Abstract
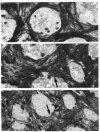
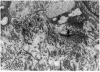
The optic nerve heads from normal and glaucomatous eyes of humans and monkeys were examined by light and electron microscopy for the presence and distribution of elastin. Elastin densely lined the insertion of the lamina cribrosa into the sclera and was prominent in the laminar beams. The long axis of elastin paralleled that of the collagen fibrils and corresponded to the directions of expected forces on the tissue. In glaucomatous eyes elastin molecules were curled instead of straight and seemed disconnected from the other elements of the connective tissue matrix. Laminar beams stretch and reorganise their substructure during glaucomatous atrophy, probably leading to changed compliance. Differences in elastin function may have a part in susceptibility to glaucomatous injury.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. R. Ultrastructure of human and monkey lamina cribrosa and optic nerve head. Arch Ophthalmol. 1969 Dec;82(6):800–814. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1969.00990020792015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene P. R. Mechanical considerations in myopia: relative effects of accommodation, convergence, intraocular pressure, and the extraocular muscles. Am J Optom Physiol Opt. 1980 Dec;57(12):902–914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenlee T. K., Jr, Ross R., Hartman J. L. The fine structure of elastic fibers. J Cell Biol. 1966 Jul;30(1):59–71. doi: 10.1083/jcb.30.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez M. R., Andrzejewska W. M., Neufeld A. H. Changes in the extracellular matrix of the human optic nerve head in primary open-angle glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 1990 Feb 15;109(2):180–188. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)75984-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez M. R., Igoe F., Neufeld A. H. Cell culture of the human lamina cribrosa. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1988 Jan;29(1):78–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez M. R., Igoe F., Neufeld A. H. Extracellular matrix of the human optic nerve head. Am J Ophthalmol. 1986 Aug 15;102(2):139–148. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(86)90134-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez M. R., Luo X. X., Igoe F., Neufeld A. H. Extracellular matrix of the human lamina cribrosa. Am J Ophthalmol. 1987 Dec 15;104(6):567–576. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(87)90165-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajikawa K., Yamaguchi T., Katsuda S., Miwa A. An improved electron stain for elastic fibers using tannic acid. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo) 1975;24(4):287–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kligman L. H. Luna's technique. A beautiful stain for elastin. Am J Dermatopathol. 1981 Summer;3(2):199–201. doi: 10.1097/00000372-198100320-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison J. C., Dorman-Pease M. E., Dunkelberger G. R., Quigley H. A. Optic nerve head extracellular matrix in primary optic atrophy and experimental glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 1990 Jul;108(7):1020–1024. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1990.01070090122053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison J. C., Jerdan J. A., L'Hernault N. L., Quigley H. A. The extracellular matrix composition of the monkey optic nerve head. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1988 Jul;29(7):1141–1150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxlund H., Andreassen T. T. The roles of hyaluronic acid, collagen and elastin in the mechanical properties of connective tissues. J Anat. 1980 Dec;131(Pt 4):611–620. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxlund H., Manschot J., Viidik A. The role of elastin in the mechanical properties of skin. J Biomech. 1988;21(3):213–218. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(88)90172-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley H. A., Addicks E. M., Green W. R., Maumenee A. E. Optic nerve damage in human glaucoma. II. The site of injury and susceptibility to damage. Arch Ophthalmol. 1981 Apr;99(4):635–649. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1981.03930010635009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley H. A., Brown A. E., Morrison J. D., Drance S. M. The size and shape of the optic disc in normal human eyes. Arch Ophthalmol. 1990 Jan;108(1):51–57. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1990.01070030057028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley H. A., Hohman R. M., Addicks E. M., Massof R. W., Green W. R. Morphologic changes in the lamina cribrosa correlated with neural loss in open-angle glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 1983 May;95(5):673–691. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(83)90389-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley H. A., Hohman R. M. Laser energy levels for trabecular meshwork damage in the primate eye. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1983 Sep;24(9):1305–1307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repka M. X., Quigley H. A. The effect of age on normal human optic nerve fiber number and diameter. Ophthalmology. 1989 Jan;96(1):26–32. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(89)32928-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbloom J. Elastin: an overview. Methods Enzymol. 1987;144:172–196. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)44178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai L. Y., Keene D. R., Engvall E. Fibrillin, a new 350-kD glycoprotein, is a component of extracellular microfibrils. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2499–2509. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer A. Intraocular pressure and glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 1989 Feb 15;107(2):186–188. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(89)90221-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tengroth B., Ammitzbøll T. Changes in the content and composition of collagen in the glaucomatous eye--basis for a new hypothesis for the genesis of chronic open angle glaucoma--a preliminary report. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1984 Dec;62(6):999–1008. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1984.tb08452.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeimer R. C., Ogura Y. The relation between glaucomatous damage and optic nerve head mechanical compliance. Arch Ophthalmol. 1989 Aug;107(8):1232–1234. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1989.01070020298042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]