated with topical halometasone cream administered twice a day. The purplish-red annular plagues subsided and disappeared almost completely one month after the treatment was started and no signs of recurrence were observed duringn the 2-month follow-up. ALP is a rare variant of lichen planus. There has been no reported case of vitiligo combined with ALP so far.
Keywords: Annular lichen planus, Lichen planus, Vitiligo
1. 病例资料
患者,女性,36岁,因“腰部白斑10+年,其上新发环状斑块6+月”来院就诊。患者入院前10+年无明显诱因于双侧腰部出现直径约4~6 cm白色斑片,边界清晰、不规则,无鳞屑,不伴疼痛、瘙痒,因白斑进展缓慢,患者未重视,未治疗。6+月前患者无明显诱因于双侧腰部白斑上及内踝部出现直径约1~3 cm紫红色环状斑块,环状边缘堤状隆起,其上可见少许白色鳞屑,偶有轻微瘙痒,无水疱、糜烂、渗出等。既往予以“萘替芬酮康唑乳膏”“他克莫司软膏”治疗,无明显好转。为求进一步诊治,遂至我院就诊。内科查体无特殊。皮肤科查体:双侧腰部可见直径约4~6 cm白色斑片,其上及内踝部可见直径约1~3 cm紫红色环状斑块,环状边缘堤状隆起,其上可见少许白色鳞屑(图1)。口腔黏膜、指甲未查见明显异常。既往史及家族史:饮食无特殊,近期无用药史、疫苗注射史、化学品接触史。实验室检查:血常规、肝肾功能、抗核抗体、抗可提取性核抗原(extrectable nuclear antigen, ENA)抗体谱结果未见异常。皮肤真菌荧光镜检:阴性。伍德灯检查阳性:左侧腰部亮白色斑片,边界清晰,部分白斑可见毛囊复色(图2)。组织病理(右腰部环状隆起边缘):表皮角化过度,颗粒层楔形增厚,基底层细胞液化变性,真皮浅层淋巴细胞呈带状浸润。结合患者典型的皮损特征、皮肤真菌荧光镜检、伍德灯检查及组织病理学结果,诊断为白癜风合并环状扁平苔藓(annular lichen planus, ALP)。予以卤米松乳膏治疗,2次/d,治疗1个月后紫红色斑块基本消退,随访2个月未见复发。但白斑尚未见明显好转,目前患者仍在随访中。
图 1.
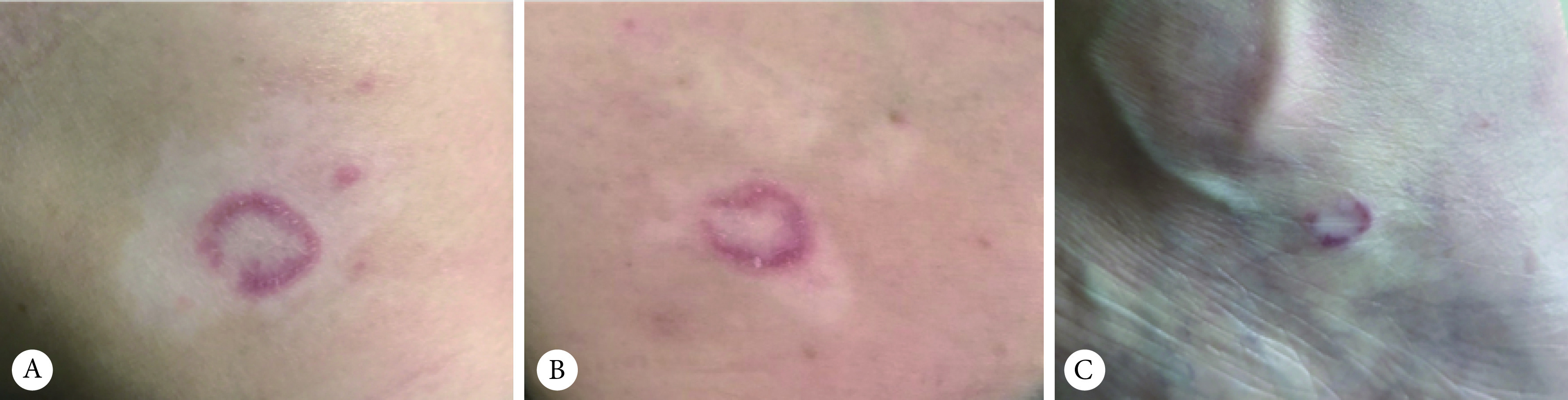
Clinical pictures
临床照片
A: left lumbar region; B: right lumbar region; C: ankle.
图 2.
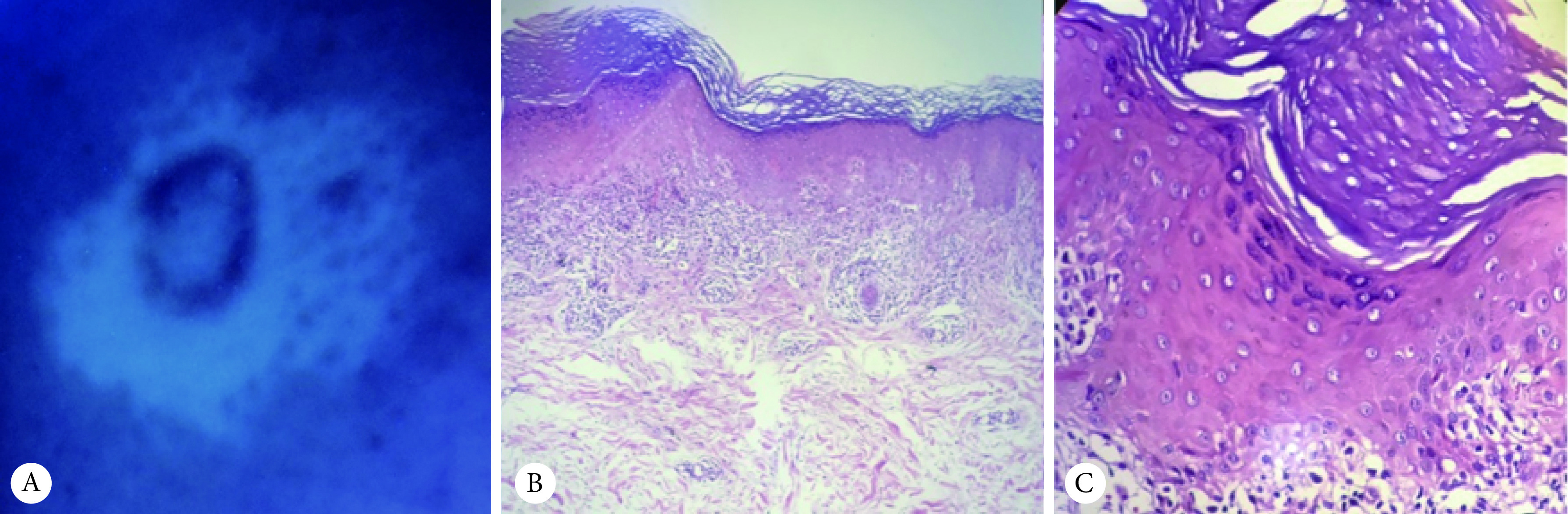
Positive result from Wood's lamp examination (A) and pathological HE staining (B, ×40; C, ×200)
伍德灯检查阳性(A)和病理HE染色(B:×40;C:×200)
2. 讨论
ALP和白癜风是两个独立的疾病,目前病因不明。ALP是扁平苔藓的一种少见亚型,约占扁平苔藓的10%[1-2]。目前研究表明,ALP可能与细胞介导的免疫反应、遗传因素、感染因素、神经精神因素、药物因素、细胞内某些蛋白的改变及合并其他疾病都有着密不可分的关系[3]。临床上环状皮损主要表现为两种类型:①多个小丘疹排列呈环状,多为单环,少数可呈多环;②单个丘疹或斑块离心性向外扩展,中央消退,可伴有中央萎缩或色素沉着[4]。ALP好发于唇、龟头及阴茎,腋窝、腹股沟和四肢也可发生,多不累及头皮、黏膜及甲[1-2]。患者通常没有自觉症状,但偶有瘙痒或灼热感。本例患者的皮损基本符合上述特点。白癜风是一种获得性、特发性色素脱失性皮肤病,发病机制主要涉及遗传、免疫、氧化应激、黑素细胞自毁等[5]。最新对T细胞介导的免疫应答机制的研究表明,T淋巴细胞在扁平苔藓和白癜风的免疫发病机制中均具有重要作用,辅助性T淋巴细胞(Th)1、Th9、Th17、Th22和细胞毒性T淋巴细胞是二者免疫发病机制的共同组成部分[6]。
通过文献检索,迄今国内外尚未见到ALP合并白癜风的病例报道。目前已有研究报道环状扁平苔藓可合并银屑病关节炎、红斑狼疮、生殖器黑子(生殖器黏膜黑斑)、Sneddon综合征、克罗恩病、人类免疫缺陷病毒感染、新型冠状病毒(SARS-CoV-2)感染等[7-13]。此外,也有一些文献报道了白癜风合并扁平苔藓的情况,二者皮损可以重叠,也可分别发生,但报道中扁平苔藓皮损主要表现为圆形、椭圆形或多角形紫红色扁平丘疹、斑块[14-20]。本例患者ALP皮损多发,位于双侧腰部及内踝部,初起均呈环状,且绝大部分ALP皮损与白癜风皮损为重叠发生,本例患者在原有的白癜风皮损基础上出现ALP皮损,进一步证实了ALP和白癜风可能存在共同的发病机制。
本例患者的ALP皮损对于局部外用糖皮质激素治疗敏感,疗效显著,但白癜风色素脱失尚未见明显恢复,仍在进一步随访中。ALP有时与环状肉芽肿、环状银屑病、持久性色素异常性红斑、皮肤癣菌感染、蕈样肉芽肿和二期梅毒等难以区分,但本例患者通过实验室检查、组织病理学检查及对糖皮质激素治疗反应可明确诊断。
* * *
利益冲突 所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突
Contributor Information
海燕 周 (Hai-yan ZHOU), Email: 389457417@qq.com.
小兰 蒲 (Xiao-lan PU), Email: 758670252@qq.com.
References
- 1.赵辨. 中国临床皮肤病学. 南京 : 江苏科学技术出版社, 2010: 1040.
- 2.REICH H L, NGUYEN J T, JAMES W D Annular lichen planus: a case series of 20 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50(4):595–599. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2003.08.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.谢辉, 董宿利, 王新慧, 等 扁平苔藓病因及发病机制研究进展. 皮肤病与性病. 2021;43(2):179–180. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1310.2021.02.009. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.汪盛, 李薇 环状扁平苔藓1例. 临床皮肤科杂志. 2007;36(9):591. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4963.2007.09.029. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.周红英, 吴一菲 白癜风发病机制的研究进展. 皮肤病与性病. 2019;41(2):181–185. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1310.2019.02.011. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.AGHAMAJIDI A, RAOUFI E, PARSAMANESH G, et al The attentive focus on T cell-mediated autoimmune pathogenesis of psoriasis, lichen planus and vitiligo. Scand J Immunol. 2021;93(4):e13000. doi: 10.1111/sji.13000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.ISBARY G, DYALL-SMITH D, CORAS-STEPANEK B, et al Penile lentigo (genital mucosal macule) following annular lichen planus: a possible association? Australas J Dermatol. 2014;55(2):159–161. doi: 10.1111/ajd.12169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.DIAZ GUIMARAENS B, DOMINGUEZ SANTAS M, SUAREZ VALLE A, et al Annular lichen planus associated with coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 disease (COVID-19) Int J Dermatol. 2021;60(2):246–247. doi: 10.1111/ijd.15338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.CHAKRABORTY S, CHOWDHURY J, DE A, et al Generalized annular lichen planus with a unique morphology in a patient seropositive for HIV. JAAD Case Rep. 2015;1(5):251–253. doi: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2015.04.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.LIPSKER D, PIETTE J C, LAPORTE J L, et al Annular Atrophic Lichen planus and Sneddon's Syndrome. Dermatology (Basel) 1997;195(4):402–403. doi: 10.1159/000245999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.SERRÃO V V, ORGAN V, PEREIRA L, et al Annular lichen planus in association with Crohn disease. Dermatol Online J. 2008;14(9):5. doi: 10.5070/D33QV3Q0GB. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.NIEBEL D, WILSMANN THEIS D, WENZEL J Successful treatment of psoriatic arthritis and comorbid annular atrophic lichen planus with etanercept. J Dermatol. 2020;47(4):397–401. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.15222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.杨国亮, 王侠生. 现代皮肤病学. 第1版. 上海: 上海医科大学出版社, 1991: 528−529.
- 14.BAGHESTANI S, MOOSAVI A, EFTEKHARI T Familial colocalization of lichen planus and vitiligo on sun exposed areas. Ann Dermatol. 2013;25(2):223–225. doi: 10.5021/ad.2013.25.2.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.SOBJANEK M, SIKORSKA M, LAKOMY J, et al Letters to the editors vitiligo and lichen planus-common etiopathogenesis or coincidence? Przegląd Dermatologiczny. 2015;1(1):51–52. doi: 10.5114/dr.2015.49202. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16.张卉, 朱文元, 范卫新 扁平苔藓并发白癜风1例. 临床皮肤科杂志. 2007;36(3):169. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4963.2007.03.019. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.GÖKTAY F, MANSUR A T, AYDINGÖZ I E Colocalization of vitiligo and lichen planus on scrotal skin: a finding contrary to the actinic damage theory. Dermatology. 2006;212(4):390–392. doi: 10.1159/000092295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.ANSTEY A, MARKS R Colocalization of lichen planus and vitiligo. Brit J Dermatol. 1993;128(1):103–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1993.tb00159.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.RUBISZ-BRZEZINSKA J, BÜCHNER S A, ITIN P Vitiligo associated with lichen planus: is there a pathogenetic relationship? Dermatology (Basel) 1996;192(2):176–178. doi: 10.1159/000246353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.BECK K, BARNES L, HARVEY V 017 Lichen planus colocalized with vitiligo: coincidence? J Invest Dermatol Symposium Proceed. 2017;18(2):S87. doi: 10.1016/j.jisp.2016.10.019. [DOI] [Google Scholar]


