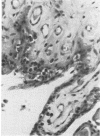
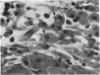
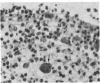
Abstract
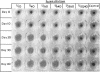
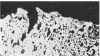
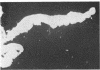
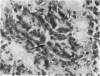
In experimental rabbits it has been shown for the first time that autologous lens protein is antigenic when injected with Freund's complete adjuvant. Although lens haemagglutinins were detected in 6 out of 7 rabbits, in only 3 of the 6 animals did the titre reach a maximum of 1:640. A weak agar precipitation reaction was obtained with only 1 of the 3 sera. It would appear, therefore, that the passive haemagglutination test is superior for the detection of autologous lens antibodies. The response to autologous lens antigen both in magnitude as well as in duration varied in different rabbits, which suggested to us the possible role played by a central control mechanism involving the immune-response (Ir) and immune-associated (Ia) genes which are part of the major histocompatibility complex. Alternatively, this variation may be the result of an antigenic competition between various autologous crystallins. Antibodies to autologous lens protein as detected by immunofluorescence and immunoperoxidase techniques were shown to be of the IgG class. Systemic autologous immunisation produces only a mild uveitis and does not lead to a granulomatous intraocular inflammation. Intravitreal injections of autologous lens protein in pre-immunised animals, however, produced an Arthus type of acute endophthalmitis. Autologous lens antisera showed limited cross-reactivity with ocular and extraocular tissues, which could be detected only by such sensitive techniques as immunofluorescence and immunoperoxidase methods.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ellman L., Green I., Martin W. J., Benacerraf B. Linkage between the poly-L-lysine gene and the locus controlling the major histocompatibility antigens in strain 2 guinea pigs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):322–328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kincses E., Szabó G. Cell-mediated and humoral immune response after lens injury. Mod Probl Ophthalmol. 1976;16:95–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manski W., Halbert S. P., Javier P. Comparison of rabbit antilens antibodies indused by iso- and heteroimmunization. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jun 30;124(1):352–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb18970.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marak G. E., Font R. L., Alepa F. P. Experimental lens-induced granulomatous endophthalmitis. Mod Probl Ophthalmol. 1976;16:75–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra R. N., Rahi A. H., Morgan G. Immunopathology of the lens. II. Humoral and cellular immune responses to homologous lens antigens and their roles in ocular inflammation. Br J Ophthalmol. 1977 Apr;61(4):285–296. doi: 10.1136/bjo.61.4.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro A. J., Taussig M. J. Two genes in the major histocompatibility complex control immune response. Nature. 1975 Jul 10;256(5513):103–106. doi: 10.1038/256103a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahi A. H., Chignell A. H. Immunoelectrophoretic analysis of subretinal fluid and its diagnostic significance. Trans Ophthalmol Soc U K. 1975 Apr;95(1):180–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahi A. H., Misra R. N., Morgan G. Immunopathology of the lens. I. Humoral and cellular immune responses to heterologous lens antigens and their roles in ocular inflammation. Br J Ophthalmol. 1977 Mar;61(3):164–176. doi: 10.1136/bjo.61.3.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taussig M. J., Mozes E., Shearer G. M., Sela M. Antigenic competition and genetic control of the immune response. A hypothesis for intramolecular competition. Cell Immunol. 1973 Aug;8(2):299–310. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90119-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber G., Kölsch E. Transfer of low zone tolerance to normal syngeneic mice by theta-positive cells. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Dec;3(12):767–772. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]