Abstract
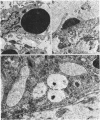
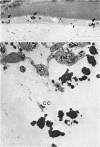
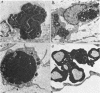
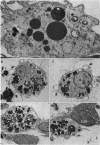
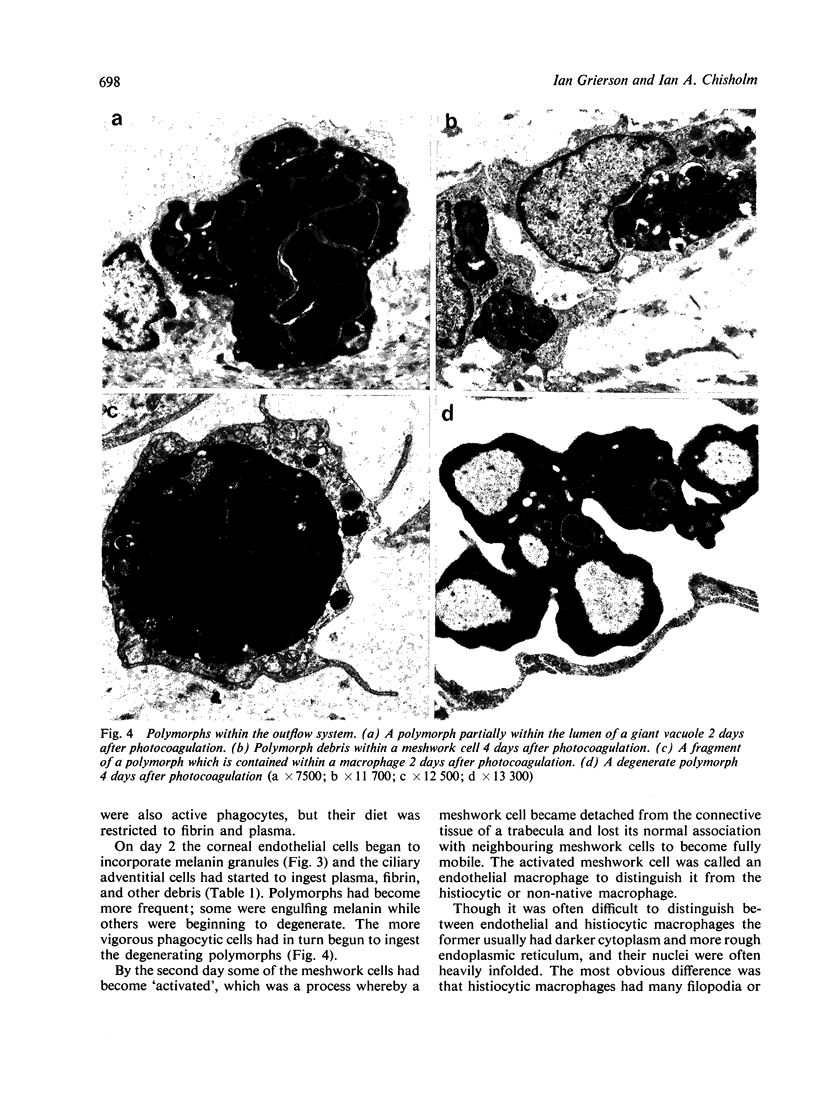
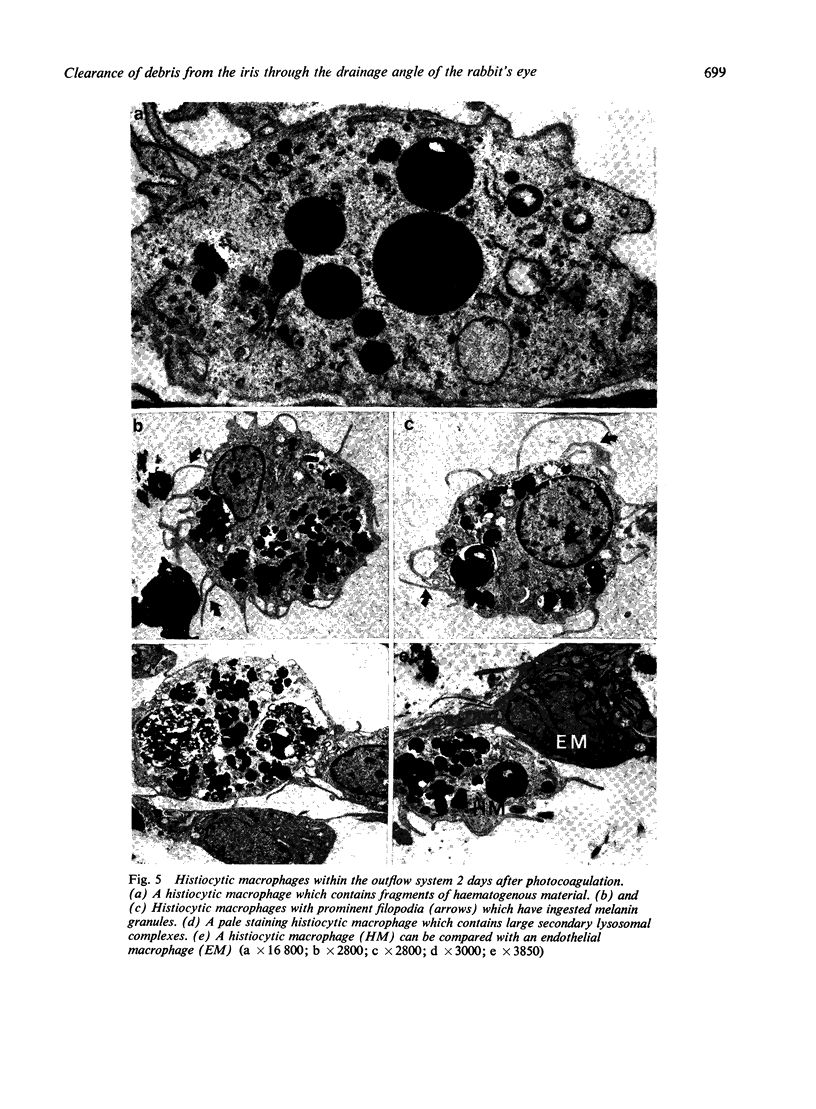
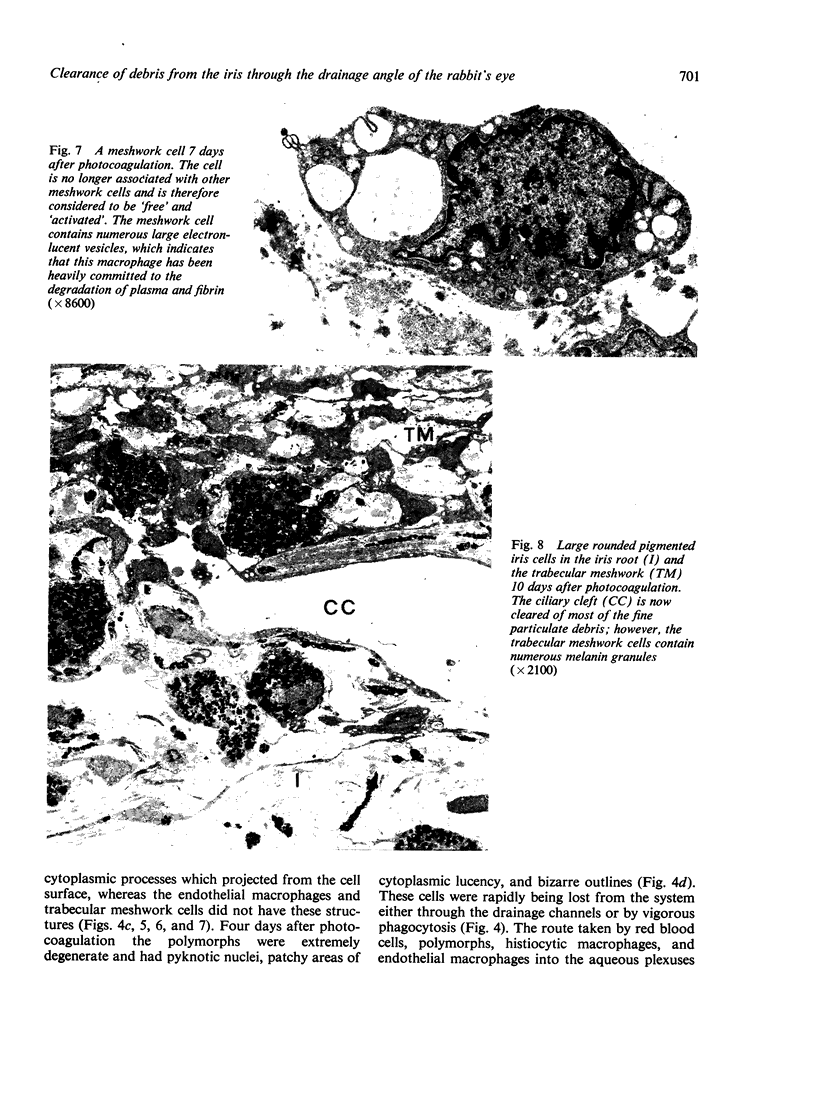
The fate of particulate material on entering the drainage angle of the rabbit's eye was investigated by transmission electron microscopy. The infiltrate was produced by photocoagulation of the iris. Initially it consisted of plasma, connective tissue and cellular debris, fibrin, and red blood cells. Later, free melanin granules, polymorphs, macrophages, and iris clump cells were all seen to enter the drainage system. Native meshwork cells were found to be active phagocytes and began to degrade various components of the infiltrate within 2 hours of the formation of the iris lesions. Corneal endothelial cells, the cells which cover the iris pillars, and the adventitial cells of the ciliary body were less active but were also phagocytic.
Full text
PDF

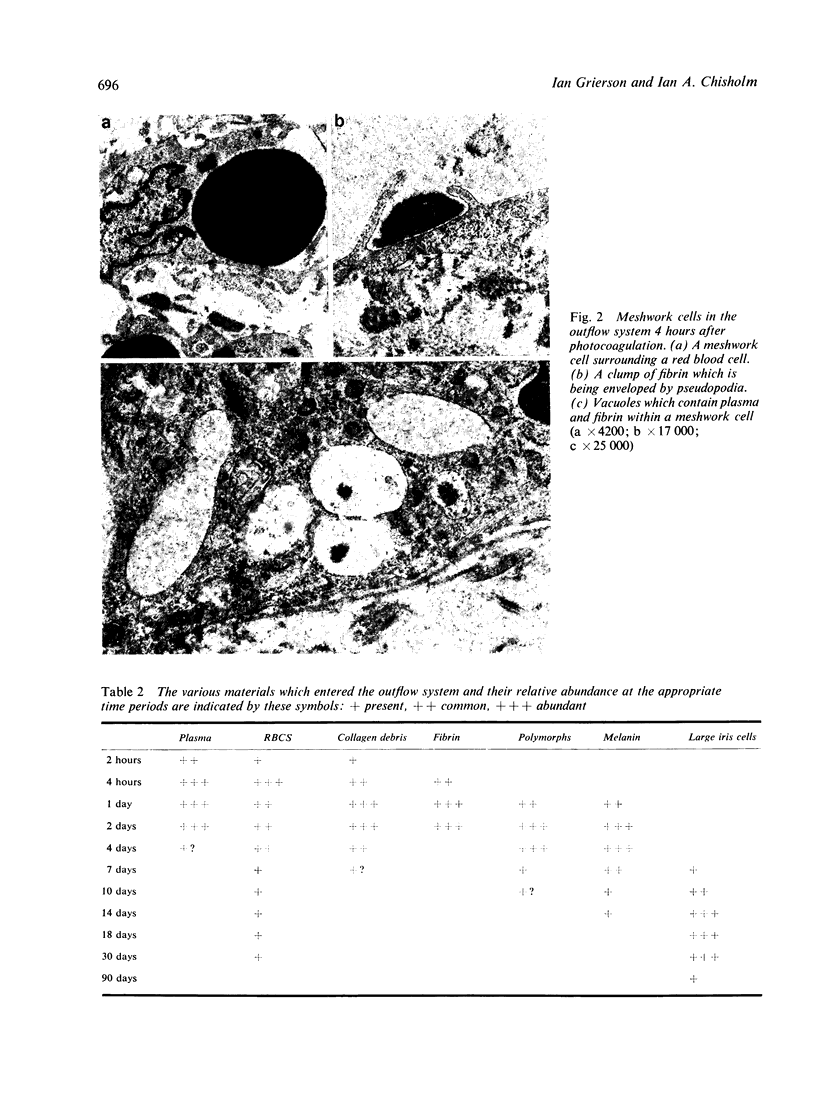





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bill A. Editorial: The drainage of aqueous humor. Invest Ophthalmol. 1975 Jan;14(1):1–3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisholm I. A., Grierson I. Particulate phagocytosis by trabecular meshwork endothelium. Can J Ophthalmol. 1977 Oct;12(4):293–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINE B. S. OBSERVATIONS ON THE DRAINAGE ANGLE IN MAN AND RHESUS MONKEY: A CONCEPT OF THE PATHOGENESIS OF CHRONIC SIMPLE GLAUCOMA. A LIGHT AND ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY. Invest Ophthalmol. 1964 Dec;3:609–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeney L. Outflow studies using an electron dense tracer. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1966 Sep-Oct;70(5):791–798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grierson I., Lee W. R. Changes in the monkey outflow apparatus at graded levels of intraocular pressure: a qualitative analysis by light microscopy and scanning electron microscopy. Exp Eye Res. 1974 Jul;19(1):21–33. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(74)90068-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grierson I., Lee W. R. Erythrocyte phagocytosis in the human trabecular meshwork. Br J Ophthalmol. 1973 Jun;57(6):400–415. doi: 10.1136/bjo.57.6.400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grierson I., Lee W. R. Pressure-induced changes in the ultrastructure of the endothelium lining Schlemm's canal. Am J Ophthalmol. 1975 Nov;80(5):863–884. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(75)90284-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inomata H., Bill A., Smelser G. K. Aqueous humor pathways through the trabecular meshwork and into Schlemm's canal in the cynomolgus monkey (Macaca irus). An electron microscopic study. Am J Ophthalmol. 1972 May;73(5):760–789. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(72)90394-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto T., Witmer R., Landolt E. Light and electron microscopy in absolute glaucoma with pigment dispersion phenomena and contusion angle deformity. Am J Ophthalmol. 1971 Aug;72(2):420–434. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(71)91315-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. R. The study of the passage of particles through the endothelium of the outflow apparatus of the monkey eye by scanning and transmission electron microscopy. Trans Ophthalmol Soc U K. 1971;91:687–705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacRae D., Sears M. L. Peroxidase passage through the outflow channels of human and rhesus eyes. Exp Eye Res. 1970 Jul;10(1):15–18. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(70)80004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringvold A., Vegge T. Electron microscopy of the trabecular meshwork in eyes with exfoliation syndrome. (Pseudoexfoliation of the lens capsule). Virchows Arch A Pathol Pathol Anat. 1971;353(2):110–127. doi: 10.1007/BF00548971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohen J. W., van der Zypen E. The phagocytic activity of the trabecularmeshwork endothelium. An electron-microscopic study of the vervet (Cercopithecus aethiops). Albrecht Von Graefes Arch Klin Exp Ophthalmol. 1968;175(2):143–160. doi: 10.1007/BF02385060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shabo A. L., Maxwell D. S. Observations on the fate of blood in the anterior chamber. A light and electron microscopic study of the monkey trabecular meshwork. Am J Ophthalmol. 1972 Jan;73(1):25–36. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(72)90300-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi R. C. Mechanism of the aqueous outflow across the trabecular wall of Schlemm's canal. Exp Eye Res. 1971 Jan;11(1):116–121. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(71)80073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi R. C. Ultrastructure of Schlemm's canal in relation to aqueous outflow. Exp Eye Res. 1968 Jul;7(3):335–341. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(68)80047-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita T., Rosen D. A. Electron microscopic study of trabecular meshwork in clinical and experimental glaucoma with anterior chamber hemorrhage. Am J Ophthalmol. 1965 Sep;60(3):427–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Zypen E. Experimental morphological study on structure and function of the filtration angel of the rat eye. Ophthalmologica. 1977;174(5):285–298. doi: 10.1159/000308617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]