Abstract
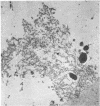
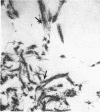
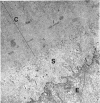
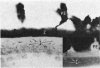
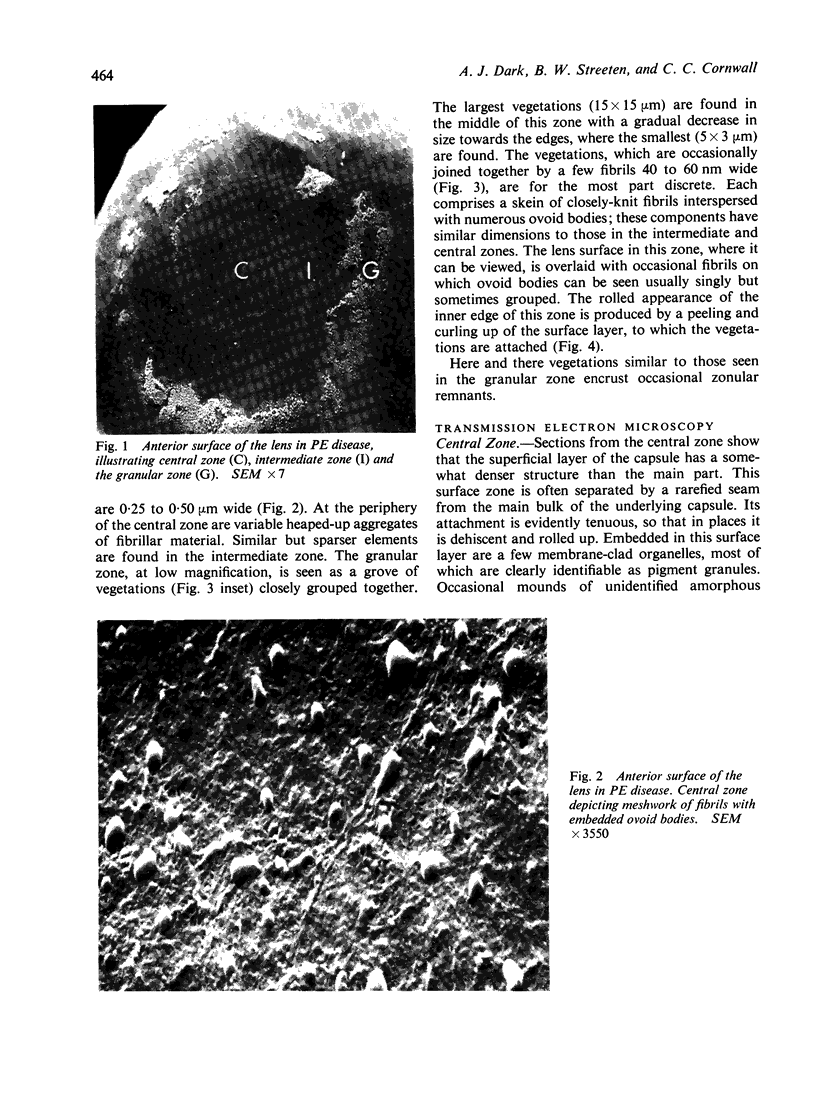
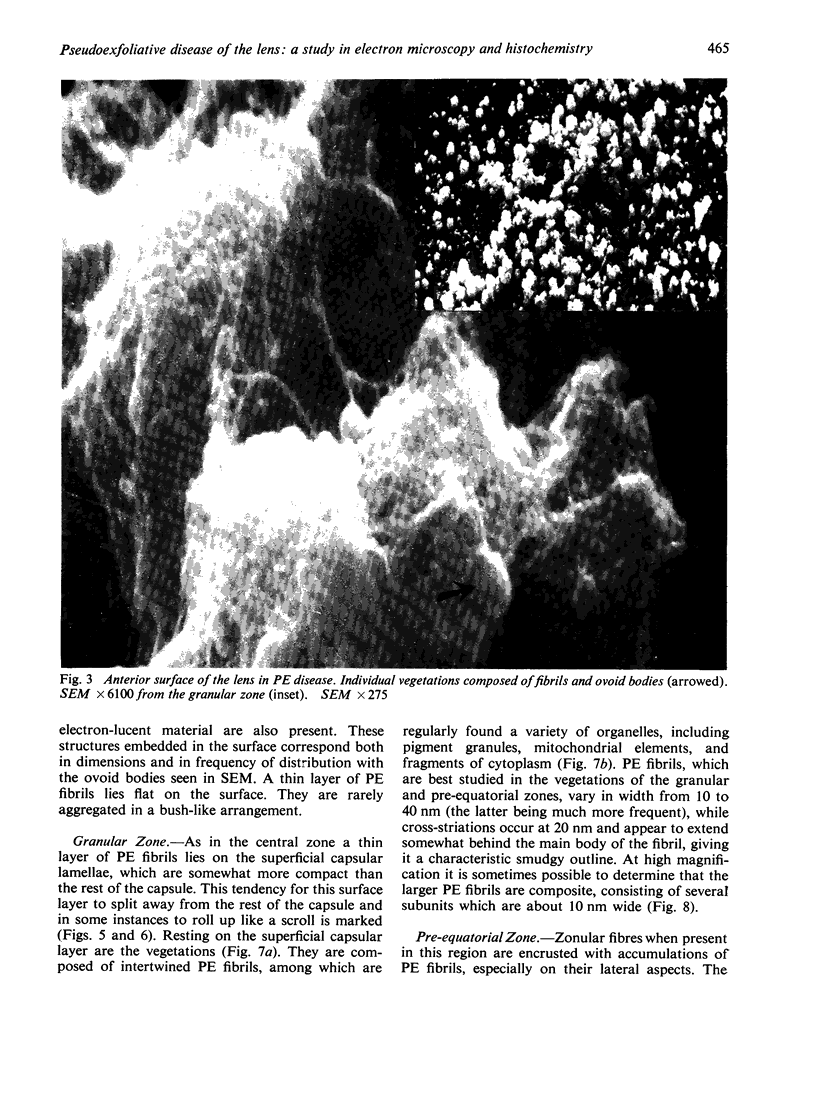
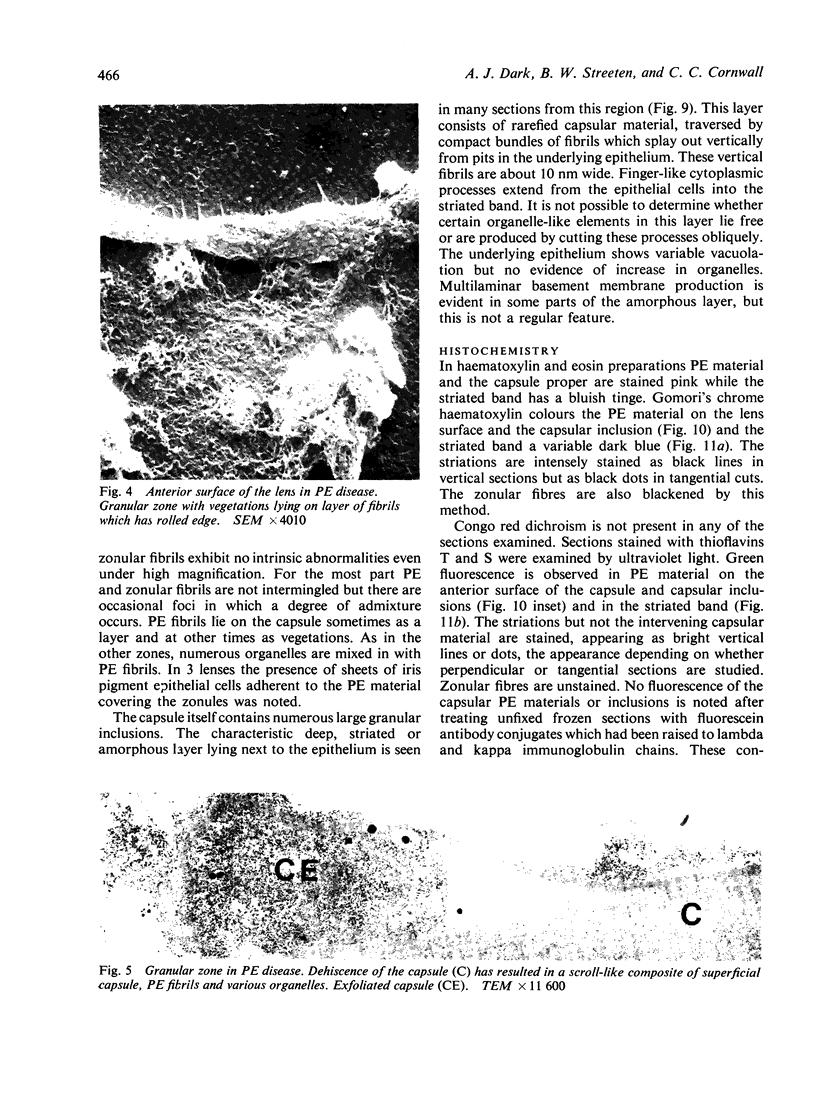
The anterior lens capsule in pseudoexfoliative (PE) disease has been investigated with scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. It shows several distinct zones which correlate with those seen clinically. True exfoliation of the anterior lens capsule is shown as an integral pathologic feature of PE disease. PE fibrils are mixed with various degraded cell products, including organelles, of which uveal pigment granules are the most frequent. Sheets of degenerating iris pigment epithelium as well as individual cells are often firmly adherent to the pre-equatorial lens capsule and zonules. PE fibrils on the capsule are 35 to 40 nm in width, often showing several subunit filaments about 10 nm wide. PF filaments forming vertical bundles in the pre-equatorial capsule are 10 nm wide, but show little tendency to aggregate laterally. Histochemical and ultrastructural properties of both types of PE fibril and those of the capsular inclusion suggest that they are closely related fibrillar proteins. PE fibrils share some of the characteristics of amyloid but are not identical substances. Nevertheless, a similar mechanism of synthesis is suggested. The participation of non-lenticular sites in the formation of PE fibrils is not precluded by this hypothesis.
Full text
PDF

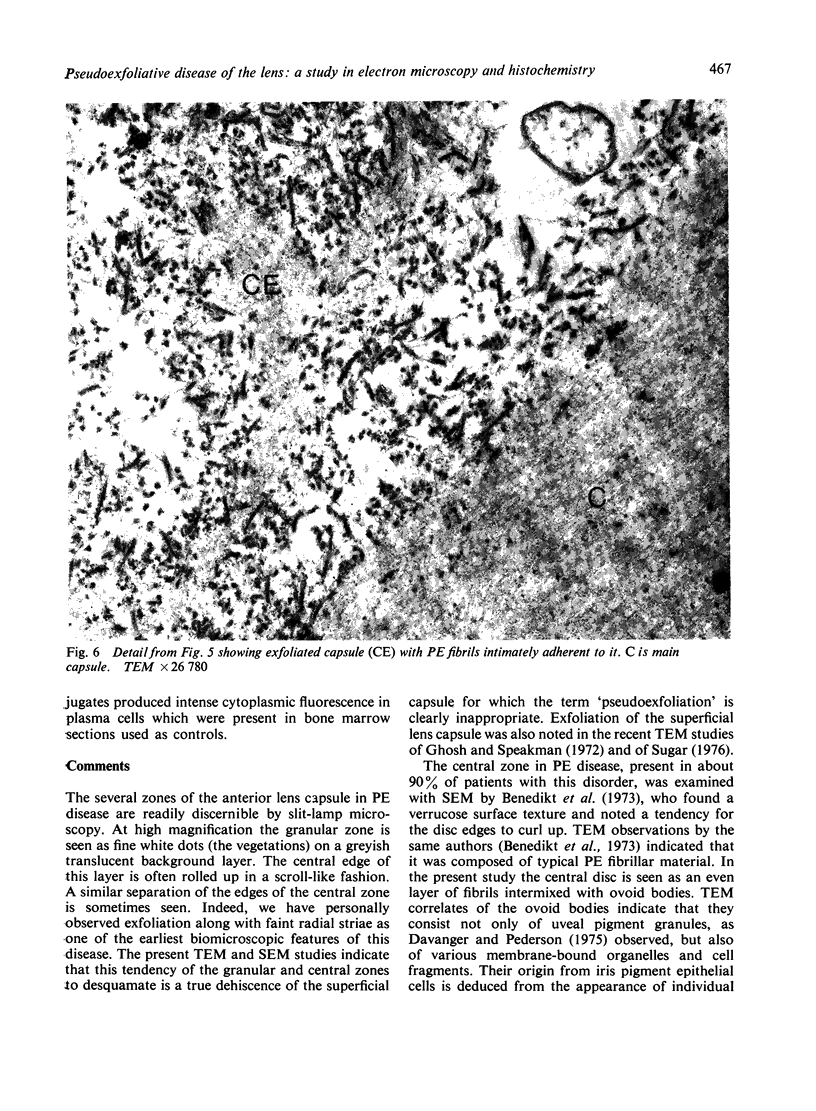



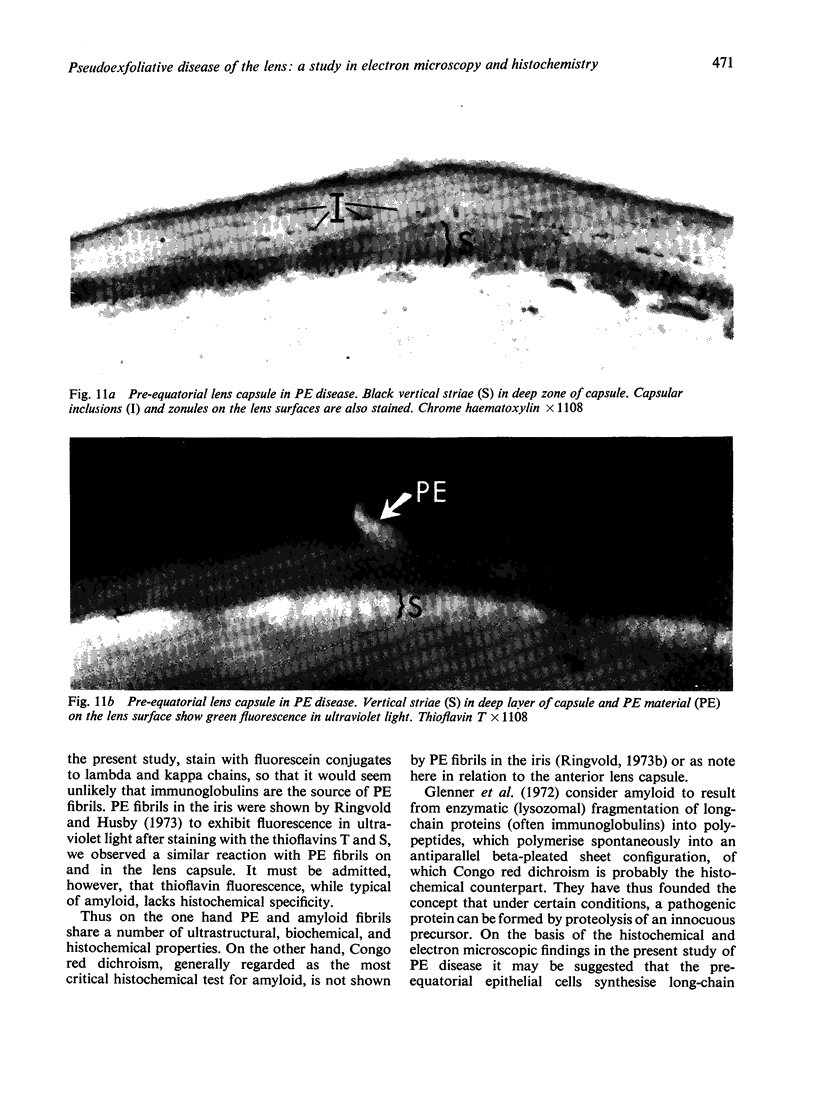

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASHTON N., SHAKIB M., COLLYER R., BLACH R. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF PSEUDO-EXFOLIATION OF THE LENS CAPSULE. I. LENS CAPSULE AND ZONULAR FIBERS. Invest Ophthalmol. 1965 Apr;4:141–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERTELSEN T. I., DRABLOES P. A., FLOOD P. R. THE SOCALLED SENILE EXFOLIATION (PSEUDOEXFOLIATION) OF THE ANTERIOR LENS CAPSULE, A PRODUCT OF THE LENS EPITHELIUM. FIBRILLOPATHIA EPITHELIOCAPSULARIS. A MICROSCOPIC, HISTOCHEMIC AND ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC INVESTIGATION. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1964;42:1096–1113. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1964.tb03676.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomew R. S. Lens displacement associated with pseudocapsular exfoliation. A report on 19 cases in the Southern Bantu. Br J Ophthalmol. 1970 Nov;54(11):744–750. doi: 10.1136/bjo.54.11.744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomew R. S. Pseudo-capsular exfoliation in the Bantu of South Africa. I. Early or pre-granular clinical stage. Br J Ophthalmol. 1971 Oct;55(10):693–699. doi: 10.1136/bjo.55.10.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedikt O., Gottinger W., Auböck L. Klinik und Ultrastruktur der zentralen Scheibe beim sogenannten Exfoliationssyndrom. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1973;51(2):211–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1973.tb03798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertelsen T. I., Ehlers N. Morphological and histochemical studies on fibrillopathia epitheliocapsularis. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1969;47(3):476–488. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1969.tb08133.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DVORAK-THEOBALD G. Pseudo-exfoliation of the lens capsule: relation to true exfoliation of the lens capsule as reported in the literature and role in the production of glaucoma capsulocuticulare. Am J Ophthalmol. 1954 Jan;37(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dark A. J., Streeten B. W., Jones D. Accumulation of fibrillar protein in the aging human lens capsule, with special reference to the pathogenesis of pseudoexfoliative disease of the lens. Arch Ophthalmol. 1969 Dec;82(6):815–821. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1969.00990020807016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davanger M., Pedersen O. O. Pseudo-exfoliation material on the anterior lens surface. Demonstration and examination of an interfibrillar ground substance. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1975 Mar;53(1):3–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1975.tb01133.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davanger M. The pseudo-exfoliation syndrome. A scanning electron microscopic study. I. The anterior lens surface. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1975 Dec;53(6):809–820. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1975.tb00399.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson D. H., Ramsay M. S. Fibrillopathia epitheliocapsularis (pseudoexfoliation): a clinical and electron microscope study. Can J Ophthalmol. 1975 Apr;10(2):148–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIFFORD H., Jr A clinical and pathologic study of exfoliation of the lens capsule. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1957;55:189–216. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh M., Speakman J. S. Inclusions in human lens capsule and their relationship to senile exfoliation. Can J Ophthalmol. 1972 Oct;7(4):413–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh M., Speakman J. S. The ciliary body in senile exfoliation of the lens. Can J Ophthalmol. 1973 Jul;8(3):394–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh M., Speakman J. S. The iris in senile exfoliation of the lens. Can J Ophthalmol. 1974 Jul;9(3):289–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Terry W. D., Isersky C. Amyloidosis: its nature and pathogenesis. Semin Hematol. 1973 Jan;10(1):65–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringvold A. A preliminary report on the amino acid composition of the pseudo-exfoliation material (PE material). Exp Eye Res. 1973 Jan 1;15(1):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(73)90187-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringvold A., Husby G. Pseudo-exfoliation material--an amyloid-like substance. Exp Eye Res. 1973 Nov 11;17(3):289–299. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(73)90180-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringvold A. On the occurrence of pseudo-exfoliation material in extrabulbar tissue from patients with pseudo-exfoliation syndrome of the eye. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1973;51(3):411–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1973.tb06018.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speakman J. S., Ghosh M. The conjunctiva in senile lens exfoliation. Arch Ophthalmol. 1976 Oct;94(10):1757–1759. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1976.03910040531012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugar H. S. The exfoliation syndrome: source of the fibrillar material on the capsule. Surv Ophthalmol. 1976 Jul-Aug;21(1):59–64. doi: 10.1016/0039-6257(76)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]