Abstract
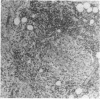
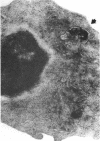
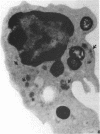
Chronic orbital inflammatory disease (COID) is usually considered non-infectious and idiopathic. Treatment is empirical, palliative, and may not prevent disease progression. COID occurs in isolation or in association with various systemic diseases. Exophthalmos may be an important presenting sign. Vasculitis, lymphoid infiltrates, and granulomas are common. Mollicute-like organisms (MLO) parasitising and destroying vitreous leucocytes are often found to cause human chronic uveitis when an appropriate search is made. Inoculation of these MLO into mouse eyelids produced chronic uveitis and exophthalmic orbital inflammatory disease. Mollicutes are cell wall deficient bacteria. Extracellular mollicutes cause human and animal diseases characterised by lymphoid infiltrates, immunosuppression, and autoantibody production. Intracellular morphologically similar bacteria are non-cultivable pathogens termed MLO. Identification is based on direct detection in diseased cells by transmission electron microscopy. MLO are cytopathogenic and detection is aided by the alterations they produce. MLO replace the cytoplasm, destroy the organelles, and alter the nucleus. This results in cell proliferation, destruction, and dysfunction. MLO parasitise lymphocytes, monocytes, and polymorphonuclear leucocytes. This report describes orbital leucocytes parasitised by MLO in three patients with isolated COID. Rifampicin treatment of MLO disease is discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arora Y. K., Sinha R. C. Enzymatic activities in cell fractions of mycoplasmalike organisms purified from aster yellows-infected plants. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):811–815. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.811-815.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bove J. M. Mycoplasma infections of plants. Isr J Med Sci. 1981 Jul;17(7):572–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. A., Wirostko E. Chronic idiopathic vitritis. Ultrastructural properties of bacteria-like bodies within vitreous leukocyte phagolysosomes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1986 Jul;86(1):19–24. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/86.1.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. A., Wirostko E., Wirostko W. J. Crohn's disease uveitis. Parasitization of vitreous leukocytes by mollicute-like organisms. Am J Clin Pathol. 1989 Mar;91(3):259–264. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/91.3.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L., Wirostko E., Wirostko B. Chronic idiopathic vitritis. Cytopathogenicity of unusual bacteria for vitreous polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Submicrosc Cytol. 1987 Jan;19(1):161–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L., Wirostko E., Wirostko W. Mouse lethal cardiovascular disease: induction by human leucocyte intracellular Mollicutes. Br J Exp Pathol. 1988 Apr;69(2):265–279. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulanova E. F. Changes in the nuclei and chloroplasts in cells of big bud-infected tomatoes. Biol Bull Acad Sci USSR. 1978 Mar-Apr;5(2):232–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirostko E., Johnson L. A., Wirostko B. M. Transmission of chronic idiopathic vitritis in mice by inoculation of human vitreous containing leucocyte phagolysosomal bacteria-like bodies. Lancet. 1986 Aug 30;2(8505):481–483. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90357-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirostko E., Johnson L. A., Wirostko W. J. Mouse interstitial lung disease and pleuritis induction by human Mollicute-like organisms. Br J Exp Pathol. 1988 Dec;69(6):891–902. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirostko E., Johnson L., Wirostko W. Chronic intracellular leucocytoclastic bacterial vitritis. A transmission electron microscopic study of the monocytes. J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol. 1988 Apr;20(2):463–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirostko E., Johnson L., Wirostko W. Chronic leucocytoclastic bacterial vitritis. A lymphocyte transmission electron microscopic study. J Submicrosc Cytol. 1987 Oct;19(4):651–656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirostko E., Johnson L., Wirostko W. Mouse exophthalmic chronic orbital inflammatory disease. Induction by human leucocyte intracellular Mollicutes. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1988;413(4):349–355. doi: 10.1007/BF00783028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]