In the title compound, the NaI atom has a distorted square-pyramidal coordination environment. The molecular structure exhibits an intramolecular bifurcated O—H⋯[N(tertiary amine), N(pyridyl)] hydrogen bond. In the crystal, the molecules are linked by the bridging Na—O(sulfonato) coordination bonds and the intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming a three-dimensional network structure.
Keywords: crystal structure, coordination polymer, sodium complex, 8-hydroxyquinoline sulfonato, C—H⋯O interactions
Abstract
In the title compound, [Na(C22H19N4O4S)(CH3CN)] n , the NaI atom adopts a distorted square-pyramidal coordination geometry, formed by one N and one O atom of the qunolinol moiety in the ligand, two O atoms of sulfonate moieties of two adjacent ligands and the N atom of the coordinated acetonitrile solvent. The NaI atom is located well above the mean basal plane of the square-based pyramid. The apical position is occupied by a sulfonate O atom of a neighboring ligand. Three N atoms of the bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amine moiety in the ligand are not coordinated by the sodium atom. The molecule forms an intramolecular bifurcated O—H⋯[N(tertiary amine),N(pyridine)] hydrogen bond, generating S(6) and S(5) rings. In the crystal, four molecules are linked by four Na—O(sulfonato) bridged coordination bonds, forming a supramolecular centrosymmetric tetramer unit comprising an eight-membered ring, and generating a two-dimensional network sheet. The molecules of different sheets form intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, and thereby a three-dimensional network structure.
1. Chemical context
8-Quinolinol (Hq) is a well-known chelating ligand and analytical reagent (Wiberley et al., 1949 ▸). Metal complexes with Hq derivatives have been investigated as pharmaceutical treatments (Mo et al., 2021 ▸), magnetic materials (Ma et al., 2021 ▸) and organic light-emitting diodes (Huo et al. 2015 ▸; Back et al., 2016 ▸). As part of our research into the development of fluorescent chelate reagents for the determination of metal ions and anions, we synthesized the pentadentate ligand, 7-{[bis-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amino]methyl}-5-chloroquinolin-8-ol (HClqdpa) containing Hq and bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amine [di-(2-picolyl)amine] (dpa) moieties (RUTSIK; Kubono et al., 2015 ▸). This ligand has only rather poor water solubility. To improve the solubility, we synthesized a new and now water-soluble fluorescent chelate reagent, based on Hq containing sulfonato-sodium and dpa moieties. Herein we report the respective synthesis and the crystal structure of its acetonitrile solvate complex.
2. Structural commentary
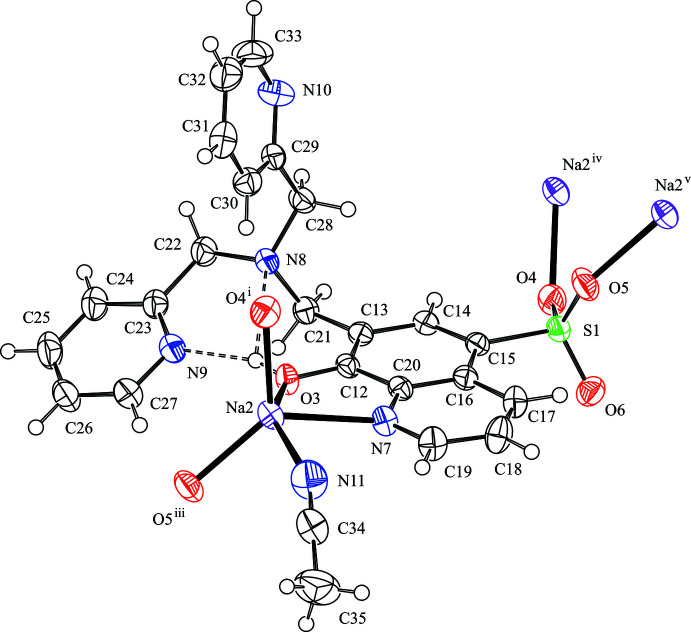
The molecular structure of the title compound is shown in Fig. 1 ▸. The NaI atom (Na2) of the asymmetric unit adopts a distorted square-pyramidal geometry and coordinates N and O atoms of the quinolinol moiety in the ligand, two O atoms of the sulfonate moieties of two neighboring ligands and the N atom of acetonitrile solvent. The phenolic hydrogen atom H3 of the quinolinol moiety is bound to the O3 atom. The proton, therefore, does not dissociate. Three N atoms of the dpa moiety in the ligand are not coordinated by the NaI atom.
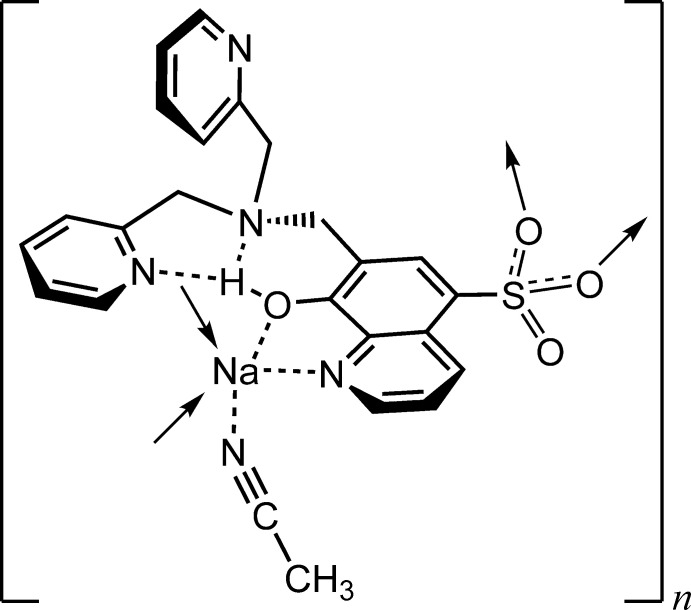
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound with atom labeling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms are represented by spheres of arbitrary radius. The intramolecular O—H⋯N hydrogen bonds are shown as double-dashed lines. [Symmetry codes: (i) 2 − x, y −
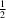 ,
,
 − z; (iii) x,
− z; (iii) x,
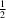 − y, z −
− y, z −
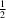 ; (iv) 2 − x, y +
; (iv) 2 − x, y +
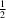 ,
,
 − z; (v) x,
− z; (v) x,
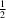 − y, z +
− y, z +
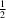 .]
.]
The five-coordinate geometry index, τ = (β − α)/60, derived from the two largest angles (α, β) in a structure has ideal values of 0 for square-pyramidal and of 1 for trigonal–bipyramidal geometry (Addison et al., 1984 ▸). In the title compound it is equal to 0.310. The NaI atom is located 0.7311 (8) Å above the mean basal plane [O3/N7/N11/O5iii; symmetry code: (iii) x,
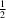 − y, z −
− y, z −
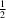 ] of the square-based pyramid. The apical position is occupied by the O4i atom of the sulfonate moiety in a neighboring ligand with the Na2—O4i bond being 2.2602 (16) Å long [symmetry code: (i) 2 − x, y −
] of the square-based pyramid. The apical position is occupied by the O4i atom of the sulfonate moiety in a neighboring ligand with the Na2—O4i bond being 2.2602 (16) Å long [symmetry code: (i) 2 − x, y −
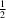 ,
,
 − z]. The Na2—O3(quinolinol) bond distance is 2.4248 (15) Å, longer than the equatorial Na—O(sulfonato) bond [Na2—O5iii; 2.2500 (16) Å]. The Na2—N7(quinolinol) distance is 2.467 (2) Å, shorter than the Na2—N11(acetonitrile) bond [2.487 (2) Å]. The chelate angle O3—Na2—N7 is 65.83 (5)°, the smallest of all the coordination angels. It agrees well with that of a related compound, (8-hydroxyquinoline-5-sulfonato-N
1,O
8)sodium(I) [UGUNOZ; Baskar Raj et al., 2002 ▸; O—Na—N; 64.86 (4)°]. The τ-parameter of this related compound is 0.505, and indicative of a significantly distorted trigonal–bipyramidal geometry with bond distances of Na—O(quinolinol) and Na—N(quinolinol) of 2.4892 (14) and 2.4418 (15) Å, respectively.
− z]. The Na2—O3(quinolinol) bond distance is 2.4248 (15) Å, longer than the equatorial Na—O(sulfonato) bond [Na2—O5iii; 2.2500 (16) Å]. The Na2—N7(quinolinol) distance is 2.467 (2) Å, shorter than the Na2—N11(acetonitrile) bond [2.487 (2) Å]. The chelate angle O3—Na2—N7 is 65.83 (5)°, the smallest of all the coordination angels. It agrees well with that of a related compound, (8-hydroxyquinoline-5-sulfonato-N
1,O
8)sodium(I) [UGUNOZ; Baskar Raj et al., 2002 ▸; O—Na—N; 64.86 (4)°]. The τ-parameter of this related compound is 0.505, and indicative of a significantly distorted trigonal–bipyramidal geometry with bond distances of Na—O(quinolinol) and Na—N(quinolinol) of 2.4892 (14) and 2.4418 (15) Å, respectively.
The title molecule forms in its crystal structure an intramolecular bifurcated O3—H3⋯(N8, N9) hydrogen bond (Table 1 ▸), resulting in S(6) and S(5) rings, which stabilize the conformation of the molecule. The N10 atom in the pyridine ring is not engaged in a coordination bond, hydrogen bond or any other inter- or intramolecular interaction. The dihedral angle between two pyridine rings in the title compound is 88.37 (11)°. In a related compound, 7-{[bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amino]methyl}-5-chloroquinolin-8-ol, HClqdpa (RUTSIK; Kubono et al., 2015 ▸), the dihedral angle between two pyridine rings is 80.97 (12)°.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O3—H3⋯N8 | 0.88 (2) | 2.46 (3) | 3.057 (2) | 125 (2) |
| O3—H3⋯N9 | 0.88 (2) | 1.87 (2) | 2.7120 (19) | 158 (3) |
| C31—H31⋯O6i | 0.95 | 2.53 | 3.397 (3) | 152 |
| C35—H35A⋯O6ii | 0.98 | 2.55 | 3.502 (4) | 166 |
Symmetry codes: (i)
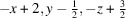 ; (ii)
; (ii)
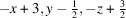 .
.
Even though in HClqdpa the dpa moiety is metal-free, and only one pyridine N atom forms an intramolecular hydrogen bond with the OH group, these angles are relatively similar. The quinoline ring of the title compound is slightly bent, with r.m.s. deviations of 0.020 (2) Å. The S—O bond distances are in the range 1.4469 (14)–1.4585 (15) Å, with O—S—O angles ranging from 112.87 (9) to 113.25 (9)°. The bond lengths and angles largely agree with those values in the related compound [UGUNOZ; Baskar Raj et al., 2002 ▸; S—O; 1.4482 (12)–1.4731 (12) Å, O—S—O; 110.92 (7)–114.35 (7)°]. The O6 atom is not coordinated by the NaI atom, and the bond distance S1—O6 is shorter than the other two.
3. Supramolecular features
In the crystal, four molecules of the title compound are linked by four bridging Na—O coordination bonds, forming a supramolecular centrosymmetric structure based on a central eight-membered ring (Na2/O4i/S1i/O5i/Na2vi/O4iii/S1iii/O5iii) [symmetry code: (vi) 2 − x, −y, 1 − z]. The tetrameric building block is shown in Fig. 2 ▸. A two-dimensional coordination polymer is formed by bridging coordination bonds between the NaI atom and two sulfonato O atoms of two adjacent ligands (Na2—O4i and Na2—O5iii) in the bc plane (Fig. 3 ▸). An intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bond (C31—H31⋯O6i, Table 1 ▸) is observed, forming a C(12) chain motif along the b-axis direction. In the crystal structure, molecules are further linked by an intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bond [C35—H35A⋯O6ii; symmetry code: (ii) 3 − x, y −
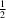 ,
,
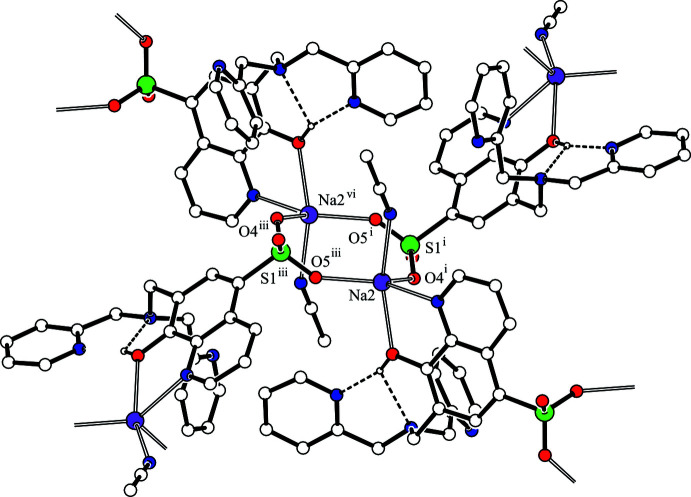
 − z] (Table 1 ▸), forming a C(8) chain motif running along the a-axis direction (Fig. 4 ▸). The molecules are linked through the bridging Na2—O4i and Na2—O5iii coordination bonds and the intermolecular C35—H35A⋯O6ii hydrogen bonds, forming a three-dimensional network structure.
− z] (Table 1 ▸), forming a C(8) chain motif running along the a-axis direction (Fig. 4 ▸). The molecules are linked through the bridging Na2—O4i and Na2—O5iii coordination bonds and the intermolecular C35—H35A⋯O6ii hydrogen bonds, forming a three-dimensional network structure.
Figure 2.
Supramolecular centrosymmetric tetrameric component of the crystal packing motif in the title compound formed by bridging coordination bonds. The intramolecular hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines. H atoms not involved in the interactions are omitted for clarity. [Symmetry code: (i) 2 − x, y −
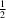 ,
,
 − z; (iii) x,
− z; (iii) x,
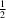 − y, z −
− y, z −
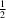 ; (vi) 2 − x, −y, 1 − z.]
; (vi) 2 − x, −y, 1 − z.]
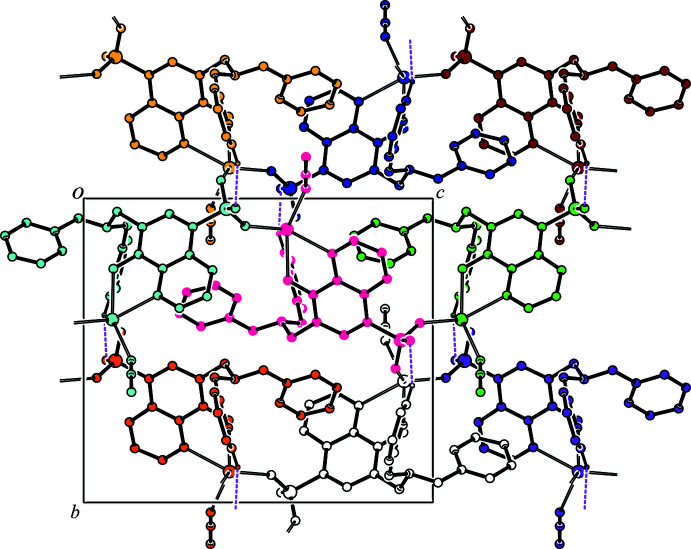
Figure 3.
A projection along the a axis of the crystal packing of the title compound. The C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed magenta lines. H atoms not involved in the interactions are omitted for clarity.
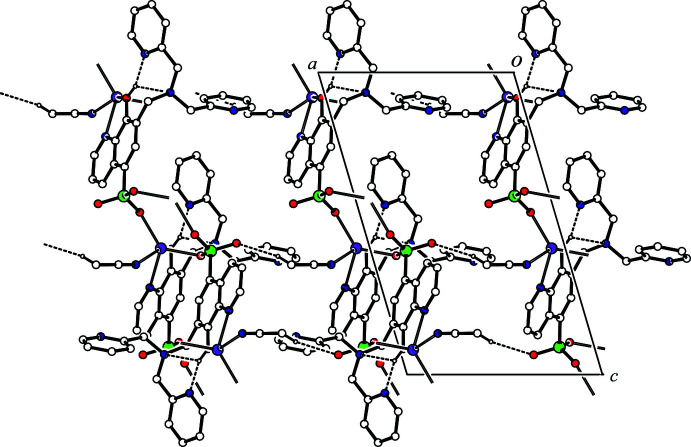
Figure 4.
A projection along the b axis of the crystal packing of the title compound. The O—H⋯N and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines. H atoms not involved in the interactions are omitted for clarity.
4. Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD, Version 5.44; April 2023; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) using ConQuest (Bruno et al., 2002 ▸) for the quinolin-8-ol-5-sulfonato fragment gave 78 hits. Of these, only two structures are NaI complexes with the quinolin-8-ol-5-sulfonato ligand, viz. (8-hydroxyquinoline-5-sulfonato-N 1,O 8)sodium(I) (UGUNOZ; Baskar Raj et al., 2002 ▸) and its trihydrate (BOXKOO; Viossat et al., 1982 ▸). Both the anhydrate and trihydrate of (quinolin-8-ol-5-sulfonato)sodium form centrosymmetric dimeric structures in their crystals. Centrosymmetric dimer structures are observed in the crystals of various metal complexes with quinolin-8-ol-5-sulfonate and its derivatives. In the crystal of the anhydrous sodium complex, four Na—O(sulfonato) bridged coordination bonds construct a supramolecular centrosymmetric eight-membered ring, similar to the title complex. A search for the fragment of 7-methyl-quinolin-8-ol-5-sulfonato gave two hits, which are 8-hydroxy-7-[(morpholin-4-ium-4-yl)methyl]quinoline-5-sulfonate acetonitrile solvate (UPAYIW; Kumar et al., 2021 ▸) and 8-hydroxy-7-[(piperidin-1-ium-1-yl)methyl]quinoline-5-sulfonate monohydrate (UPAYOC; Kumar et al., 2021 ▸). These compounds are metal-free ligands, and the crystal structures of their sodium salts or complexes are not reported. A search for a compound fragment in which the substituent is moved to the pyridyl ring, 2-methyl-quinolin-8-ol-5-sulfonato, gave two hits, namely aqua-{2,2′-[(1,4,10,13-tetraoxa-7,16-diazacyclo-octadecane-7,16-diyl)-bis(methylene)]bis[8-(hydroxy)quinoline-5-sulfonato]}-barium octahydrate (BINXEE; Thiele et al., 2018 ▸), and 2-methyl-8-hydroxyquinoline-5-sulfonic acid monohydrate (MHQUSO; Merritt Jr, et al., 1970 ▸).
5. Synthesis and crystallization
A suspension of paraformaldehyde (0.41 g, 14 mmol) and bis(2-pyridylmethyl)amine (1.99 g, 10 mmol) in 100 mL of MeOH was stirred for 18 h at room temperature. The solvent was removed in vacuo. To the product was added 90 mL of methanol, 8-hydroxyquinoline-5-sulfonic acid monohydrate (1.80 g, 10 mmol) and sodium hydroxide (0.40 g, 10 mmol) in 10 mL of water, the mixture was heated for 24 h at 353 K. The solvent was removed in vacuo to give an oily product, which was precipitated by addition of acetone (0.72 g, 31.4%). A small amount of crude solid was recrystallized from acetonitrile to obtain colorless crystals of the title compound. 1H NMR (CD3OD, 400 MHz): δ = 2.03 (s, 3H, acetonitrile), 3.90 (s, 4H), 3.97 (s, 2H), 7.23–7.26 (m, 2H), 7.56–7.59 (dd, J = 8.8 Hz, J = 4.4 Hz, 1H), 7.63 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.75–7.78 (td, J = 8.0 Hz, J = 1.6 Hz, 2H), 8.22 (s, 1H), 8.45–8.47 (m, 2H), 8.81–8.83 (dd, J = 4.4 Hz, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H), 9.10–9.15 (dd, J = 8.8 Hz, J = 1.6 Hz, 1H). TG: expected weight loss for acetonitrile: 8.21%; found: 8.23% (around 447 to 465 K).
6. Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. The hydroxy H atom was located in a difference-Fourier map and freely refined. All H atoms bound to carbon were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model, with C—H = 0.95–0.99 Å and U iso(H) = 1.2 or 1.5U eq(C).
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | [Na(C22H19N4O4S)(C2H3N)] |
| M r | 499.52 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 173 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 10.4951 (4), 14.1401 (5), 16.9249 (6) |
| β (°) | 106.378 (8) |
| V (Å3) | 2409.77 (18) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.19 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.25 × 0.20 × 0.15 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Rigaku R-AXIS RAPID |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (ABSCOR; Higashi, 1995 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.867, 0.971 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [F 2 > 2.0σ(F 2)] reflections | 23162, 5490, 4023 |
| R int | 0.042 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.648 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.044, 0.103, 1.01 |
| No. of reflections | 5490 |
| No. of parameters | 321 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.32, −0.30 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989023005959/yz2037sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989023005959/yz2037Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 2279961
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| [Na(C22H19N4O4S)(C2H3N)] | F(000) = 1040.00 |
| Mr = 499.52 | Dx = 1.377 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71075 Å |
| a = 10.4951 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 16856 reflections |
| b = 14.1401 (5) Å | θ = 2.1–27.4° |
| c = 16.9249 (6) Å | µ = 0.19 mm−1 |
| β = 106.378 (8)° | T = 173 K |
| V = 2409.77 (18) Å3 | Block, colorless |
| Z = 4 | 0.25 × 0.20 × 0.15 mm |
Data collection
| Rigaku R-AXIS RAPID diffractometer | 4023 reflections with F2 > 2.0σ(F2) |
| Detector resolution: 10.000 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.042 |
| ω scans | θmax = 27.4°, θmin = 2.5° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (ABSCOR; Higashi, 1995) | h = −13→13 |
| Tmin = 0.867, Tmax = 0.971 | k = −18→18 |
| 23162 measured reflections | l = −20→21 |
| 5490 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.044 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.103 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.01 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0403P)2 + 1.2511P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 5490 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 321 parameters | Δρmax = 0.32 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.30 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement was performed using all reflections. The weighted R-factor (wR) and goodness of fit (S) are based on F2. R-factor (gt) are based on F. The threshold expression of F2 > 2.0 sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factor (gt). |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 1.18114 (5) | 0.46635 (3) | 0.90911 (3) | 0.03024 (12) | |
| Na2 | 1.07043 (8) | 0.10172 (5) | 0.58208 (5) | 0.03309 (19) | |
| O3 | 1.02142 (14) | 0.26904 (9) | 0.58507 (8) | 0.0319 (3) | |
| O4 | 1.12279 (14) | 0.55994 (10) | 0.89339 (9) | 0.0394 (3) | |
| O5 | 1.12432 (16) | 0.40982 (11) | 0.96284 (9) | 0.0444 (4) | |
| O6 | 1.32483 (13) | 0.46752 (10) | 0.93467 (9) | 0.0395 (3) | |
| N7 | 1.18687 (17) | 0.18141 (11) | 0.71220 (10) | 0.0315 (4) | |
| N8 | 0.78852 (16) | 0.40512 (11) | 0.56663 (9) | 0.0291 (3) | |
| N9 | 0.85965 (17) | 0.32740 (12) | 0.43831 (10) | 0.0363 (4) | |
| N10 | 0.49005 (19) | 0.36242 (14) | 0.62557 (13) | 0.0472 (5) | |
| N11 | 1.2229 (2) | −0.03275 (15) | 0.63619 (14) | 0.0582 (6) | |
| C12 | 1.05317 (18) | 0.31647 (13) | 0.65748 (11) | 0.0261 (4) | |
| C13 | 1.00738 (18) | 0.40634 (12) | 0.66745 (11) | 0.0269 (4) | |
| C14 | 1.04797 (18) | 0.44926 (13) | 0.74581 (11) | 0.0272 (4) | |
| H14 | 1.014363 | 0.510196 | 0.752534 | 0.033* | |
| C15 | 1.13363 (18) | 0.40683 (13) | 0.81249 (11) | 0.0267 (4) | |
| C16 | 1.18340 (18) | 0.31472 (13) | 0.80365 (11) | 0.0275 (4) | |
| C17 | 1.2732 (2) | 0.26440 (14) | 0.86880 (12) | 0.0349 (5) | |
| H17 | 1.301928 | 0.291025 | 0.922443 | 0.042* | |
| C18 | 1.3174 (2) | 0.17810 (15) | 0.85359 (13) | 0.0421 (5) | |
| H18 | 1.378379 | 0.144070 | 0.896296 | 0.051* | |
| C19 | 1.2722 (2) | 0.13945 (14) | 0.77409 (13) | 0.0388 (5) | |
| H19 | 1.305452 | 0.079314 | 0.764561 | 0.047* | |
| C20 | 1.14255 (18) | 0.26954 (12) | 0.72610 (11) | 0.0260 (4) | |
| C21 | 0.91430 (19) | 0.45661 (13) | 0.59585 (12) | 0.0303 (4) | |
| H21A | 0.896845 | 0.521199 | 0.612841 | 0.036* | |
| H21B | 0.956231 | 0.462263 | 0.550483 | 0.036* | |
| C22 | 0.7130 (2) | 0.43493 (15) | 0.48490 (12) | 0.0364 (5) | |
| H22A | 0.716550 | 0.504736 | 0.481568 | 0.044* | |
| H22B | 0.618938 | 0.416526 | 0.475797 | 0.044* | |
| C23 | 0.7636 (2) | 0.39248 (14) | 0.41728 (12) | 0.0324 (4) | |
| C24 | 0.7072 (2) | 0.42029 (16) | 0.33616 (13) | 0.0409 (5) | |
| H24 | 0.640408 | 0.467689 | 0.323134 | 0.049* | |
| C25 | 0.7503 (2) | 0.37761 (18) | 0.27478 (13) | 0.0487 (6) | |
| H25 | 0.713422 | 0.395451 | 0.218858 | 0.058* | |
| C26 | 0.8473 (2) | 0.30886 (17) | 0.29556 (14) | 0.0475 (6) | |
| H26 | 0.877040 | 0.277717 | 0.254261 | 0.057* | |
| C27 | 0.9004 (2) | 0.28629 (17) | 0.37764 (14) | 0.0437 (5) | |
| H27 | 0.968416 | 0.239856 | 0.392049 | 0.052* | |
| C28 | 0.7092 (2) | 0.41116 (14) | 0.62489 (12) | 0.0329 (4) | |
| H28A | 0.666499 | 0.474147 | 0.619956 | 0.040* | |
| H28B | 0.768646 | 0.405127 | 0.681603 | 0.040* | |
| C29 | 0.60371 (19) | 0.33608 (14) | 0.61095 (12) | 0.0313 (4) | |
| C30 | 0.6250 (2) | 0.24534 (14) | 0.58610 (13) | 0.0375 (5) | |
| H30 | 0.706913 | 0.229419 | 0.575984 | 0.045* | |
| C31 | 0.5256 (2) | 0.17819 (16) | 0.57619 (13) | 0.0448 (5) | |
| H31 | 0.537800 | 0.115726 | 0.558990 | 0.054* | |
| C32 | 0.4090 (2) | 0.20405 (19) | 0.59181 (15) | 0.0523 (6) | |
| H32 | 0.338984 | 0.159710 | 0.586228 | 0.063* | |
| C33 | 0.3958 (2) | 0.2952 (2) | 0.61563 (18) | 0.0590 (7) | |
| H33 | 0.314422 | 0.312303 | 0.625879 | 0.071* | |
| C34 | 1.3112 (3) | −0.07824 (16) | 0.63605 (14) | 0.0474 (6) | |
| C35 | 1.4259 (3) | −0.1369 (2) | 0.6367 (2) | 0.0806 (10) | |
| H35A | 1.481852 | −0.103827 | 0.608024 | 0.121* | |
| H35B | 1.395569 | −0.196938 | 0.608878 | 0.121* | |
| H35C | 1.477330 | −0.149253 | 0.693795 | 0.121* | |
| H3 | 0.958 (2) | 0.2949 (17) | 0.5457 (16) | 0.051 (7)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0311 (2) | 0.0346 (3) | 0.0258 (2) | −0.0037 (2) | 0.00925 (19) | −0.00541 (19) |
| Na2 | 0.0414 (4) | 0.0325 (4) | 0.0282 (4) | −0.0002 (3) | 0.0143 (3) | −0.0019 (3) |
| O3 | 0.0414 (8) | 0.0307 (7) | 0.0218 (7) | 0.0043 (6) | 0.0058 (6) | 0.0001 (5) |
| O4 | 0.0424 (8) | 0.0370 (8) | 0.0375 (8) | 0.0038 (6) | 0.0093 (7) | −0.0093 (6) |
| O5 | 0.0543 (10) | 0.0549 (9) | 0.0285 (8) | −0.0145 (8) | 0.0190 (7) | −0.0051 (6) |
| O6 | 0.0324 (7) | 0.0416 (8) | 0.0412 (8) | −0.0034 (6) | 0.0048 (6) | −0.0066 (7) |
| N7 | 0.0405 (9) | 0.0257 (8) | 0.0282 (9) | 0.0011 (7) | 0.0095 (7) | 0.0010 (6) |
| N8 | 0.0304 (8) | 0.0344 (8) | 0.0232 (8) | 0.0014 (7) | 0.0088 (7) | 0.0002 (6) |
| N9 | 0.0389 (10) | 0.0418 (10) | 0.0293 (9) | 0.0014 (8) | 0.0112 (8) | −0.0003 (7) |
| N10 | 0.0402 (10) | 0.0538 (12) | 0.0549 (12) | 0.0031 (9) | 0.0255 (9) | 0.0010 (9) |
| N11 | 0.0693 (15) | 0.0459 (12) | 0.0577 (14) | 0.0152 (11) | 0.0152 (11) | −0.0014 (10) |
| C12 | 0.0290 (9) | 0.0279 (9) | 0.0238 (9) | −0.0044 (7) | 0.0112 (8) | −0.0003 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0265 (9) | 0.0287 (9) | 0.0266 (9) | −0.0023 (7) | 0.0093 (8) | 0.0021 (7) |
| C14 | 0.0285 (9) | 0.0265 (9) | 0.0285 (9) | −0.0006 (7) | 0.0112 (8) | −0.0006 (7) |
| C15 | 0.0264 (9) | 0.0303 (9) | 0.0255 (9) | −0.0039 (7) | 0.0106 (8) | −0.0035 (7) |
| C16 | 0.0281 (9) | 0.0298 (9) | 0.0258 (9) | −0.0046 (8) | 0.0096 (8) | 0.0020 (7) |
| C17 | 0.0411 (12) | 0.0346 (11) | 0.0258 (10) | −0.0037 (9) | 0.0044 (9) | 0.0001 (8) |
| C18 | 0.0497 (13) | 0.0323 (11) | 0.0354 (12) | 0.0048 (10) | −0.0026 (10) | 0.0054 (9) |
| C19 | 0.0490 (13) | 0.0281 (10) | 0.0361 (11) | 0.0064 (9) | 0.0066 (10) | 0.0025 (8) |
| C20 | 0.0294 (9) | 0.0261 (9) | 0.0249 (9) | −0.0023 (7) | 0.0115 (8) | 0.0019 (7) |
| C21 | 0.0337 (10) | 0.0292 (10) | 0.0281 (10) | −0.0002 (8) | 0.0090 (8) | 0.0027 (8) |
| C22 | 0.0367 (11) | 0.0412 (11) | 0.0295 (11) | 0.0061 (9) | 0.0061 (9) | 0.0025 (9) |
| C23 | 0.0343 (11) | 0.0340 (10) | 0.0275 (10) | −0.0041 (9) | 0.0065 (8) | 0.0010 (8) |
| C24 | 0.0452 (12) | 0.0435 (12) | 0.0306 (11) | −0.0026 (10) | 0.0053 (9) | 0.0036 (9) |
| C25 | 0.0575 (15) | 0.0606 (15) | 0.0256 (11) | −0.0131 (12) | 0.0079 (10) | 0.0011 (10) |
| C26 | 0.0533 (14) | 0.0608 (15) | 0.0327 (12) | −0.0085 (12) | 0.0191 (11) | −0.0100 (10) |
| C27 | 0.0448 (13) | 0.0514 (13) | 0.0371 (12) | −0.0003 (11) | 0.0153 (10) | −0.0065 (10) |
| C28 | 0.0358 (11) | 0.0349 (11) | 0.0305 (10) | 0.0031 (8) | 0.0133 (9) | −0.0036 (8) |
| C29 | 0.0312 (10) | 0.0397 (11) | 0.0233 (9) | 0.0025 (8) | 0.0081 (8) | 0.0029 (8) |
| C30 | 0.0357 (11) | 0.0387 (11) | 0.0372 (12) | 0.0026 (9) | 0.0087 (9) | −0.0010 (9) |
| C31 | 0.0507 (14) | 0.0426 (12) | 0.0350 (12) | −0.0069 (10) | 0.0021 (10) | 0.0012 (9) |
| C32 | 0.0462 (14) | 0.0641 (16) | 0.0454 (14) | −0.0189 (12) | 0.0112 (11) | 0.0054 (12) |
| C33 | 0.0385 (13) | 0.0741 (19) | 0.0722 (19) | −0.0056 (13) | 0.0286 (13) | 0.0041 (15) |
| C34 | 0.0618 (16) | 0.0419 (13) | 0.0405 (13) | 0.0019 (12) | 0.0179 (12) | 0.0003 (10) |
| C35 | 0.074 (2) | 0.087 (2) | 0.092 (2) | 0.0236 (18) | 0.0406 (19) | −0.0027 (19) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—O6 | 1.4469 (14) | C17—H17 | 0.9500 |
| S1—O4 | 1.4510 (15) | C18—C19 | 1.405 (3) |
| S1—O5 | 1.4585 (15) | C18—H18 | 0.9500 |
| S1—C15 | 1.7808 (18) | C19—H19 | 0.9500 |
| S1—Na2i | 3.2984 (9) | C21—H21A | 0.9900 |
| Na2—O5ii | 2.2500 (16) | C21—H21B | 0.9900 |
| Na2—O4iii | 2.2602 (16) | C22—C23 | 1.515 (3) |
| Na2—O3 | 2.4248 (15) | C22—H22A | 0.9900 |
| Na2—N7 | 2.4690 (18) | C22—H22B | 0.9900 |
| Na2—N11 | 2.487 (2) | C23—C24 | 1.390 (3) |
| Na2—Na2iv | 3.9829 (15) | C24—C25 | 1.383 (3) |
| O3—C12 | 1.354 (2) | C24—H24 | 0.9500 |
| O3—H3 | 0.88 (3) | C25—C26 | 1.380 (3) |
| N7—C19 | 1.312 (3) | C25—H25 | 0.9500 |
| N7—C20 | 1.373 (2) | C26—C27 | 1.380 (3) |
| N8—C22 | 1.449 (2) | C26—H26 | 0.9500 |
| N8—C28 | 1.461 (2) | C27—H27 | 0.9500 |
| N8—C21 | 1.466 (2) | C28—C29 | 1.504 (3) |
| N9—C23 | 1.337 (3) | C28—H28A | 0.9900 |
| N9—C27 | 1.350 (3) | C28—H28B | 0.9900 |
| N10—C29 | 1.338 (3) | C29—C30 | 1.388 (3) |
| N10—C33 | 1.347 (3) | C30—C31 | 1.386 (3) |
| N11—C34 | 1.129 (3) | C30—H30 | 0.9500 |
| C12—C13 | 1.386 (3) | C31—C32 | 1.372 (3) |
| C12—C20 | 1.433 (3) | C31—H31 | 0.9500 |
| C13—C14 | 1.411 (3) | C32—C33 | 1.369 (4) |
| C13—C21 | 1.504 (3) | C32—H32 | 0.9500 |
| C14—C15 | 1.367 (3) | C33—H33 | 0.9500 |
| C14—H14 | 0.9500 | C34—C35 | 1.459 (4) |
| C15—C16 | 1.427 (3) | C35—H35A | 0.9800 |
| C16—C20 | 1.413 (3) | C35—H35B | 0.9800 |
| C16—C17 | 1.423 (3) | C35—H35C | 0.9800 |
| C17—C18 | 1.356 (3) | ||
| O6—S1—O4 | 113.25 (9) | C17—C18—H18 | 120.3 |
| O6—S1—O5 | 113.25 (9) | C19—C18—H18 | 120.3 |
| O4—S1—O5 | 112.87 (9) | N7—C19—C18 | 123.96 (19) |
| O6—S1—C15 | 106.16 (9) | N7—C19—H19 | 118.0 |
| O4—S1—C15 | 105.55 (9) | C18—C19—H19 | 118.0 |
| O5—S1—C15 | 104.82 (9) | N7—C20—C16 | 122.71 (17) |
| O6—S1—Na2i | 139.46 (6) | N7—C20—C12 | 117.21 (16) |
| O4—S1—Na2i | 34.63 (6) | C16—C20—C12 | 120.07 (16) |
| O5—S1—Na2i | 79.43 (7) | N8—C21—C13 | 110.84 (15) |
| C15—S1—Na2i | 107.18 (6) | N8—C21—H21A | 109.5 |
| O5ii—Na2—O4iii | 127.68 (7) | C13—C21—H21A | 109.5 |
| O5ii—Na2—O3 | 101.42 (6) | N8—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| O4iii—Na2—O3 | 92.56 (6) | C13—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| O5ii—Na2—N7 | 130.30 (7) | H21A—C21—H21B | 108.1 |
| O4iii—Na2—N7 | 101.50 (6) | N8—C22—C23 | 113.07 (16) |
| O3—Na2—N7 | 65.83 (5) | N8—C22—H22A | 109.0 |
| O5ii—Na2—N11 | 88.66 (7) | C23—C22—H22A | 109.0 |
| O4iii—Na2—N11 | 104.46 (7) | N8—C22—H22B | 109.0 |
| O3—Na2—N11 | 148.91 (7) | C23—C22—H22B | 109.0 |
| N7—Na2—N11 | 85.14 (7) | H22A—C22—H22B | 107.8 |
| O5ii—Na2—S1iii | 113.91 (5) | N9—C23—C24 | 122.47 (19) |
| O4iii—Na2—S1iii | 21.39 (4) | N9—C23—C22 | 118.05 (17) |
| O3—Na2—S1iii | 112.83 (4) | C24—C23—C22 | 119.46 (19) |
| N7—Na2—S1iii | 115.19 (5) | C25—C24—C23 | 118.7 (2) |
| N11—Na2—S1iii | 88.83 (6) | C25—C24—H24 | 120.6 |
| O5ii—Na2—Na2iv | 57.30 (5) | C23—C24—H24 | 120.6 |
| O4iii—Na2—Na2iv | 76.32 (5) | C26—C25—C24 | 119.3 (2) |
| O3—Na2—Na2iv | 132.85 (5) | C26—C25—H25 | 120.3 |
| N7—Na2—Na2iv | 160.89 (5) | C24—C25—H25 | 120.3 |
| N11—Na2—Na2iv | 77.20 (6) | C25—C26—C27 | 118.6 (2) |
| S1iii—Na2—Na2iv | 57.86 (2) | C25—C26—H26 | 120.7 |
| C12—O3—Na2 | 120.18 (11) | C27—C26—H26 | 120.7 |
| C12—O3—H3 | 114.9 (16) | N9—C27—C26 | 122.8 (2) |
| Na2—O3—H3 | 120.7 (16) | N9—C27—H27 | 118.6 |
| S1—O4—Na2i | 123.98 (9) | C26—C27—H27 | 118.6 |
| S1—O5—Na2v | 148.14 (10) | N8—C28—C29 | 112.78 (16) |
| C19—N7—C20 | 117.48 (17) | N8—C28—H28A | 109.0 |
| C19—N7—Na2 | 124.08 (13) | C29—C28—H28A | 109.0 |
| C20—N7—Na2 | 117.42 (12) | N8—C28—H28B | 109.0 |
| C22—N8—C28 | 111.39 (16) | C29—C28—H28B | 109.0 |
| C22—N8—C21 | 112.06 (15) | H28A—C28—H28B | 107.8 |
| C28—N8—C21 | 111.93 (15) | N10—C29—C30 | 122.79 (19) |
| C23—N9—C27 | 118.06 (18) | N10—C29—C28 | 115.47 (18) |
| C29—N10—C33 | 116.2 (2) | C30—C29—C28 | 121.73 (18) |
| C34—N11—Na2 | 151.4 (2) | C31—C30—C29 | 119.4 (2) |
| O3—C12—C13 | 124.01 (17) | C31—C30—H30 | 120.3 |
| O3—C12—C20 | 116.23 (16) | C29—C30—H30 | 120.3 |
| C13—C12—C20 | 119.75 (17) | C32—C31—C30 | 118.4 (2) |
| C12—C13—C14 | 119.07 (17) | C32—C31—H31 | 120.8 |
| C12—C13—C21 | 120.28 (17) | C30—C31—H31 | 120.8 |
| C14—C13—C21 | 120.64 (16) | C33—C32—C31 | 118.5 (2) |
| C15—C14—C13 | 122.77 (17) | C33—C32—H32 | 120.8 |
| C15—C14—H14 | 118.6 | C31—C32—H32 | 120.8 |
| C13—C14—H14 | 118.6 | N10—C33—C32 | 124.7 (2) |
| C14—C15—C16 | 119.26 (17) | N10—C33—H33 | 117.6 |
| C14—C15—S1 | 119.96 (14) | C32—C33—H33 | 117.6 |
| C16—C15—S1 | 120.78 (14) | N11—C34—C35 | 179.4 (3) |
| C20—C16—C17 | 117.06 (17) | C34—C35—H35A | 109.5 |
| C20—C16—C15 | 119.07 (17) | C34—C35—H35B | 109.5 |
| C17—C16—C15 | 123.87 (17) | H35A—C35—H35B | 109.5 |
| C18—C17—C16 | 119.36 (19) | C34—C35—H35C | 109.5 |
| C18—C17—H17 | 120.3 | H35A—C35—H35C | 109.5 |
| C16—C17—H17 | 120.3 | H35B—C35—H35C | 109.5 |
| C17—C18—C19 | 119.39 (19) | ||
| O6—S1—O4—Na2i | −146.44 (9) | Na2—N7—C20—C12 | −13.3 (2) |
| O5—S1—O4—Na2i | −16.08 (13) | C17—C16—C20—N7 | −0.6 (3) |
| C15—S1—O4—Na2i | 97.84 (10) | C15—C16—C20—N7 | 179.29 (17) |
| O6—S1—O5—Na2v | 78.3 (2) | C17—C16—C20—C12 | −179.41 (17) |
| O4—S1—O5—Na2v | −52.0 (2) | C15—C16—C20—C12 | 0.5 (3) |
| C15—S1—O5—Na2v | −166.41 (18) | O3—C12—C20—N7 | −0.3 (2) |
| Na2i—S1—O5—Na2v | −61.26 (19) | C13—C12—C20—N7 | −178.66 (16) |
| Na2—O3—C12—C13 | −167.32 (14) | O3—C12—C20—C16 | 178.61 (16) |
| Na2—O3—C12—C20 | 14.4 (2) | C13—C12—C20—C16 | 0.2 (3) |
| O3—C12—C13—C14 | −179.49 (17) | C22—N8—C21—C13 | −163.21 (16) |
| C20—C12—C13—C14 | −1.2 (3) | C28—N8—C21—C13 | 70.82 (19) |
| O3—C12—C13—C21 | 1.3 (3) | C12—C13—C21—N8 | 63.1 (2) |
| C20—C12—C13—C21 | 179.60 (16) | C14—C13—C21—N8 | −116.12 (18) |
| C12—C13—C14—C15 | 1.6 (3) | C28—N8—C22—C23 | −155.23 (16) |
| C21—C13—C14—C15 | −179.20 (17) | C21—N8—C22—C23 | 78.5 (2) |
| C13—C14—C15—C16 | −0.9 (3) | C27—N9—C23—C24 | −1.4 (3) |
| C13—C14—C15—S1 | 179.41 (14) | C27—N9—C23—C22 | 176.90 (19) |
| O6—S1—C15—C14 | −126.08 (15) | N8—C22—C23—N9 | 6.4 (3) |
| O4—S1—C15—C14 | −5.59 (17) | N8—C22—C23—C24 | −175.17 (18) |
| O5—S1—C15—C14 | 113.80 (16) | N9—C23—C24—C25 | 1.3 (3) |
| Na2i—S1—C15—C14 | 30.51 (16) | C22—C23—C24—C25 | −177.0 (2) |
| O6—S1—C15—C16 | 54.26 (17) | C23—C24—C25—C26 | 0.1 (3) |
| O4—S1—C15—C16 | 174.74 (15) | C24—C25—C26—C27 | −1.3 (3) |
| O5—S1—C15—C16 | −65.86 (17) | C23—N9—C27—C26 | 0.2 (3) |
| Na2i—S1—C15—C16 | −149.16 (13) | C25—C26—C27—N9 | 1.2 (4) |
| C14—C15—C16—C20 | −0.1 (3) | C22—N8—C28—C29 | 72.0 (2) |
| S1—C15—C16—C20 | 179.53 (13) | C21—N8—C28—C29 | −161.71 (16) |
| C14—C15—C16—C17 | 179.75 (18) | C33—N10—C29—C30 | 0.6 (3) |
| S1—C15—C16—C17 | −0.6 (3) | C33—N10—C29—C28 | −178.2 (2) |
| C20—C16—C17—C18 | 1.6 (3) | N8—C28—C29—N10 | −145.01 (18) |
| C15—C16—C17—C18 | −178.31 (19) | N8—C28—C29—C30 | 36.2 (3) |
| C16—C17—C18—C19 | −0.9 (3) | N10—C29—C30—C31 | −0.4 (3) |
| C20—N7—C19—C18 | 1.9 (3) | C28—C29—C30—C31 | 178.36 (19) |
| Na2—N7—C19—C18 | −166.24 (17) | C29—C30—C31—C32 | −0.3 (3) |
| C17—C18—C19—N7 | −0.9 (4) | C30—C31—C32—C33 | 0.7 (3) |
| C19—N7—C20—C16 | −1.1 (3) | C29—N10—C33—C32 | −0.2 (4) |
| Na2—N7—C20—C16 | 167.84 (13) | C31—C32—C33—N10 | −0.4 (4) |
| C19—N7—C20—C12 | 177.74 (18) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, y+1/2, −z+3/2; (ii) x, −y+1/2, z−1/2; (iii) −x+2, y−1/2, −z+3/2; (iv) −x+2, −y, −z+1; (v) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O3—H3···N8 | 0.88 (2) | 2.46 (3) | 3.057 (2) | 125 (2) |
| O3—H3···N9 | 0.88 (2) | 1.87 (2) | 2.7120 (19) | 158 (3) |
| C31—H31···O6iii | 0.95 | 2.53 | 3.397 (3) | 152 |
| C35—H35A···O6vi | 0.98 | 2.55 | 3.502 (4) | 166 |
Symmetry codes: (iii) −x+2, y−1/2, −z+3/2; (vi) −x+3, y−1/2, −z+3/2.
Funding Statement
Funding for this research was provided by: JSPS KAKENHI (grant No. JP20K05565).
References
- Addison, A. W., Rao, N. T., Reedijk, J., van Rijn, J. & Verschoor, G. C. (1984). J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. pp. 1349–1356.
- Altomare, A., Cascarano, G., Giacovazzo, C. & Guagliardi, A. (1993). J. Appl. Cryst. 26, 343–350.
- Back, S. H., Park, J. H., Cui, C. & Ahn, D. J. (2016). Nat. Commun. 7, 10234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Baskar Raj, S., Muthiah, P. T., Bocelli, G. & Olla, R. (2002). Acta Cryst. E58, m513–m516.
- Bruno, I. J., Cole, J. C., Edgington, P. R., Kessler, M., Macrae, C. F., McCabe, P., Pearson, J. & Taylor, R. (2002). Acta Cryst. B58, 389–397. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Higashi, T. (1995). ABSCOR. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Huo, Y., Lu, J., Lu, T., Fang, X., Ouyang, X., Zhang, L. & Yuan, G. (2015). New J. Chem. 39, 333–341.
- Kubono, K., Kado, K., Kashiwagi, Y., Tani, K. & Yokoi, K. (2015). Acta Cryst. E71, 1545–1547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A., Sardhalia, V., Sahoo, P. R., Kumar, A. & Kumar, S. (2021). J. Mol. Struct. 1235, 130233.
- Ma, S., Zhang, T., Zhao, J.-P., Liu, Z.-Y. & Liu, F.-C. (2021). Dalton Trans. 50, 1307–1312. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Merritt, L. L. Jr & Duffin, B. (1970). Acta Cryst. B26, 734–744.
- Mo, X., Chen, K., Chen, Z., Chu, B., Liu, D., Liang, Y., Xiong, J., Yang, Y., Cai, J. & Liang, F. (2021). Inorg. Chem. 60, 16128–16139. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rigaku (2006). RAPID-AUTO. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Rigaku (2016). CrystalStructure. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spek, A. L. (2020). Acta Cryst. E76, 1–11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Thiele, N. A., MacMillan, S. N. & Wilson, J. J. (2018). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140, 17071–17078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Viossat, B., Khodadad, P. & Rodier, N. (1982). Bull. Soc. Chim. Fr. 72, 289–291.
- Wiberley, S. E. & Bassett, L. G. (1949). Anal. Chem. 21, 609–612.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989023005959/yz2037sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989023005959/yz2037Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 2279961
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report