Abstract
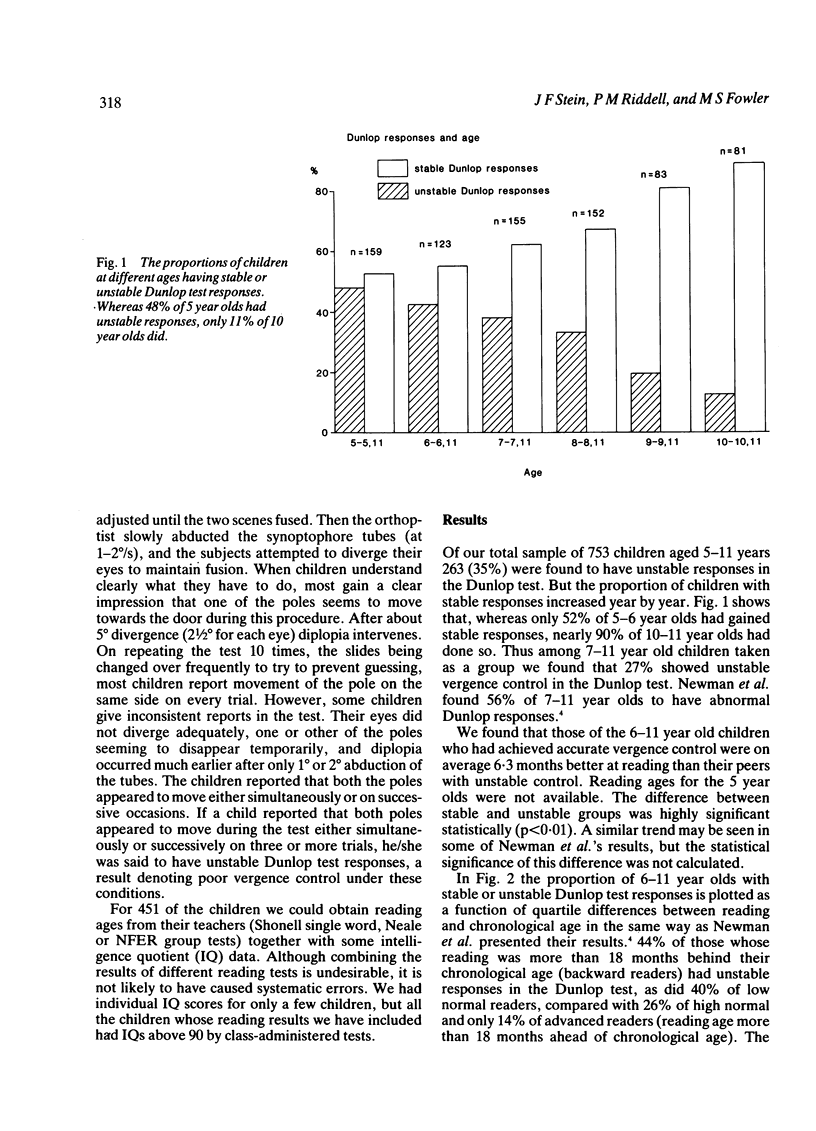
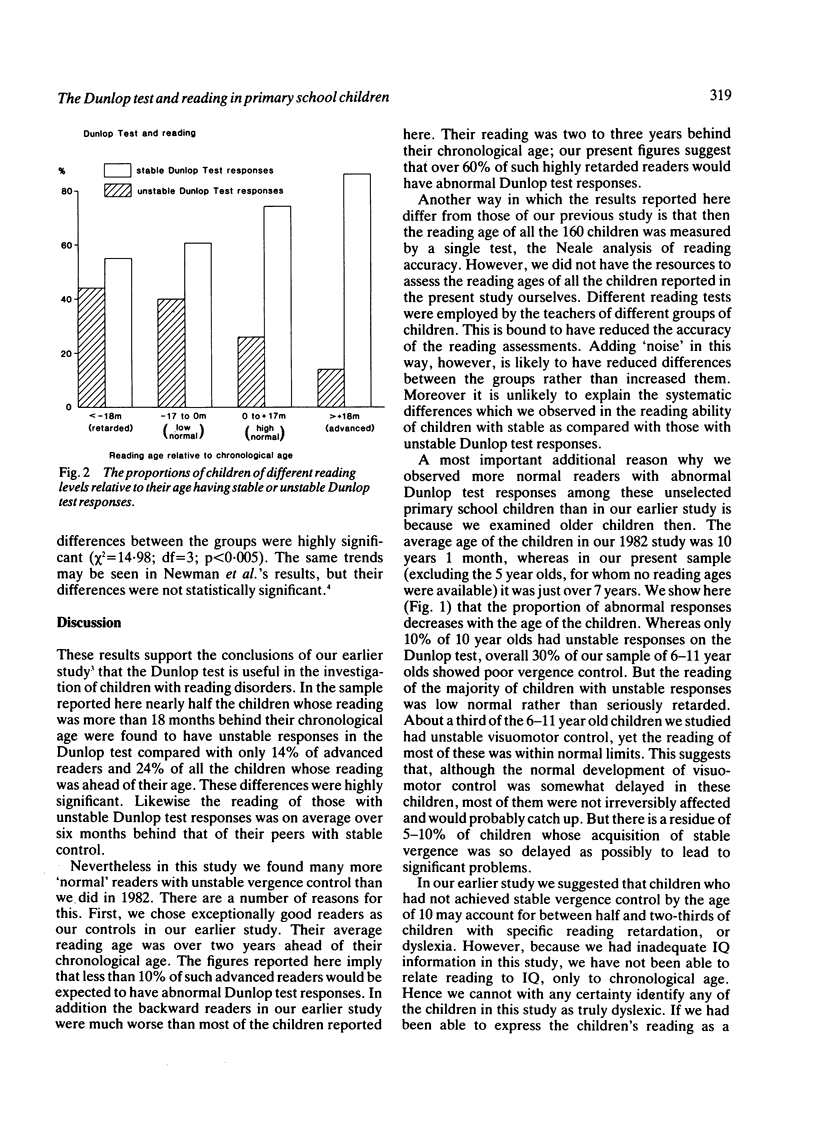
Using the Dunlop synoptophore test we have examined the reliability of vergence control for small fusion targets in 753 primary school children aged 7-11, and we have compared these results with the reading performance of 451 of them. 30% of the total sample of children had unstable responses in the Dunlop test. The proportion decreased with age, ranging from 49% of 5-year-olds to only 11% of 10-year-olds. The reading of children who had developed accurate vergence control was on average 6.3 months in advance of those who had not. Those with unstable Dunlop test responses were much more likely to be backward or low normal readers than children with stable responses. We conclude that in experienced hands the Dunlop test is a useful indicator of the development of vergence control and that immaturity of vergence control may contribute to children's reading problems.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Newman S. P., Wadsworth J. F., Archer R., Hockly R. Ocular dominance, reading, and spelling ability in schoolchildren. Br J Ophthalmol. 1985 Mar;69(3):228–232. doi: 10.1136/bjo.69.3.228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J. F., Fowler S. Diagnosis of dyslexia by means of a new indicator of eye dominance. Br J Ophthalmol. 1982 May;66(5):332–336. doi: 10.1136/bjo.66.5.332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J., Fowler S. Effect of monocular occlusion on visuomotor perception and reading in dyslexic children. Lancet. 1985 Jul 13;2(8446):69–73. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90179-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


