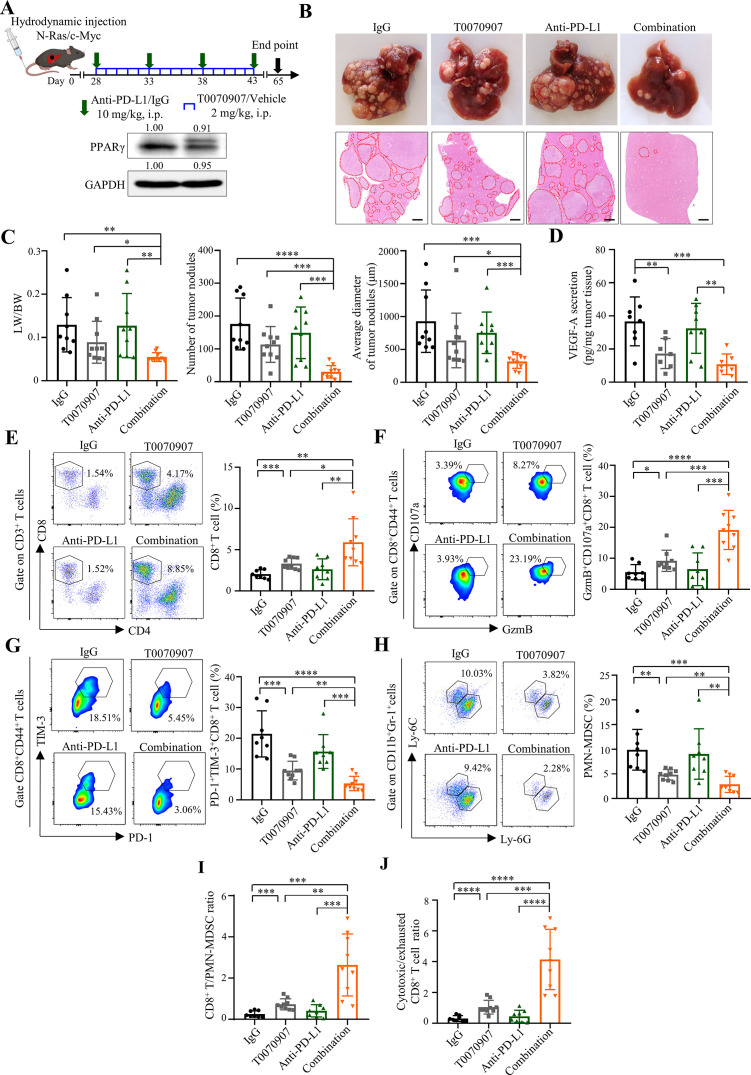
Figure 6.
PPARγ antagonist T0070907 overcomes ICB resistance in the spontaneous HCC model. (A) Combinatory treatment schedule of T0070907 and anti-PD-L1 antibody 10F.9G2 in N-Ras/c-Myc-induced spontaneous HCC model (top). Representative western blot images of PPARγ in N-Ras/c-Myc-induced tumours (bottom). GAPDH served as loading controls. (B) Representative photos (top) and H&E staining images (bottom) of liver tumours of indicated groups (n=9 to 10). Scale bars, 500 µm. Tumour area is circled by red dotted line. (C) Tumour burden in indicated groups was evaluated by liver versus body weight ratios (LW/BW; left), numbers (middle) and average diameters (right) of tumour nodules per mouse from H&E images. (D) VEGF-A secretion levels in tumour tissues from indicated groups (n=7 to 8). (E) The proportions of CD8+ T cells, (F) GzmB+CD107a+ and (G) PD-1+TIM-3+ cells in tumorous CD8+ T cells as well as (H) PMN-MDSCs in tumorous CD45+ cells from indicated groups (n=8 to 9). (I) The ratios of CD8+ T/PMN-MDSC and (J) cytotoxic/exhausted CD8+ T cell in indicated groups. Data represent as mean±SD. Statistical significance was determined by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. *P<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001. BW, body weight; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; ICB, immune-checkpoint blockade; LW, liver weight; MDSC, myeloid-derived suppressor cell; PD-L1, programmed death-1-ligand-1; PMN, polymorphonuclear; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma; TIM, T cell immunoglobulin; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.