Abstract
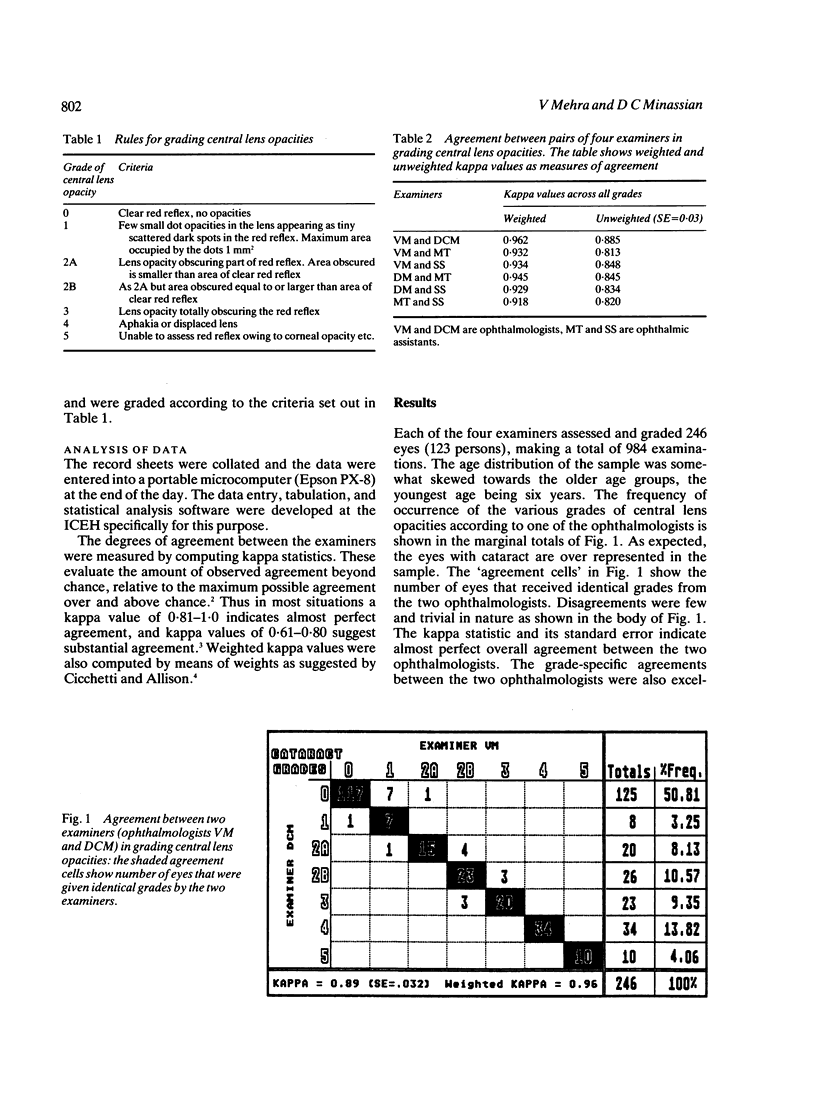
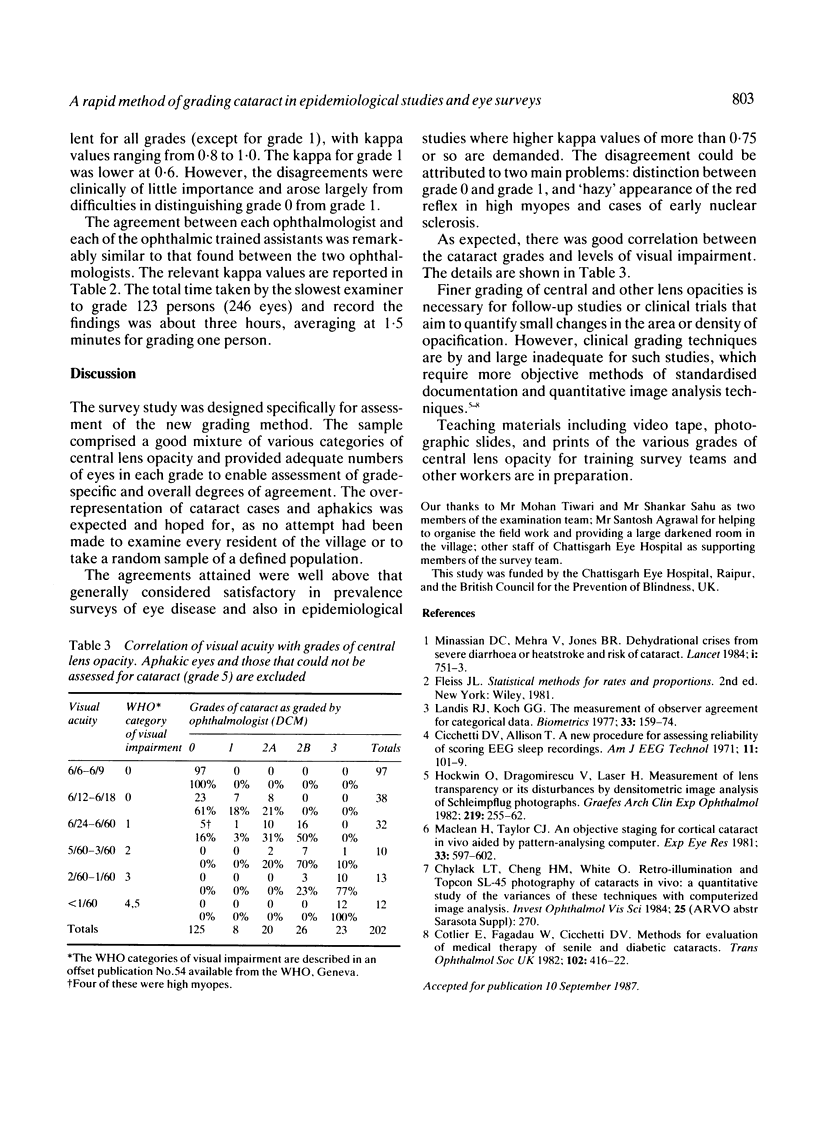
A rapid method of grading clinically important central lens opacities has been developed for use in eye surveys and in epidemiological studies of cataract and has been field-tested in a specifically designed observer agreement study in a survey of a rural community in Central India. The grading method is based on simple measurement of the area of lens opacity that obscures the red reflex relative to the area of clear red reflex, as visualised through the undilated normal pupil. Good to almost perfect agreements were attained between two ophthalmologists and two trained ophthalmic assistants for overall grades of central lens opacity. Most disagreements were trivial in nature and were concerned with difficulties in distinguishing grade 0 from grade 1, and with hazy appearance of the red reflex in high myopes and in cases of early nuclear sclerosis. Teaching materials including video tape and slides for training survey teams and other workers are in preparation.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cotlier E., Fagadau W., Cicchetti D. V. Methods for evaluation of medical therapy of senile and diabetic cataracts. Trans Ophthalmol Soc U K. 1982;102(Pt 3):416–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockwin O., Dragomirescu V., Laser H. Measurements of lens transparency or its disturbances by densitometric image analysis of Scheimpflug photographs. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1982;219(6):255–262. doi: 10.1007/BF00231409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landis J. R., Koch G. G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977 Mar;33(1):159–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maclean H., Taylor C. J. An objective staging for cortical cataract in vivo aided by pattern-analysing computer. Exp Eye Res. 1981 Dec;33(6):597–602. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(81)80099-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minassian D. C., Mehra V., Jones B. R. Dehydrational crises from severe diarrhoea or heatstroke and risk of cataract. Lancet. 1984 Apr 7;1(8380):751–753. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91274-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


