Abstract
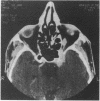
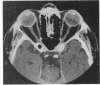
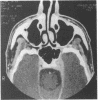
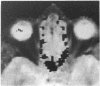
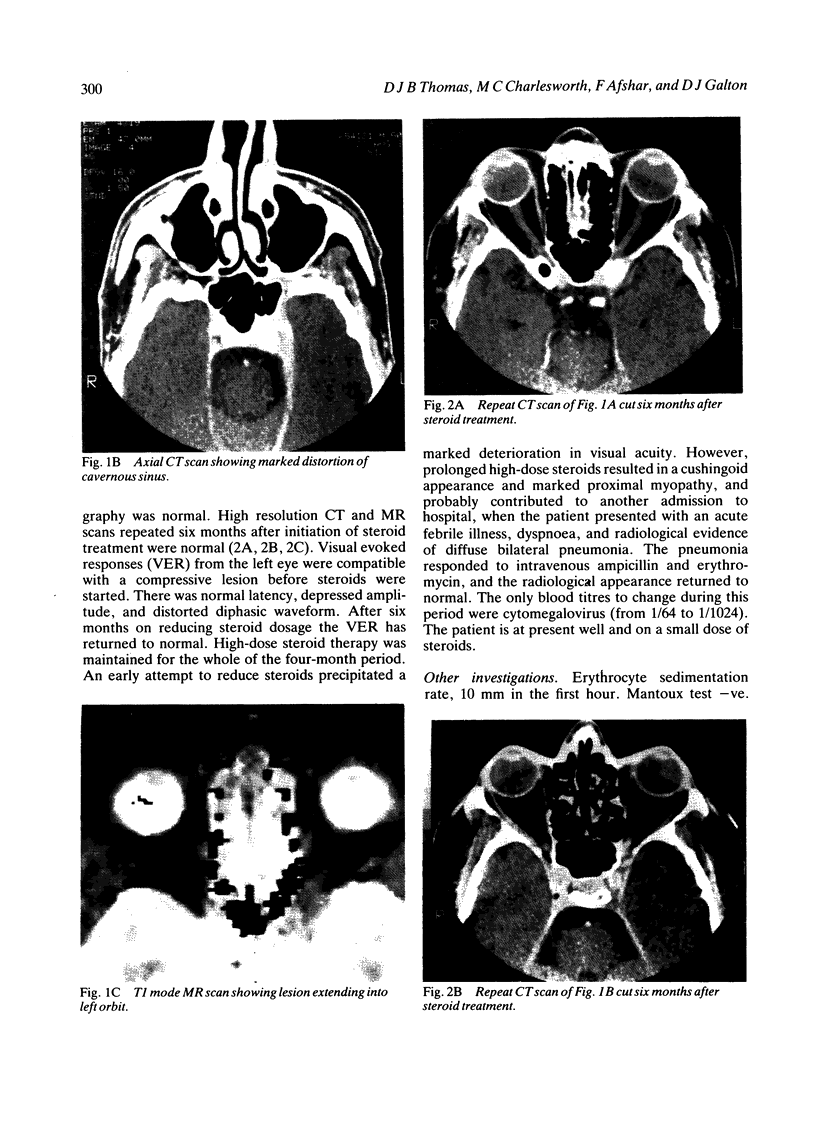
A 50-year-old Asian male presented with a left sixth nerve palsy, left temporal pain, and rapidly deteriorating visual acuity in the left eye. A high resolution CT scan and magnetic resonance scan showed a left retro-orbital enhancing lesion extending from the lateral margin of the cavernous sinus on to the greater wing of the sphenoid and into the left orbit. Arteriography was normal. On high dose steroid therapy there was total resolution of the lesion. The value of imaging techniques in this condition is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dornan T. L., Espir M. L., Gale E. A., Tattersall R. B., Worthington B. S. Remittent painful ophthalmoplegia: the Tolosa-Hunt syndrome? A report of seven cases and review of the literature. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1979 Mar;42(3):270–275. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.42.3.270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fallowfield L. J., Rees J. E. Psychophysical assessment of a patient with Tolosa-Hunt syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1983 Jun;46(6):576–578. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.46.6.576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT W. E., MEAGHER J. N., LEFEVER H. E., ZEMAN W. Painful opthalmoplegia. Its relation to indolent inflammation of the carvernous sinus. Neurology. 1961 Jan;11:56–62. doi: 10.1212/wnl.11.1.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Idell S., Johnson M., Beauregard L., Learner N. Pneumonia associated with rising cytomegalovirus antibody titres in a healthy adult. Thorax. 1983 Dec;38(12):957–958. doi: 10.1136/thx.38.12.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabs D. A., Miller N. R., Green W. R. Ischaemic optic neuropathy with painful ophthalmoplegia in diabetes mellitus. Br J Ophthalmol. 1981 Oct;65(10):673–678. doi: 10.1136/bjo.65.10.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAKKE J. P. Superior orbital fissure syndrome. Report of a case caused by local pachymeningitis. Arch Neurol. 1962 Oct;7:289–300. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1962.04210040041004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew N. T., Chandy J. Painful ophthalmoplegia. J Neurol Sci. 1970 Sep;11(3):243–256. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(70)90064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowed D. W., Kassel E. E., Lewis A. J. Transorbital intracavernous needle biopsy in painful ophthalmoplegia. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1985 May;62(5):776–780. doi: 10.3171/jns.1985.62.5.0776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith F. W., Cherryman G. R., Singh A. K., Forrester J. V. Nuclear magnetic resonance tomography of the orbit at 3.4 MHz. Br J Radiol. 1985 Oct;58(694):947–957. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-58-694-947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spillane J. D. The geography of neurology. Br Med J. 1972 May 27;2(5812):506–512. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5812.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]