Abstract
Bats are described as the natural reservoir host for a wide range of viruses. Although an increasing number of bat-associated, potentially human pathogenic viruses were discovered in the past, the full picture of the bat viromes is not explored yet. In this study, the virome composition of Miniopterus phillipsi bats (formerly known as Miniopterus fuliginosus bats in Sri Lanka) inhabiting the Wavul Galge cave, Sri Lanka, was analyzed. To assess different possible excretion routes, oral swabs, feces and urine were collected and analyzed individually by using metagenomic NGS. The data obtained was further evaluated by using phylogenetic reconstructions, whereby a special focus was set on RNA viruses that are typically associated with bats. Two different alphacoronavirus strains were detected in feces and urine samples. Furthermore, a paramyxovirus was detected in urine samples. Sequences related to Picornaviridae, Iflaviridae, unclassified Riboviria and Astroviridae were identified in feces samples and further sequences related to Astroviridae in urine samples. No viruses were detected in oral swab samples. The comparative virome analysis in this study revealed a diversity in the virome composition between the collected sample types which also represent different potential shedding routes for the detected viruses. At the same time, several novel viruses represent first reports of these pathogens from bats in Sri Lanka. The detection of two different coronaviruses in the samples indicates the potential general persistence of this virus species in M. phillipsi bats. Based on phylogenetics, the identified viruses are closely related to bat-associated viruses with comparably low estimation of human pathogenic potential. In further studies, the seasonal variation of the virome will be analyzed to identify possible shedding patterns for particular viruses.
Subject terms: Biodiversity, Molecular biology
Introduction
Bats are species-rich and taxonomically diverse mammals in the order Chiroptera that are distributed worldwide1. They represent a large group (20%) of mammals and share unique features like their ability to fly. A number of viruses from different viral families, including human pathogenic viruses like Hendra and Nipah virus, coronaviruses, lyssaviruses and others, have been associated with bats2. It is assumed that these viruses evolved together with their natural reservoir hosts. Because of this co-speciation and adaptation process, the viruses are often less pathogenic for their bat hosts. It is assumed that the bats’ immune system is adapted to virus infections and hence able to control them without developing visible symptomatic diseases3–5.
With the increasing focus on bat virus research, the detection of potentially zoonotic viruses with species-specific or family-specific PCR assays (e.g., paramyxoviruses, lyssaviruses and coronaviruses) has been a convenient standard method. However, conventional detection methods are reliant on primers designed from known diversity, and this may lead to bias focusing only on certain viruses or on those of particular interest6–9. To investigate the unknown viral diversity that may be present within the host species, metagenomic NGS methods (mNGS) for virus discovery can allow for untargeted and more unbiased sequencing of novel viruses. The analysis of the viral composition from bat samples (viromes) allows to reduce the bias and to constantly increase the number of viral sequences deposited in sequence databases such as GenBank of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI)10–12.
However, in several regions of the world the investigation of bats in their role as potential reservoir host of zoonotic viruses has been barely conducted6. In Sri Lanka, zoology is an important research field and ecological aspects of bats are well investigated13. Bats significantly contribute to the biodiversity and account for about a third of the Sri Lankan mammals with 30 different species14. Furthermore, they are essential for the maintenance of the ecosystem by providing ecoservices such as pollination, seed dispersal and insect control13.
In contrast, only few studies have focused on bats as reservoir host for pathogens in Sri Lanka15–18. Here we present the first virome analysis of M. phillipsi bats inhabiting the Wavul Galge cave (Koslanda, Sri Lanka) in the interior of Sri Lanka. M. phillipsi bats are roosting sympatrically with the other bat species Hipposideros lankadiva, Hipposideros speoris, Rhinolophus rouxii and Rousettus leschenaultii. In three individual field studies at different time points, we captured bats of all representative species and collected different sample material depending on availability19. Selected sample sets had been analyzed in previous investigations focusing on different research questions17,18,20,21. In this study, we focus on the virome analysis of urine swabs (US), oral swabs (OS) and feces (F) collected from M. phillipsi bats at one sampling point (July 2018). The presented results give first insights into the virome composition of this bat species in the Wavul Galge cave and in general. Furthermore, the results may point to differences in viral shedding routes by analyzing the different sample types. This study is the stepping stone for the further investigation of selected viruses in this species and cave.
Methods
The study was approved by the local government authority (Department of Wildlife Conservation, Sri Lanka, permit No. WL/3/2/05/18, issued on 10 January 2018). Catching and sampling of bats was carried out according to previously assessed, established and described standard procedures to maximize the safety of the research group and to minimize the stress for the bats during the sampling procedure19. We adhered to relevant guidelines and regulations of the Fauna and Flora Protection Ordinance.
Bat sampling
Sampling of bats inhabiting the Wavul Galge cave (Sri Lanka) was performed in March and July 2018 and January 2019 as described before19. For the results presented in this study, a subset of samples was selected from 188 M. phillipsi bats sampled in July 2018. Details about the sex, age status and morphometric measures taken from each bat are given in the supplementary material (Table ST1). Different sample types were collected depending on availability. From the selected subset of M. phillipsi bats a total of 187 oral swabs (OS) and 102 urine swabs (US) were collected with Minitip FLOQSwabs® (Copan Diagnostics, Murrieta, CA, USA); furthermore 77 fecal pellets (F) were collected with forceps. An overview of the collected samples per individual bat is given in the supplementary material (Table ST1).
The samples were collected in cryotubes without any additives and then snap-frozen by using liquid nitrogen. After transportation samples were stored at − 80 °C until further processing. The general workflow of subsequent laboratory work and bioinformatic analysis of NGS data is shown in Fig. 1.
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the general NGS workflow (wet lab) with subsequent bioinformatic analysis of obtained data (dry lab). Created with BioRender.com.
Metagenomic NGS
The processing of samples was conducted with appropriate precautions in biosafety-2 laboratories. All samples were initially processed by adding 500 µL of sterile PBS. For OS and US, samples were mixed by vortexing before 140 µL were used for extraction with the Viral RNA Mini Kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany). Fecal pellets were homogenized with sterile ceramic beads by using the FastPrep-24 device for 60 s (3 cycles for 20 s at full speed and cooled on ice between cycles) (MP Biomedicals, Eschwege, Germany), followed by centrifugation for 5 min at 8000 × g and extraction of 140 µL of the supernatant with the Viral RNA Mini Kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Prior to further processing a maximum of 10 RNA extracts were pooled by taking 5 µL per sample to obtain a final volume of 50 µL. Pools were prepared per sample type, resulting in 19 OS pools, 13 US pools and 8 F pools. The pooled RNA samples were treated with 4 U TURBO DNase for 30 min at 37 °C by using a TURBO DNA-free Kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA), followed by inactivation of the TURBO DNase according to the manufacturer’s protocol. 20 µl of the treated RNA was transcribed into cDNA by using the SuperScript IV Reverse Transcriptase reagent (Invitrogen) and 50 µM random hexamer primers; the reaction was incubated at 23 °C for 10 min, 50 °C for 10 min and inactivated at 80 °C for 10 min. Second strand was synthesized for 1 h at 16 °C by using the NEBNext® Ultra™ II Non-Directional RNA Second Strand Synthesis Module (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. dsDNA was purified by using the Agencourt AMPure XP bead system (Beckman Coulter Life Sciences, Krefeld, Germany) following the manufacturer’s instructions, and dsDNA was eluted in 40 µL of PCR-grade H2O. The final DNA concentration was determined by using a NanoDrop™ 1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Hennigsdorf, Germany). Sample libraries were sequenced on a HiSeq 2500 or a NextSeq 550 sequencing device (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) with a paired end read output of 2 × 250 bp (HiSeq) or 2 × 150 bp (NextSeq) and a total output of up to 8 million reads per pool. A detailed overview of the pools, included samples and obtained read output is given in the supplementary material (Table ST2).
NGS data analysis and virome assembly
Prior to NGS data analysis, sequencing reads were trimmed and filtered by length and quality by using the tool Trimmomatic v0.3922. Surviving reads were mapped to the non-redundant protein virus database (NCBI, RefSeq release 210 from 3 January 2022) by using the diamond BLASTx algorithm (–sensitive) to12,23. The results and the distribution of assigned viral reads per pool were visualized in MEGAN24. This was also compared between the different sample types and among the pools of each sample type.
After obtaining a general overview in MEGAN, a selection of viral hits was further analyzed in detail. This selection focused mainly on RNA viruses that are known to be found in bats, humans or other mammals, but further viral hits with a high number of assigned reads were also selected for further investigation. Other viral hits that are typical sequencing contaminants or assigned to bacteriophages were not considered in the subsequent analysis.
The selected viral reads were extracted and assembled using Velvet with default quality settings to produce larger contigs25. These contigs were blasted to the NCBI database by using the BLASTn algorithm and default settings to identify the closest related sequence in the database. If available, the full genome sequence (with the highest identity on nt level) was downloaded to serve as reference. The initially trimmed NGS data was mapped to this reference to identify more reads and to evaluate the mapping quality visually in Geneious Prime software (version 2020.2.3, Biomatters Ltd., Auckland, New Zealand). Wherever possible, the nucleotide identities to related strains were calculated for the longest contig assembled on a conserved gene such as the RNA polymerase gene.
For all analyzed viral sequences of high interest, suitable primers were designed on contigs supported by high read coverage. Subsequently, the presence of the obtained viral sequences was confirmed in the initial individual cDNA samples by using conventional PCR under standard conditions (available on request). PCR products appearing as bands in the analytic agarose gel were purified and Sanger sequenced when sufficient quantity was reached.
Phylogenetic reconstruction
For viral sequences of interest for this study, suitable contigs were used for phylogenetic reconstruction. To this end, preferably the longest contig on a conserved gene of the virus genome (e.g., RNA polymerase gene) was selected. A number of reference sequences were downloaded from NCBI database and an end-gap free nucleotide alignment was calculated by using the MAFFT algorithm26. The phylogenetic trees were calculated based on this alignment by using the Bayesian MCMC algorithm (MrBayes version 3.2.6)27. A suitable model for each alignment was estimated by using the Akaike information criterion prediction with the tool JModelTest28,29. The calculation parameters were different depending on the virus and are each specified in the results section (see legends for Figs. 4, 5 and 6).
Figure 4.
Phylogenetic tree based on a 224-nt contig on the conserved ORF1B CDS of CoV obtained from the virome of US sample pools (highlighted in blue) and a selection of α-CoVs and β-CoVs as specified. For use as outgroup, the γ-CoV avian infectious bronchitis virus (NC_001451) was included in the calculation. Phylogenetic reconstruction was calculated with the Bayesian MCMC algorithm: 1,000,000 generations were calculated with a subsampling frequency of 100 and a burn-in of 10%. The substitution model GTR was selected with a gamma-distributed rate variation. Visualized as molecular clock with uniform branch lengths.
Figure 5.
Phylogenetic tree based on the mNGS sequences obtained from the virome of US sample pools (highlighted in blue) and a selection of PMVs. Sendai virus (NC_001552) was selected as outgroup for the calculation. Phylogenetic reconstruction was calculated with the Bayesian MCMC algorithm: 1,000,000 generations were calculated with a subsampling frequency of 100 and a burn-in of 10%. The substitution model GTR was selected with a gamma-distributed rate variation. Visualized as molecular clock with uniform branch lengths.
Figure 6.
Phylogenetic tree based on the mNGS sequences obtained from the virome of F sample pools (highlighted in blue) and a selection of picornaviruses. Human parechovirus 1 (NC_038319) was selected as outgroup for the calculation. Phylogenetic reconstruction was calculated with the Bayesian MCMC algorithm: 1,000,000 generations were calculated with a subsampling frequency of 100 and a burn-in of 10%. The substitution model GTR was selected with a gamma-distributed rate variation. Visualized as molecular clock with uniform branch lengths.
Ethical statement
The study was approved by the local government authority (Department of Wildlife Conservation, Sri Lanka, permit No. WL/3/2/05/18, issued on 10 January 2018). Catching and sampling of bats was carried out according to relevant guidelines and regulations of the Fauna and Flora Protection Ordinance, Sri Lanka. The results reported in this study were obtained without conducting animal experiments. All bat samples were collected non-invasively and bats were released after the sampling procedure. Relevant guidelines for animal research in vivo (ARRIVE) are not applicable.
Results
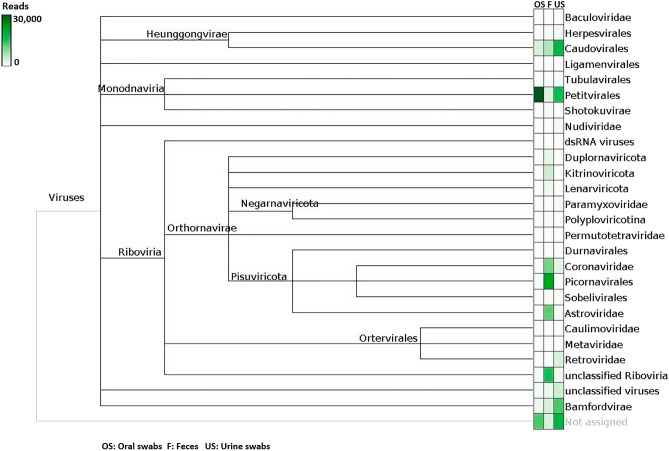
Following mNGS, the sequence reads were trimmed and analyzed separately per pool as described in the methods section. Comparison of the pools per sample type revealed mainly homogenous distributions of viral reads assigned to the respective viral orders (see supplemental Figures SF1–SF3). For further analysis, viral reads of all pools per sample type were combined and the assigned viral reads compared between OS, F and US by using MEGAN as shown in Fig. 2.
Figure 2.
Normalized comparison of viral hits from different sample types in MEGAN after diamond BLASTx. Sample types are depicted in the following order: oral swabs (OS), feces (F) and urine swabs (US). The intensity of green color represents the quantity of reads assigned to the respective viral family or order.
As shown in Fig. 2, bacteriophages (e.g., Caudovirales and Petitvirales) were found in all sample types but in different amounts. For OS, no other viral hits of interest were assigned from the NGS data. Viral reads belonging to five different families (Coronaviridae, Iflaviridae, Picornaviridae, Astroviridae and Paramyxoviridae) and unclassified Riboviria were found in F samples and confirmed by mapping to the respective reference sequence and by PCR in the initial cDNA samples. In the US samples, viral reads of three families (Paramyxoviridae, Coronaviridae and Astroviridae) were detected and also confirmed by PCR in the initial cDNA samples.
Some of the other preliminary results from BLASTx (depicted in Fig. 2) could not be confirmed in the subsequent in silico analysis and were considered as possible artefacts from the NGS run (e.g., Herpesvirales and Bamfordvirae) as commonly described30. An overview of the confirmed results after quality checks is given in Table 1, specifying details of the obtained NGS data, related viruses and novel identified virus strains.
Table 1.
Overview of the results obtained from mNGS data analysis of feces and urine swab samples from M. phillipsi bats collected in July 2018.
| Astroviridae | ||
| Name of related virus | Bat astrovirus 1 isolate AFCD77 (EU847151) | |
| Sample type | Feces samples | Urine swab samples |
| Pool numbers | F1, F2, F3, F4, F5, F6, F7, F8 | U4, U8, U9, U14, U15 |
| Assigned reads/longest contig | 289/1068 nt | 422/379 nt |
| Nucleotide identity | 82% | 85.6% |
| Name of novel virus strain | Bat astrovirus strain F2/18 (Acc. OP141159) | Bat astrovirus strain US2/18 (Acc. OP141166) |
| Name of related virus | Mamastrovirus 14 isolate AFCD57 (NC_043099) | |
| Sample type | Feces samples | |
| Pool numbers | F3 | |
| Assigned reads/longest contig | 1045/1366 nt | |
| Nucleotide identity | 86.5% | |
| Name of novel virus strain | Mamastrovirus 14 strain F2/18 (Acc. OP141160) | |
| Name of related virus | Mamastrovirus 18 isolate AFCD337 (NC_043102) | |
| Sample type | Urine swab samples | |
| Pool numbers | U3, U5, U6, U9, U11, U12, U14 | |
| Assigned reads/longest contig | 282/311 nt | |
| Nucleotide identity | 84.4% | |
| Name of novel virus strain | Mamastrovirus 18 strain US2/18 (Acc. OP141167) | |
| Coronaviridae | ||
| Name of related virus | Bat alphacoronavirus isolate batCoV/MinFul/2018/SriLanka (OL956935) | |
| Sample type | Feces samples | Urine swab samples |
| Pool numbers | F1, F2, F3, F4, F5, F6, F7, F8 | U2, U3, U4, U5, U6, U8, U9, U12, U13, U14 |
| Assigned reads/longest contig | 994/729 nt | 10,753/1226 nt |
| Nucleotide identity | 83.1% | 98.6% |
| Name of novel virus strain | Bat alphacoronavirus strain MinPhil/F2/2018/SriLanka (Acc. OP141161) | Bat alphacoronavirus strain MinPhil/U2/2018/SriLanka (Acc. OP141168) |
| Name of related virus | BtMf-AlphaCoV/GD2012 (KJ473797) | |
| Sample type | Feces samples | Urine swab samples |
| Pool numbers | F1, F2, F3, F4, F5, F7 | U4, U6, U9, U12, U13, U14 |
| Assigned reads/longest contig | 2443/1113 nt | 2182/769 nt |
| Nucleotide identity | 83.1% | 85.5% |
| Name of novel virus strain | Bat alphacoronavirus strain AlphaCoV/F2/2018 (Acc. OP141162) | Bat alphacoronavirus strain AlphaCoV/U2/2018 (Acc. OP141169) |
| Iflaviridae | ||
| Name of related virus | Spodoptera exigua iflavirus 2 isolate Korean (JN870848) | |
| Sample type | Feces samples | |
| Pool numbers | F1 | |
| Assigned reads/longest contig | 373/1283 nt | |
| Nucleotide identity | 96.8% | |
| Name of novel virus strain | Spodoptera exigua iflavirus strain F2/18 (Acc. OP141163) | |
| Paramyxoviridae | ||
| Name of related virus | Jingmen Miniopterus schreibersii paramyxovirus 1 (MZ328288) | |
| Sample type | Urine swab samples | |
| Pool numbers | U2, U3, U6, U7, U9, U11, U12, U14 | |
| Assigned reads/longest contig | 573/450 nt | |
| Nucleotide identity | 84% | |
| Name of novel virus strain | Miniopterus phillipsi paramyxovirus strain US2/18 (Acc. OP141170) | |
| Picornaviridae | ||
| Name of related virus | Miniopterus schreibersii picornavirus 1 (JQ814851) | |
| Sample type | Feces samples | |
| Pool numbers | F1, F2, F3, F4, F5, F6, F7, F8 | |
| Assigned reads/longest contig | 5714/3452 nt | |
| Nucleotide identity | 86% | |
| Name of novel virus strain | Miniopterus phillipsi picornavirus strain F2/18 (Acc. OP141164) | |
| Unclassified Riboviria | ||
| Name of related virus | Hubei sobemo-like virus 21 strain CC64469 (KX882813) | |
| Sample type | Feces samples | |
| Pool numbers | F1, F3, F4 | |
| Assigned reads/longest contig | 439/534 nt | |
| Nucleotide identity | 82.1% | |
| Name of novel virus strain | Hubei sobemo-like virus strain F2/18 (Acc. OP141165) | |
The table indicates the related viruses (in bold), sample types and pool numbers from which the results were obtained, including the number of assigned reads, longest contig and nucleotide identity. The name and accession number of the novel virus strains as uploaded to GenBank are indicated, respectively.
For the families Coronaviridae, Picornaviridae, Astroviridae and Paramyxoviridae, the presence of viral sequences was furthermore confirmed in the original RNA pools (see Table 1) by using PCR and specifically designed primers based on the NGS data. The remaining viruses (Iflaviridae and unclassified Riboviria) were solely confirmed with in silico analysis of the data by BLASTn.
From all viral assemblies, either the longest contig or the contig used for phylogenetic reconstruction was uploaded to GenBank. These sequences of newly detected virus strains were named in relation to the closest related reference virus and with respect to current ICTV classification criteria (see Table 1).
Astroviridae
Astroviruses (n = 3) were found in F and US samples. In F samples, 1045 reads were assigned to Mamastrovirus 14 isolate AFCD57 (NC_043099) with a nucleotide identity of 86.8% on the longest contig (1366 nt), located overlapping on polyprotein 1AB and capsid protein CDS. Further 289 reads from F samples were assembled and mapped to Bat astrovirus 1 isolate AFCD77 polyprotein 1AB gene (EU847151) with a nucleotide identity of 82% on the longest contig (1068 nt).
A total of 422 reads from US samples were also assembled to EU847151, with a nucleotide identity of 85.6% on the longest contig (379 nt).
From US samples, further 282 reads were assembled to Mamastrovirus 18 isolate AFCD337 (NC_043102) with a nucleotide identity of 84.4% on the longest contig (311 nt), located on the polyprotein 1AB gene.
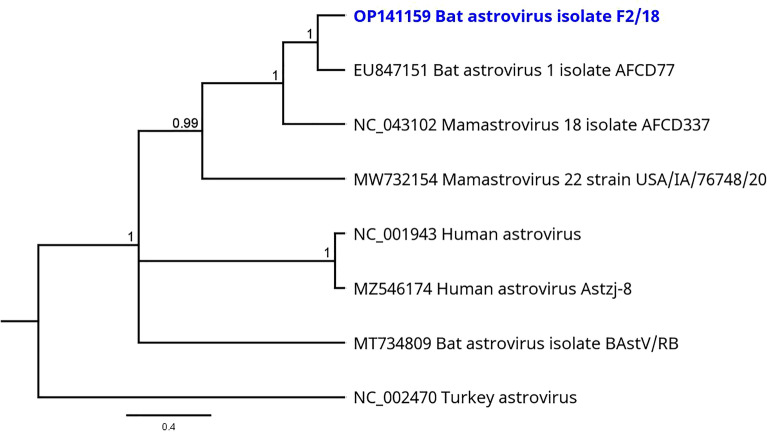
Because of the lack of overlapping sequences, phylogenetic reconstruction was calculated exemplarily with Bat astrovirus strain F2/18 (OP141159); the results are shown in Fig. 3.
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic tree based on the mNGS sequences obtained from the virome of F sample pools (highlighted in blue) and a selection of other astrovirus species. Turkey astrovirus (NC_002470) was used as outgroup. Phylogenetic reconstruction was calculated with the Bayesian MCMC algorithm: 500,000 generations were calculated with a subsampling frequency of 100 and a burn-in of 10%. The substitution model GTR was selected with a gamma-distributed rate variation. Visualized as molecular clock with uniform branch lengths.
Coronaviridae
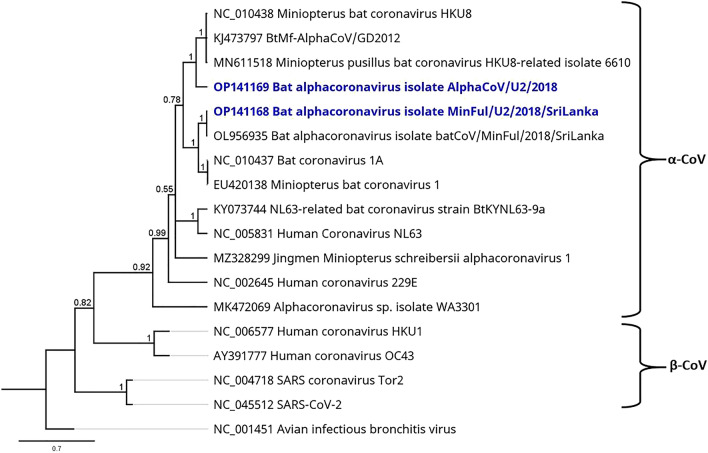
Two coronaviruses (CoV) were found in US and F samples, respectively. A total of 994 reads from F samples and 10,753 reads from US samples were mapped to the bat alphacoronavirus strain batCoV/MinFul/2018/SriLanka (OL956935) with nt identities on conserved ORF1B CDS of 80.36% (F, 668 nt contig) and 98.37% (US, 735 nt contig). In addition, 2443 reads from F sample pools and 2182 reads from US sample pools were mapped to BtMf-AlphaCoV/GD2012 (KJ473797), an alphacoronavirus HKU8 strain from China. Nucleotide identities on the conserved ORF1B CDS were calculated with 82.9% (F, 1113 nt contig) and 85.5% (US, 769 nt contig). For phylogenetic reconstruction, contigs on the ORF1B CDS were selected. Because of the lack of overlapping contigs, phylogeny was calculated separately for the sequences from F and US samples but by using the same reference strains including common human pathogenic CoVs. For the conserved ORF1B CDS, overlapping contigs of 182 nt (F samples) and 224 nt (US samples) were obtained. Figure 4 shows the phylogenetic reconstruction of CoV from US sample pools.
The calculation confirms the presence of two different strains that are allocated to different branches inside the genus Minunacovirus. The identified Bat alphacoronavirus batCoV/MinFul/2018/SriLanka US2/2018 clusters with strains of the species Miniopterus bat coronavirus 1, whereas the other Miniopterus AlphaCoV strain US2/2018 clusters with HKU8-related strains. BatCoV/MinFul/2018/SriLanka US2/2018 was identified in the described sample set and further investigation, extension and analysis led to the assembly of the whole genome of this novel strain20.
Iflaviridae
An iflavirus was found in F samples with a total of 373 reads assembled to Spodoptera exigua iflavirus 2 isolate Korean (JN870848), covering 93.6% of the genome. The longest contig of 1283 nt, located at the beginning of the polyprotein CDS, shares a nucleotide identity of 96.8% to the related Spodoptera exigua iflavirus 2.
Paramyxoviridae
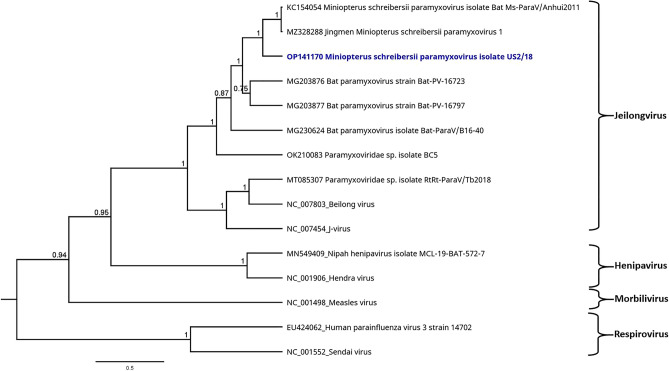
A paramyxovirus (PMV) was found in US samples and confirmed by PCR (compare Table 1). A total of 573 reads were mapped to the full genome of Jingmen Miniopterus schreibersii paramyxovirus 1 (MZ328288). The longest contig (450 nt) on the conserved L gene showed highest nucleotide identities to this strain (84%) and to the partial genome of Miniopterus schreibersii paramyxovirus isolate Bat Ms-ParaV/Anhui2011 (KC154054; 84.6% nt identity). This contig was also selected for phylogenetic reconstruction. The phylogenetic tree of 16 paramyxoviruses, including the novel sequence from Sri Lanka and selected human pathogenic strains, is shown in Fig. 5.
The phylogenetic reconstruction confirms that the novel paramyxovirus from Sri Lanka is closely related to the two PMV strains as described before. Other Miniopterus-related PMVs from China cluster in the same branch of the tree, representing the subgenus Jeilong virus. Apart from this, the subgenera Henipavirus, Morbillivirus and Respirovirus were each allocated to distinct branches of the tree. These subgenera also include the human pathogenic strains that were selected for this phylogenetic reconstruction.
Picornaviridae
A picornavirus was found in F samples: a total of 5714 NGS reads were assembled to Miniopterus schreibersii picornavirus 1 (JQ814851), covering most parts of the genome. The longest contig of 3452 nt, located at the end of the polyprotein CDS, shares a nucleotide identity of 86% to the Miniopterus schreibersii picornavirus 1. For phylogenetic reconstruction, a well-covered contig of 311 nt was selected on the highly conserved 2C peptide on the picornaviral polyprotein. The phylogenetic reconstruction is illustrated in Fig. 6.
As shown in Fig. 6, the novel bat picornavirus strain from F samples clusters monophyletically with its closest related strain Miniopterus schreibersii picornavirus 1 and the Bat picornavirus strain BatPV/V11/13/Hun, both obtained from Miniopterus schreibersii bats. Other bat- and Miniopterus-hosted picornaviruses were allocated to different branches of the phylogenetic tree. The human pathogenic representative picornaviruses are clearly distant from the novel Sri Lankan strain.
Unclassified Riboviria
From F samples, 439 reads were assembled to a Hubei sobemo-like virus 21 strain CC64469 (KX882813) with a nucleotide identity of 82.1% on the longest contig (534 nt).
Phages
A number of phages were found in each sample type as described. Considerable amounts of reads were assigned to the bacteriophage orders Caudovirales (OS: 576; F: 1278; US: 663,683) and Petitvirales (OS: 44,741; F: 235; US: 554,119), respectively.
Discussion
In our study, we analyzed the virome of M. phillipsi bats inhabiting the Wavul Galge cave in the interior of the island of Sri Lanka. By taking oral swabs, urine swabs and feces, we aimed to examine if different viruses are detectable via differing shedding routes represented by the individual sample types. This assumption was confirmed and we have been able to obtain different virome compositions for each sample type.
In OS samples, the primary viral hits were assigned to phages belonging to the orders Caudovirales and Petitvirales. The presence of any other viral sequences in OS samples was not confirmed after quality assessment (in-depth analysis of sequences found and comparison with the database) of analyzed NGS data. However, the detection of Caudovirales and Petitvirales in OS underlines the possibility of virus detection also for this sample type.
Apart from this, different other viruses were detected in the F and US samples as discussed in the following sections.
Phages and diet-related viruses
Sequence reads assigned to phages were found in high numbers in all three sample types. Although these were not inspected in detail in this study, the large number and variety of reads also indicates the presence of numerous bacteria in the collected samples. In combination with 16S bacterial metagenomic analysis, these results will be interesting to be further explored in future studies.
In F samples, viral sequences were identified matching Hubei sobemo-like virus 21 strain CC64469 (China), belonging to unclassified Riboviria. This virus was originally isolated from invertebrates within the phylum Annelida31. Most probably a worm carrying this virus was taken in as nutrition by the bat, passaged and excreted with the feces afterwards.
In addition to this, viral sequences assigned to Spodoptera exigua iflavirus 2 (Korea) were identified in F samples. This virus belonging to the family Iflaviridae within the order Picornavirales was isolated from insects of the genus Spodoptera (moths)32. Here again it is very likely that the virus was taken in with moths for nutrition, passaged and excreted afterwards. In both examples, it is impossible to conclude whether the virus infected the bats as well or was merely digested, passaged and excreted. For this purpose, tissues and organs would need to be investigated.
However, the identified phages as well as these two examples show that the viromes derived from NGS data are complex and do not only comprise the bat-related viruses. Moreover, the data also reveal a number of other viruses derived from the inherent bacterial flora within the bat as well as viruses derived from insects serving as nutrition for the bats. This in turn has the potential to analyze virome compositions of whole habitats, including different organisms. This may be the basis or part of further investigations regarding the bacterial flora and dietary habits of the bats.
Astroviridae
The viruses within the family Astroviridae are common in a wide range of birds (genus Avastroviruses) and mammals (genus Mamastrovirus), including bats and humans33. Human astrovirus infections mainly cause gastroenteritis in children34. Members of this family have a high genetic diversity depending on the respective host species and a wide host range (birds and mammals). However, the zoonotic potential of bat-hosted astroviruses is widely unexplored as yet35. Members of the Mamastrovirus genus are classified based on the amino acid sequences of the capsid region and can be further divided into species, depending on the host and other genetic criteria36. Based on the analyzed sequence data, the examined bats carried multiple astrovirus strains. Thus, bat astrovirus sequences were detected for the first time in a bat species from Sri Lanka, namely M. phillipsi.
From US samples, Bat astrovirus strain US2/18 (OP141166) and Mamastrovirus 18 strain US2/18 (OP141167) were identified, whereas Bat astrovirus isolate F2/18 (OP141159) and Mamastrovirus 14 strain F2/18 (OP141160) were identified from F samples. All three viruses were originally detected in Miniopterus bat species, which may indicate a high host specificity of these viruses. In addition, the circulation of different bat astrovirus strains within one bat population is conceivable, as already reported in other studies37–39.
Phylogenetic reconstruction allowed for a rough classification of the Bat astrovirus strain F2/18 from Sri Lanka, as an example. Although only few suitable reference strains from bats were available in the databases, the phylogeny distinguished astroviruses of bats from astroviruses of other vertebrates (turkey or human) by allocation to different tree branches.
Most available bat astroviral references from the databases contained partial genomes only, located in different gene regions. Further sequence analysis and phylogenetic comparison between all newly obtained astrovirus sequences from Sri Lanka were therefore not possible with the available data. Consequently, we cannot finally prove the presence of multiple astrovirus strains in the collected samples. It may be possible that the sequences were originally derived from a single astrovirus but were mapped to the different partial genomes obtained from the database. Therefore isolation of these viruses followed by in-depth sequencing of the missing genome sequences could be helpful in order to obtain full genome data or at least full gene sequences. With further sequence information it could be examined whether the astroviral reads were actually derived from different strains or whether they belonged to a single astrovirus within the samples.
Coronaviridae
Presence of two different CoVs in M. phillipsi bats was confirmed in F and US samples. Both related virus strains were originally detected in Miniopterus bats20,40,41. The CoV full genome from Sri Lanka (OL956935) was derived from rectal swabs collected during the same bat sampling session as this study and was reported previously20. With the virome sequence data of F and US samples in this study, we were able to confirm the presence of this virus strain also in these samples. In addition, we identified Bat alphacoronavirus strain AlphaCoV/F2/2018 and Bat alphacoronavirus strain AlphaCoV/U2/2018 which are closely related to Miniopterus bat coronavirus HKU8 strains. All identified viruses belong to Minunacoviruses, an α-CoV subgenus containing Miniopterus-hosted viruses. The slight differences between the two virus species within the subgenus are also visible in the phylogenetic reconstruction of different CoVs. Representative strains of the virus species Miniopterus bat coronavirus 1 and Miniopterus bat coronavirus HKU8 were divided into two different clusters within the branch of Minunacoviruses. Co-existence of these two virus species and different CoVs in general have already been reported before42–44. Therefore it can be assumed that these two or even more CoV strains circulate steadily in this population of M. phillipsi bats. Regarding the zoonotic potential of the detected CoVs, further investigation of full genes and specific receptor-binding domains would be necessary for more precise statements. Based on the available data and phylogenies calculated from this, we did not find indications for a human pathogenic potential of the detected viruses17,20. Human pathogenic CoVs that cause outbreaks and pandemics, like SARS, MERS and Covid-19, all belong to the genus of β-CoV and are genetically diverse from the genus α-CoV. Although mildly human pathogenic viruses such as HCoVs NL63 and 229E are represented in the α-CoV genus as well, the phylogeny ranks these species as rather distantly related to the Minunacoviruses.
Paramyxoviridae
Representatives of Chiroptera-hosted PMVs are able to cause zoonotic diseases in humans; therefore this virus family was of high interest for the virome analysis of the bat samples45. The detection of PMVs in US samples was expected, as this is the usual shedding route of these viruses46. The presence of PMVs in the collected US samples has been reported before by using semi-nested PCR7 and Sanger sequencing18. These results indicated the presence of multiple PMVs in the examined samples. The co-circulation of multiple PMVs in general is common in bats and has been reported before47,48. In this study, we proved the presence of previously identified PMVs in the samples by using another molecular virus detection method. However, the NGS data did not reveal enough sequence information to confirm multiple PMV strains. For this purpose, NGS of single US samples instead of pools or more sequencing depth would be necessary to compare sequence data between individuals.
As expected, the identified Miniopterus schreibersii paramyxovirus strain US2/18 (OP141170) has the highest similarities to other Miniopterus-hosted PMVs. In the phylogenetic tree, all Miniopterus-derived strains are assigned to the group of Jeilong virus (Fig. 5). The other branches of the phylogenetic tree depict only a small number of representative strains, including human pathogenic PMVs, whereas the actual Orthoparamyxovirinae subfamily is notably more diverse45,49. In accordance to this, different PMVs can cause diseases of different severity in humans (e.g., Human parainfluenzavirus vs. Nipah virus), whereas other PMVs have a rather low zoonotic potential. The preliminary analysis of the limited sequence data and the phylogenetic reconstruction give no indication of a human pathogenic potential of the novel PMVs. Further sequence data will be needed to allow for a detailed and complex analysis and taxonomic classification of the novel PMV strain50.
Picornaviridae
The family of picornaviruses is a highly diverse family with 68 genera and 158 virus species according to ICTV36. They are globally distributed in a number of bat species including Miniopterus bats51,52. Additionally, they are found in a number of other host species including birds, livestock and humans. Cross-species transmissions between different bats or mammals are possible as well as zoonotic transmissions to humans53. In humans, picornaviruses such as enterovirus, rhinovirus, coxsackievirus, hepatovirus A and human parechovirus can cause diseases of the nervous system and the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts54.
A number of sequences related to Miniopterus schreibersii picornavirus 1 were identified in F samples, which is a described shedding route of bat picornaviruses55. The novel strain from Sri Lanka, Miniopterus schreibersii picornavirus strain F2/18 (OP141164), shares an identity of 86% to the reference strain from China56. For phylogenetic reconstruction in this study, a suitable sequence on the 2C peptide was selected which is a highly conserved region on the picornaviral polyprotein and therefore suitable for this analysis57. The phylogenetic reconstruction included several bat picornaviruses and human pathogenic strains. The novel picornavirus strain from Sri Lankan M. phillipsi bats was assigned to a branch with other Miniopterus-hosted picornaviruses, and the human pathogenic species were assigned to other branches of the tree. The available results did not indicate a human pathogenic potential of the identified picornavirus. Although the phylogenetic analysis was limited to a small proportion of the Picornaviridae family, we were able to get a general idea on phylogenetic relationships of the novel bat picornavirus from Sri Lanka. For proper species classification, a full protein sequence analysis of P1, 2C, 3C and 3D proteins will be necessary but was not possible from the obtained data. However, the results represent the first detection of a picornavirus in the bat species M. phillipsi from Sri Lanka.
Conclusion
We were able to analyze the different compositions of the M. phillipsi virome by potential shedding route obtained from oral swabs, urine swabs and feces samples. Depending on the sample types, different viruses were detected by using NGS analysis, each corresponding to their typical shedding routes.
Independent of the sample type, we were able to detect the co-existence of astroviruses, coronaviruses, paramyxoviruses and picornaviruses circulating simultaneously in the M. phillipsi bat population. However, we point out that viruses in excretions, i.e., urine and feces, can naturally cross-contaminate each other. We assess the possibility of detecting viruses by different sampling routes; the detection does not necessarily represent the origin of replication and the transmission route. Co-existence of these viruses may be common in bats, and even a co-speciation of virus species with their specific host is discussed58,59. It is assumed that virus–virus interaction is also possible and may influence the host, resulting in very specific viral shedding patterns depending on the virome composition48. In future, the epidemiological consequences of co-existing viruses in the bats should be further examined.
It is remarkable that mainly bacteriophages were identified in OS samples, although saliva is also known as common shedding route for other virus families. Lyssaviruses, including bat rabies-related ones, have been detected in other studies focusing on bat lyssaviruses; if these viruses are prevalent in the bats they are excreted by salivary glands and therefore shed with the saliva60. However, the excretion of viruses is generally affected by seasonal patterns and may have been low at the respective sampling point. Since we only used non-invasive sampling methods and could not examine bat brain or other tissue samples, we cannot conclude whether or not such viruses were prevalent in bat organs at the time of bat sampling. A long-term and frequent bat sampling will help to understand seasonality and shedding patterns of different viruses of interest. Probably the virome of all different sample types would change over time as it is influenced by seasons and environmental factors like temperature, humidity, rainfall, migration and reproduction cycles1,48,61,62.
In general, all collected sample types also represent possible transmission routes from bats to humans. The way of viral shedding depends on the respective tissue where the virus replicates: e.g., replication in kidneys and shedding via urine or replication in intestine organs and shedding via feces63.
Transmission of viruses via saliva would be possible from bites when catching and handling the bats. Urine and feces are constantly shed by the bats in the Wavul Galge cave, and the intake of these aerosols containing viral particles may possibly lead to virus exposure when entering the cave without any protective equipment64. In this context, it would also be of interest in the future to investigate the virome of the other bat species inhabiting the cave and to determine whether they are also susceptible to the same viruses.
Although the fecal–oral transmission route is rather unlikely, local people are in close contact to bats when collecting bat guano to use as organic fertilizer65. Especially in rural areas like those around the Wavul Galge cave, the use of bat guano in agriculture is common and represents a potential transmission risk to the farmers. Although our data points towards a rather low zoonotic potential, this does not exclude the seasonal presence of potentially pathogenic agents. A special awareness regarding possible transmissions should be raised. Concurrently, the fear of zoonotic viruses in bat hosts should not justify their eradication. On the contrary, the natural habitat of the bat population in the cave should be recognized and respected.
In summary, the virome composition of different sample types obtained from M. phillipsi bats in Sri Lanka was analyzed for the first time. Recently, DNA barcoding and morphological studies on this species suggest that the Miniopterus bats inhabiting the island of Sri Lanka are in fact a new species of bat not described hitherto and named Miniopterus phillipsi66. All studies on Miniopterus bats from Sri Lanka, conducted before the renaming of the species, identified them as Miniopterus fuliginosus due to lack of more precise information in the database. Based on these findings, the results from our work would represent the first virome analysis for this newly described bat species. This study is the baseline for further in-depth investigation of pathogens of bats inhabiting the Wavul Galge cave in Sri Lanka.
Supplementary Information
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to two anonymous reviewers for their valuable input and suggestions. We are further grateful to the MF2 unit at Robert Koch Institute for the sequencing of the samples and to Ursula Erikli for copy-editing. Furthermore, we thank the Department of Wildlife Conservation, Sri Lanka, for granting the research permit.
Author contributions
Conceptualization of the project by G.P., S.P., W.Y., A.N. and C.K.; methodology by T.M., T.P., S.S., D.B., F.B., M.Ö., B.B.-Z., F.S., G.P., S.P., I.P., W.Y., A.N. and C.K.; investigation by T.M., T.P., S.S., D.B., F.B., M.Ö., B.B.-Z., A.N. and C.K.; writing of the manuscript by T.M.; visualization and preparation of figures by T.M.; review and editing of the manuscript by G.P., S.P., I.P., J.W., S.H., W.Y., A.N. and C.K.; supervision, W.Y., A.N. and C.K.; project administration, F.S., I.P., W.Y., A.N. and C.K.
Funding
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL. Funding was provided by Global Health Protection Programme of the German Federal Ministry of Health (Grant No. ZMVI1-2517-GHP-703 (TP01)).
Data availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available in GenBank of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) repository, accession numbers OP141159 to OP141169.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1038/s41598-023-39534-3.
References
- 1.Calisher CH, Childs JE, Field HE, Holmes KV, Schountz T. Bats: Important reservoir hosts of emerging viruses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006;19(3):531–545. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00017-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Allocati N, Petrucci AG, Di Giovanni P, Masulli M, Di Ilio C, De Laurenzi V. Bat–man disease transmission: Zoonotic pathogens from wildlife reservoirs to human populations. Cell Death Discov. 2016;2(1):16048. doi: 10.1038/CDDISCOVERY.2016.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.O’Shea TJ, et al. Bat flight and zoonotic viruses. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014;20(5):741–745. doi: 10.3201/eid2005.130539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Brook CE, Dobson AP. Bats as ‘special’ reservoirs for emerging zoonotic pathogens. Trends Microbiol. 2015;23(3):172–180. doi: 10.1016/J.TIM.2014.12.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kumar, V. Learning from bats to escape from potent or severe viral infections. In SARS-CoV-2 Origin and COVID-19 Pandemic Across the Globe, [Internet], (ed Kumar, V.) 216–244, (INTECHOPEN LIMITED, London, 2021). 10.5772/intechopen.98916
- 6.Hayman DTS. Bats as viral reservoirs. Ann. Rev. Virol. 2016;3(1):77–99. doi: 10.1146/annurev-virology-110615-042203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tong S, Chern SWW, Li Y, Pallansch MA, Anderson LJ. Sensitive and broadly reactive reverse transcription-PCR assays to detect novel paramyxoviruses. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008;46(8):2652–2658. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00192-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.De Souza Luna LK, et al. Generic detection of coronaviruses and differentiation at the prototype strain level by reverse transcription-PCR and nonfluorescent low-density microarray. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007;45(3):1049–1052. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02426-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Suin V, et al. A two-step lyssavirus real-time polymerase chain reaction using degenerate primers with superior sensitivity to the fluorescent antigen test. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014;2014:256175. doi: 10.1155/2014/256175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Van Brussel K, Holmes EC. Zoonotic disease and virome diversity in bats. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2022;52:192–202. doi: 10.1016/J.COVIRO.2021.12.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chen L, Liu B, Yang J, Jin Q. DBatVir: The database of bat-associated viruses. Database. 2014;2014:bau021. doi: 10.1093/database/bau021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sayers EW, et al. Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49(D1):D10–D17. doi: 10.1093/NAR/GKAA892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Yapa, W. B. A Field Guide to the Bats of Sri Lanka, 1st ed. (Dilmah Ceylon Tea Company PLC., Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2017).
- 14.Yapa, W. B., & Ratnasooriya, W. D. Ecology and biology of Sri Lankan bats. Univ. Colombo Rev., 1(1), 63–85. (2006). [Online]. Available: http://archive.cmb.ac.lk:8080/research/handle/70130/1081.
- 15.Kudagammana HDWS, Thevanesam V, Chu DKW, Eriyagama NB, Peiris JSM, Noordeen F. Coronaviruses in guano from Pteropus medius bats in Peradeniya, Sri Lanka. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018;65(4):1122–1124. doi: 10.1111/tbed.12851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gunawardena PS, et al. Lyssavirus in Indian flying foxes, Sri Lanka. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016;22(8):1456–1459. doi: 10.3201/EID2208.151986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Muzeniek T, et al. Detection of alpha- and betacoronaviruses in Miniopterus fuliginosus and Rousettus leschenaultii, two species of Sri Lankan bats. Vaccines. 2021;9(6):650. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9060650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Muzeniek T, et al. Paramyxovirus diversity within one population of Miniopterus fuliginosus bats in Sri Lanka. Pathogens. 2022;11(4):434. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11040434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.T. Perera et al., “One Health Approach for the sampling of different bat species living in a sympatric colony,” bioRxiv, 2022, doi: 10.1101/2022.09.22.508887.
- 20.Muzeniek T, et al. Full genome of batCoV/MinFul/2018/SriLanka, a novel alpha-coronavirus detected in Miniopterus fuliginosus, Sri Lanka. Viruses. 2022;14(2):337. doi: 10.3390/v14020337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Perera T, et al. First complete cytochrome B sequences and molecular taxonomy of bat species from Sri Lanka. Animals (Basel) 2022;12(13):1674. doi: 10.3390/ANI12131674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics. 2014;30(15):2114–2120. doi: 10.1093/BIOINFORMATICS/BTU170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Buchfink B, Xie C, Huson DH. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods. 2015;12(1):59–60. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Huson DH, Auch AF, Qi J, Schuster SC. MEGAN analysis of metagenomic data. Genome Res. 2007;17(3):377–386. doi: 10.1101/gr.5969107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zerbino DR, Birney E. Velvet: Algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res. 2008;18(5):821–829. doi: 10.1101/GR.074492.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Katoh K, Standley DM. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013;30(4):772–780. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics. 2001;17(8):754–755. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/17.8.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Guindon S, Gascuel O. A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst. Biol. 2003;52(5):696–704. doi: 10.1080/10635150390235520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Darriba D, Taboada GL, Doallo R, Posada D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods. 2012;9(8):772. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Jurasz H, Pawłowski T, Perlejewski K. Contamination issue in viral metagenomics: Problems, solutions, and clinical perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2021;12:745076. doi: 10.3389/FMICB.2021.745076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Shi M, et al. Redefining the invertebrate RNA virosphere. Nature. 2016;540(7634):539–543. doi: 10.1038/nature20167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Choi JY, et al. Complete genome sequence of a novel picorna-like virus isolated from Spodoptera exigua. J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2012;15(2):259–263. doi: 10.1016/J.ASPEN.2012.01.006. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Gough, R. E. & McNulty, M. S. Astroviridae. In Poultry diseases (Eds Pattison, M., McMullin, P. F., Bradbury, J. M., Alexander, D. J.) 6th Edn. 392–397 (Elsevier/Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2008). 10.1016/B978-0-7020-2862-5.50038-6
- 34.Mitchell DK. Astrovirus gastroenteritis. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2002;21(11):1067–1069. doi: 10.1097/00006454-200211000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Fischer K, dos Reis VP, Balkema-Buschmann A. Bat astroviruses: Towards understanding the transmission dynamics of a neglected virus family. Viruses. 2017;9(2):34. doi: 10.3390/V9020034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Walker PJ, et al. Changes to virus taxonomy and the Statutes ratified by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2020) Arch. Virol. 2020;165(11):2737–2748. doi: 10.1007/S00705-020-04752-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Zhu HC, et al. Detection of diverse astroviruses from bats in China. J. Gen. Virol. 2009;90(4):883–887. doi: 10.1099/VIR.0.007732-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Fischer K, et al. Insectivorous bats carry host specific astroviruses and coronaviruses across different regions in Germany. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016;37:108–116. doi: 10.1016/J.MEEGID.2015.11.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Dufkova L, et al. Detection of diverse novel bat astrovirus sequences in the Czech Republic. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2015;15(8):518–521. doi: 10.1089/VBZ.2015.1813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wu Z, et al. Deciphering the bat virome catalog to better understand the ecological diversity of bat viruses and the bat origin of emerging infectious diseases. ISME J. 2016;10(3):609–620. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2015.138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Du J, et al. Genetic diversity of coronaviruses in Miniopterus fuliginosus bats. Sci. China Life Sci. 2016;59(6):604–614. doi: 10.1007/s11427-016-5039-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Chu DKW, Peiris JSM, Chen H, Guan Y, Poon LLM. Genomic characterizations of bat coronaviruses (1A, 1B and HKU8) and evidence for co-infections in Miniopterus bats. J. Gen. Virol. 2008;89(5):1282–1287. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.83605-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ge XY, et al. Coexistence of multiple coronaviruses in several bat colonies in an abandoned mineshaft. Virol. Sin. 2016;31(1):31–40. doi: 10.1007/s12250-016-3713-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Lin X-D, et al. Extensive diversity of coronaviruses in bats from China. Virology. 2017;507(July):1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2017.03.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Thibault PA, Watkinson RE, Moreira-Soto A, Drexler JF, Lee B. Zoonotic potential of emerging paramyxoviruses: Knowns and unknowns. Adv. Virus Res. 2017;98:1–55. doi: 10.1016/bs.aivir.2016.12.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Edson D, et al. Routes of Hendra virus excretion in naturally-infected flying-foxes: Implications for viral transmission and spillover risk. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(19):e0140670. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Darcissac E, Donato D, de Thoisy B, Lacoste V, Lavergne A. Paramyxovirus circulation in bat species from French Guiana. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021;90:104769. doi: 10.1016/J.MEEGID.2021.104769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Peel AJ, et al. Synchronous shedding of multiple bat paramyxoviruses coincides with peak periods of Hendra virus spillover. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019;8(1):1314–1323. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2019.1661217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Drexler JF, et al. Bats host major mammalian paramyxoviruses. Nat. Commun. 2012;3(1):796. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Rima B, et al. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Paramyxoviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2019;100(12):1593–1594. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Lukashev AN, et al. Close genetic relatedness of picornaviruses from European and Asian bats. J. Gen. Virol. 2017;98(5):955–961. doi: 10.1099/JGV.0.000760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Kemenesi G, et al. Genetic characterization of a novel picornavirus detected in Miniopterus schreibersii bats. J. Gen. Virol. 2015;96(4):815–821. doi: 10.1099/JGV.0.000028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Bergner LM, et al. Characterizing and evaluating the zoonotic potential of novel viruses discovered in vampire bats. Viruses. 2021;13(2):252. doi: 10.3390/V13020252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Storch, G. A. Diagnostic virology. In Fields Virology, 4th ed., (eds Knipe, D. M., Howley, P. M., Griffin, D. E., Lamb, R. A., Martin, M. A., Roizman, B., Straus, S. E.), 493–531 (Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA, 2001).
- 55.Rotbart, H. A. Clinical significance, diagnosis, and treatment of picornavirus infections. In Molecular Biology of Picornavirus, (eds Semler, B. L. & Wimmer, E.), 355–365. (ASM Press, Washington, 2002). 10.1128/9781555817916.CH28.
- 56.Wu Z, et al. Virome analysis for identification of novel mammalian viruses in bat species from Chinese provinces. J. Virol. 2012;86(20):10999–11012. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01394-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Cheng Z, et al. The nonstructural protein 2C of a picorna-like virus displays nucleic acid helix destabilizing activity that can be functionally separated from its ATPase activity. J. Virol. 2013;87(9):5205–5218. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00245-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Liang J, Zhu C, Zhang L. Cospeciation of coronavirus and paramyxovirus with their bat hosts in the same geographical areas. BMC Ecol. Evol. 2021;21(1):148. doi: 10.1186/S12862-021-01878-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Hoarau AOG, et al. Investigation of astrovirus, coronavirus and paramyxovirus co-infections in bats in the western Indian Ocean. Virol. J. 2021;18(1):205. doi: 10.1186/S12985-021-01673-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Begeman L, et al. Faeces as a novel material to estimate lyssavirus prevalence in bat populations. Zoonoses Public Health. 2020;67(2):198–202. doi: 10.1111/ZPH.12672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Plowright RK, et al. Ecological dynamics of emerging bat virus spillover. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014;282(1798):20142124. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2014.2124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Dietrich M, Kearney T, Seamark ECJ, Paweska JT, Markotter W. Synchronized shift of oral, faecal and urinary microbiotas in bats and natural infection dynamics during seasonal reproduction. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018;5(5):180041. doi: 10.1098/RSOS.180041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Subudhi S, Rapin N, Misra V. Immune system modulation and viral persistence in bats: Understanding viral spillover. Viruses. 2019;11(2):192. doi: 10.3390/v11020192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Han HJ, et al. Bats as reservoirs of severe emerging infectious diseases. Virus Res. 2015;205:1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2015.05.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Dimkić I, et al. The microbiome of bat guano: For what is this knowledge important? Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021;105(4):1407–1419. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11143-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Kusuminda T, et al. DNA barcoding and morphological analyses reveal a cryptic species of Miniopterus from India and Sri Lanka. Acta Chiropterologica. 2022;24(1):1–17. doi: 10.3161/15081109acc2022.24.1.001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available in GenBank of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) repository, accession numbers OP141159 to OP141169.