Abstract
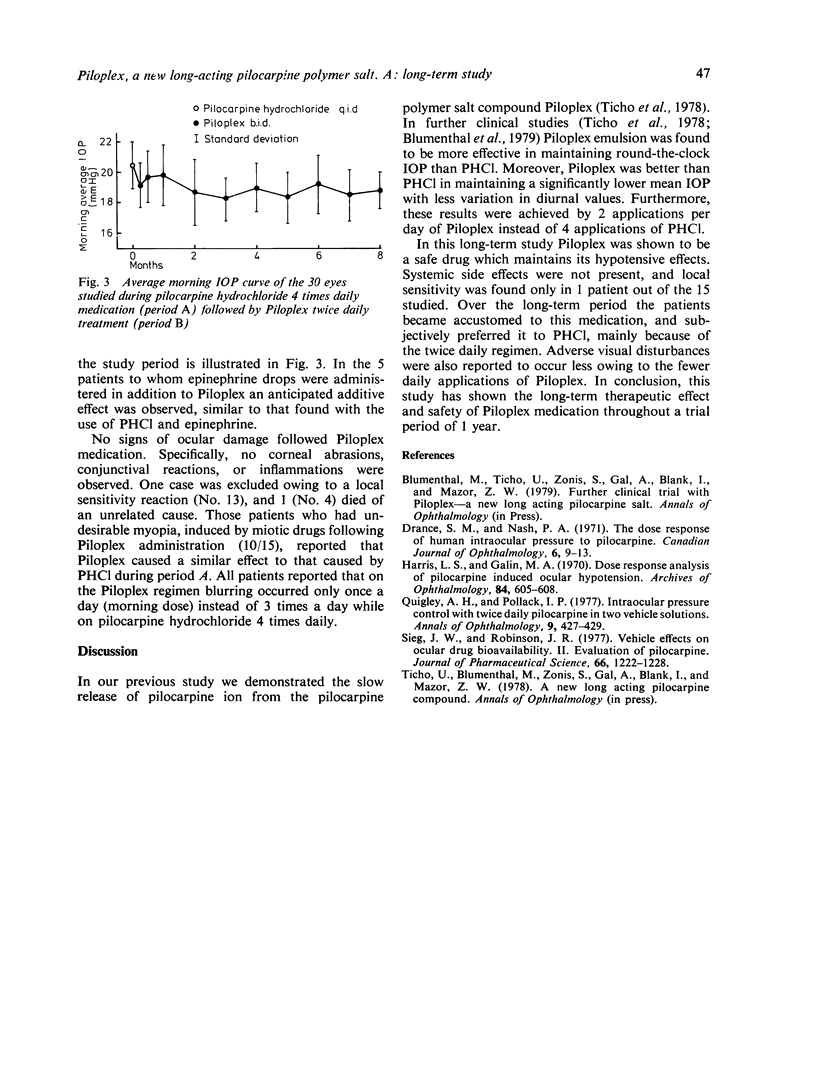
Thirty eyes of 15 patients with open-angle glaucoma were followed up for a period of up to 1 year while being treated with Piloplex eye drops containg a new long-acting pilocarpine polymer salt. Average morning intraocular pressure (IOP) values during treatment with pilocarpine hydrochloride administered 4 times daily was 20.5 mmHg. Average morning IOP values during Piloplex medication administered only twice daily were 19.8 to 18.2 mmHg (range of averages on 14 sessions). These findings indicate the lower average pressure during Piloplex medication and show its prolonged hypotensive effect. Both medications contained an equivalent total daily amount of pilocarpine. Throughout the 1-year study period no adverse side effects were reported, and only 1 patient complained of local sensitivity reaction. Visual disturbances characteristic of pilocarpine eye drops were reduced from 3 times a day on pilocarpine hydrochloride 4 times daily to once a day on Piloplex twice daily.
Full text
PDF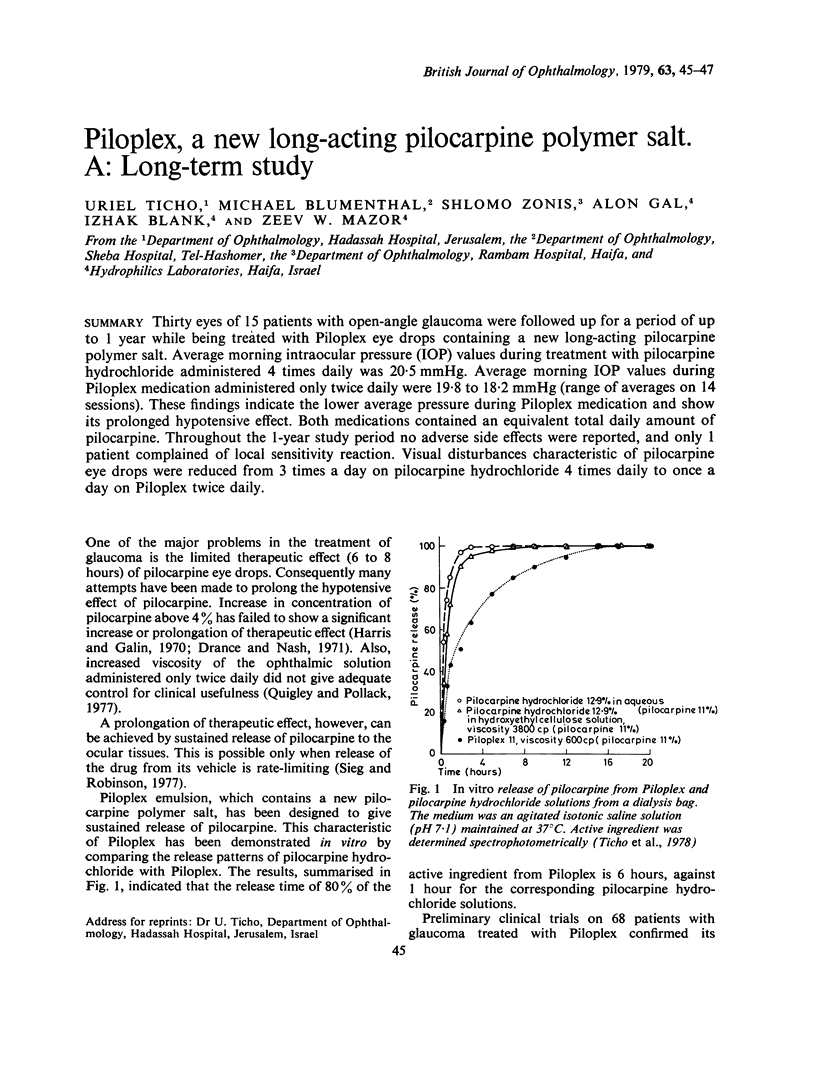

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Drance S. M., Nash P. A. The dose response of human intraocular pressure to pilocarpine. Can J Ophthalmol. 1971 Jan;6(1):9–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris L. S., Galin M. A. Dose response analysis of pilocarpine-induced ocular hypotension. Arch Ophthalmol. 1970 Nov;84(5):605–608. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1970.00990040607008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley H. A., Pollack I. P. Intraocular pressure control with twice-daily pilocarpine in two vehicle solutions. Ann Ophthalmol. 1977 Apr;9(4):427–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieg J. W., Robinson J. R. Vehicle effects on ocular drug bioavailability II: Evaluation of pilocarpine. J Pharm Sci. 1977 Sep;66(9):1222–1228. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600660905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


