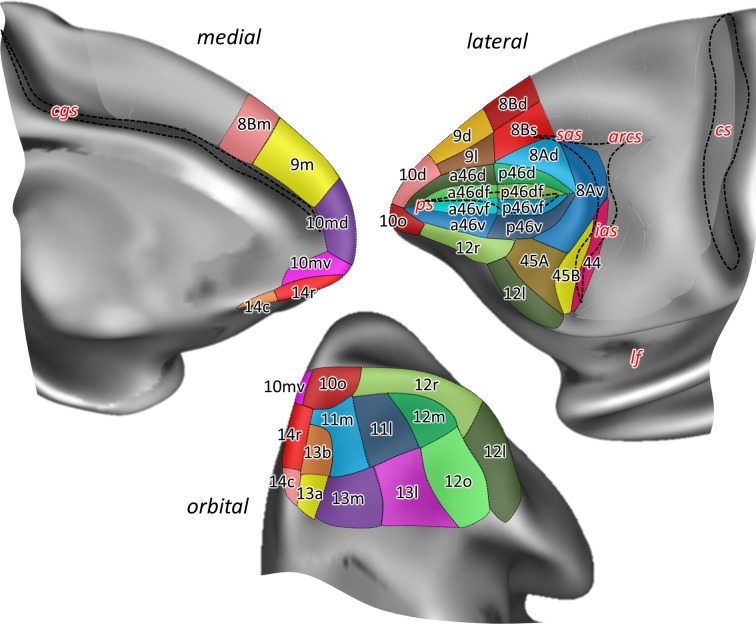
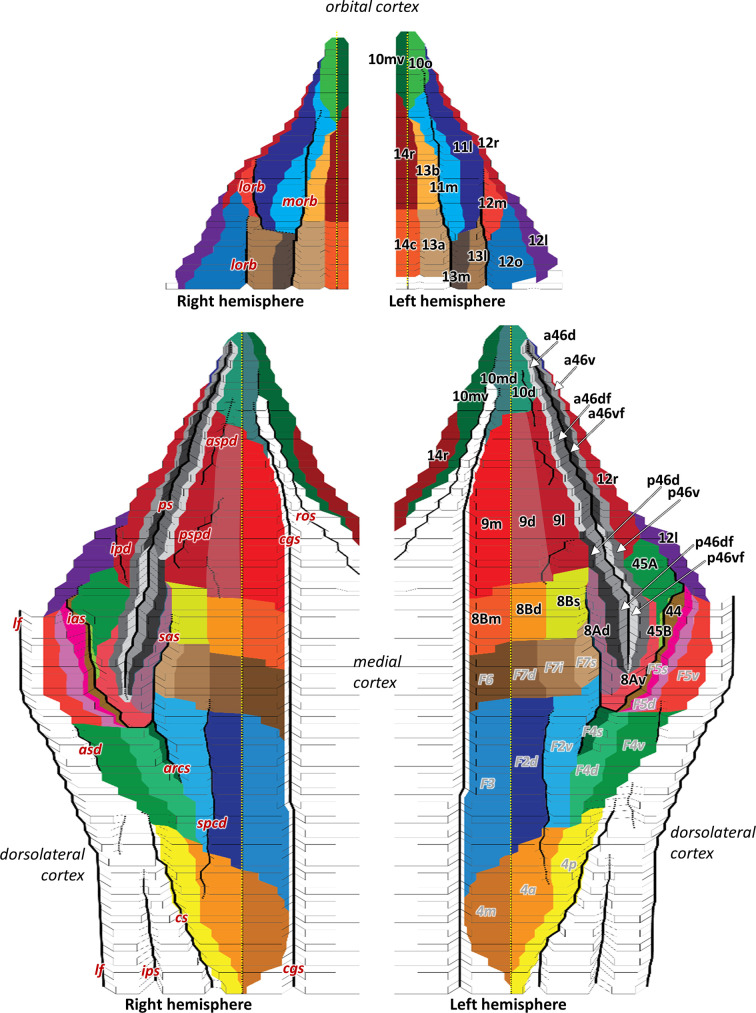
Figure 2. Position and extent of the prefrontal areas on the medial, lateral, and orbital views of the Yerkes19 surface.
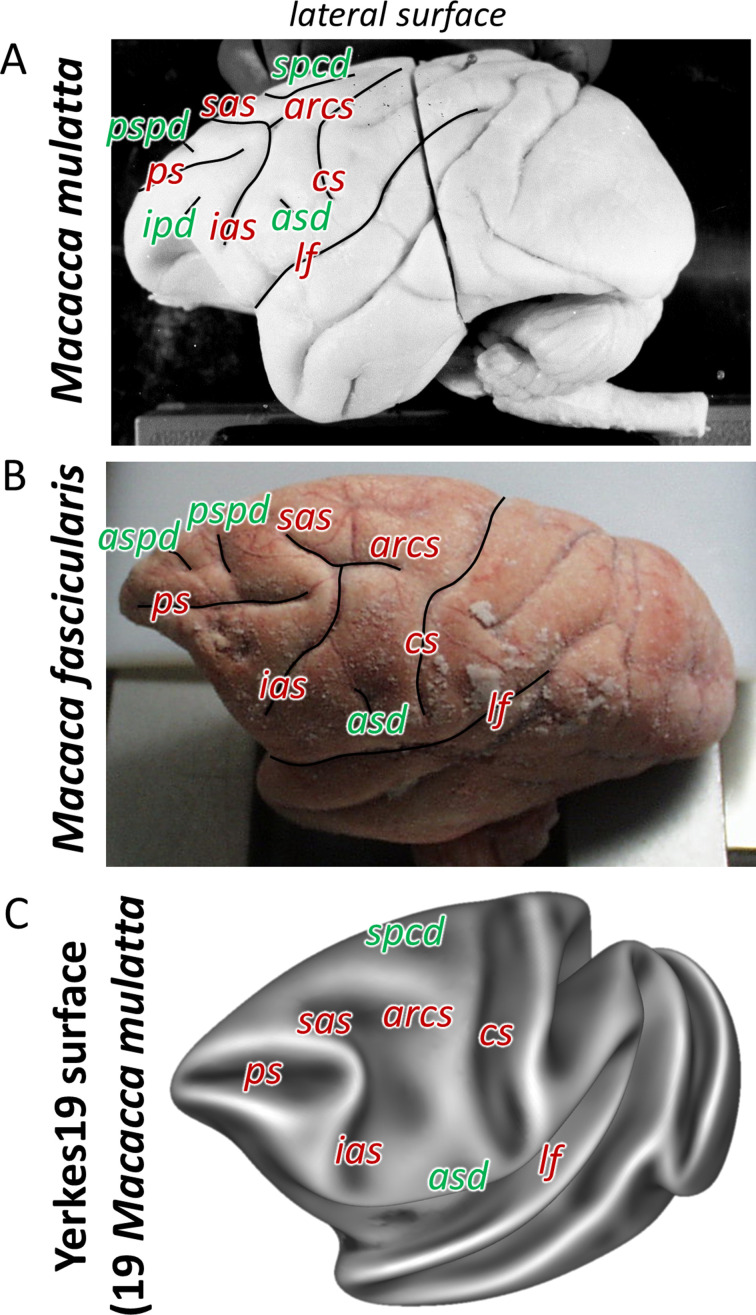
The files with the parcellation scheme are available via EBRAINS platform of the Human Brain Project (https://search.kg.ebrains.eu/instances/Project/e39a0407-a98a-480e-9c63-4a2225ddfbe4) and the BALSA neuroimaging site (https://balsa.wustl.edu/study/7xGrm). Macroanatomical landmarks are marked in red letters, while black dashed lines mark fundus of sulci. arcs, spur of the arcuate sulcus; cgs, cingulate sulcus; cs, central sulcus; ias, inferior arcuate sulcus; lf, lateral fissure; ps, principal sulcus; sas, superior arcuate sulcus.