Int J Mol Med 44: 683-683, 2019; DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4241
Following the publication of the above article, an interested reader drew to the authors' attention that, for the Transwell migration assays shown in Figs. 1B and 3B on p. 685 and p. 688 respectively, the images selected for the '5637 / DMSO' experiment in Fig. 1B and the DMSO experiment in Fig. 3B were apparently the same, such that these data appeared to have been derived from the same original source. After having consulted their original data, the authors have realized that the 5637 DMSO data panel in Fig. 3B had been selected incorrectly.
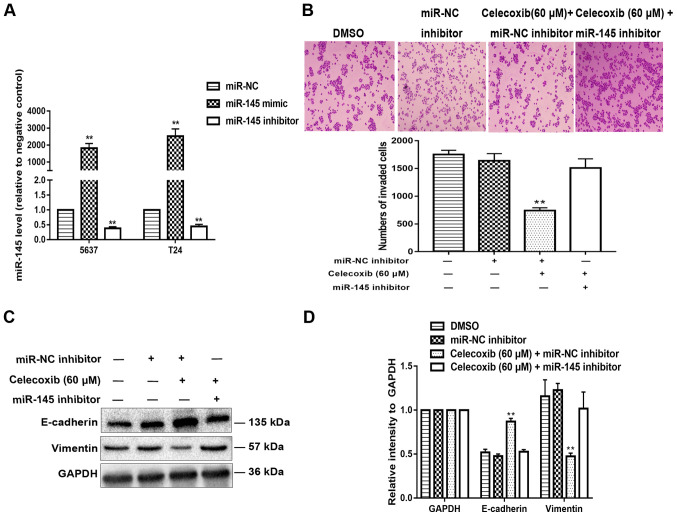
Figure 3.
miR-145 is required for the celecoxib-mediated inhibition of EMT. (A) Quantified results from reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis following the transfection of 5637 and T24 cells with miR-145 mimics and inhibitors. (B) Celecoxib inhibited the invasion of 5637 cells, while miR-145 inhibitor treatment rescued the effect. (C) Alteration of the expression levels of the EMT-associated markers E-cadherin and Vimentin, caused by celecoxib (60 µM) treatment, were rescued by transfection with the miR-145 inhibitor. (D) Statistical analysis of (C). **P<0.05 vs. miR-NC or the celecoxib (60 µM) + miR-145 inhibitor group. miR, microRNA; EMT, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; NC, negative control; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide..
The revised version of Fig. 3, showing the correct data for the DMSO experiment in Fig. 3B, is shown on the next page. The authors regret that these errors went unnoticed prior to the publication of this article, and thank the Editor of International Journal of Molecular Medicine for allowing them the opportunity to publish this corrigendum. All the authors agree with the publication of this corrigendum; furthermore, they also apologize to the readership of the journal for any inconvenience caused.