Abstract
Background
Telehealth interventions have become increasingly important in health care provision, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic. Video calls have emerged as a popular and effective method for delivering telehealth services; however, barriers limit the adoption among allied health professionals and nurses.
Objective
This review aimed to identify and map the perceived barriers to the use of video call–based telehealth interventions among allied health professionals and nurses.
Methods
A comprehensive literature search was conducted in the PubMed and CINAHL databases on June 22, 2022, and updated on January 3, 2023, following the PRISMA-ScR (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews) guidelines. Only original studies published in English or German since June 2017 that reported barriers to the use of video call–based telehealth interventions were eligible for inclusion. The studies had to involve interviews, focus groups, or questionnaires with physical therapists, occupational therapists, speech and language therapists, audiologists, orthoptists, dieticians, midwives, or nurses. Each publication was coded for basic characteristics, including country, health profession, and target group. Inductive coding was used to identify the patterns, themes, and categories in the data. Individual codings were analyzed and summarized narratively, with similarities and differences in barriers identified across health professions and target groups.
Results
A total of 56 publications were included in the review, with barriers identified and categorized into 8 main categories and 23 subcategories. The studies were conducted in various countries, predominantly the United States, Australia, the United Kingdom, Canada, Israel, and India. Questionnaires were the most commonly used evaluation method, with 10,245 health professionals involved. Interviews or focus groups were conducted with 288 health professionals. Most of the included publications focused on specific health care professions, with the highest number addressing barriers for physical therapists, speech and language therapists, and audiologists. The barriers were related to technology issues, practice issues, patient issues, environmental issues, attributions, interpersonal issues, policies and regulations, and administration issues. The most reported barriers included the lack of hands-on experience, unreliable network connection, the lack of technology access, diminished fidelity of observations and poor conditions for visual instructions, the lack of technology skills, and diminished client-practitioner interaction and communication.
Conclusions
This review identified key barriers to video call–based telehealth use by allied health professionals and nurses, which can foster the development of stable infrastructure, education, training, guidelines, policies, and support systems to improve telehealth services. Further research is necessary to identify potential solutions to the identified barriers.
Keywords: telehealth, telemedicine, eHealth, barriers, allied health professions, nursing, video call, videoconferencing, web-based consultation, remote consultation, mobile phone
Introduction
Background
Allied health professionals and nurses are an integral part of our health care system. The allied health professions do not constitute a clearly defined group of professions, as definitions and classifications vary at the international level [1]. For the purposes of this review, the allied health professions are occupational therapists (OTs), physical therapists (PTs), speech and language therapists (SLTs), audiologists, dietitians, orthoptists, and midwives. In addition, nurses were identified as a crucial professional group within the context of allied health services. Allied health professionals and nurses have in common that they play an important role in patient care to protect, restore, and maintain physical, sensory, psychological, cognitive, social, and cultural functions [2].
The COVID-19 pandemic has profoundly challenged the work of health care professionals because of contact restrictions and the risk of infections [3,4]. Access to health services was limited worldwide [5,6] and affected, among others, access to rehabilitation services [7,8] and maternal health services [9]. The health care contacts of acute [10] and chronically ill patients [10-12] decreased during this period. Therefore, the pandemic has led to fundamental changes in service provision and advanced the integration of telehealth services in various disciplines and health fields [13]. Telehealth offers advantages for allied health professionals by overcoming barriers related to distance [14] and addressing health and services disparities [15-17]. This facilitates improved access to services and supports individuals with chronic illnesses in maintaining continuity of care, ultimately optimizing health and well-being [15,16,18]. However, there remains a concern that telehealth may inadvertently exacerbate health care disparities for susceptible populations, particularly those with limited digital literacy or restricted access to digital resources [19].
Telemedicine or telehealth can be defined as “the use of information and communication technology (ICT) to provide health services where there is physical separation between providers of care and/or recipients over long and short distances” [20]. Terminology in this area lacks agreement on the definitions of the telehealth or telemedicine concepts [21]. Telehealth might be related to telemedicine in the same way that health is related to medicine [22]. Consequently, the World Medicine Association describes telehealth and telemedicine to be used for remote clinical services to serve for patient-physician consultation where access is limited and to be used for consultation with ≥2 physicians [23]. Furthermore, telehealth refers to remote clinical and nonclinical services, such as preventive health support, research, training, and continuing medical education for health professionals [23]. Similar terms, such as telerehabilitation, telecare, telepractice, or telephysiotherapy, refer to specializations, the context of care, or a specific profession. Telehealth services can be divided into 3 types: synchronous, where health information is delivered in real time; asynchronous, where health information is stored and forwarded; and patient monitoring, where patient clinical status is continuously evaluated over the distance [24].
Video calls are a common method for providing telehealth services synchronously, as they have become prevalent in personal and professional lives. Everyday technologies, such as computers, tablets, smartphones, webcams, videoconferencing software, and an internet connection, make such services relatively accessible. Especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, there was a demand for readily available solutions without the need for additional infrastructure or equipment. The rapid implementation of video visits with health care professionals prevented infections [25] and kept the health care system running [26-29]. For instance, telehealth services offered by physiotherapists were used to support patients in isolation [30] or to address the ongoing needs of children with neurodevelopmental or musculoskeletal issues [31]. This approach enabled the provision of acute care while maintaining continuity in therapeutic interventions.
Telehealth also has potential benefits in addition to the prevention of infections. Such services have been established long before facing a pandemic, especially in rural areas, to increase access to physical or occupational therapy, speech and language therapy, nursing, and other health services [32-34]. People who are bedridden or have limited mobility can also benefit from easier access [35]. Furthermore, increased independence and reassurance have been described through telehealth use [36]. Studies have shown that telehealth can yield equivalent or even superior clinical outcomes for patients [18,37,38]. However, such services are not a common component of health services.
Objectives
The implementation of telehealth faces organizational, personal, and technological barriers, such as the lack of infrastructure, missing skills, poor strategic alignment, resistance to necessary cultural changes, and cost or reimbursement issues [39]. However, to date, no review has systematically mapped these barriers. An illustration and analysis of telehealth barriers is important to address them in the future by tailored actions such as training, organizational redesigns, or infrastructure measurements.
To systematically map barriers to video call–based telehealth from nonmedical health professionals, a mapping and scoping review with the following research question was conducted: What barriers are indicated and described by allied health professionals and nurses toward video call–based telehealth?
Methods
Overview
First, a scoping review was conducted based on the PRISMA-ScR (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews) guidelines [40,41]. Before initiating the review, a review protocol was developed, stored in the institutional database, and followed. It was not published publicly. Second, the identified barriers were systematically mapped with respect to the health profession, the context of care, and the research method.
Eligibility Criteria
Only articles that have been published since June 2017 were eligible to ensure that the studies applied technology that is comparable with current standards. Publications that met the inclusion criteria were eligible (Textboxes 1 and 2).
Inclusion criteria.
Article type
Original studies and journal articles
Language
English or German
Article scope
Article reports barriers or challenges with video call–based telehealth interventions
Health professions
Barriers or challenges are based on the perspective of physical therapists, occupational therapists, speech and language therapists or audiologists, orthoptists, dieticians, nurses, or midwives
Methods
Survey, interview, or focus group results
Telehealth target
Video call–based telehealth targeted patient-to-provider interaction
Time
Published since June 2017
Exclusion criteria.
Article type
Review articles, conference papers, abstracts, editorials, newspaper articles, study protocols, and other formats
Language
Other languages
Article scope
Article reports no barriers or challenges and article reports barriers or challenges with other telehealth interventions than video call based (if other technologies were included in the study, the results must be clearly distinguishable)
Health professions
Barriers or challenges are based on the perspective of patients, caregivers, medical doctors, or other health professionals. If they were included in the study, the results must be clearly distinguishable
Methods
Results from other resources
Telehealth target
Video call–based telehealth targeted academic education or continuing education and video call–based telehealth targeted provider-to-provider interaction
Time
Published before June 2017
Search and Selection Strategy
A comprehensive literature search was carried out in the PubMed and CINAHL databases on June 22, 2022, and updated on January 3, 2023. In addition, citation tracking was performed to identify additional relevant literature. Relevant topics for the search were video call–based telehealth; barriers or challenges; health professions of interest; and resources from interviews, focus groups, surveys, or questionnaires. The complete search strings can be found in Multimedia Appendix 1.
All references were imported to Zotero (Corporation for Digital Scholarship). In a first step, all duplicates were eliminated, and then all titles and abstracts of the sources were screened for inclusion criteria. The full text of the remaining articles was obtained, thoroughly reviewed for eligibility, and searched for further publications that met the inclusion criteria by citation tracking.
Data Charting Process
The full-text articles of the selected publications were imported into MAXQDA (2022; VERBI GmbH), a software for qualitative content analysis. Each publication was coded for country, health profession, and target group of telehealth intervention to compare basic characteristics. The sample sizes were noted. Furthermore, all articles were thoroughly examined for the mentioned barriers, and codes were inductively assigned to text passages. The inductive coding process involved identifying patterns, themes, and categories in the data without the use of preexisting codes to allow for the identification of new and unexpected themes that may not have been anticipated. The codes were continuously refined, structured, and consolidated.
Finally, every publication had a code for country, health profession, target group, and if applicable, the following barrier codes were assigned: interpersonal issues, administration issues, practice issues, patient issues, environmental issues, telehealth attributes, technology issues, policy and regulation issues, and others. Subcodes for topics requiring further refinement were created.
Synthesis of Results
Individual coding (passages with an assigned code) was analyzed and summarized for each code topic narratively. Similarities in the barriers mentioned were identified, and barriers for specific health professions or target groups were determined. Each barrier mentioned was equal in weight. A quantitative outline of barriers was performed only with respect to the number of articles that mentioned each barrier but not in terms of how often it was mentioned within an article.
Results
Overview
The search yielded 786 records (n=609 in June 2022 and n=177 in January 2023). A total of 611 records were screened (n=474 in June 2022 and n=137 in January 2023), and 107 full-text papers were assessed for eligibility (n=77 in June 2022 and n=30 in January 2023). Finally, the review included 56 publications (n=44 in June 2022 and n=12 in January 2023). The selection process is illustrated in the flowchart (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
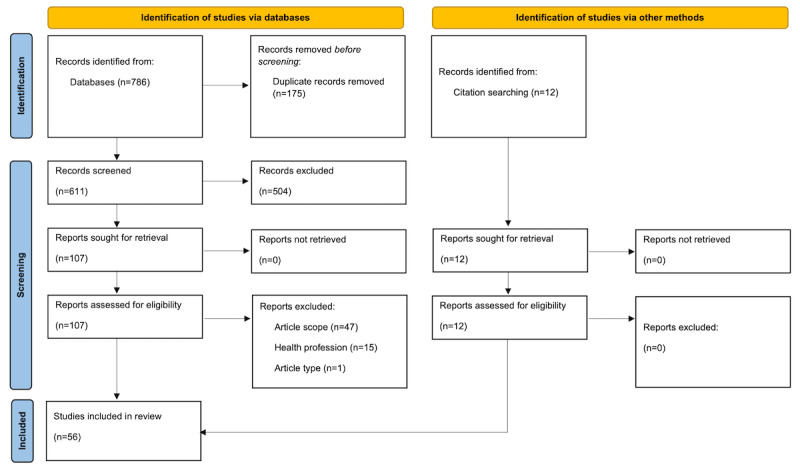
Study selection process.
Study Characteristics
Table 1 presents all included publications with details for authors, publication year, country, included professions, health context, and assessment methods.
Table 1.
Characteristics of sources.
| Study | Country | Professions | Health contexta | Methodsb |
| Abbott-Gaffney and Jacobs [47], 2020 | United States | OTc | Various | Questionnaire |
| Abbott-Gaffney et al [72], 2022 | United States | OT | Pediatrics | Questionnaire |
| Albahrouh and Buabbas [49], 2021 | Kuwait | PTd | Various | Mixed methods |
| Almog and Gilboa [73], 2022 | Israel | OT | Various | Questionnaire |
| Alrushud et al [74], 2022 | Saudi Arabia | PT | Osteoarthritis | Mixed methods |
| Barrett [42], 2017 | United Kingdom | Nure | Various | Interview |
| Bayati and Ayatollahi [50], 2021 | Iran | SLTf and Audg,h | Various | Interview |
| Bennell et al [51], 2021 | Australia | PT | Various | Questionnaire |
| Bhattarai et al [75], 2022 | India | SLT and Aud | Various | Questionnaire |
| Bican et al [52], 2021 | United States | PT and OT | Pediatrics | Questionnaire |
| Bolden [76], 2022 | United States | PT, OT, and SLT and Aud | Pediatrics | Questionnaire |
| Buabbas et al [77], 2022 | Kuwait | PT | Musculoskeletal | Interview |
| Ceprnja et al [78], 2022 | Australia | PT | Various | Questionnaire |
| Chaudhari and Talreja [79], 2022 | India | PT | Various | Questionnaire |
| Dissanayaka et al [80], 2022 | Sri Lanka | PT | Osteoarthritis | Questionnaire |
| Ditwiler et al [81], 2022 | United States | PT | Various | Interview |
| D’Souza and Rebello [53], 2021 | India | PT | Various | Questionnaire |
| Eguia and Capio [82], 2022 | Philippines | PT, OT, and SLT and Aud | Pediatrics | Questionnaire |
| Eikelboom et al [83], 2022 | Australia | SLT and Aud | Various | Questionnaire |
| Fong et al [54], 2021 | Hong Kong | SLT and Aud | Various | Questionnaire |
| Grant et al [84], 2022 | Australia | PT | Pediatrics | Interview |
| Haines et al [85], 2022 | Australia | PT | Various | Interview |
| Hall et al [55], 2021 | United States | PT | Pediatrics | Questionnaire |
| Harrell et al [56], 2021 | United States | PT | Vestibular | Questionnaire |
| Hasani et al [57], 2021 | Australia | PT | Achilles tendinopathy | Interview |
| Hughes et al [86], 2022 | United Kingdom | Nur | Various | Interview |
| Kaufman-Shriqui et al [58], 2021 | Israel | Diei | Various | Questionnaire |
| Kaur et al [87], 2022 | United States | PT and OT | Pediatrics | Questionnaire |
| Kienle et al [59], 2021 | Germany | PT | Older adults | Interview |
| Klamroth-Marganska et al [60], 2021 | Switzerland | OT and Midj | Various | Questionnaire |
| Koppel et al [88], 2022 | United States | Nur | Cancer | Interview |
| Krasovsky et al [61], 2021 | Israel | PT, OT, and SLT and Aud | Pediatrics | Questionnaire |
| Kwok et al [29], 2022 | Canada | SLT and Aud | Pediatrics | Interview |
| Lawford et al [43], 2018 | Australia | PT | Osteoarthritis | Questionnaire |
| Malliaras et al [62], 2021 | Australia | PT and OT | Musculoskeletal | Questionnaire |
| Martin et al [63], 2021 | Australia | PT | Various | Interview |
| McPherson and Nahon [64], 2021 | Australia | PT | Pelvic health | Questionnaire |
| Nazreen and Seethapathy [89], 2022 | India | SLT and Aud | Various | Questionnaire |
| Parmar et al [90], 2022 | United Kingdom | SLT and Aud | Various | Questionnaire |
| Peh et al [91], 2022 | Singapore | SLT and Aud | Various | Questionnaire |
| Peters et al [65], 2021 | Canada | PT | Assessment | Questionnaire |
| Pollard and Hogan [66], 2021 | United Kingdom | SLT and Aud | Pediatrics | Questionnaire |
| Rettinger et al [67], 2021 | Austria | PT, OT, and SLT and Aud | Various | Questionnaire |
| Richter et al [92], 2022 | Germany | PT, OT, and SLT and Aud | Various | Questionnaire |
| Rortvedt and Jacobs [45], 2019 | United States | OT | Pediatrics | Questionnaire |
| Rozga et al [68], 2021 | United States | Die | Various | Questionnaire |
| Rygg et al [44], 2018 | Norway | Nur | Cancer | Interview |
| Rygg et al [69], 2021 | Norway | Nur | Cancer | Interview |
| Singh et al [70], 2021 | United States | Die | Diabetes or metabolic disorder | Questionnaire |
| Spiby et al [46], 2019 | United Kingdom | Mid | Early labor | Interview |
| Sutherland et al [71], 2021 | Australia | SLT and Aud | Pediatrics | Questionnaire |
| Tar-Mahomed and Kater [93], 2022 | South Africa | SLT and Aud | Various | Questionnaire |
| Van Eerdenbrugh et al [94], 2022 | Belgium | SLT and Aud | Various | Questionnaire |
| Wittmeier et al [95], 2022 | Canada | PT and OT | Pediatrics | Interview |
| Wundersitz et al [48], 2020 | Australia | Die, SLT and Aud, and PT | Various | Interview |
| Yosef et al [96], 2022 | Israel | OT | Older adults | Questionnaire |
aHealth context refers to specific patient or target groups or matter of interest in the included study.
bMethods were summarized as “Interview” when individual interviews or focus groups were conducted, “Questionnaire” when participants gave written answers, and “Mixed methods” when both methods were applied.
cOT: occupational therapist.
dPT: physical therapist.
eNur: nurse.
fSLT: speech and language therapist.
gAud: audiologist.
hSLT and Aud were combined, as they are a single profession in some countries and 2 professions in others.
iDie: dietitian.
jMid: midwife.
The included studies were published in 2017 (n=1) [42], 2018 (n=2) [43,44], 2019 (n=2) [45,46], 2020 (n=2) [47,48], 2021 (n=23) [49-71], and 2022 (n=26) [29,72-96]. Of the 56 papers, 48 (86%) papers focused on COVID-19 [29,47,49,51-56,58-96]. In total, 80% (45/56) of publications focused on 1 specific health care profession [29,42-47,49-51,53-59,63-66,68-75,77-81,83-86,88-91,93,94,96], and 20% (11/56) of articles targeted a mix of health care professions [48,52,60-62,67,76,82,87,92,95]. Most articles covered barriers for PTs (29/56, 52%) [43,48,49,51-53,55-57,59,61-65,67,74,76-82,84,85,87,92,95], followed by those for SLTs and audiologists (18/56, 32%) [29,48,50,52,59-61,73,79-81,83,85,92-94,96]. Furthermore, publications were concentrated on OTs (15/56, 27%) [45,47,52,60-62,67,72,73,76,82,87,92,95,96], nurses (5/56, 9%) [42,44,69,86,88], dieticians (4/56, 7%) [48,58,68,70], and midwives (2/56, 4%) [46,60]. No studies with orthoptists were included.
The studies focused on various health contexts. Health professionals treated various target groups (27/56, 48%) [42,45,47-51,53,54,58,60,63,67,73,75,78,79,81,83,85,86,89-94] or focused on specific target groups, such as children (13/56, 23%) [29,45,52,55,61,66,71,72,76,82,84,87,95] or older adults (2/56, 4%) [59,96], or patients with specific diseases or issues, such as musculoskeletal disorders (2/56, 4%) [62,77], cancer (3/56, 5%) [44,69,88], osteoarthritis (3/56, 5%) [43,74,80], vestibular disorders (1/56, 2%) [56], early labor (1/56, 2%) [46], diabetes (1/56, 2%) [70], pelvic health (1/56, 2%) [64], and Achilles tendinopathy (1/56, 2%) [57]. Overall, 2% (1/56) of studies focused on the execution of assessments via telehealth [65]. Figure 2 shows the study characteristics based on the included professions and health contexts [29,42-96].
Figure 2.

Mapping of study characteristics. Summary of the study characteristics from inner to outer circle: health profession, health context, method, authors, and year. Aud: audiologist; Die: dietitian; Mid: midwife; Nur: nurse; OT: occupational therapist; PT: physical therapist; SLT: speech and language therapist.
The publications were from the United States (12/56, 21%) [45,47,52,55,56,68,70,72,76,81,87,88], Australia (12/56, 21%) [43,48,51,57,62-64,71,78,83-85], the United Kingdom (5/56, 9%) [42,46,66,86,90], Israel (4/56, 7%) [58,61,73,96], India (4/56, 7%) [53,75,79,89], Canada (3/56, 5%) [29,65,95], Germany (2/56, 4%) [59,92], Kuwait (2/56, 4%) [49,77], Norway (2/56, 4%) [44,69], Iran (1/56, 2%) [50], Hong Kong (1/56, 2%) [54], Switzerland (1/56, 2%) [60], Austria (1/56, 2%) [67], Belgium (1/56, 2%) [94], Singapore (1/56, 2%) [91], South Africa (1/56, 2%) [93], the Philippines (1/56, 2%) [82], Sri Lanka (1/56, 2%) [80], and Saudi Arabia (1/56, 2%) [74]. Study participants from a variety of continents and countries were included: 27% (15/56) of the participants were from North America, 21% (12/56) were from Europe and Australia each, 14% (8/56) were from the Middle East and South and East Asia each, and 2% (1/56) were from Africa. A visual representation of the worldwide distribution of study participants can be found in Figure 3.
Figure 3.
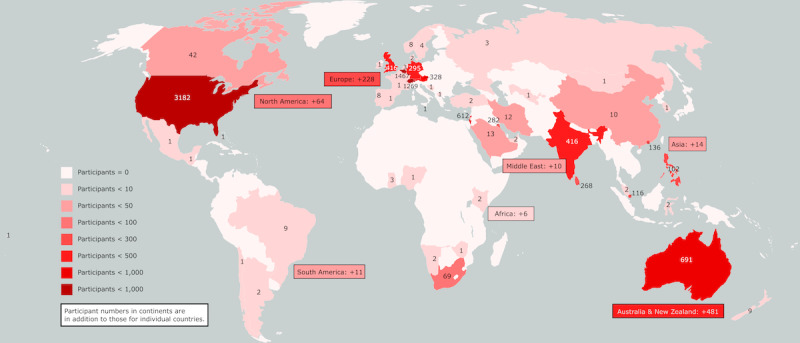
Total number of participants in the included studies according to region. The combined participant numbers of the included studies were based on the country, continent, or region.
Questionnaires (37/56, 66%) were used with a total of 10,245 health professionals [43,45,47,51-56,58,60-62,64-68,70-73,75,76,78-80,82,83,87,89-94,96], and interviews or focus groups (17/56, 30%) were conducted with 288 health professionals [29,42,44,46,48,50,57,59,63,69,77,81,84-86,88,95]. The methods used were mixed in 2 publications [49,74]. The evaluation methods, according to the included professions and their combined sample sizes, are presented in Table 2.
Table 2.
Participants in the included studies according to profession and evaluation methods.
|
|
OTa (n=1519), n (%) | PTb (n=2857), n (%) | SLTc and Audd (n=2852), n (%) | Nure (n=68), n (%) | Dief (n=2435), n (%) | Midg (n=679), n (%) | PT or OT (n=16), n (%) | PT, OT, or SLT and Aud (n=102), n (%) | Total (n=10,533), n (%) |
| Questionnaire | 1515 (99.7) | 2722 (95.3) | 2822 (98.9) | —h | 2433 (99.9) | 630 (92.8) | 16 (100) | 102 (100) | 10,245 (97.3) |
| Interview | 4 (0.3) | 135 (4.7) | 30 (1.1) | 68 (100) | 2 (0.1) | 49 (7.2) | — | — | 288 (2.7) |
aOT: occupational therapist.
bPT: physical therapist.
cSLT: speech and language therapist.
dAud: audiologist.
eNur: nurse.
fDie: dietitian.
gMid: midwife.
hNot available.
Barriers to Video Call–Based Telehealth
Barriers were assigned to 8 categories: technology issues, practice issues, patient issues, environmental issues, attributions, interpersonal issues, policies and regulations, and administration issues. Technology issues were found to encompass several subcategories, including limited access to technology, concerns about the reliability and usability of technology, network issues, a lack of technology skills among health care providers and patients, and other unspecified technological barriers. The analysis indicated that practice issues covered aspects such as diminished fidelity of observations and poor conditions for visual instructions; a lack of knowledge, skills, or experience; a lack of training, guidelines, or protocols; and the inability to provide hands-on care. Subcategories attributed to patient issues included addressing inappropriate target groups, managing patient behaviors, and addressing safety issues. Furthermore, physical, sensory, and social environmental issues were identified. Barriers to telehealth identified under the attributions category were negative attitudes toward telehealth from providers, patients, and caregivers, along with perceived drawbacks associated with telehealth use. Moreover, policy and regulation issues, which included privacy and security issues, billing and reimbursement topics, and workplace or health policies, were relevant barriers. Interpersonal barriers included reduced client-practitioner interaction and communication as well as the presence of ethical and cultural concerns. Finally, administration issues, such as a lack of support and a perceived increase in workload, were identified. A detailed description of the barriers for each subcategory and their references are provided in Table 3. The percentages of publications mentioning this barrier are depicted in Figure 4.
Table 3.
Details of each category and subcategory and the corresponding references.
| Categories and subcategories | References | ||
| Technology issues | |||
|
|
Lack of technology access | ||
|
|
Lack of reliability and usability of technology | ||
|
|
Network issues | ||
|
|
Lack of technology skills | ||
|
|
Technological barriers | ||
| Practice issues | |||
|
|
Diminished fidelity of observations and poor conditions for visual instructions |
|
|
|
|
Lack of knowledge, skills, or experience | ||
|
|
Lack of training, guidelines, or protocols | ||
|
|
Lack of hands-on methods |
|
|
| Patient issues | |||
|
|
Inappropriate target group | ||
|
|
Patient behavior | ||
|
|
Safety issues | ||
| Environmental issues | |||
|
|
Physical and sensory environment | ||
|
|
Social environment | ||
| Attributions | |||
|
|
Negative attitudes |
|
|
|
|
Perceived drawbacks | ||
| Policy and regulation issues | |||
|
|
Privacy and security issues | ||
|
|
Billing and reimbursement issues | ||
|
|
Policies | ||
| Interpersonal issues | |||
|
|
Diminished client-practitioner interaction and communication |
|
|
|
|
Ethical and cultural issues |
|
|
| Administration issues | |||
|
|
Lack of support | ||
|
|
Workload increase | ||
Figure 4.
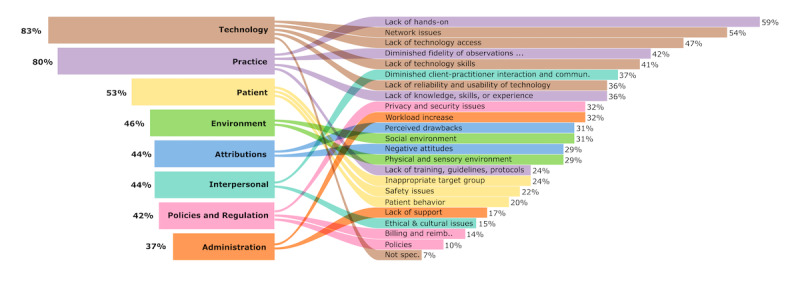
Barriers addressed by the publications according to category and subcategory in total. The bars on the left side represent the percentage of publications reporting barriers in the respective category. The bars on the right side represent the percentages of publications reporting barriers in the respective subcategory.
Publications reporting the barriers of PT, OT, and SLT covered all main categories, whereas nurse publications did not report any policy and regulation barriers. Dietitian and midwife publications had no information about patient issues, and midwife publications did not address category attributions. An overview of the distribution of reported barriers in the health profession is shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5.
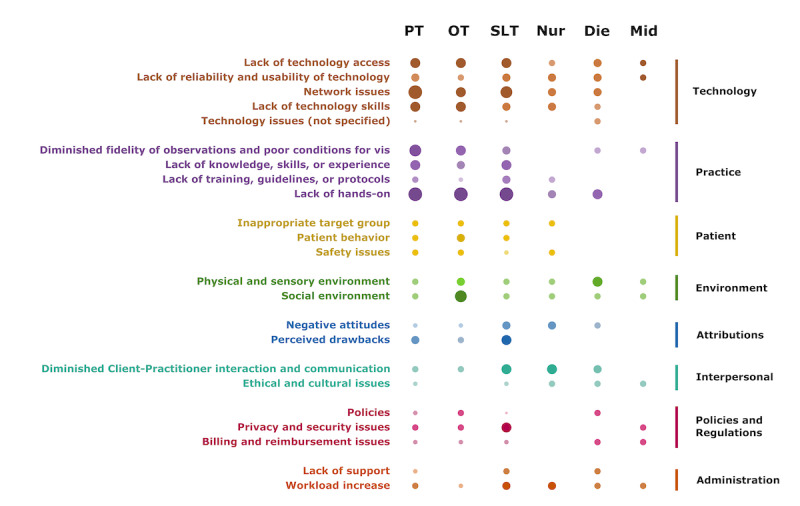
Barriers addressed by the publications according to the explored health profession. The size of the dots represents the relative number of documents addressing this barrier (row) based on this health profession (column). Die: dietitian; Mid: midwife; Nur: nurse; OT: occupational therapist; PT: physical therapist; SLT: speech and language therapist.
For further reference, Multimedia Appendix 2 provides an overview of the categories and subcategories of the barriers addressed in the individual studies [29,42-96].
Discussion
Principal Findings
This review aimed to map and condense the perceived barriers of allied health professionals concerning the use of video call–based telehealth, as understanding these barriers is crucial for improving telehealth adoption, efficiency, and effectiveness. By providing information to health care professionals and health services on barrier identification, this study serves as the first step toward addressing and overcoming these obstacles. We included 56 publications that reported barriers for OTs, PTs, SLTs and audiologists, dieticians, midwives, and nurses. Barriers were assigned to 8 topics: technology issues, practice issues, patient issues, environmental issues, attributions, policy and regulation issues, interpersonal issues, and administration issues. Previous publications on telemedicine barriers also used similar, but also different, classification schemes. The Pan American Health Organization refers to barriers by technological, organizational, human, and economic environments [39]. Almathami et al [98] described internal and external barriers, and Scott Kruse et al [99] differentiated between organizational barriers and patient barriers. However, similar barriers underpin these different classifications.
The barriers mentioned most frequently pertain to technological issues. Although video call technologies are widespread in a large part of the population, certain groups or individuals lack suitable hardware or network access. This could be the case not only for some older adults but also for patient groups living in rural areas or those who are socioeconomically disadvantaged. The limited access of patient groups should be considered when telehealth services are offered to avoid possible disadvantages. Furthermore, the risk of a digital divide extends beyond mere access to technology. It also encompasses a lack of knowledge of digital health or technology skills [100,101], as they were reported in numerous included studies of this and previous reviews [99]. To facilitate the acceptance and effective use of telehealth tools, hardware and software must be designed to accommodate users’ needs [98]. According to common frameworks, perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use affect the acceptance of a technology and are further influenced by experience [102]. To overcome these barriers, it is important to develop and use video call software that meets the specific needs of providers and patients and adheres to usability principles. In addition, health professionals, as well as patients, need to have the knowledge and skills to use technology. Thorough preparation of video visits or calling on e-helpers can facilitate successful implementation [51,86,95]. However, it is essential to recognize that network issues may still occur, potentially causing interruptions during video calls and affecting the overall telehealth experience. These were the second most cited barriers in this review, showing similarity to the review by Almathami et al [98], where this barrier held the top rank. To reduce network problems, it would be necessary to invest in and prioritize the development and maintenance of robust and reliable telecommunication infrastructure. This includes improving broadband connectivity in rural and underserved areas, which are often specifically addressed by telehealth services. In addition, providing telehealth users with guidelines for troubleshooting network-related problems could further enhance the overall experience and success of telehealth initiatives.
Second, most publications have reported barriers related to practice issues. Health care provision involves various physical, verbal, and observational measures. Providing care on the web on the screen involves a variety of challenges concerning this matter. Although physical therapy often involves whole body movements and hands-on techniques, dietitians are more based on conversation. Occupational therapy is often oriented toward daily activities, incorporating many different objects, and speech and language therapy is dependent on good sound quality. However, most practice-related barriers are applicable to all involved health care professions. First, hands-on methods cannot be applied to examinations, demonstrations, interventions, and assistance. This barrier was mentioned in 59% (33/56) of the publications and therefore seems to represent a core barrier for the explored health professions. Notably, it was not represented as a key barrier in earlier reviews that included a wider range of health professions [98,99] and might be more specific for the professions examined in this study. To address the lack of hands-on methods, they must be replaced by other actions that target the same outcome of comparable quality. For this, health professionals need specific training, guidelines, or protocols that expand their skill sets. However, if there are no adequate replacements for hands-on techniques, telehealth services may solely not be appropriate. Practitioners could combine telehealth and in-person services or work closely with local health care professionals to coordinate in-person care when needed. This collaborative approach ensures that patients receive comprehensive care that combines the convenience of telehealth with the benefits of in-person care. Second, limitations are also prevalent with respect to the diminished conditions for observations. Issues that negatively contribute to this are poor video and audio quality, difficulties with camera placement, and a lack of perception of body language, as described previously [98]. Establishing a professional setting on both sides can help minimize this barrier. However, these might be associated with additional costs, which were also found to hinder telehealth adoption [99]. Furthermore, encouraging the development and implementation of digital assessment tools tailored for telehealth sessions could aid health care professionals in making more accurate observations despite the limitations of the web-based setting [103,104]. Training, guidelines, or protocols are needed to guide health professionals in creating optimal conditions for valid observations and high-quality therapy.
Telehealth provision, in addition to visual observations, is highly dependent on communication. Therefore, a limited interaction between the client and the practitioner was described as a barrier. There exists the fear that information might be lost along the way, and misunderstandings can occur. Moreover, it was mentioned that it is more difficult to establish relationships or trust. Such communication issues and perceptions of impersonal care have been reported previously [98,99]. Therefore, special emphasis should be placed on expanding the communication skills of health care providers to overcome those barriers [105-107]. Health care professionals should be trained to be more aware of and skilled in nonverbal communication cues, such as facial expressions, gestures, and body language. This can help to better understand patients’ needs, emotions, and reactions during telehealth sessions, thereby improving overall communication and rapport building. Moreover, health care professionals reported a decrease in communication quality, especially when language barriers were present. By implementing appropriate strategies, telehealth on the other hand could also help overcome language barriers when providers on the web collaborate with professional interpreters [108] or integrate language support features, such as real-time translation [109]. Comprehensive training modules that familiarize health care providers with the available language support services and their use in telehealth settings would be needed.
When discussing patient selection for telehealth services, it is crucial to consider several factors, including the demographic, physiological, and personal characteristics of patients. Some health professionals expressed the need for algorithms to establish clear inclusion and exclusion criteria. Certain diagnoses or health restrictions may limit a patient’s ability to interact effectively through telehealth or pose risks that cannot be adequately managed within this service model. Ensuring patient safety and addressing potential risks should be integral to the planning and management of telehealth services [110]. In the context of telehealth for children, some publications highlighted challenges related to maintaining attention, engagement, and managing challenging behaviors. To address these issues, health professionals may need to use innovative approaches in adapting methods and materials to suit web-based settings [111-113]. In addition, prioritizing coaching and support for relatives can help overcome barriers associated with telehealth in children [100,101].
Caregivers can play an important role in supporting the patient with technology or other tasks. Furthermore, they are directly addressed by health professions for training or support [114]. If they are not available or struggle with the responsibilities assigned, telehealth provision can be challenging, especially if patients depend on them [98]. Therefore, the social system of patients should be considered to determine whether telehealth services are appropriate. Furthermore, it is important to evaluate the physical and sensory environments of patients, as described by Almathami et al [98]. Depending on the goals and types of health care provision, space and material needs should be considered and evaluated. If possible, providers could conduct home assessments to evaluate the physical and sensory environment of patients and make recommendations for modifications or improvements to the space. In addition, a lack of privacy at home can be an issue. To address this barrier, health care providers can offer guidance on how to create a private space for telehealth visits, such as using a separate room or wearing headphones to ensure confidentiality. Finally, health care providers should consider alternative methods of care for patients who do not have access to a private space for telehealth visits.
Privacy issues also refer to the transmission of sensible health data over the internet and have been widely discussed [98,99]. Many health professionals mentioned that they feared that their patient’s privacy was at risk and that they had concerns about data protection. Telehealth requires secure platforms where data are encrypted to protect patient privacy and confidentiality [115]. Therefore, it is important to educate health care professionals about suitable platforms and provide guidelines so that they can make informed decisions about IT security measures [116]. Commercial platforms are not always in compliance with the General Data Protection Regulations [115] or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act [98] and should be transparent about how they store, transmit, encrypt, and use data so that health providers can compare those measures with current guidelines [117].
In addition to fear of a lack of data privacy, other negative attitudes toward telehealth influence the acceptance of telehealth. This applies to the reluctance to telehealth of health care providers, patients, and caregivers, also described as resistance to change [99]. Most often, statements about clinical effectiveness or clinical usefulness were reported as reasons. The body of evidence for telehealth effectiveness varies depending on the health context and the involved health care professions. To give some examples, 2 meta-analyses found positive clinical results, even comparable with conventional face-to-face rehabilitation approaches, for PT and OT telerehabilitation services [118,119]. A systematic review of telepractice for adult speech language therapy supports the use of telepractice as an appropriate service delivery model [120]. Moreover, the benefits of using telepractice to provide parent-implemented interventions to children with autism spectrum disorders have been described [121]. Telehealth services from dieticians or nutritionists can improve protein intake and quality of life in malnourished older adults [122]. Yet, there is a lack of high-quality evidence and training courses to inform health care providers about current evidence.
Finally, all the mentioned barriers can lead to an increase in the workload and stress of health care professionals, especially when experience with telehealth has not been established. In such cases, providers may face challenges such as technological difficulties, ineffective communication with patients, and patient selection issues, which can lead to increased stress and a decrease in work efficiency. They need administrative and technological support, protocols, and guidelines to help them establish a well-functioning telehealth practice. To achieve sustainable telehealth services, it is important to ensure that health care professionals are willing and able to use these tools effectively. This means that health organizations must provide adequate resources and training to support the adoption and use of telehealth technology, as their acceptance is crucial to the success of sustainable telehealth services [123].
Limitations
This review only covered original studies, which were found in the PubMed and CINAHL databases, in German or English language and were published since June 2017. Although these are widely recognized and commonly used databases in the field of health care research, this may have resulted in the exclusion of relevant studies published in other databases. However, efforts have been made to minimize this limitation using comprehensive search strings and citation tracking to identify additional relevant literature. Future studies could expand the search to include a wider range of databases to increase the comprehensiveness of the search strategy. Furthermore, only 1 researcher conducted the search, selection, and mapping process. A broader search process, with more languages and researchers included, might have increased the number of publications and reliability of the results.
Publications were selected based on included health care professions. In case, professions out of scope were involved, the author selected only information from health care professionals that were within the scope of all conscience but with the risk of interference. Furthermore, there were big differences between the number of publications and included participants in the health care profession of interest. Although more than half of the publications addressed barriers of PTs and another third addressed those of SLTs and audiologists, other professions were less represented. Furthermore, SLTs and audiologists were combined, as they are 1 profession in some countries, whereas in others, they are 2 separate professions. Owing to these quantitative differences, it is difficult to compare the mentioned barriers between these professions and discuss whether there are significant differences. Furthermore, the number of publications that mentioned a barrier might not reflect its relevance. Therefore, all numbers and corresponding figures should be interpreted with caution.
Another limitation is that this review focused on health contexts rather than health settings. The included studies covered a range of health professions and contexts of care but did not distinguish between different settings, such as acute, tertiary, or community settings. There may be differences in the barriers and challenges faced by telehealth interventions across different health settings; therefore, the findings of this study may not be generalizable to all health settings.
This review has a slightly more balanced distribution of publication sites when compared with other reviews that focused on telehealth barriers. It incorporates approximately half of the publications from North America (15/56, 27%) and Europe (12/56, 21%) and the other half from Australia (12/56, 21%), the Middle East (8/56, 14%), South and East Asia (8/56, 14%), and Africa (1/56, 2%). Earlier reviews that focused on telemedicine barriers reported nearly 73% [99] or even 84% [98] of references from North America or Europe. However, there is a huge underrepresentation of African countries especially.
This review covered most studies that were conducted during the COVID-19 pandemic. As this period was highly influenced by contact restrictions, many publications have included participants who used telehealth services as a matter of imperative necessity. This could have influenced their attitudes and may have led to increased confrontation with barriers that could have been prevented with more time for preparation. In addition, the review included only a limited number of prepandemic studies, which may limit the generalizability of our findings beyond the pandemic period. Nonetheless, no differences were observed in the reported barrier categories between studies with and without a COVID-19 context. However, further research is needed to examine the challenges and barriers to telehealth interventions in different settings and contexts.
Finally, qualitative and quantitative results from these studies were synthesized in this review. It should be considered that participants give different answers when they reply to open-ended or closed-ended questions.
Conclusions
This study systematically reports the barriers of allied health professionals toward video call–based telehealth within 59 original studies with OTs, PTs, SLTs and audiologists, dieticians, midwives, and nurses. Through the review, a range of barriers were identified, including technology, practice, patient, environmental, attributions, policy and regulation, interpersonal, and administration issues. The results emphasize the need for stable infrastructure, education, training, guidelines, policies, and support systems to establish high-quality allied telehealth services. The identification of these barriers is crucial, as it highlights the areas where improvements are needed in telehealth services to better meet the needs of allied health professionals, nurses, and their patients. The information gathered in this review can be used to improve telehealth services in health care organizations.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank RAWgraphs [124] for their open-source data visualization framework and INKSCAPE draw freely [125] for their open-source vector graphics editor.
Abbreviations
- OT
occupational therapist
- PRISMA-ScR
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews
- PT
physical therapist
- SLT
speech and language therapist
Search strings used in PubMed and CINAHL databases.
Barriers addressed by the publications according to category and subcategory for each publication.
Full data excel sheet.
Data Availability
The data set analyzed during this study is available in Multimedia Appendix 3.
Footnotes
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
References
- 1.Nancarrow S, Borthwick A. The Allied Health Professions: A Sociological Perspective. Bristol, UK: Policy Press; 2021. Mar 10, [Google Scholar]
- 2.What is allied health? Allied Health Professions Australia. [2022-11-19]. https://ahpa.com.au/what-is-allied-health/
- 3.Coto J, Restrepo A, Cejas I, Prentiss S. The impact of COVID-19 on allied health professions. PLoS One. 2020 Oct 30;15(10):e0241328. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0241328. https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0241328 .PONE-D-20-15411 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hughes MT, Rushton CH. Ethics and well-being: the health professions and the COVID-19 pandemic. Acad Med. 2022 Mar 01;97(3S):S98–103. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000004524. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/34789657 .00001888-202203001-00016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tuczyńska M, Matthews-Kozanecka M, Baum E. Accessibility to Non-COVID health services in the world during the COVID-19 pandemic: review. Front Public Health. 2021 Dec 16;9:760795. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.760795. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/34976922 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Núñez A, Sreeganga SD, Ramaprasad A. Access to Healthcare during COVID-19. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Mar 14;18(6):2980. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18062980. https://www.mdpi.com/resolver?pii=ijerph18062980 .ijerph18062980 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.De Biase S, Cook L, Skelton DA, Witham M, Ten Hove R. The COVID-19 rehabilitation pandemic. Age Ageing. 2020 Aug 24;49(5):696–700. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afaa118. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/32470131 .5848215 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.D'souza J, Biswas A, Gada P, Mangroliya J, Natarajan M. Barriers leading to increased disability in neurologically challenged populations during COVID-19 pandemic: a scoping review. Disabil Rehabil. 2022 Dec;44(24):7693–706. doi: 10.1080/09638288.2021.1986747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Pant S, Koirala S, Subedi M. Access to maternal health services during COVID-19. Europasian J Med Sci. 2020 Jul 08;2:46–50. doi: 10.46405/ejms.v2i2.110. https://www.europasianjournals.org/ejms/index.php/ejms/article/view/110 . [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mauro V, Lorenzo M, Paolo C, Sergio H. Treat all COVID 19-positive patients, but do not forget those negative with chronic diseases. Intern Emerg Med. 2020 Jun 09;15(5):787–90. doi: 10.1007/s11739-020-02395-z. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11739-020-02395-z . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ryder M, Guerin S, Forde R, Lowe G, Jaarsma T, O'Neill M, Halley C, Connolly M. The perceived effects of COVID-19 while living with a chronic illness. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2023 Jan;55(1):154–62. doi: 10.1111/jnu.12835. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/36281970 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chudasama YV, Gillies CL, Zaccardi F, Coles B, Davies MJ, Seidu S, Khunti K. Impact of COVID-19 on routine care for chronic diseases: a global survey of views from healthcare professionals. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2020 Sep;14(5):965–7. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.06.042. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/32604016 .S1871-4021(20)30211-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Doraiswamy S, Abraham A, Mamtani R, Cheema S. Use of telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic: scoping review. J Med Internet Res. 2020 Dec 01;22(12):e24087. doi: 10.2196/24087. https://www.jmir.org/2020/12/e24087/ v22i12e24087 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sprianu C, Krpalek D, Kugel JD, Bains G, Gharibvand L. COVID-19 and telehealth use among occupational therapy, physical therapy, and speech-language pathology practitioners in the United States. Internet J Allied Health Sci Pract. 2022 Mar 31;20(2) doi: 10.46743/1540-580x/2022.2129. https://nsuworks.nova.edu/ijahsp/vol20/iss2/20/ [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Grundstein MJ, Fisher C, Titmuss M, Cioppa-Mosca J. The role of virtual physical therapy in a post-pandemic world: pearls, pitfalls, challenges, and adaptations. Phys Ther. 2021 Sep 01;101(9):pzab145. doi: 10.1093/ptj/pzab145.6294522 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kelly JT, Allman-Farinelli M, Chen J, Partridge SR, Collins C, Rollo M, Haslam R, Diversi T, Campbell KL. Dietitians Australia position statement on telehealth. Nutr Diet. 2020 Sep;77(4):406–15. doi: 10.1111/1747-0080.12619. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/32596950 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sarsak HI. Telerehabilitation services: a successful paradigm for occupational therapy clinical services? Int J Phys Med Rehabil. 2020 Apr 16;5(2):93–8. doi: 10.15406/ipmrj.2020.05.00237. https://medcraveonline.com/IPMRJ/IPMRJ-05-00237.pdf . [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Krzyzaniak N, Cardona M, Peiris R, Michaleff ZA, Greenwood H, Clark J, Scott AM, Glasziou P. Telerehabilitation versus face-to-face rehabilitation in the management of musculoskeletal conditions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Phys Ther Rev. 2023 Apr 12;:1–17. doi: 10.1080/10833196.2023.2195214. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/10833196.2023.2195214 . [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Eddison N, Leone E, Healy A, Royse C, Chockalingam N. The potential impact of allied health professional telehealth consultations on health inequities and the burden of treatment. Int J Equity Health. 2022 Jun 30;21(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s12939-022-01689-2. https://equityhealthj.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12939-022-01689-2 .10.1186/s12939-022-01689-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gogia S. Fundamentals of Telemedicine and Telehealth. London, UK: Academic Press; 2019. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Fatehi F, Wootton R. Telemedicine, telehealth or e-health? A bibliometric analysis of the trends in the use of these terms. J Telemed Telecare. 2012 Dec;18(8):460–4. doi: 10.1258/jtt.2012.gth108.jtt.2012.GTH108 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bashshur R, Shannon G, Krupinski E, Grigsby J. The taxonomy of telemedicine. Telemed J E Health. 2011 Jul;17(6):484–94. doi: 10.1089/tmj.2011.0103. http://hdl.handle.net/2027.42/90498 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.WMA statement on digital health. World Medical Association. 2022. [2023-02-06]. https://www.wma.net/policies-post/wma-statement-on-guiding-principles-for-the-use-of-telehealth-for-the-provision-of-health-care/
- 24.Mechanic OJ, Persaud Y, Kimball AB. Telehealth Systems. StatPearls Treasure Island: StatPearls Publishing; [2023-02-06]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459384/ [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Monaghesh E, Hajizadeh A. The role of telehealth during COVID-19 outbreak: a systematic review based on current evidence. BMC Public Health. 2020 Aug 01;20(1):1193. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-09301-4. https://bmcpublichealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12889-020-09301-4 .10.1186/s12889-020-09301-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kalin ML, Garlow SJ, Thertus K, Peterson MJ. Rapid implementation of telehealth in hospital psychiatry in response to COVID-19. Am J Psychiatry. 2020 Jul 01;177(7):636–7. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2020.20040372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hron JD, Parsons CR, Williams LA, Harper MB, Bourgeois FC. Rapid implementation of an inpatient telehealth program during the COVID-19 pandemic. Appl Clin Inform. 2020 May;11(3):452–9. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1713635. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/32610350 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Dosaj A, Thiyagarajan D, Ter Haar C, Cheng J, George J, Wheatley C, Ramanathan A. Rapid implementation of telehealth services during the COVID-19 pandemic. Telemed J E Health. 2021 Feb;27(2):116–20. doi: 10.1089/tmj.2020.0219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kwok EY, Chiu J, Rosenbaum P, Cunningham BJ. The process of telepractice implementation during the COVID-19 pandemic: a narrative inquiry of preschool speech-language pathologists and assistants from one center in Canada. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022 Jan 16;22(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s12913-021-07454-5. https://bmchealthservres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12913-021-07454-5 .10.1186/s12913-021-07454-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kalirathinam D, Guruchandran R, Subramani P. Comprehensive physiotherapy management in COVID-19 – a narrative review. Sci Med. 2020 May 26;30(1):38030. doi: 10.15448/1980-6108.2020.1.38030. https://revistaseletronicas.pucrs.br/ojs/index.php/scientiamedica/article/view/38030 . [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Alonazi A. Effectiveness and acceptability of telerehabilitation in physical therapy during COVID-19 in children: findings of a systematic review. Children (Basel) 2021 Nov 29;8(12):1101. doi: 10.3390/children8121101. https://www.mdpi.com/resolver?pii=children8121101 .children8121101 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Harkey LC, Jung SM, Newton ER, Patterson A. Patient satisfaction with telehealth in rural settings: a systematic review. Int J Telerehabil. 2020 Dec 08;12(2):53–64. doi: 10.5195/ijt.2020.6303. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/33520095 .ijt.2020.6303 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Moffatt JJ, Eley DS. The reported benefits of telehealth for rural Australians. Aust Health Rev. 2010 Aug;34(3):276–81. doi: 10.1071/AH09794.AH09794 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Shigekawa E, Fix M, Corbett G, Roby DH, Coffman J. The current state of telehealth evidence: a rapid review. Health Aff (Millwood) 2018 Dec;37(12):1975–82. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2018.05132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Molini-Avejonas DR, Rondon-Melo S, de La Higuera Amato CA, Samelli AG. A systematic review of the use of telehealth in speech, language and hearing sciences. J Telemed Telecare. 2015 Oct;21(7):367–76. doi: 10.1177/1357633X15583215.1357633X15583215 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Cox A, Lucas G, Marcu A, Piano M, Grosvenor W, Mold F, Maguire R, Ream E. Cancer survivors' experience with telehealth: a systematic review and thematic synthesis. J Med Internet Res. 2017 Jan 09;19(1):e11. doi: 10.2196/jmir.6575. https://www.jmir.org/2017/1/e11/ v19i1e11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Coufal K, Parham D, Jakubowitz M, Howell C, Reyes J. Comparing traditional service delivery and telepractice for speech sound production using a functional outcome measure. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2018 Feb 06;27(1):82–90. doi: 10.1044/2017_AJSLP-16-0070.2665178 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Seron P, Oliveros MJ, Gutierrez-Arias R, Fuentes-Aspe R, Torres-Castro RC, Merino-Osorio C, Nahuelhual P, Inostroza J, Jalil Y, Solano R, Marzuca-Nassr GN, Aguilera-Eguía R, Lavados-Romo P, Soto-Rodríguez FJ, Sabelle C, Villarroel-Silva G, Gomolán P, Huaiquilaf S, Sanchez P. Effectiveness of telerehabilitation in physical therapy: a rapid overview. Phys Ther. 2021 Jun 01;101(6):pzab053. doi: 10.1093/ptj/pzab053. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/33561280 .6131423 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Framework for the implementation of a telemedicine service. Pan American Health Organization. 2016. [1999-11-30]. https://iris.paho.org/bitstream/handle/10665.2/28414/9789275119037_eng.pdf .
- 40.Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O'Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, Moher D, Peters MD, Horsley T, Weeks L, Hempel S, Akl EA, Chang C, McGowan J, Stewart L, Hartling L, Aldcroft A, Wilson MG, Garritty C, Lewin S, Godfrey CM, Macdonald MT, Langlois EV, Soares-Weiser K, Moriarty J, Clifford T, Tunçalp Ö, Straus SE. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018 Oct 02;169(7):467–73. doi: 10.7326/M18-0850. https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/abs/10.7326/M18-0850?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori:rid:crossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub0pubmed .2700389 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Peters MD, Marnie C, Tricco AC, Pollock D, Munn Z, Alexander L, McInerney P, Godfrey CM, Khalil H. Updated methodological guidance for the conduct of scoping reviews. JBI Evid Synth. 2020 Oct;18(10):2119–26. doi: 10.11124/JBIES-20-00167.02174543-202010000-00004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Barrett D. Rethinking presence: a grounded theory of nurses and teleconsultation. J Clin Nurs. 2017 Oct;26(19-20):3088–98. doi: 10.1111/jocn.13656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Lawford BJ, Bennell KL, Kasza J, Hinman RS. Physical therapists' perceptions of telephone- and internet video-mediated service models for exercise management of people with osteoarthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2018 Mar;70(3):398–408. doi: 10.1002/acr.23260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Rygg LO, Brataas HV, Nordtug B. Introducing videoconferencing on tablet computers in nurse-patient communication: technical and training challenges. Int J Telemed Appl. 2018 Oct 18;2018:8943960. doi: 10.1155/2018/8943960. doi: 10.1155/2018/8943960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Rortvedt D, Jacobs K. Perspectives on the use of a telehealth service-delivery model as a component of school-based occupational therapy practice: designing a user-experience. Work. 2019;62(1):125–31. doi: 10.3233/WOR-182847.WOR182847 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Spiby H, Faucher MA, Sands G, Roberts J, Kennedy HP. A qualitative study of midwives' perceptions on using video-calling in early labor. Birth. 2019 Mar;46(1):105–12. doi: 10.1111/birt.12364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Abbott-Gaffney C, Jacobs K. Telehealth in school-based practice: perceived viability to bridge global OT practitioner shortages prior to COVID-19 global health emergency. Work. 2020;67(1):29–35. doi: 10.3233/WOR-203240.WOR203240 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wundersitz C, Caelli A, Georgy J, Musovic A, Manning R, Prause M, Robertson J, Taylor NF. Conducting community rehabilitation review sessions via videoconference: a feasibility study. Aust J Rural Health. 2020 Dec;28(6):603–12. doi: 10.1111/ajr.12665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Albahrouh SI, Buabbas AJ. Physiotherapists' perceptions of and willingness to use telerehabilitation in Kuwait during the COVID-19 pandemic. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2021 Apr 08;21(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s12911-021-01478-x. https://bmcmedinformdecismak.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12911-021-01478-x .10.1186/s12911-021-01478-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Bayati B, Ayatollahi H. Speech therapists' perspectives about using tele-speech therapy: a qualitative study. Disabil Rehabil Assist Technol. 2023 Jul;18(5):621–6. doi: 10.1080/17483107.2021.1900933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Bennell KL, Lawford BJ, Metcalf B, Mackenzie D, Russell T, van den Berg M, Finnin K, Crowther S, Aiken J, Fleming J, Hinman RS. Physiotherapists and patients report positive experiences overall with telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic: a mixed-methods study. J Physiother. 2021 Jul;67(3):201–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jphys.2021.06.009. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1836-9553(21)00052-7 .S1836-9553(21)00052-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Bican R, Christensen C, Fallieras K, Sagester G, O'Rourke S, Byars M, Tanner K. Rapid implementation of telerehabilitation for pediatric patients during COVID-19. Int J Telerehabil. 2021 Jun 22;13(1):e6371. doi: 10.5195/ijt.2021.6371. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/34345345 .ijt.2021.6371 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.D'Souza AF, Rebello SR. Perceptions and willingness of physiotherapists in India to use telerehabilitation during the COVID-19 pandemic. Int J Telerehabil. 2021 Dec 16;13(2):e6425. doi: 10.5195/ijt.2021.6425. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/35646229 .ijt.2021.6425 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Fong R, Tsai CF, Yiu OY. The implementation of telepractice in speech language pathology in Hong Kong during the COVID-19 pandemic. Telemed J E Health. 2021 Jan;27(1):30–8. doi: 10.1089/tmj.2020.0223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Hall JB, Woods ML, Luechtefeld JT. Pediatric physical therapy telehealth and COVID-19: factors, facilitators, and barriers influencing effectiveness-a survey study. Pediatr Phys Ther. 2021 Jul 01;33(3):112–8. doi: 10.1097/PEP.0000000000000800. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/34086621 .00001577-900000000-99849 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Harrell RG, Schubert MC, Oxborough S, Whitney SL. Vestibular rehabilitation telehealth during the SAEA-CoV-2 (COVID-19) pandemic. Front Neurol. 2022 Jan 20;12:781482. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.781482. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/35126289 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Hasani F, Malliaras P, Haines T, Munteanu SE, White J, Ridgway J, Nicklen P, Moran A, Jansons P. Telehealth sounds a bit challenging, but it has potential: participant and physiotherapist experiences of gym-based exercise intervention for Achilles tendinopathy monitored via telehealth. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021 Feb 04;22(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s12891-020-03907-w. https://bmcmusculoskeletdisord.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12891-020-03907-w .10.1186/s12891-020-03907-w [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Kaufman-Shriqui V, Sherf-Dagan S, Boaz M, Birk R. Virtual nutrition consultation: what can we learn from the COVID-19 pandemic? Public Health Nutr. 2021 Apr;24(5):1166–73. doi: 10.1017/S1368980021000148. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/33436134 .S1368980021000148 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Kienle GS, Werthmann P, Grotejohann B, Hundhammer T, Schmoor C, Stumpe C, Voigt-Radloff S, Huber R. Addressing COVID-19 challenges in a randomised controlled trial on exercise interventions in a high-risk population. BMC Geriatr. 2021 May 01;21(1):287. doi: 10.1186/s12877-021-02232-8. https://bmcgeriatr.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12877-021-02232-8 .10.1186/s12877-021-02232-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Klamroth-Marganska V, Gemperle M, Ballmer T, Grylka-Baeschlin S, Pehlke-Milde J, Gantschnig BE. Does therapy always need touch? A cross-sectional study among Switzerland-based occupational therapists and midwives regarding their experience with health care at a distance during the COVID-19 pandemic in spring 2020. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021 Jun 15;21(1):578. doi: 10.1186/s12913-021-06527-9. https://bmchealthservres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12913-021-06527-9 .10.1186/s12913-021-06527-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Krasovsky T, Silberg T, Barak S, Eisenstein E, Erez N, Feldman I, Guttman D, Liber P, Patael SZ, Sarna H, Sadeh Y, Steinberg P, Landa J. Transition to multidisciplinary pediatric telerehabilitation during the COVID-19 pandemic: strategy development and implementation. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Feb 04;18(4):1484. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18041484. https://www.mdpi.com/resolver?pii=ijerph18041484 .ijerph18041484 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Malliaras P, Merolli M, Williams CM, Caneiro JP, Haines T, Barton C. 'It's not hands-on therapy, so it's very limited': telehealth use and views among allied health clinicians during the coronavirus pandemic. Musculoskelet Sci Pract. 2021 Apr;52:102340. doi: 10.1016/j.msksp.2021.102340. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/33571900 .S2468-7812(21)00024-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Martin R, Mandrusiak A, Russell T, Forbes R. New-graduate physiotherapists' training needs and readiness for telehealth. Physiother Theory Pract. 2022 Nov;38(13):2788–97. doi: 10.1080/09593985.2021.1955423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.McPherson K, Nahon I. Telehealth and the provision of pelvic health physiotherapy in regional, rural and remote Australia. Aust N Z Cont J. 2021 Aug;27(3):66–70. doi: 10.33235/anzcj.27.3.66-70. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Peters S, Botero M, Evers A, Fong B, Jakab B, Petter E, Eng JJ. Development and feasibility of a modified Fugl-Meyer lower extremity assessment for telerehabilitation: a pilot study. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2021 Jun 07;7(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s40814-021-00862-8. https://pilotfeasibilitystudies.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40814-021-00862-8 .10.1186/s40814-021-00862-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Pollard R, Hogan S. Parental and practitioner views of telepractice for pediatric auditory verbal habilitation at a time of global pandemic. Perspective. 2021 Dec;6(6):1832–56. doi: 10.1044/2021_persp-21-00062. https://pubs.asha.org/doi/epdf/10.1044/2021_PERSP-21-00062 . [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Rettinger L, Klupper C, Werner F, Putz P. Changing attitudes towards teletherapy in Austrian therapists during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Telemed Telecare. 2023 Jun;29(5):406–14. doi: 10.1177/1357633X20986038. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/1357633X20986038?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori:rid:crossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub0pubmed . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Rozga M, Handu D, Kelley K, Jimenez EY, Martin H, Schofield M, Steiber A. Telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic: a cross-sectional survey of registered dietitian nutritionists. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2021 Dec;121(12):2524–35. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2021.01.009. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/33612436 .S2212-2672(21)00036-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Rygg LØ, Brataas HV, Nordtug B. Oncology nurses' lived experiences of video communication in follow-up care of home-living patients: a phenomenological study in rural Norway. Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2021 Jun;52:101955. doi: 10.1016/j.ejon.2021.101955. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1462-3889(21)00061-2 .S1462-3889(21)00061-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Singh RH, Pringle T, Kenneson A. The use of telemedicine and other strategies by registered dietitians for the medical nutrition therapy of patients with inherited metabolic disorders during the COVID-19 pandemic. Front Nutr. 2021 Apr 27;8:637868. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.637868. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/33987197 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Sutherland R, Hodge A, Chan E, Silove N. Barriers and facilitators: clinicians' opinions and experiences of telehealth before and after their use of a telehealth platform for child language assessment. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2021 Nov;56(6):1263–77. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.12666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Abbott-Gaffney CR, Gafni-Lachter L, Cason J, Sheaffer K, Harasink R, Donehower K, Jacobs K. Toward successful future use of telehealth in occupational therapy practice: what the COVID-19 rapid shift revealed. Work. 2022;71(2):385–94. doi: 10.3233/WOR-210789.WOR210789 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Almog T, Gilboa Y. Remote delivery of service: a survey of occupational therapists' perceptions. Rehabil Process Outcome. 2022 Sep 06;11:11795727221117503. doi: 10.1177/11795727221117503. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/36091866 .10.1177_11795727221117503 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Alrushud A, Alamam D, Alharthi A, Shaheen A, Alotaibi N, AlSabhan R, Alharbi S, Ali N, Mohammed E, Sweeh J. Physical therapists' perceptions of and satisfaction with delivering telerehabilitation sessions to patients with knee osteoarthritis during the COVID-19 pandemic: preliminary study. Musculoskeletal Care. 2022 Dec;20(4):926–36. doi: 10.1002/msc.1666. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/35698900 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Bhattarai B, Sanghavi T, Abhishek BP. Challenges in delivering tele-practice services for communication disorders among audiologists and speech language pathologists. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022 Dec;74(Suppl 3):4360–5. doi: 10.1007/s12070-021-03032-7. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/35043086 .3032 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Bolden III W. Telehealth across the therapies: examining the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on clinical staff working with low socioeconomic status populations. Perspective. 2022 Aug;7(4):1236–55. doi: 10.1044/2022_persp-21-00099. https://pubs.asha.org/doi/10.1044/2022_PERSP-21-00099 . [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Buabbas AJ, Albahrouh SE, Alrowayeh HN, Alshawaf H. Telerehabilitation during the COVID-19 pandemic: patients and physical therapists' experiences. Med Princ Pract. 2022;31(2):156–64. doi: 10.1159/000523775. doi: 10.1159/000523775.000523775 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Ceprnja D, Clark T, Young J, Lee R, Flynn K, Maka K. Evaluating experiences, usability and patient satisfaction with telehealth for tertiary outpatient physiotherapy services during COVID-19: a mixed-methods study. Physiother Theory Pract (Forthcoming) 2022 Apr 06;:1–9. doi: 10.1080/09593985.2022.2059423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Chaudhari C, Talreja A. Emerging challenges faced by private clinic physiotherapist in new normal times during the COVID-19 pandemic in Pune city. Indian J Occup Ther. 2022 Aug 09;16(3):103–8. doi: 10.37506/ijpot.v16i3.18405. https://medicopublication.com/index.php/ijpot/article/view/18405 . [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Dissanayaka T, Nakandala P, Sanjeewa C. Physiotherapists' perceptions and barriers to use of telerehabilitation for exercise management of people with knee osteoarthritis in Sri Lanka. Disabil Rehabil Assist Technol (Forthcoming) 2022 Sep 13;:1–10. doi: 10.1080/17483107.2022.2122606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Ditwiler RE, Swisher LL, Hardwick DD. Doing things you never imagined: professional and ethical issues in the U.S. outpatient physical therapy setting during the COVID-19 pandemic. Musculoskelet Sci Pract. 2022 Dec;62:102684. doi: 10.1016/j.msksp.2022.102684. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/36356408 .S2468-7812(22)00185-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Eguia KF, Capio CM. Teletherapy for children with developmental disorders during the COVID-19 pandemic in the Philippines: a mixed-methods evaluation from the perspectives of parents and therapists. Child Care Health Dev. 2022 Nov;48(6):963–9. doi: 10.1111/cch.12965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Eikelboom RH, Bennett RJ, Manchaiah V, Parmar B, Beukes E, Rajasingam SL, De Swanepoel W. International survey of audiologists during the COVID-19 pandemic: use of and attitudes to telehealth. Int J Audiol. 2022 Apr;61(4):283–92. doi: 10.1080/14992027.2021.1957160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Grant CM, Jones A, Land H. Physiotherapists’ perspectives on the use of telehealth for service delivery to children with developmental delays: a qualitative focus group study. Internet J Allied Health Sci Pract. 2022 Mar 31;20(2):1–10. doi: 10.46743/1540-580x/2022.2124. https://nsuworks.nova.edu/ijahsp/vol20/iss2/5/ [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Haines KJ, Sawyer A, McKinnon C, Donovan A, Michael C, Cimoli C, Gregory M, Berney S, Berlowitz DJ. Barriers and enablers to telehealth use by physiotherapists during the COVID-19 pandemic. Physiotherapy. 2023 Mar;118:12–9. doi: 10.1016/j.physio.2022.09.003. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/36308980 .S0031-9406(22)00094-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Hughes L, Petrella A, Phillips N, Taylor RM. Virtual care and the impact of COVID-19 on nursing: a single centre evaluation. J Adv Nurs. 2022 Feb;78(2):498–509. doi: 10.1111/jan.15050. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/34590738 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Kaur M, Eddy EZ, Tiwari D. Exploring practice patterns of pediatric telerehabilitation during COVID-19: a survey study. Telemed J E Health. 2022 Oct;28(10):1505–16. doi: 10.1089/tmj.2021.0506. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/35263191 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Koppel PD, De Gagne JC, Docherty S, Smith S, Prose NS, Jabaley T. Exploring nurse and patient experiences of developing rapport during oncology ambulatory care videoconferencing visits: qualitative descriptive study. J Med Internet Res. 2022 Sep 08;24(9):e39920. doi: 10.2196/39920. https://www.jmir.org/2022/9/e39920/ v24i9e39920 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Nazreen Nihara MR, Seethapathy J. Tele-audiology in India: current and future trends in knowledge, attitude, and practice among audiologists. J Audiol Otol. 2022 Jul;26(3):130–41. doi: 10.7874/jao.2021.00584. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/35538867 .jao.2021.00584 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Parmar B, Beukes E, Rajasingam S. Int J Audiol. 2022 Mar;61(3):228–38. doi: 10.1080/14992027.2021.1921292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Peh HP, Yee K, Mantaring EJ. Changes in telepractice use and perspectives among speech and language therapists in Singapore through the COVID-19 pandemic. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2023 May;58(3):802–12. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.12823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Richter B, Wattenberg I, Vollmer AL, Hornberg C, Wrede B, Lätzsch R. The COVID-19 pandemic as an opportunity for teletherapy? - A survey of non-medical therapy professionals in the health sector. Gesundheitswesen. 2022 Apr;84(4):319–25. doi: 10.1055/a-1537-8933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Tar-Mahomed Z, Kater KA. The perspectives of speech-language pathologists: providing teletherapy to patients with speech, language and swallowing difficulties during a COVID-19 context. S Afr J Commun Disord. 2022 Aug 11;69(2):e1–7. doi: 10.4102/sajcd.v69i2.902. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/36073074 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Van Eerdenbrugh S, Schraeyen K, Leysen H, Mostaert C, D'haenens W, Vandenborre D. Delivery of speech-language therapy and audiology services across the world at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic: a survey. Perspect. 2022 Apr 14;7(2):635–46. doi: 10.1044/2021_PERSP-21-00134. https://pubs.asha.org/doi/full/10.1044/2021_PERSP-21-00134 . [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Wittmeier KD, Hammond E, Tymko K, Burnham K, Janssen T, Pablo AJ, Russell K, Pierce S, Costello C, Protudjer JL. "Another tool in your toolkit": pediatric occupational and physical therapists' perspectives of initiating telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic. Phys Occup Ther Pediatr. 2022;42(5):465–81. doi: 10.1080/01942638.2022.2065898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Beit Yosef A, Maeir T, Khalailh F, Gilboa Y. Perceived feasibility of an occupation-based telerehabilitation intervention for older adults with chronic health conditions in Israel. Hong Kong J Occup Ther. 2022 Jun;35(1):62–70. doi: 10.1177/15691861221080311. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/15691861221080311?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori:rid:crossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub0pubmed .10.1177_15691861221080311 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Kaur M, Eddy EZ, Tiwari D. A survey of physical therapists and occupational therapists to explore practice patterns of pediatric telerehabilitation during COVID-19. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2021 Oct;102(10):e15–6. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2021.07.435. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S000399932100959X . [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Almathami HK, Win KT, Vlahu-Gjorgievska E. Barriers and facilitators that influence telemedicine-based, real-time, online consultation at patients' homes: systematic literature review. J Med Internet Res. 2020 Feb 20;22(2):e16407. doi: 10.2196/16407. https://www.jmir.org/2020/2/e16407/ v22i2e16407 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Scott Kruse C, Karem P, Shifflett K, Vegi L, Ravi K, Brooks M. Evaluating barriers to adopting telemedicine worldwide: a systematic review. J Telemed Telecare. 2018 Jan;24(1):4–12. doi: 10.1177/1357633X16674087. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/1357633X16674087?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori:rid:crossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub0pubmed . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Ramsetty A, Adams C. Impact of the digital divide in the age of COVID-19. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2020 Jul 01;27(7):1147–8. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocaa078. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/32343813 .5826352 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Cortelyou-Ward K, Atkins DN, Noblin A, Rotarius T, White P, Carey C. Navigating the digital divide: barriers to telehealth in rural areas. J Health Care Poor Underserved. 2020;31(4):1546–56. doi: 10.1353/hpu.2020.0116.S1548686920400075 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Venkatesh V, Thong YL, Xu TX. Consumer acceptance and use of information technology: extending the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology. MIS Q. 2012 Mar;36(1):157–78. doi: 10.2307/41410412. https://www.jstor.org/stable/41410412 . [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Ben-David BM, Mentzel M, Icht M, Gilad M, Dor YI, Ben-David S, Carl M, Shakuf V. Challenges and opportunities for telehealth assessment during COVID-19: iT-RES, adapting a remote version of the test for rating emotions in speech. Int J Audiol. 2021 May;60(5):319–21. doi: 10.1080/14992027.2020.1833255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Sprowls GR, Brown JC, Robin BN. The shoulder telehealth assessment tool in transition to distance orthopedics. Arthrosc Tech. 2020 Oct 24;9(11):e1673–81. doi: 10.1016/j.eats.2020.07.008. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2212-6287(20)30181-X .S2212-6287(20)30181-X [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.van Galen LS, Wang CJ, Nanayakkara PW, Paranjape K, Kramer MH, Car J. Telehealth requires expansion of physicians' communication competencies training. Med Teach. 2019 Jun;41(6):714–5. doi: 10.1080/0142159X.2018.1481284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Newcomb AB, Duval M, Bachman SL, Mohess D, Dort J, Kapadia MR. Building rapport and earning the surgical patient's trust in the era of social distancing: teaching patient-centered communication during video conference encounters to medical students. J Surg Educ. 2021 Jan;78(1):336–41. doi: 10.1016/j.jsurg.2020.06.018. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/32709566 .S1931-7204(20)30211-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Adams JE, Ecker DJ. Telehealth: from the abstract to necessity to competency. FASEB Bioadv. 2021 Apr 03;3(7):475–81. doi: 10.1096/fba.2020-00098. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/33821234 .FBA21201 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Shin TM, Ortega P, Hardin K. Educating clinicians to improve telemedicine access for patients with limited English proficiency. Challenges. 2021 Dec 15;12(2):34. doi: 10.3390/challe12020034. https://www.mdpi.com/2078-1547/12/2/34 . [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Wołk K, Marasek K, Glinkowski W. Telemedicine as a special case of machine translation. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2015 Dec;46 Pt 2:249–56. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2015.09.005.S0895-6111(15)00127-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Shulver W, Killington M, Crotty M. 'Massive potential' or 'safety risk'? Health worker views on telehealth in the care of older people and implications for successful normalization. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2016 Oct 12;16(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s12911-016-0373-5. https://bmcmedinformdecismak.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12911-016-0373-5 .10.1186/s12911-016-0373-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Crutchley S, Campbell M, Christiana D. Implementing a school-based telepractice program. Perspect Telepract. 2012 Sep;2(1):31–41. doi: 10.1044/tele2.1.31. https://pubs.asha.org/doi/10.1044/tele2.1.31 . [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Hines M, Lincoln M, Ramsden R, Martinovich J, Fairweather C. Speech pathologists' perspectives on transitioning to telepractice: what factors promote acceptance? J Telemed Telecare. 2015 Dec;21(8):469–73. doi: 10.1177/1357633X15604555.1357633X15604555 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Caplan-Colon L. Coaching parents on feeding techniques via telepractice. American Speech-Language-Hearing Association. 2021. Feb, [2023-02-06]. https://leader.pubs.asha.org/do/10.1044/leader.IPP.26012021.42/full/
- 114.Chi N, Demiris G. The roles of telehealth tools in supporting family caregivers: current evidence, opportunities, and limitations. J Gerontol Nurs. 2017 Feb 01;43(2):3–5. doi: 10.3928/00989134-20170111-04. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.CPME policy on telemedicine. Standing Committee of European Doctors. 2021. [2023-02-21]. https://www.cpme.eu/api/documents/adopted/2021/3/CPME_AD_Board_20032021_012.FINAL_.CPME_.Policy.on_.Telemedicine.pdf .
- 116.Watzlaf VJ, Zhou L, Dealmeida DR, Hartman LM. A systematic review of research studies examining telehealth privacy and security practices used by healthcare providers. Int J Telerehabil. 2017 Nov 20;9(2):39–59. doi: 10.5195/ijt.2017.6231. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/29238448 .ijt-09-39 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Zhou L, Thieret R, Watzlaf V, Dealmeida D, Parmanto B. A telehealth privacy and security self-assessment questionnaire for telehealth providers: development and validation. Int J Telerehabil. 2019 Jun 12;11(1):3–14. doi: 10.5195/ijt.2019.6276. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/31341542 .ijt-11-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Suso-Martí L, La Touche R, Herranz-Gómez A, Angulo-Díaz-Parreño S, Paris-Alemany A, Cuenca-Martínez F. Effectiveness of telerehabilitation in physical therapist practice: an umbrella and mapping review with meta-meta-analysis. Phys Ther. 2021 May 04;101(5):pzab075. doi: 10.1093/ptj/pzab075. https://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/33611598 .6145901 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Alageel SM. Effects of telerehabilitation on occupational therapy services in the coronavirus disease 2019 era: an umbrella and mapping review with meta– meta-analysis. Ann Physiother Occup Ther. 2021 May 24;4(2):1–8. doi: 10.23880/aphot-16000199. https://medwinpublishers.com/APhOT/effects-of-tele-rehabilitation-on-occupational-therapy-services-in-the-coronavirus-disease-2019-era-an-umbrella-and-mapping-review-with-meta-meta-analysis.pdf . [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Weidner K, Lowman J. Telepractice for adult speech-language pathology services: a systematic review. Perspect. 2020 Feb 21;5(1):326–38. doi: 10.1044/2019_persp-19-00146. https://pubs.asha.org/doi/10.1044/2019_PERSP-19-00146 . [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Akemoglu Y, Muharib R, Meadan H. A systematic and quality review of parent-implemented language and communication interventions conducted via telepractice. J Behav Educ. 2019 Nov 11;29(2):282–316. doi: 10.1007/s10864-019-09356-3. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10864-019-09356-3 . [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Marx W, Kelly JT, Crichton M, Craven D, Collins J, Mackay H, Isenring E, Marshall S. Is telehealth effective in managing malnutrition in community-dwelling older adults? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Maturitas. 2018 May;111:31–46. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2018.02.012.S0378-5122(18)30050-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Wade VA, Eliott JA, Hiller JE. Clinician acceptance is the key factor for sustainable telehealth services. Qual Health Res. 2014 May;24(5):682–94. doi: 10.1177/1049732314528809.1049732314528809 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.A free and open source tool for data visualization. RAWGraphs. [2023-07-07]. https://www.rawgraphs.io/
- 125.Home page. InkSpace. [2023-07-07]. https://inkscape.org/
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Search strings used in PubMed and CINAHL databases.
Barriers addressed by the publications according to category and subcategory for each publication.
Full data excel sheet.
Data Availability Statement
The data set analyzed during this study is available in Multimedia Appendix 3.


