Abstract
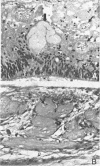
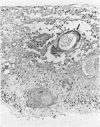
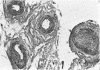
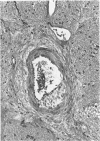
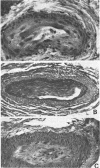
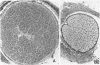
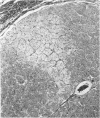
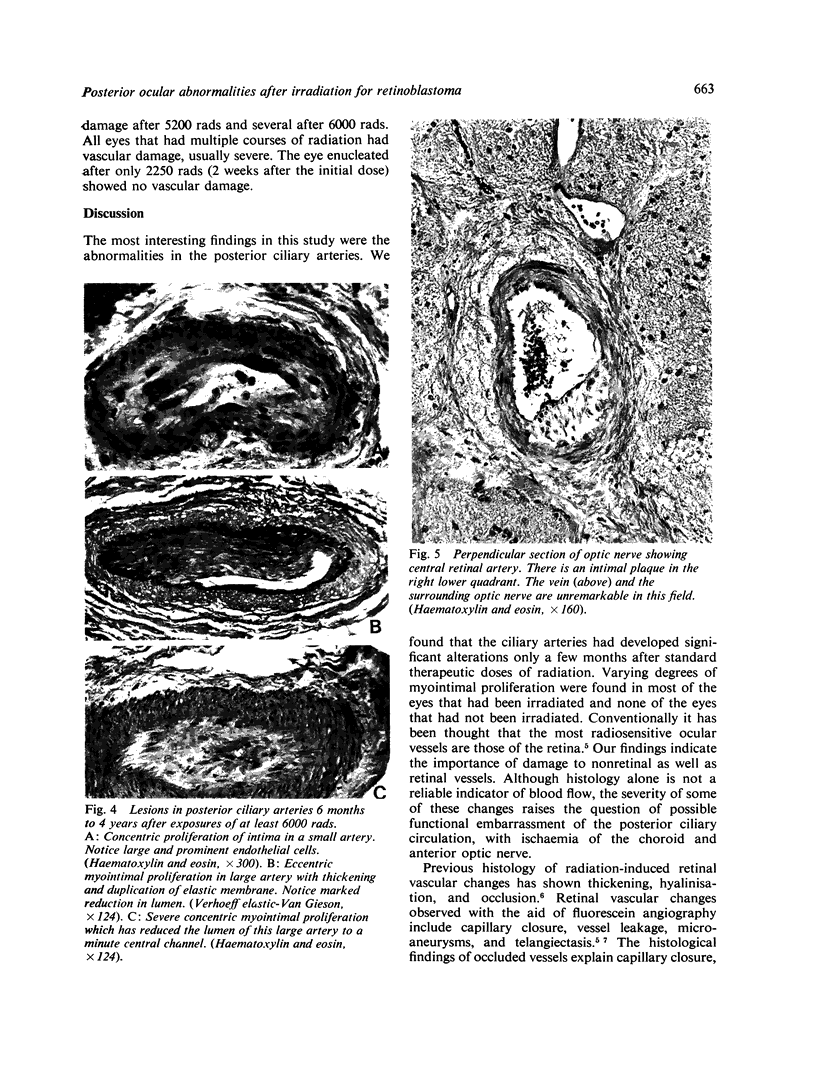
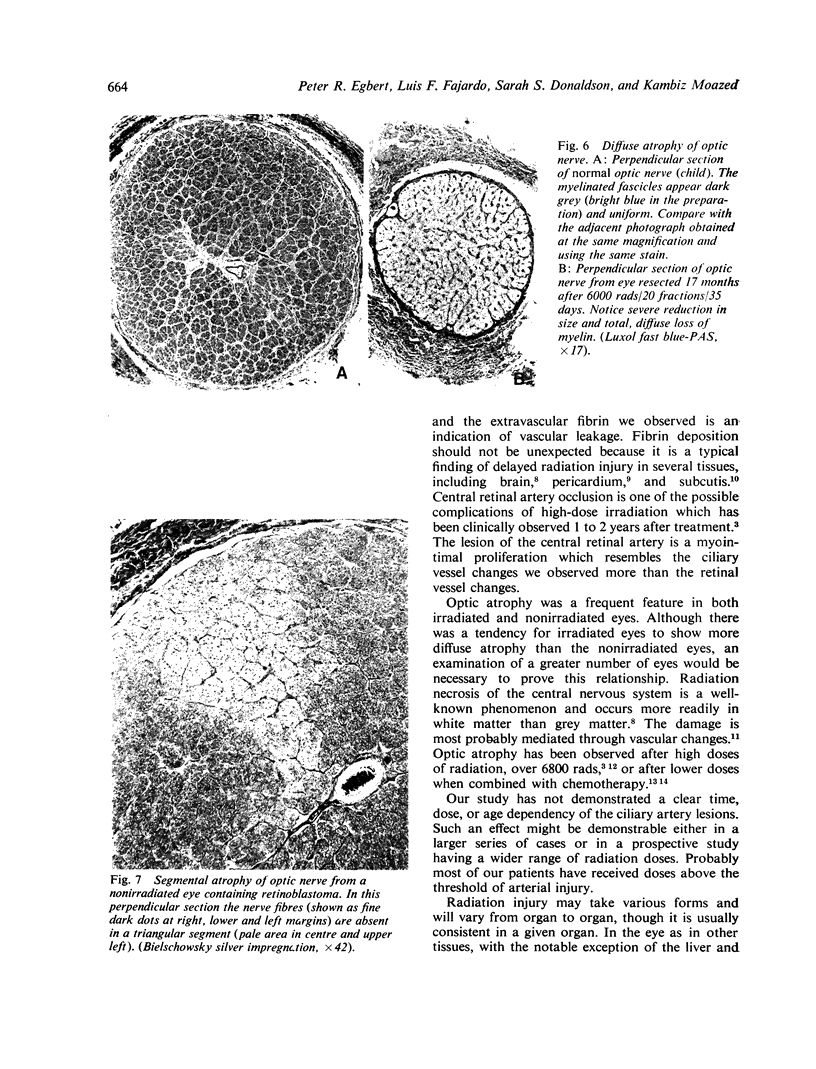
Radiation-induced ocular lesions in the posterior eye and orbit were investigated in 33 surgical specimens of patients with retinoblastoma. The eyes were obtained from children 7 months to 6 years of age. Seventeen eyes were irradiated; 16 eyes had not received irradiation and served as controls. The majority of the irradiated eyes were treated with 6000 rads of external beam radiation. They were removed at a mean of 23 months after radiotherapy. All specimens were examined simultaneously by 2 observers without knowledge of treatment and analysed for the presence or absence of 15 lesions. The most consistent lesions in the irradiated eyes were abnormalities of the retinal vessels (11 of 17 eyes) and striking changes in the ciliary arteries (13 of 17 eyes). The retinal vessels showed thickening of the wall, often caused by deposition of fibrillary material, sometimes with fibrin deposits. The most consistent lesion was myointimal proliferation with narrowing of the ciliary arteries. Lesions of the central retinal artery were less common but occurred only in irradiated patients.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chan R. C., Shukovsky L. J. Effects of irradiation on the eye. Radiology. 1976 Sep;120(3):673–675. doi: 10.1148/120.3.673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chee P. H. Radiation retinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1968 Nov;66(5):860–865. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(68)92800-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egbert P. R., Donaldson S. S., Moazed K., Rosenthal A. R. Visual results and ocular complications following radiotherapy for retinoblastoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 1978 Oct;96(10):1826–1830. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1978.03910060338008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajardo L. F., Berthrong M. Radiation injury in surgical pathology. Part I. Am J Surg Pathol. 1978 Jun;2(2):159–199. doi: 10.1097/00000478-197806000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajardo L. F., Stewart J. R. Experimental radiation-induced heart disease. I. Light microscopic studies. Am J Pathol. 1970 May;59(2):299–316. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman M. L., Bean S. C., Cogan D. G. Optic atrophy following prophylactic chemotherapy and cranial radiation for acute lymphocytic leukemia. Am J Ophthalmol. 1976 Oct;82(4):571–576. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(76)90544-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haymaker W., Ibrahim M. Z., Miquel J., Call N., Riopelle A. J. Delayed radiation effects in the brains of monkeys exposed to x- and gamma-rays. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1968 Jan;27(1):50–79. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196801000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayreh S. S. Post-radiation retinopathy. A fluorescence fundus angiographic study. Br J Ophthalmol. 1970 Nov;54(11):705–714. doi: 10.1136/bjo.54.11.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard G. M. Ocular effects of radiation and photocoagulation. A study of 100 globes with retinoblastoma, some of which were treated prior to enucleation. Arch Ophthalmol. 1966 Jul;76(1):7–10. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1966.03850010009004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross H. S., Rosenberg S., Friedman A. H. Delayed radiation necrosis of the optic nerve. Am J Ophthalmol. 1973 Nov;76(5):683–686. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(73)90563-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shukovsky L. J., Fletcher G. H. Retinal and optic nerve complications in a high dose irradiation technique of ethmoid sinus and nasal cavity. Radiology. 1972 Sep;104(3):629–634. doi: 10.1148/104.3.629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]