Abstract
Trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) is an antibody drug conjugate with a topoisomerase I payload that targets the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2). T-DXd is approved for patients with previously treated HER2-positive or HER2-low (immunohistochemistry [IHC] 1+ or IHC 2+/ISH−) metastatic/unresectable breast cancer (BC). In a second-line HER2-positive metastatic BC (mBC) population (DESTINY-Breast03 [ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03529110]), T-DXd demonstrated significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) over ado-trastuzumab emtansine (12-month rate: 75.8% v 34.1%; hazard ratio, 0.28; P < .001), and in patients with HER2-low mBC treated with one prior line of chemotherapy (DESTINY-Breast04 [ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03734029]), T-DXd demonstrated significantly longer PFS and overall survival than physician's choice chemotherapy (10.1 v 5.4 months; hazard ratio, 0.51; P < .001, and 23.4 v 16.8 months; hazard ratio, 0.64; P < .001, respectively).
Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is an umbrella term used for a group of diseases characterized by lung injury including pneumonitis, which can lead to irreversible lung fibrosis. ILD is a well-described adverse event associated with certain anticancer therapies, including T-DXd. An important part of T-DXd therapy for mBC consists of monitoring for and managing ILD. Although information on ILD management strategies is included in the prescribing information, additional information on patient selection, monitoring, and treatment can be beneficial in routine clinical practice. The objective of this review is to describe real-world, multidisciplinary clinical practices and institutional protocols used for patient selection/screening, monitoring, and management related to T-DXd–associated ILD.
INTRODUCTION
Overexpression of the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) plays a central role in the pathogenesis of breast cancer (BC).1 Approvals of targeted therapies have provided unprecedented benefit in the treatment of HER2-positive disease and that benefit now extends beyond HER2 positivity as historically defined.2,3 Trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) is approved for the treatment of metastatic HER2-positive and HER2-low BC. Specifically, it is indicated for adult patients with unresectable or HER2-positive metastatic BC (mBC) who have received a prior anti-HER2–based regimen either in the metastatic setting or in the neoadjuvant or adjuvant setting and have developed disease recurrence during or within 6 months of completing therapy, as well as in adult patients with unresectable or metastatic HER2-low (immunohistochemistry [IHC] 1+ or IHC 2+/ISH−) BC who have received a prior chemotherapy in the metastatic setting or developed disease recurrence during or within 6 months of completing adjuvant chemotherapy.4 T-DXd is a HER2-directed antibody drug conjugate composed of the following three components: (1) a humanized anti-HER2 immunoglobulin G1 monoclonal antibody with the same amino acid sequence as trastuzumab, covalently linked to (2) a topoisomerase I inhibitor payload, an exatecan derivative, and via (3) a tetrapeptide-based cleavable linker.4-6 T-DXd binds to the HER2 receptor on tumor cells and is internalized by endocytosis. The linker is then cleaved via lysosomal enzymes, releasing the topoisomerase I inhibitor payload that initiates DNA damage, causing apoptosis of the tumor cell. Additionally, the T-DXd antibody drug conjugate technology offers a bystander antitumor effect, in which the membrane permeable payload is able to cause cell death of surrounding tumor cells, regardless of HER2 expression.4-5
In the phase 3 DESTINY-Breast03 (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03529110) trial in patients with HER2-positive mBC, T-DXd treatment resulted in significantly longer median progression-free survival (PFS) compared with ado-trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) in the second- or greater-line setting (not reached [95% CI, 18.5 months to nonevaluable] v 6.8 months [95% CI, 5.6 to 8.2 months] [hazard ratio, 0.28; 95% CI, 0.22 to 0.37]; median duration of follow-up was 16.2 months for T-DXd and 15.3 months for T-DM1).7 Most recently, positive results from the phase 3 DESTINY-Breast02 (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03523585) trial in patients with HER2-positive mBC previously treated with T-DM1 were reported, indicating significant improvement in both PFS (primary end point) and overall survival (key secondary end point).8
Efficacy of T-DXd in previously treated HER2-low mBC was demonstrated in the phase 3 DESTINY-Breast04 (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03734029) trial, which included patients with IHC 1+ or IHC 2+/ISH− BC and who had received one or two prior lines of chemotherapy. Both median PFS and median overall survival were significantly improved compared with physician's choice chemotherapy (10.1 v 5.4 months [hazard ratio, 0.51; P < .001], and 23.4 v 16.8 months [hazard ratio, 0.64; P < .001], respectively).9
The emergence of novel agents to treat BC necessitates recognition of associated adverse events (AEs) and a need to develop and refine monitoring and management strategies for these AEs. T-DXd has multiple indications in HER2-expressing (HER2-positive and -low) mBC, including for patients with hormone receptor–positive disease. This means that a large proportion of patients with mBC will receive treatment with T-DXd at some point in their treatment journey, and it is therefore especially critical to understand the monitoring and management of T-DXd–associated toxicities.
Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is an umbrella term used for a range of sequelae including pneumonitis that can progress to fibrosis of the lungs.10 Pneumonitis/ILD is a well-described AE associated with certain anticancer therapies, including T-DXd.4,11-24 In the DESTINY-Breast03 trial, 10.5% of patients were found to have pneumonitis/ILD by an independent adjudication panel with a median time to onset of 5.5 months (range, 1-16.7 months). All cases were grades 1-3 (median follow-up of 16.2 months) with the majority of cases resolved or resolving (70.3%).7 In the DESTINY-Breast04 trial, 12.1% (n = 45) of patients who received T-DXd experienced adjudicated pneumonitis/ILD, primarily grade 1 or 2 (11.3%). There were three (0.8%) grade 5 events. The median time to onset was approximately 4.3 months (range, 0.9-23.7 months). Pneumonitis/ILD occurred in one (0.6%) patient in the physician's choice group.9 In a pooled analysis of drug-related pneumonitis/ILD in nine single-arm T-DXd studies, the incidence of pneumonitis/ILD was 15.4% (177/1,150). Most of these patients (11.9% [137/1,150]) had grade 1 or 2 events; 15 (1.3%) patients had a grade 3 or 4 event, and 25 (2.2%) had a grade 5 event.25
Multiple mechanisms of action play a role in pneumonitis/ILD related to various anticancer therapies (eg, radiation, cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors, and chemotherapy). Both cytotoxic and immune mechanisms of action may be involved. A recent study in cynomolgus monkeys suggested that alveolar macrophage update and redistribution of T-DXd could be involved in the development of pneumonitis/ILD. However, further research is still necessary to delineate the exact mechanism.26-28
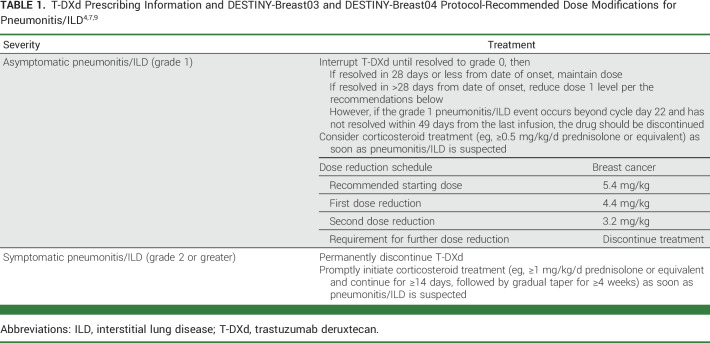
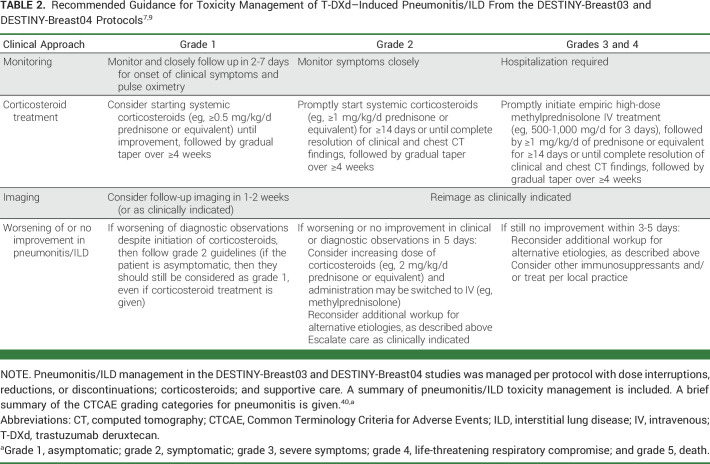
Because specific guidelines are not available for patient selection, prophylaxis, screening, monitoring, and management of pneumonitis/ILD associated with HER2-targeted therapies, clinicians administering T-DXd can benefit from guidance on this topic. Recommendations are available via the warnings, precautions, and dose modifications for pneumonitis/ILD detailed in the T-DXd prescribing information (Table 1)4 and the protocols from the DESTINY-Breast03 and DESTINY-Breast04 trials (Tables 1 and 2)7,9; however, the perspectives of practicing clinicians with experience in administering T-DXd may provide additional guidance for clinicians treating mBC. To bridge the gap between clinical research and practice, five oncologists, two oncology clinical pharmacists, and one pulmonologist with experience in administering T-DXd collaborated to write this paper. The objective of this review article is to describe real-world, multidisciplinary clinical practices and institutional protocols used for patient selection/screening, monitoring, and management related to pneumonitis/ILD associated with T-DXd use.
TABLE 1.
TABLE 2.
THE DEVELOPMENT OF COMPREHENSIVE PROTOCOLS FOR MONITORING FOR AND TREATING ILD IN T-DXd–TREATED PATIENTS
Some institutions designed and implemented comprehensive protocols for monitoring and treating ILD in patients who are receiving T-DXd. The decision to develop these protocols was based on a thorough review of the DESTINY-Breast01 (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03248492) data, which resulted in a recognized need for pneumonitis/ILD vigilance, owing to the safety data coupled with a desire to make this agent available for their patients because of the strong efficacy data. As a result, standardized plans were designed, in conjunction with pulmonologists involved in mBC patient care, using resources such as the DESTINY-Breast01 exclusion criteria and monitoring strategies, data on the timing of onset of pneumonitis/ILD in that study, and the literature and guidelines on drug-induced pneumonitis/ILD.29,30 The resultant protocols incorporate tests that are easily obtainable and interpretable in the context of pneumonitis/ILD.
CONSIDERATIONS FOR SELECTING PATIENTS FOR T-DXd
There are no ILD-specific contraindications to T-DXd treatment; however, when evaluating a patient for T-DXd treatment, it is important to consider general risk factors (eg, history of ILD/lung disease, smoking status, advanced age, ethnicity, and prior therapies) that are associated with drug-induced pneumonitis/ILD.31-35 Pneumonitis/ILD was analyzed in a pooled analysis of nine single-arm phase 1 and 2 T-DXd monotherapy studies,25 and a stepwise, multivariate Cox regression model evaluated the association of potential factors with time to occurrence of any-grade pneumonitis/ILD. Of note, in most of these clinical trials, active pneumonitis/ILD on screening or prior pneumonitis/ILD requiring corticosteroids were exclusion criteria. Within the approved dose, risk factors included were patients treated in Japan versus non-Japan, dose, baseline peripheral oxygen saturation, moderate/severe renal impairment at baseline versus no impairment, presence of lung comorbidities, obesity, and time since initial diagnosis. Given the limitations to the study (eg, extensive prior treatment, differences in treatment durations, and heterogeneity of the patient population), the nature of the relationship between these factors and development of pneumonitis/ILD could not be confirmed.36 These factors were further assessed in a pooled analysis of two phase 1 studies (J101 and A104) and the phase 2 DESTINY-Breast01 trial, which was also performed via a stepwise Cox regression model37 but in a more homogenous population of patients with HER2-positive mBC who received the recommended starting dose of T-DXd monotherapy (5.4 mg/kg once every 3 weeks).38 This analysis demonstrated that being treated in Japan and having moderate/severe renal impairment at baseline were potential factors of interest in the development of pneumonitis/ILD. The relationship between these factors and ILD needs to be confirmed and will be further investigated in larger, randomized controlled trials.37 The studies excluded patients who had corticosteroids for therapeutic reasons like lung disease or a prior diagnosis of pneumonitis/ILD regardless of cause. However, in clinical practice, these definitions are less clear because of the known ILD risks with other drugs used in this population like mechanistic target of rapamycin inhibitors (mammalian target of rapamycin), checkpoint inhibitors, or cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors. To our knowledge, there is no information to date about the safety or risk of pneumonitis/ILD with T-DXd in patients who have had a prior diagnosis of ILD that has completely resolved. If T-DXd is used in this setting, significant caution should be exercised with very close follow-up and patient education about potential risks.
SCREENING AND MONITORING STRATEGIES FOR ILD
In addition to a thorough pretreatment history and physical examination, the authors recommend that clinicians consider pre–T-DXd testing, which should include high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) of the chest. Pulmonary function tests have been considered but as yet have not been demonstrated to provide additional risk assessment or predictive value for ILD. Baseline oxygen saturation levels should be included with vital sign measurements at each patient visit. In the first year, all patients should have HRCT scans at least every 12 weeks and every 6-9 weeks for patients with respiratory symptoms. Patients with lower oxygen saturation levels, Japanese ancestry, and poor renal function should have more frequent chest HRCT scans. It is important to identify ILD when asymptomatic because effective therapy can be continued in those patients, which may improve treatment outcomes.
Consultation with a pulmonologist before T-DXd therapy should be considered if any concern exists for underlying ILD. Taking a full patient history before starting T-DXd with particular attention paid to possible lung disease (eg, ILD, pneumonitis, pulmonary fibrosis, and severe radiation pneumonitis) and reduced baseline lung function is recommended, as preexisting lung comorbidities may be related to or exacerbate pneumonitis/ILD associated with T-DXd administration. If such a condition is present or the patient has a preexisting chronic lung condition requiring the use of corticosteroids within the past 6 months, the benefits of the use of T-DXd should be weighed against potential risks. In some institutions, an alternative to T-DXd is also recommended in patients with lymphangitic carcinomatosis because of concern for a possible bystander effect. However, there are no data at present to support excluding these patients, and other providers have successfully treated patients with lymphangitic carcinomatosis.
Institutional guidelines for COVID-19 testing should be followed. If the forced vital capacity or diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO) is ≤70% predicted and/or the HRCT findings are indicative of chronic lung conditions, the multidisciplinary team (MDT) should be consulted, along with the patient, to consider the benefit-to-risk profile for T-DXd use. Although there are no specific contraindications for T-DXd administration for patients with COVID-19, these criteria can serve as a guide to assess the benefits and risks of T-DXd use in appropriate patients4 and provide a baseline to assess deterioration in lung function after starting T-DXd.
Once a patient is identified as a candidate for T-DXd treatment, it is necessary that they receive education on the potential for pneumonitis/ILD. This should quantify the potential risk of pneumonitis/ILD, and describe how this AE may be managed, should it occur. This may include explaining the risk of pneumonitis/ILD in phase 3 studies, such as in DESTINY-Breast03 and DESTINY-Breast04, where there was a 10.5% and 12.1% overall rate of pneumonitis/ILD, respectively.7,9 It is also important to describe symptoms indicative of pneumonitis/ILD, such as cough (particularly dry cough),29 dyspnea,29,30 and fever,29 and the monitoring protocols/approaches and management strategies that clinicians apply should pneumonitis/ILD arise. This information encourages self-monitoring and reporting of potential symptoms while on treatment, during scheduled appointments, when providers will engage with patients, and between visits. Generally, patients should be encouraged to err on the side of caution and immediately report any new or worsening respiratory symptom(s) suggestive of pneumonitis/ILD.
HRCT or radiographic changes potentially consistent with pneumonitis/ILD and/or an acute onset or worsening of pulmonary symptoms call for immediate interruption of T-DXd therapy and further evaluations to confirm the diagnosis (Table 1 and Figs 1A and 1B).30 Diagnosis should be based on holistic consideration of clinical symptoms, physical findings, detailed medical history, diagnostic imaging, lung function tests, and possibly pathologic findings, if applicable.29 Other pulmonary disorders (eg, underlying chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, pulmonary edema), progression of an underlying disease, and exclusion of concomitant infection, including a viral workup, should be considered.29,30
FIG 1.
(A) Monitoring and management of pneumonitis/ILD associated with T-DXd treatment per the DESTINY-Breast03 and DESTINY-Breast04 protocols.7,9 (B) Diagnostic algorithm for T-DXd–induced pneumonitis/ILD.7,9 ABG, arterial blood gas; BAL, bronchoalveolar lavage; HRCT, high-resolution computerized tomography; ILD, interstitial lung disease; PFT, pulmonary function test; SpO2, peripheral oxygen saturation; T-DXd, trastuzumab deruxtecan.
Because of the complex nature of diagnosing pneumonitis/ILD, this comprehensive workup of pulmonary signs and symptoms is essential to ensure therapy is not permanently or unnecessarily stopped. At one institution, pneumonitis/ILD was suspected in patients being treated with T-DXd because of concerning lung imaging findings and declining DLCO. Pneumonitis/ILD was later ruled out, with differential diagnoses including infectious processes and lymphangitic carcinomatosis.
THE MANAGEMENT OF ILD ASSOCIATED WITH T-DXd TREATMENT
Early consultation with a pulmonologist for management and exclusion is warranted. Once pneumonitis/ILD is confirmed, clinical approaches to management align with those detailed in the T-DXd prescribing information (Table 1)4 and the protocols from DESTINY-Breast03 and DESTINY-Breast04 (Table 2).7,9 T-DXd administration must be interrupted for any pneumonitis/ILD events, regardless of grade. For grade 1 pneumonitis/ILD, the patient should be closely followed regarding clinical symptoms and pulse oximetry. Systemic corticosteroids (≥0.5 mg/kg/d prednisone) may be given until improvement, followed by gradual taper over ≥4 weeks.7,9 Repeat HRCT in 2-3 weeks should be performed as clinically indicated to evaluate resolution and to allow reinstitution of T-DXd.
For patients with grade 2 or 3 pneumonitis/ILD, T-DXd treatment must be permanently discontinued. For grade 2 pneumonitis/ILD, corticosteroids (eg, ≥1 mg/kg/d prednisolone or equivalent) are promptly administered. For grade 3 pneumonitis/ILD, hospitalization is required for closer monitoring and prompt administration of empiric high-dose pulse corticosteroids (eg, methylprednisolone 500-1,000 mg/d for 3 days, followed by ≥1 mg/kg/d prednisone or equivalent). Corticosteroids are given for ≥14 days or until clinical improvement, followed by gradual taper over ≥4 weeks. All patients with pneumonitis/ILD need to be closely monitored for worsening symptoms and reimaged as clinically indicated. Worsening or no improvement in clinical or diagnostic observations indicates the need for corticosteroid treatment escalation and additional workups for alternative etiologies.7,9 Following this guidance and treatment with T-DXd in a less heavily pretreated population in DESTINY-Breast03 may have resulted in the observed decrease in overall incidence and severity of pneumonitis/ILD.7
MULTIDISCIPLINARY COLLABORATION
A multidisciplinary approach to pneumonitis/ILD monitoring and management is an important part of mBC treatment with T-DXd. Important aspects of this approach are comprehensive staff education, including members of the MDT, such as nurses, patient navigators, and advanced practice providers/clinicians, who are actively involved in the frontline patient communication throughout treatment. It is not unusual for a patient to provide direct information, such as a potential symptom of pneumonitis/ILD, to an infusion nurse who is closely caring for them during a T-DXd infusion. A radiologist reading imaging studies should be made aware of the patient's clinical history, including ongoing treatments. Furthermore, emergency department staff, in cases of severe pneumonitis/ILD, may be seeing patients at presentation and need to be aware of appropriate workup and management.
Pulmonologists are key players once pneumonitis/ILD is suspected to rule T-DXd–related pneumonitis/ILD in or out and to provide additional clinical insights. If the patient is experiencing cough but scans show no infiltrates, a pulmonology consultation may be warranted because the diagnosis of pneumonitis/ILD is questionable. The most important intervention is to hold the drug and, when in doubt, initiate corticosteroids. If corticosteroids are needed, prompt initiation is critical. Most clinicians prefer to have the patient be seen by the pulmonologist before treatment for pneumonitis/ILD is started, but corticosteroids can be started before this consultation. As pneumonitis/ILD is a diagnosis of exclusion, proper workup to identify the correct diagnosis is necessary for optimal patient management.
PROTOCOL OUTCOMES
After implementation of their institution-specific protocol for pneumonitis/ILD monitoring and management with T-DXd administration, clinicians at the Duke Cancer Institute performed a retrospective chart review to assess its impact. Reviewed patients had received ≥5 cycles of T-DXd from January 1, 2020, through June 30, 2020. Evaluation for clinical symptoms of pneumonitis/ILD (eg, cough, shortness of breath, dyspnea, and new or worsening respiratory symptoms), chest imaging, and pulmonary function tests with DLCO were performed at baseline before initiation of T-DXd and every 6 weeks before cycles 3 and 5. Pulmonologists were consulted if a corrected DLCO decrease >10% from baseline was observed. Seven patients with HER2-positive (n = 6) and HER2-low (n = 1) mBC were monitored per the predefined pneumonitis/ILD monitoring protocol described above, with 100% completion. There were no confirmed cases of ILD/pneumonitis. Two (28.6%) patients experienced DLCO decreases >10%. These patients had a history of lung disease or significant metastatic disease involvement, including asthma and lymphangitic carcinomatosis, respectively. Pneumonitis/ILD was ruled out with pulmonary consultation while patients continued T-DXd treatment without delay or pneumonitis to date. The fact that imaging and clinical history were able to safely rule out pneumonitis/ILD indicates that this comprehensive protocol is feasible for patients receiving T-DXd and may prevent treatment delay; the benefit of routine DLCO testing is unknown. Data collection and analysis have been completed for this retrospective chart review and the manuscript is in preparation.39
In conclusion, in pretreated patients with HER2-positive mBC (DESTINY-Breast03), T-DXd demonstrated a statistically significant 72% reduction of risk of progression or death over T-DM1. In pretreated patients with HER2-low mBC (DESTINY-Breast04), T-DXd showed a statistically significant 50% lower risk of progression or death than physician's choice of chemotherapy.7,9 Given this widespread efficacy and long duration of drug exposure, careful monitoring and management of toxicity is critical. However, pneumonitis/ILD is an important AE also associated with T-DXd, and vigilance in monitoring and managing pneumonitis/ILD is an important aspect of the T-DXd treatment plan to improve patient outcomes. Guidance presented from the T-DXd prescribing information, the DESTINY-Breast03 and DESTINY-Breast04 protocols, and the perspectives provided in this paper can help best practices for pneumonitis/ILD monitoring and management and optimize the benefits of T-DXd for mBC.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
Medical writing and/or editorial assistance were provided by Rachel E. Bejarano, PharmD, Stacey E. Shehin, PhD, and Kristi Lenz, PharmD, of The Lockwood Group (Stamford, CT) and funded by AstraZeneca, Inc.
Hope S. Rugo
Consulting or Advisory Role: Napo Pharmaceuticals, Scorpion Therapeutics, Blueprint Medicines, Puma Biotechnology
Research Funding: OBI Pharma (Inst), Pfizer (Inst), Novartis (Inst), Lilly (Inst), Genentech (Inst), Merck (Inst), Daiichi Sankyo (Inst), Sermonix Pharmaceuticals (Inst), AstraZeneca (Inst), Gilead Sciences (Inst), Astellas Pharma (Inst), Pionyr (Inst), Taiho Oncology (Inst), Veru (Inst), GlaxoSmithKline (Inst)
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Merck, AstraZeneca, Gilead Sciences
Open Payments Link: https://openpaymentsdata.cms.gov/summary
Yaron B. Gesthalter
Honoraria: Noah Medical
Heather B. Moore
Consulting or Advisory Role: Novartis, Lilly, AstraZeneca/Daiichi Sankyo
Mothaffar F. Rimawi
Consulting or Advisory Role: Macrogenics, Daiichi Sankyo, Seagen, Genentech, Novartis, AstraZeneca
Research Funding: Pfizer (Inst), Genentech (Inst)
Kelly E. Westbrook
Honoraria: Gilead Sciences
Research Funding: Novartis, Seagen
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
See accompanying editorial on page 526
SUPPORT
Supported by AstraZeneca, Inc. The funders had no role in the preparation, review, or approval of the article, or the decision to submit the article for publication. Any opinions, findings, or conclusions expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of AstraZeneca, Inc.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conception and design: Hope S. Rugo, Yaron B. Gesthalter, Heather B. Moore, Mothaffar F. Rimawi, Kelly E. Westbrook, Saundra S. Buys
Provision of study materials or patients: All authors
Collection and assembly of data: Hope S. Rugo, Christine L. Crossno, Kristen Kelley, Kelly E. Westbrook, Saundra S. Buys
Data analysis and interpretation: Hope S. Rugo, Christine L. Crossno, Mothaffar F. Rimawi
Manuscript writing: All authors
Final approval of manuscript: All authors
Accountable for all aspects of the work: All authors
AUTHORS' DISCLOSURES OF POTENTIAL CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
Real-World Perspectives and Practices for Pneumonitis/Interstitial Lung Disease Associated With Trastuzumab Deruxtecan Use in Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2–Expressing Metastatic Breast Cancer
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to www.asco.org/rwc or ascopubs.org/op/authors/author-center.
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (Open Payments).
Hope S. Rugo
Consulting or Advisory Role: Napo Pharmaceuticals, Scorpion Therapeutics, Blueprint Medicines, Puma Biotechnology
Research Funding: OBI Pharma (Inst), Pfizer (Inst), Novartis (Inst), Lilly (Inst), Genentech (Inst), Merck (Inst), Daiichi Sankyo (Inst), Sermonix Pharmaceuticals (Inst), AstraZeneca (Inst), Gilead Sciences (Inst), Astellas Pharma (Inst), Pionyr (Inst), Taiho Oncology (Inst), Veru (Inst), GlaxoSmithKline (Inst)
Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Merck, AstraZeneca, Gilead Sciences
Open Payments Link: https://openpaymentsdata.cms.gov/summary
Yaron B. Gesthalter
Honoraria: Noah Medical
Heather B. Moore
Consulting or Advisory Role: Novartis, Lilly, AstraZeneca/Daiichi Sankyo
Mothaffar F. Rimawi
Consulting or Advisory Role: Macrogenics, Daiichi Sankyo, Seagen, Genentech, Novartis, AstraZeneca
Research Funding: Pfizer (Inst), Genentech (Inst)
Kelly E. Westbrook
Honoraria: Gilead Sciences
Research Funding: Novartis, Seagen
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
REFERENCES
- 1.Iqbal N, Iqbal N: Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) in cancers: Overexpression and therapeutic implications. Mol Biol Int 2014:852748, 2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Winstanley J, Cooke T, Murray GD, et al. : The long term prognostic significance of c-erbB-2 in primary breast cancer. Br J Cancer 63:447-450, 1991 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Seah DS, Luis IV, Macrae E, et al. : Use and duration of chemotherapy in patients with metastatic breast cancer according to tumor subtype and line of therapy. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 12:71-80, 2014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.ENHERTU: Prescribing Information. Daiichi Sankyo, 2022. https://daiichisankyo.us/prescribing-information-portlet/getPIContent?productName=Enhertu&inline=true [Google Scholar]
- 5.Nakada T, Sugihara K, Jikoh T, et al. : The latest research and development into the antibody-drug conjugate, [fam-] trastuzumab deruxtecan (DS-8201a), for HER2 cancer therapy. Chem Pharm Bull 67:173-185, 2019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ogitani Y, Aida T, Hagihara K, et al. : DS-8201a, a novel HER2-targeting ADC with a novel DNA topoisomerase I inhibitor, demonstrates a promising antitumor efficacy with differentiation from T-DM1. Clin Cancer Res 22:5097-5108, 2016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cortés J, Kim SB, Chung WP, et al. : Trastuzumab deruxtecan versus trastuzumab emtansine for breast cancer. N Engl J Med 386:1143-1154, 2022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.André F, Park YH, Kim S, et al. : Trastuzumab deruxtecan versus treatment of physician's choice in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer (DESTINY-Breast02): A randomised, open-label, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet 401:1773-1785, 2023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Modi S, Jacot W, Yamashita T, et al. : Trastuzumab deruxtecan in previously treated HER2-low advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med 387:9-20, 2022 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.American Lung Association : Interstitial Lung Disease, 2023. https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/interstitial-lung-disease
- 11.HERCEPTIN: Prescribing Information. Genentech, 2022. https://www.herceptin.com/hcp/adjuvant-breast-cancer/dosing-and-administration/dosing.html?c=ahr-17e30d903c6&gclsrc=aw.ds&gclid=CjwKCAjwuqiiBhBtEiwATgvixCsU56274z_hPtLkl6_ivuyFqCG7trliBXcPMTrJVBvqDFbrvCR8qhoCTMwQAvD_BwE [Google Scholar]
- 12.ONIVYDE: Prescribing Information. Ipsen Biopharmaceuticals, Inc., 2023. https://www.ipsen.com/websites/Ipsen_Online/wp-content/uploads/sites/9/2019/01/21083350/ONIVYDE_USPI.pdf [Google Scholar]
- 13.PERJETA: Prescribing Information. Genentech Inc., 2021. https://www.gene.com/download/pdf/perjeta_prescribing.pdf [Google Scholar]
- 14.KADCYLA: Prescribing Information. Genentech Inc., 2022. https://www.gene.com/download/pdf/kadcyla_prescribing.pdf [Google Scholar]
- 15.TYKERB: Prescribing Information. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, 2022, https://www.novartis.com/us-en/sites/novartis_us/files/tykerb.pdf [Google Scholar]
- 16.IRESSA: Prescribing Information. AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP, 2018. http://www.astrazeneca-us.com/cgi-bin/az_pi.cgi?product=iressa&country=us&popup=no [Google Scholar]
- 17.AFINITOR: Prescribing Information. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, 2022. https://www.novartis.com/us-en/sites/novartis_us/files/afinitor.pdf [Google Scholar]
- 18.IBRANCE: Prescribing Information. Pfizer Labs, 2022. https://labeling.pfizer.com/ShowLabeling.aspx?id=12921 [Google Scholar]
- 19.KISQALI: Prescribing Information. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, 2022. https://www.novartis.com/us-en/sites/novartis_us/files/kisqali.pdf [Google Scholar]
- 20.VERZENIO: Prescribing Information. Eli Lilly and Company, 2023. https://uspl.lilly.com/verzenio/verzenio.html?s=pi [Google Scholar]
- 21.OPDIVO: Prescribing Information. Bristol Myers Squibb Company, 2023. https://packageinserts.bms.com/pi/pi_opdivo.pdf [Google Scholar]
- 22.KEYTRUDA: Prescribing Information. Merck & Co, 2023. https://www.merck.com/product/usa/pi_circulars/k/keytruda/keytruda_pi.pdf [Google Scholar]
- 23.TECENTRIQ: Prescribing Information. Genentech, 2022. https://www.gene.com/download/pdf/tecentriq_prescribing.pdf [Google Scholar]
- 24.YERVOY: Prescribing Information. Bristol Myers Squibb Company, 2023. https://packageinserts.bms.com/pi/pi_yervoy.pdf [Google Scholar]
- 25.Powell CA, Modi S, Iwata H, et al. : Pooled analysis of drug-related interstitial lung disease and/or pneumonitis in nine trastuzumab deruxtecan monotherapy studies. ESMO Open 7:100554, 2022 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Matsuno O: Drug-induced interstitial lung disease: Mechanisms and best diagnostic approaches. Respir Res 13:39, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Raschi E, Fusaroli M, Ardizzoni A, et al. : Cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors and interstitial lung disease in the FDA adverse event reporting system: A pharmacovigilance assessment. Breast Cancer Res Treat 186:219-227, 2021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kumagai K, Aida T, Tsuchiya Y, et al. : Interstitial pneumonitis related to trastuzumab deruxtecan, a human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-targeting Ab-drug conjugate, in monkeys. Cancer Sci 111:4636-4645, 2020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kubo K, Azuma A, Kanazawa M, et al. : Consensus statement for the diagnosis and treatment of drug-induced lung injuries. Respir Invest 51:260-277, 2013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Raghu G, Remy-Jardin M, Myers JL, et al. : Diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT clinical practice guideline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 198:e44-e68, 2018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Schwaiblmair M, Behr W, Haeckel T, et al. : Drug induced interstitial lung disease. Open Respir Med J 6:63-74, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Skeoch S, Weatherley N, Swift AJ, et al. : Drug-induced interstitial lung disease: A systematic review. J Clin Med 7:356, 2018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Osawa M, Kudoh S, Sakai F, et al. : Clinical features and risk factors of panitumumab-induced interstitial lung disease: A postmarketing all-case surveillance study. Int J Clin Oncol 20:1063-1071, 2015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Yonemori K, Hirakawa A, Kawachi A, et al. : Drug induced interstitial lung disease in oncology phase I trials. Cancer Sci 107:1830-1836, 2016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Vansteenkiste J: Nivolumab for NSCLC in Japanese patients: Similar benefits, but beware of pneumonitis. ESMO Open 2:e000119, 2017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Powell CA, Modi S, Iwata H, et al. : Abstract CT167: Pooled analysis of drug-related interstitial lung disease (ILD) in 8 single-arm trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) studies. Cancer Res 81:CT167, 2021 [Google Scholar]
- 37.Powell C, Modi S, Iwata H, et al. : Analysis of study drug-related interstitial lung disease (ILD) in patients (pts) with HER2+ metastatic breast cancer (mBC) treated with trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd). ESMO Breast Cancer Virtual Congress, May 5-8, 2021 [Google Scholar]
- 38.Powell C, Modi S, Iwata H, et al. : Analysis of study drug-related interstitial lung disease (ILD) in patients (pts) with HER2+ metastatic breast cancer (mBC) treated with trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd). Ann Oncol 32:S60-S78, 2021 [Google Scholar]
- 39.Moore H, Shofer S, Guisinger A, et al. : Abstract PS13-33: Feasibility of a comprehensive monitoring protocol for the prevention and treatment of interstitial lung disease in patients undergoing treatment with fam-trastuzumab deruxtecan. Cancer Res 81:PS13-PS33, 2021 [Google Scholar]
- 40.US Department of Health and Human Services : Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE), Washington, DC, Version 5.0. 2017. <u>https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocoldevelopment/electronic_applications/docs/ctcae_v5_quick_reference_5x7.pdf</u> [Google Scholar]