The mononuclear nickel(II) complex is bis-chelated by dithiocarbazato ligands bearing a thienyl ring and an n-octyl alkyl chain.
Keywords: crystal structure, nickel(II) complex, dithiocarbazato ligand
Abstract
In the title complex, [Ni(C14H21N2S3)2], the nickel(II) atom is located on a crystallographic inversion center and exhibits a square-planar coordination environment, being coordinated by two negatively charged N,S-chelating ligands in a trans configuration. In the crystal, the non-H atoms of the complex are practically coplanar (r.m.s. deviation of fitted atoms = 0.135 Å), and the angle between the thienyl and the chelating rings is 6.7 (1)°. The molecules stack at a distance of 3.623 (2) Å along the b-axis direction.
1. Chemical context
Thiosemicarbazones, semicarbazones, hydrazide/hydrazones and dithiocarbazate ligands have been widely employed for the preparation of metal complexes. Over the last few decades, dithiocarbazate Schiff bases and their metal complexes have gained considerable interest because of their promising bioactivities against diverse cancer cell lines (Yusof et al., 2015 ▸; Ramilo-Gomes et al., 2021 ▸; Low et al., 2016 ▸), as well as antimicrobial activity (Zangrando et al., 2017 ▸). Clearly, the biological properties of these compounds can be modulated by using different organic substituents, leading to concomitant structural modifications (How et al., 2008 ▸; Yusof et al., 2022 ▸). A study of structure–activity relationships was described by Beshir et al. (2008 ▸).
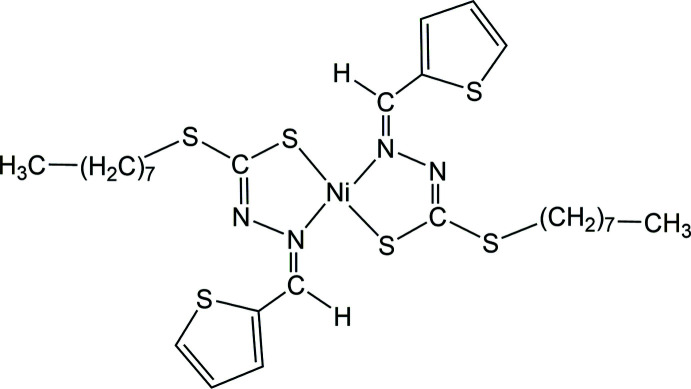
Therefore, considering the diverse significance of dithiocarbazate bases and their role in a variety of biological applications, herein we report a novel NiII complex with a dithiocarbazate Schiff base ligand bearing an octyl alkyl chain and a thienyl ring (Fig. 1 ▸).
Figure 1.
An ellipsoid plot (50% probability) of the title compound.
2. Structural commentary
The nickel(II) atom is located on a crystallographic center of symmetry and exhibits a square-planar coordination sphere, being coordinated by two negatively charged N,S-chelating ligands in a trans configuration. The Ni—N1 and Ni—S1 bond distances are 1.9168 (19) and 2.1735 (7) Å, respectively with a chelating N1—Ni—S1 bond angle of 85.88 (6)°. These values agree with those reported in previous papers (Begum et al., 2016 ▸; Islam et al., 2014 ▸; Howlader et al., 2015 ▸) for related compounds. It is worth mentioning that nickel(II) and copper(II) complexes with dithiocarbazate ligands have been reported to crystallize in both cis and trans configurations, although the latter is slightly more frequent (Begum et al., 2020 ▸).
All of the non-H atoms of the complex are almost coplanar, with S1 and C1 [−0.28 Å] and C13, C14 [+0.24, +0.31 Å], respectively deviating the most from its mean plane (r.m.s. deviation of fitted atoms = 0.135 Å). The thienyl ring forms a small dihedral angle of 6.7 (1)° with respect to the chelating five-membered ring. The long alkyl chain is in a staggered conformation with torsion angles along the chain that range between 176.7 (2) and 179.8 (2)°.
The molecule is stabilized by an intramolecular unconventional hydrogen bond between C5—H5 with S1′ [at 1 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z] of the symmetry-related ligand [C5⋯S1′ distance of 3.067 (3) Å, C5—H5⋯S1′ angle of 125°].
3. Supramolecular features
The molecules stack with an interplanar distance of 3.623 (2) Å, and the crystal packing shows that all hydrophobic n-octyl chains segregate together, so as to share the same regions of space (Fig. 2 ▸), as already observed in similar complexes (Begum et al., 2016 ▸). Fig. 3 ▸ overlays this structure of the complex superimposed onto that of a 4-methoxybenzyl derivative (WEGKEB: Begum et al., 2018 ▸), where it is worth noting the different orientation of octyl chains in the two cases. This is due to the different torsion angle C6—S2—C7—C8 of −177.36 (18)° in this structure vs 86.8 (6)° and −160.0 (9)° (for the two disorder components of the equivalent torsion angle in WEGKEB), likely induced by crystal-packing requirements. Details of hydrogen-bonding interactions are given in Table 1 ▸.
Figure 2.
A partial packing view showing complexes stacked in the b-axis direction.
Figure 3.
Superposition of this structure with the 4-methoxybenzyl derivative WEGKEB (Begum et al., 2018 ▸; only one disorder component shown), where it is worth noting the different orientation of the octyl moiety, likely induced by crystal-packing requirements.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2—H2⋯S1i | 0.95 | 3.00 | 3.684 (3) | 131 |
| C2—H2⋯S2ii | 0.95 | 2.93 | 3.752 (3) | 146 |
| C5—H5⋯S1iii | 0.95 | 2.42 | 3.067 (3) | 125 |
| C7—H7A⋯S3 | 0.99 | 2.93 | 3.406 (3) | 110 |
Symmetry codes: (i)
 ; (ii)
; (ii)
 ; (iii)
; (iii)
 .
.
4. Database survey
For comparison, NiII complexes with comparable ligands bearing long alkyl chains have been reported from these laboratories (Begum et al., 2016 ▸, 2017 ▸, 2018 ▸, 2020 ▸, 2023 ▸; CSD refcodes = JUYCAJ, WEGKEB, BIQTIH, TILVUJ and PICMOH, respectively).
5. Synthesis and crystallization
A solution of Ni(CH3COO)2·4H2O (0.12 g, 0.5 mmol in 10 mL methanol) was added to a solution of S-octyl-β-N-(2-thienyl)methylenedithiocarbazate (0.314 g, 1.0 mmol in 30 mL of methanol). The resulting mixture was stirred at room temperature for 4 h. The dark-orange precipitate that formed was filtered off, washed with methanol and dried in vacuo over anhydrous CaCl2. Orange needle-shaped single crystals, suitable for X-ray diffraction, were obtained by slow evaporation of the compound from a mixture of chloroform and acetonitrile (4:1, v/v) after 14 days. Yield: 66%; m. p. (377-378) K.
FT–IR (KBr, cm−1): 2920 ν(C—H, alkyl), 1639, 1572 ν(C=N—N=C).
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, ppm) δ: 7.999 (s, 2×1H, CH=N, C-5), 7.715 (d, 2×1H, C-1, J = 5.2 Hz), 7.468 (d, 2×1H, C-3, J = 5.2 Hz), 7.103 (t, 2×1H, C-2), 3.269 (t, 2×2H, –SCH2, C-7), 1.764 (p, 2×2H, C-8), 1.460 (p, 2×2H, C-9), 1.318–1.270 (m, 2×8H, C-10, 11, 12, 13), 0.878 (t, 2×3H, C-14).
UV–Vis spectrum [CHCl3, λmax nm]: 475, 400, 276.
HRMS (FAB) Calculated for C28H42N4NiS6 [M+H]+: 685.11599, found [M+H]+: 685.11549.
6. Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement are summarized in Table 2 ▸. Hydrogen atoms were placed at calculated positions (C–H = 0.95–0.99 Å) and refined as riding with U iso(H) = 1.2–1.5U eq(C).
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | [Ni(C14H21N2S3)2] |
| M r | 685.72 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 173 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 15.5444 (6), 5.5388 (3), 20.1592 (8) |
| β (°) | 103.675 (7) |
| V (Å3) | 1686.44 (13) |
| Z | 2 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.97 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.08 × 0.02 × 0.01 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Rigaku R-AXIS RAPID |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (ABSCOR; Rigaku, 1995 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.815, 0.990 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 15791, 3850, 2621 |
| R int | 0.077 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.649 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.045, 0.079, 1.00 |
| No. of reflections | 3850 |
| No. of parameters | 179 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.44, −0.27 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989023005935/pk2690sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989023005935/pk2690Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 2254902
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
MBHH and SSK are grateful to the Department of Chemistry, Rajshahi University for the provision of laboratory facilities. MCS and RM acknowledge the Center for Environmental Conservation and Research Safety, University of Toyama, for providing facilities for single-crystal X-ray analyses.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| [Ni(C14H21N2S3)2] | F(000) = 724 |
| Mr = 685.72 | Dx = 1.350 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71075 Å |
| a = 15.5444 (6) Å | Cell parameters from 10434 reflections |
| b = 5.5388 (3) Å | θ = 2.1–27.5° |
| c = 20.1592 (8) Å | µ = 0.97 mm−1 |
| β = 103.675 (7)° | T = 173 K |
| V = 1686.44 (13) Å3 | Needle, orange |
| Z = 2 | 0.08 × 0.02 × 0.01 mm |
Data collection
| Rigaku R-AXIS RAPID diffractometer | 2621 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 10.000 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.077 |
| ω scans | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 2.7° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (ABSCOR; Rigaku, 1995) | h = −19→20 |
| Tmin = 0.815, Tmax = 0.990 | k = −7→7 |
| 15791 measured reflections | l = −26→25 |
| 3850 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.045 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.079 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0329P)2 + 0.0128P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.00 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 3850 reflections | Δρmax = 0.44 e Å−3 |
| 179 parameters | Δρmin = −0.27 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Ni1 | 0.500000 | 0.500000 | 0.500000 | 0.02461 (12) | |
| S1 | 0.43249 (4) | 0.34173 (13) | 0.57239 (3) | 0.03295 (17) | |
| S2 | 0.30020 (4) | −0.04469 (12) | 0.55073 (3) | 0.03283 (17) | |
| S3 | 0.33321 (4) | −0.17114 (13) | 0.33566 (3) | 0.03364 (17) | |
| N1 | 0.43677 (12) | 0.2681 (4) | 0.43617 (10) | 0.0263 (5) | |
| N2 | 0.37776 (13) | 0.1034 (4) | 0.45452 (10) | 0.0274 (5) | |
| C1 | 0.32299 (17) | −0.2689 (5) | 0.25377 (13) | 0.0364 (7) | |
| H1 | 0.290649 | −0.408991 | 0.235505 | 0.044* | |
| C2 | 0.36579 (17) | −0.1259 (5) | 0.21773 (13) | 0.0384 (7) | |
| H2 | 0.366185 | −0.152919 | 0.171263 | 0.046* | |
| C3 | 0.40956 (16) | 0.0668 (5) | 0.25668 (12) | 0.0331 (6) | |
| H3 | 0.443110 | 0.184342 | 0.239444 | 0.040* | |
| C4 | 0.39872 (15) | 0.0677 (4) | 0.32296 (12) | 0.0273 (6) | |
| C5 | 0.44139 (15) | 0.2400 (5) | 0.37290 (12) | 0.0289 (6) | |
| H5 | 0.478965 | 0.351305 | 0.357540 | 0.035* | |
| C6 | 0.37280 (14) | 0.1323 (4) | 0.51739 (12) | 0.0255 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.25455 (16) | −0.2377 (5) | 0.47858 (12) | 0.0317 (6) | |
| H7A | 0.228117 | −0.136545 | 0.438453 | 0.038* | |
| H7B | 0.302730 | −0.334361 | 0.467263 | 0.038* | |
| C8 | 0.18415 (17) | −0.4070 (5) | 0.49347 (13) | 0.0338 (6) | |
| H8A | 0.210547 | −0.512821 | 0.532553 | 0.041* | |
| H8B | 0.136169 | −0.311795 | 0.505600 | 0.041* | |
| C9 | 0.14665 (17) | −0.5596 (5) | 0.43057 (13) | 0.0364 (7) | |
| H9A | 0.123844 | −0.450452 | 0.391478 | 0.044* | |
| H9B | 0.195365 | −0.655482 | 0.419806 | 0.044* | |
| C10 | 0.07291 (17) | −0.7307 (5) | 0.43757 (13) | 0.0368 (6) | |
| H10A | 0.025185 | −0.637168 | 0.450618 | 0.044* | |
| H10B | 0.096283 | −0.847621 | 0.474588 | 0.044* | |
| C11 | 0.03444 (17) | −0.8679 (5) | 0.37195 (13) | 0.0393 (7) | |
| H11A | 0.011898 | −0.749798 | 0.335090 | 0.047* | |
| H11B | 0.082584 | −0.960448 | 0.359172 | 0.047* | |
| C12 | −0.03979 (17) | −1.0408 (5) | 0.37605 (14) | 0.0403 (7) | |
| H12A | −0.016871 | −1.163148 | 0.411632 | 0.048* | |
| H12B | −0.087282 | −0.949827 | 0.390228 | 0.048* | |
| C13 | −0.0790 (2) | −1.1686 (7) | 0.30929 (15) | 0.0569 (9) | |
| H13A | −0.102651 | −1.046174 | 0.273913 | 0.068* | |
| H13B | −0.031228 | −1.257274 | 0.294768 | 0.068* | |
| C14 | −0.1521 (2) | −1.3442 (7) | 0.31334 (18) | 0.0693 (11) | |
| H14A | −0.128788 | −1.469718 | 0.347054 | 0.083* | |
| H14B | −0.174872 | −1.418856 | 0.268549 | 0.083* | |
| H14C | −0.200158 | −1.257687 | 0.327044 | 0.083* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Ni1 | 0.0294 (2) | 0.0213 (3) | 0.0228 (2) | −0.0016 (2) | 0.00554 (18) | −0.00261 (19) |
| S1 | 0.0420 (4) | 0.0320 (4) | 0.0256 (3) | −0.0103 (3) | 0.0095 (3) | −0.0052 (3) |
| S2 | 0.0415 (4) | 0.0294 (4) | 0.0287 (3) | −0.0086 (3) | 0.0105 (3) | 0.0004 (3) |
| S3 | 0.0419 (4) | 0.0278 (4) | 0.0300 (3) | −0.0062 (3) | 0.0062 (3) | −0.0026 (3) |
| N1 | 0.0299 (11) | 0.0220 (12) | 0.0270 (11) | −0.0014 (9) | 0.0067 (9) | −0.0013 (9) |
| N2 | 0.0345 (11) | 0.0225 (12) | 0.0265 (11) | −0.0050 (9) | 0.0098 (9) | −0.0008 (9) |
| C1 | 0.0406 (15) | 0.0330 (17) | 0.0324 (14) | −0.0041 (13) | 0.0021 (12) | −0.0101 (12) |
| C2 | 0.0391 (15) | 0.0460 (19) | 0.0297 (13) | −0.0038 (13) | 0.0076 (13) | −0.0126 (13) |
| C3 | 0.0365 (14) | 0.0368 (17) | 0.0265 (12) | −0.0044 (12) | 0.0087 (12) | −0.0051 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0298 (13) | 0.0232 (14) | 0.0278 (12) | −0.0008 (10) | 0.0046 (11) | −0.0025 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0327 (13) | 0.0260 (15) | 0.0298 (13) | −0.0038 (11) | 0.0109 (11) | −0.0015 (11) |
| C6 | 0.0270 (12) | 0.0202 (14) | 0.0285 (13) | 0.0008 (10) | 0.0049 (11) | 0.0037 (10) |
| C7 | 0.0377 (14) | 0.0261 (15) | 0.0306 (13) | −0.0045 (11) | 0.0068 (12) | −0.0009 (11) |
| C8 | 0.0373 (14) | 0.0291 (15) | 0.0347 (14) | −0.0064 (11) | 0.0077 (12) | 0.0019 (11) |
| C9 | 0.0379 (14) | 0.0314 (17) | 0.0398 (15) | −0.0074 (12) | 0.0091 (13) | −0.0027 (12) |
| C10 | 0.0397 (14) | 0.0300 (16) | 0.0421 (15) | −0.0072 (12) | 0.0122 (13) | −0.0020 (12) |
| C11 | 0.0396 (15) | 0.0370 (18) | 0.0405 (15) | −0.0097 (13) | 0.0078 (13) | −0.0037 (13) |
| C12 | 0.0419 (15) | 0.0355 (18) | 0.0430 (15) | −0.0089 (13) | 0.0090 (13) | −0.0027 (13) |
| C13 | 0.0565 (19) | 0.060 (2) | 0.0522 (19) | −0.0206 (17) | 0.0084 (16) | −0.0114 (17) |
| C14 | 0.063 (2) | 0.062 (3) | 0.072 (2) | −0.0261 (19) | −0.0053 (19) | −0.009 (2) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Ni1—N1i | 1.9168 (19) | C7—H7B | 0.9900 |
| Ni1—N1 | 1.9168 (19) | C8—C9 | 1.521 (3) |
| Ni1—S1i | 2.1735 (7) | C8—H8A | 0.9900 |
| Ni1—S1i | 2.1735 (7) | C8—H8B | 0.9900 |
| Ni1—S1 | 2.1735 (7) | C9—C10 | 1.519 (3) |
| S1—C6 | 1.717 (2) | C9—H9A | 0.9900 |
| S2—C6 | 1.745 (2) | C9—H9B | 0.9900 |
| S2—C7 | 1.809 (2) | C10—C11 | 1.520 (3) |
| S3—C1 | 1.709 (3) | C10—H10A | 0.9900 |
| S3—C4 | 1.725 (3) | C10—H10B | 0.9900 |
| N1—C5 | 1.304 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.516 (4) |
| N1—N2 | 1.404 (3) | C11—H11A | 0.9900 |
| N2—C6 | 1.298 (3) | C11—H11B | 0.9900 |
| C1—C2 | 1.351 (4) | C12—C13 | 1.515 (4) |
| C1—H1 | 0.9500 | C12—H12A | 0.9900 |
| C2—C3 | 1.402 (4) | C12—H12B | 0.9900 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C13—C14 | 1.513 (4) |
| C3—C4 | 1.386 (3) | C13—H13A | 0.9900 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C13—H13B | 0.9900 |
| C4—C5 | 1.431 (3) | C14—H14A | 0.9800 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C14—H14B | 0.9800 |
| C7—C8 | 1.524 (3) | C14—H14C | 0.9800 |
| C7—H7A | 0.9900 | ||
| N1i—Ni1—N1 | 180.0 | C9—C8—H8A | 109.8 |
| N1i—Ni1—S1i | 85.88 (6) | C7—C8—H8A | 109.8 |
| N1—Ni1—S1i | 94.12 (6) | C9—C8—H8B | 109.8 |
| N1i—Ni1—S1i | 85.88 (6) | C7—C8—H8B | 109.8 |
| N1—Ni1—S1i | 94.12 (6) | H8A—C8—H8B | 108.3 |
| S1i—Ni1—S1i | 0.00 (2) | C10—C9—C8 | 114.7 (2) |
| N1i—Ni1—S1 | 94.12 (6) | C10—C9—H9A | 108.6 |
| N1—Ni1—S1 | 85.88 (6) | C8—C9—H9A | 108.6 |
| S1i—Ni1—S1 | 180.0 | C10—C9—H9B | 108.6 |
| S1i—Ni1—S1 | 180.0 | C8—C9—H9B | 108.6 |
| C6—S1—Ni1 | 96.42 (8) | H9A—C9—H9B | 107.6 |
| C6—S2—C7 | 100.88 (12) | C9—C10—C11 | 112.4 (2) |
| C1—S3—C4 | 91.32 (13) | C9—C10—H10A | 109.1 |
| C5—N1—N2 | 111.8 (2) | C11—C10—H10A | 109.1 |
| C5—N1—Ni1 | 126.77 (17) | C9—C10—H10B | 109.1 |
| N2—N1—Ni1 | 121.46 (14) | C11—C10—H10B | 109.1 |
| C6—N2—N1 | 111.74 (19) | H10A—C10—H10B | 107.9 |
| C2—C1—S3 | 112.9 (2) | C12—C11—C10 | 114.6 (2) |
| C2—C1—H1 | 123.6 | C12—C11—H11A | 108.6 |
| S3—C1—H1 | 123.6 | C10—C11—H11A | 108.6 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 112.4 (2) | C12—C11—H11B | 108.6 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 123.8 | C10—C11—H11B | 108.6 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 123.8 | H11A—C11—H11B | 107.6 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 112.9 (2) | C13—C12—C11 | 113.4 (2) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 123.5 | C13—C12—H12A | 108.9 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 123.5 | C11—C12—H12A | 108.9 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 122.6 (2) | C13—C12—H12B | 108.9 |
| C3—C4—S3 | 110.53 (18) | C11—C12—H12B | 108.9 |
| C5—C4—S3 | 126.78 (19) | H12A—C12—H12B | 107.7 |
| N1—C5—C4 | 130.1 (2) | C14—C13—C12 | 113.7 (3) |
| N1—C5—H5 | 115.0 | C14—C13—H13A | 108.8 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 115.0 | C12—C13—H13A | 108.8 |
| N2—C6—S1 | 124.49 (19) | C14—C13—H13B | 108.8 |
| N2—C6—S2 | 119.99 (18) | C12—C13—H13B | 108.8 |
| S1—C6—S2 | 115.51 (14) | H13A—C13—H13B | 107.7 |
| C8—C7—S2 | 111.63 (17) | C13—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7A | 109.3 | C13—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| S2—C7—H7A | 109.3 | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7B | 109.3 | C13—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| S2—C7—H7B | 109.3 | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| H7A—C7—H7B | 108.0 | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 109.2 (2) | ||
| C5—N1—N2—C6 | −179.6 (2) | N1—N2—C6—S1 | −1.3 (3) |
| Ni1—N1—N2—C6 | 0.4 (3) | N1—N2—C6—S2 | 177.52 (15) |
| C4—S3—C1—C2 | −1.0 (2) | Ni1—S1—C6—N2 | 1.4 (2) |
| S3—C1—C2—C3 | 0.9 (3) | Ni1—S1—C6—S2 | −177.45 (11) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.3 (3) | C7—S2—C6—N2 | 2.3 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 176.5 (2) | C7—S2—C6—S1 | −178.84 (14) |
| C2—C3—C4—S3 | −0.5 (3) | C6—S2—C7—C8 | −177.36 (18) |
| C1—S3—C4—C3 | 0.8 (2) | S2—C7—C8—C9 | 178.55 (18) |
| C1—S3—C4—C5 | −176.0 (2) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | −177.8 (2) |
| N2—N1—C5—C4 | −2.1 (4) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 176.7 (2) |
| Ni1—N1—C5—C4 | 177.9 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −179.8 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—N1 | 178.5 (3) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 178.0 (3) |
| S3—C4—C5—N1 | −5.1 (4) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 179.1 (3) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C2—H2···S1ii | 0.95 | 3.00 | 3.684 (3) | 131 |
| C2—H2···S2iii | 0.95 | 2.93 | 3.752 (3) | 146 |
| C5—H5···S1i | 0.95 | 2.42 | 3.067 (3) | 125 |
| C7—H7A···S3 | 0.99 | 2.93 | 3.406 (3) | 110 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (ii) x, −y+1/2, z−1/2; (iii) x, −y−1/2, z−1/2.
References
- Begum, K., Begum, S., Sheikh, C., Miyatake, R. & Zangrando, E. (2020). Acta Cryst. E76, 692–696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Begum, K., Zangrando, E., Begum, M. S., Sheikh, C. & Miyatake, R. (2018). IUCrData, 3, x181684.
- Begum, M. S., Das, D., Zangrando, E., Rahman, S., Alodhayb, A., Begum, M. K., Sheikh, C. M., Miyatake, R., Howlader, M. B. H., Karim, M. R. & Chowdhury, M. B. (2023). J. Mol. Struct. 1277, 134808.
- Begum, M. S., Zangrando, E., Howlader, M. B. H., Sheikh, M. C., Miyatake, R., Hossain, M. M., Alam, M. M. & Hasnat, M. A. (2016). Polyhedron, 105, 56–61.
- Begum, M. S., Zangrando, E., Sheikh, M. C., Miyatake, R., Howlader, M. B. H., Rahman, M. N. & Ghosh, A. (2017). Transit. Met. Chem. 42, 553–563.
- Beshir, A. B., Guchhait, S. K., Gascón, J. A. & Fenteany, G. (2008). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 18, 498–504. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Brandenburg, K. (1999). DIAMOND. Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- How, F. N.-F., Crouse, K. A., Tahir, M. I. M., Tarafder, M. T. H. & Cowley, A. R. (2008). Polyhedron, 27, 3325–3329.
- Howlader, M. B. H., Begum, M. S., Sheikh, M. C., Miyatake, R. & Zangrando, E. (2015). Acta Cryst. E71, m26–m27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Islam, M. A. A. A. A., Sheikh, M. C., Alam, M. S., Zangrando, E., Alam, M. A., Tarafder, M. T. H. & Miyatake, R. (2014). Transition Met. Chem. 39, 141–149.
- Low, M. L., Maigre, L., Tahir, M. I. M., Tiekink, E. R. T., Dorlet, P., Guillot, R., Ravoof, T. B., Rosli, R., Pagès, J.-M., Policar, C., Delsuc, N. & Crouse, K. A. (2016). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 120, 1–12. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ramilo-Gomes, F., Addis, Y., Tekamo, I., Cavaco, I., Campos, D. L., Pavan, F. R., Gomes, C. S. B., Brito, V., Santos, A. O., Domingues, F., Luís, Â., Marques, M. M., Pessoa, J. C., Ferreira, S., Silvestre, S. & Correia, I. (2021). J. Inorg. Biochem. 216, 111331. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rigaku (1995). ABSCOR. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Rigaku (2018). RAPID AUTO. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Yusof, E. N. M., Azam, M., Sirat, S. S., Ravoof, T. B. S. A., Page, A. J., Veerakumarasivam, A., Karunakaran, T. & Razali, M. R. (2022). Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2004052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Yusof, E. N. M., Ravoof, T. B. S. A., Jamsari, J., Tiekink, E. R. T., Veerakumarasivam, A., Crouse, K. A., Tahir, M. I. M. & Ahmad, H. (2015). Inorg. Chim. Acta, 438, 85–93.
- Zangrando, E., Begum, M. S., Sheikh, M. C., Miyatake, R., Hossain, M. M., Alam, M. M., Hasnat, M. A., Halim, M. A., Ahmed, S., Rahman, M. N. & Ghosh, A. (2017). Arab. J. Chem. 10, 172–184.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989023005935/pk2690sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989023005935/pk2690Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 2254902
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report





