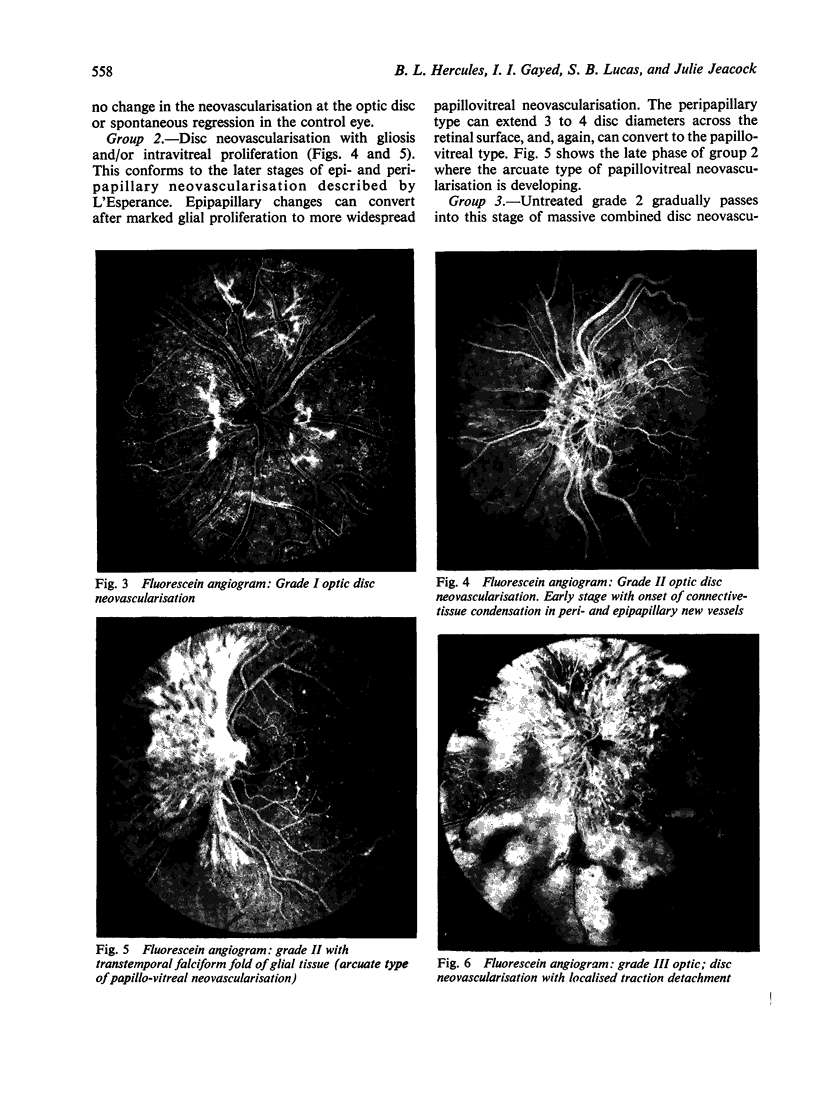
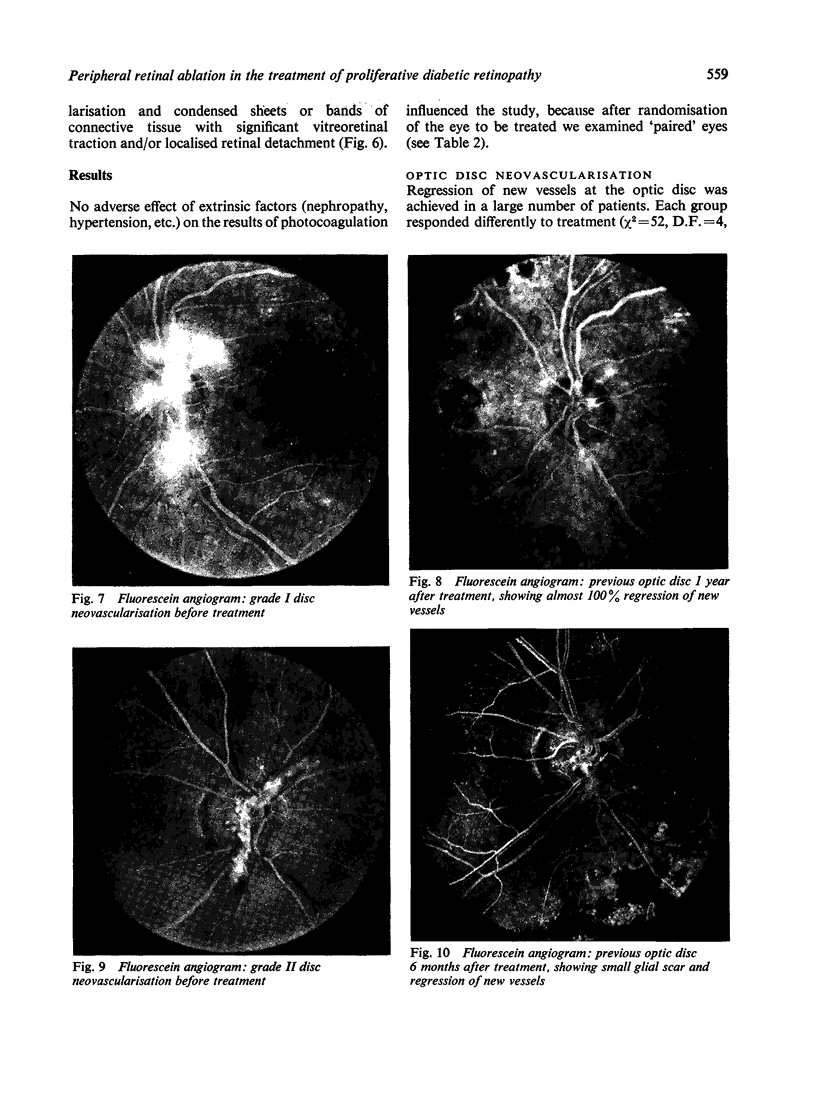
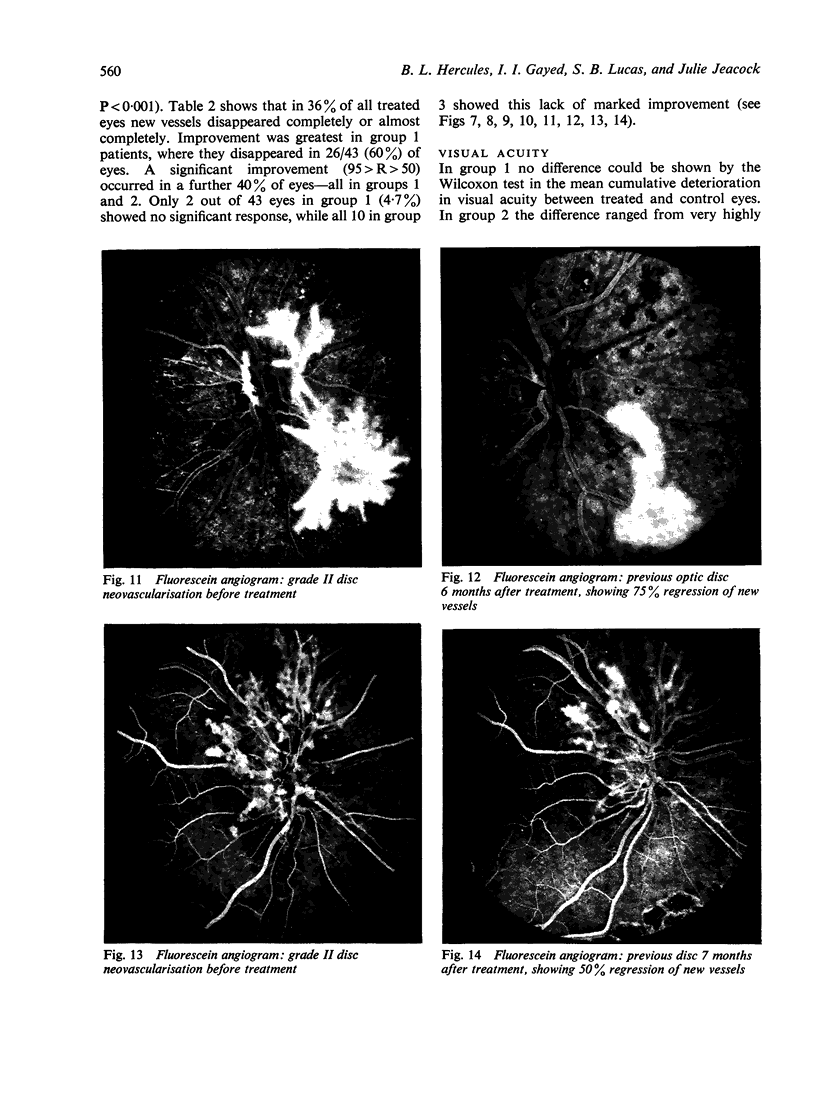
Abstract
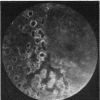
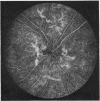
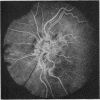
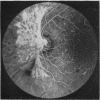
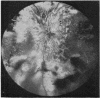
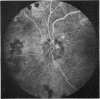
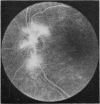
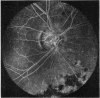
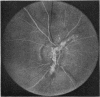
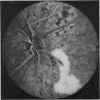
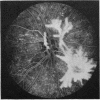
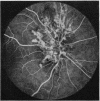
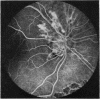
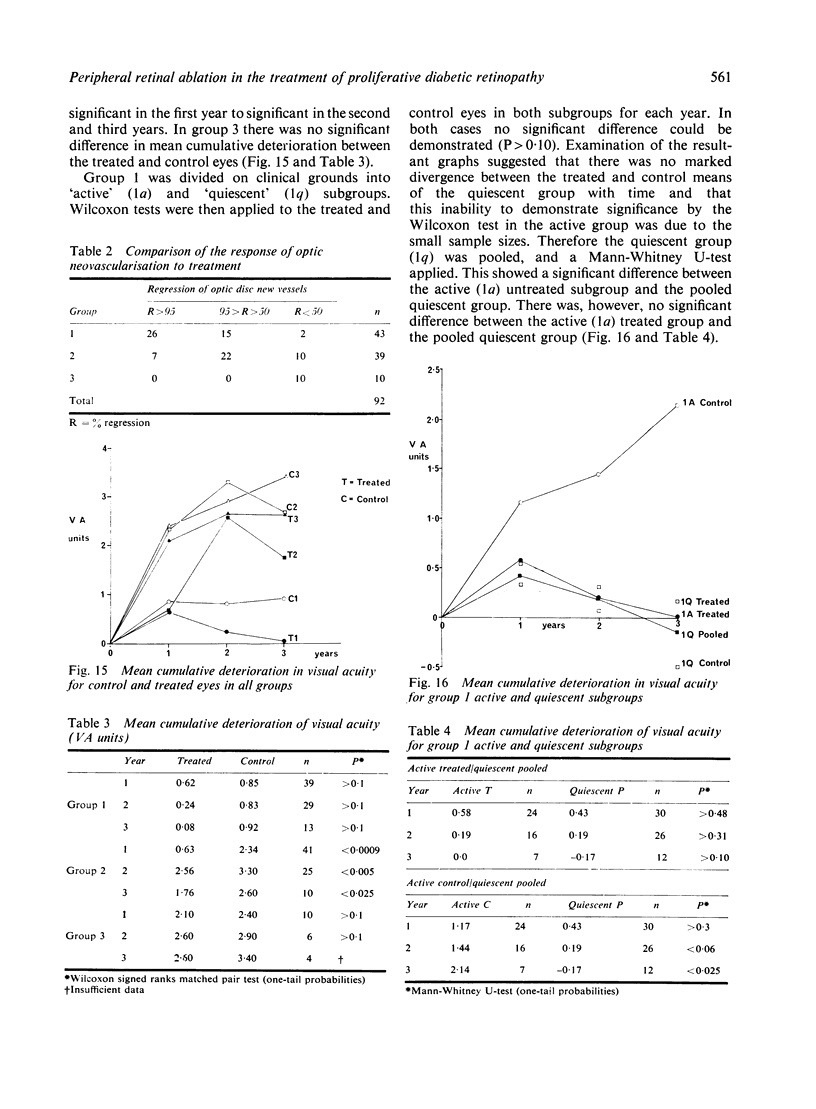
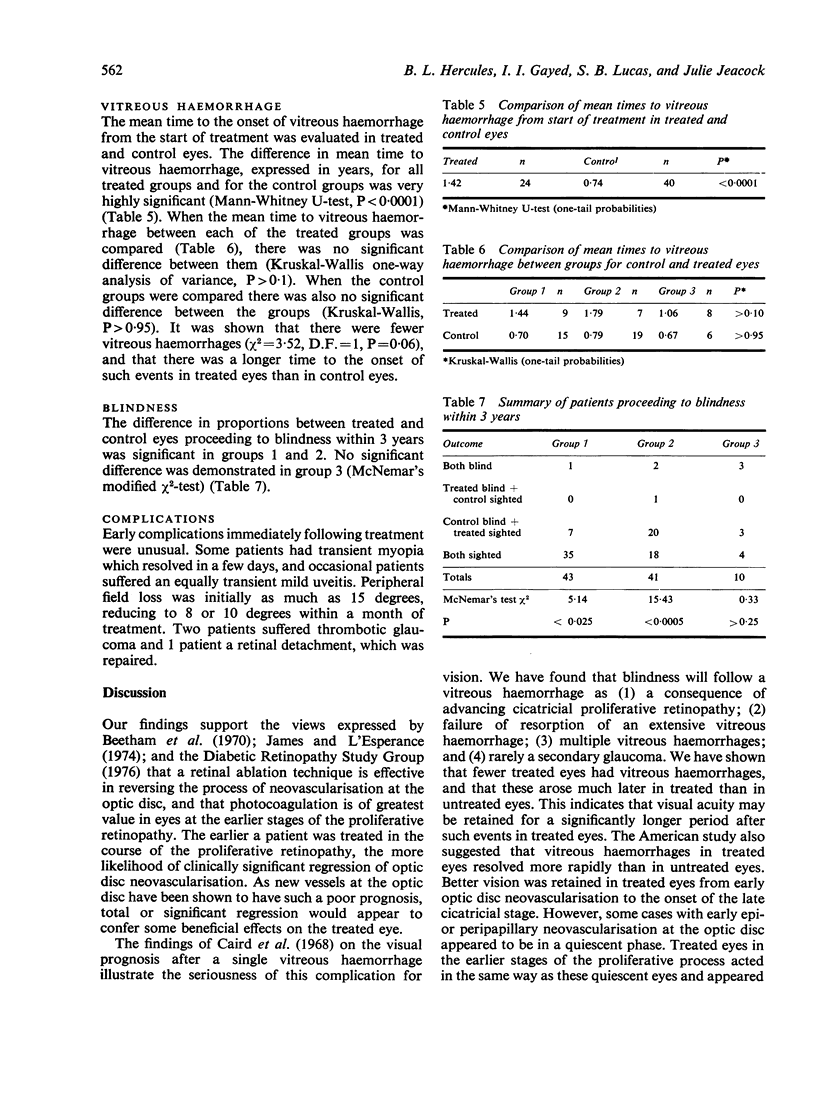
A randomised controlled trial is reported of 94 patients with a symmetrical proliferative diabetic retinopathy involving the optic disc, who were treated by a peripheral retinal ablation technique using the argon laser. A highly significant difference in mean cumulative deterioration of visual acuity and blindness was shown in all but the late stages of the disease process between treated and untreated eyes. The untreated eyes exhibited far worse results. The earlier photocoagulation is initiated in the course of the proliferative process in this disease to control or preferably eliminate optic disc neovascularisation, the better the visual prognosis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beetham W. P., Aiello L. M., Balodimos M. C., Koncz L. Ruby laser photocoagulation of early diabetic neovascular retinopathy. Preliminary report of a long-term controlled study. Arch Ophthalmol. 1970 Mar;83(3):261–272. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1970.00990030263001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caird F. I., Burditt A. F., Draper G. J. Diabetic retinopathy. A further study of prognosis for vision. Diabetes. 1968 Mar;17(3):121–123. doi: 10.2337/diab.17.3.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deckert T., Simonsen S. E., Poulsen J. E. Prognosis of proliferative retinopathy in juvenile diabetics. Diabetes. 1967 Oct;16(10):728–733. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.10.728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James W. A., Jr, L'Esperance F. A. Treatment of diabetic optic nerve neovascularization by extensive retinal photocoagulation. Am J Ophthalmol. 1974 Dec;78(6):939–947. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(74)90806-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krill A. E., Archer D. B., Newell F. W., Chishti M. I. Photocoagulation in diabetic retinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1971 Aug;72(2):299–321. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(71)91300-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krill A. E., Archer D., Newell F. W. Photocoagulation in complications secondary to branch vein occlusion. Arch Ophthalmol. 1971 Jan;85(1):48–60. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1971.00990050050008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- L'Esperance F. A., Jr An opthalmic argon laser photocoagulation system: design, construction, and laboratory investigations. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1968;66:827–904. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little H. L., Zweng H. C., Jack R. L., Vassiliadis A. Techniques of argon laser photocoagulation of diabetic disk new vessels. Am J Ophthalmol. 1976 Nov;82(5):675–683. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(76)90001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYER-SCHWICKERATH G. Lichtkoagulation; eine Methode zur Behandlung und Verhütung der Netzhautablösung. Albrecht Von Graefes Arch Ophthalmol. 1954;156(1):2–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okun E. The effectiveness of photocoagulation in the therapy of proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR). (A controlled study in 50 patients). Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1968 Mar-Apr;72(2):246–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patz A., Berkow J. W. Visual and systemic prognosis in diabetic retinopathy. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1968 Mar-Apr;72(2):253–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor E., Dobree J. H. Proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Site and size of initial lesions. Br J Ophthalmol. 1970 Jan;54(1):11–18. doi: 10.1136/bjo.54.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]